Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Build MVC Applications with Connectivity to ADP Data
This article shows how to use only the Entity Framework and the CData ADO.NET provider to access ADP from an ASP.NET MVC application.
In this article, we will guide you through the process of utilizing wizards within Visual Studio to seamlessly integrate the CData ADO.NET Provider for ADP into a basic MVC (Model, View, Controller) project.
Create the Entity Framework Model
Follow the steps below to save connection properties and map tables to entities in the data model.
- Create a new MVC project in Visual Studio. In this example, the project name is MvcADPApp.
If you are using Entity Framework 6, you will need to take the preliminary step of registering the ADP Entity Framework provider for your project. See the "LINQ and Entity Framework" chapter in the help documentation for a guide.
Note that MVC 3 scaffolding and MVC 4 scaffolding do not support Entity Framework 6. You can use your scaffolding with Entity Framework 6 by upgrading to the latest version of MVC.- To add the .edmx file from the designer, right-click your Models folder and click Add New Item. Select ADO.NET Entity Data Model, name the model, and click Add. In this example, the name of the model is ADPModel.
- In the Entity Data Model wizard, select the option 'EF Designer from database'. The Entity Data Model wizard is displayed.
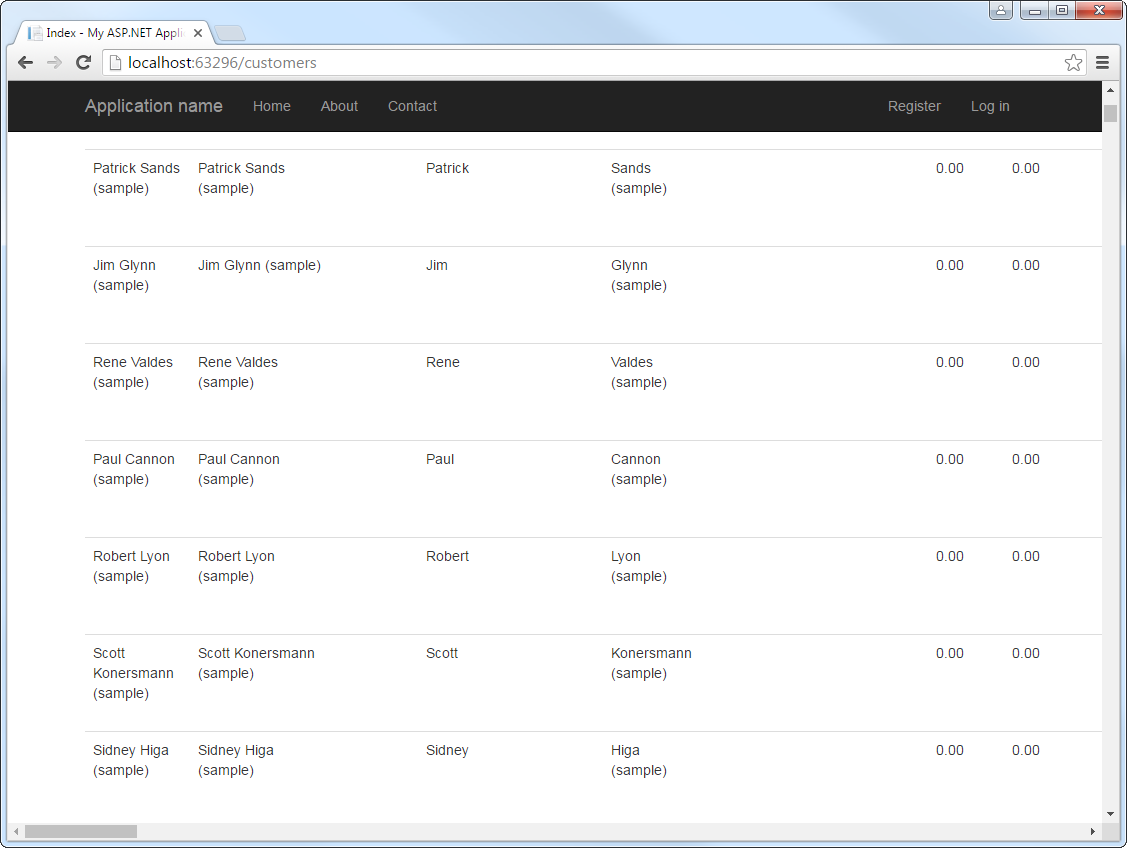
- Click New Connection. Select CData ADP Data Source in the dialog that is displayed.
Specify the required connection string properties.
Connect to ADP by specifying the following properties:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the certificate provided during registration.
- SSLClientCertPassword: Set this to the password of the certificate.
- UseUAT: The connector makes requests to the production environment by default. If using a developer account, set UseUAT = true.
- RowScanDepth: The maximum number of rows to scan for the custom fields columns available in the table. The default value will be set to 100. Setting a high value may decrease performance.
The connector uses OAuth to authenticate with ADP. OAuth requires the authenticating user to interact with ADP using the browser. For more information, refer to the OAuth section in the Help documentation.
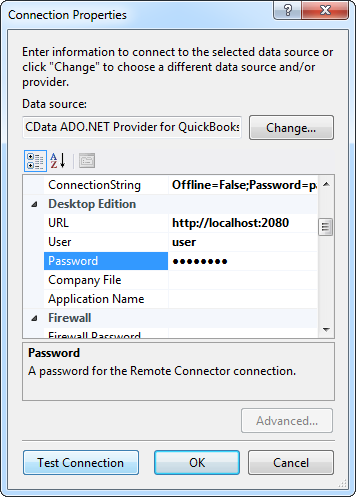
A typical connection string is below:
OAuthClientId=YourClientId;OAuthClientSecret=YourClientSecret;SSLClientCert='c:\cert.pfx';SSLClientCertPassword='admin@123'InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH![The connection for the model. (QuickBooks is shown.)]()
Name the connection and select whether to include sensitive information, such as connection credentials, in the connection string. For simplicity, this example saves sensitive information in Web.config. The connection settings are saved as ADPEntities.
![The completed connection step in the ADO.NET Entity Data Model wizard. (A QuickBooks connection is shown.)]()
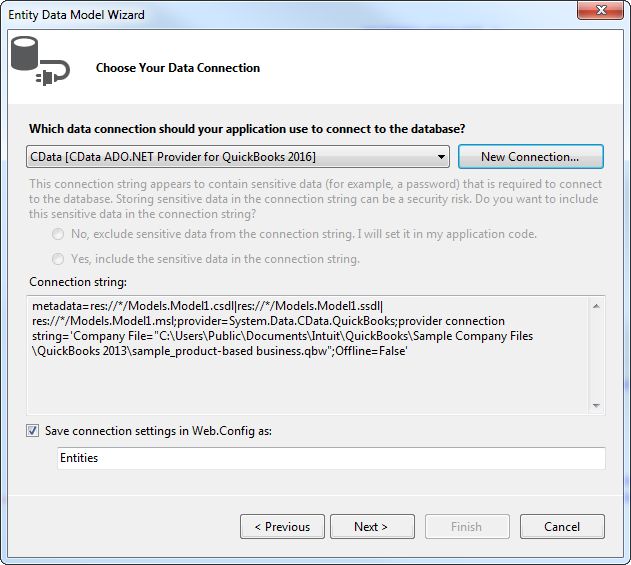
- Select the tables and views you need. In this example, Workers is imported. Also, the option to pluralize object names is deselected in this example. Click Finish to create the .edmx file.
![Tables to be imported into the .edmx file. (QuickBooks is shown.)]()
- Build your project to complete this step.
Scaffold the Controller and Views
Once you've established the model and completed the project build, you can employ ASP.NET Scaffolding wizards to generate both the controller and the views.
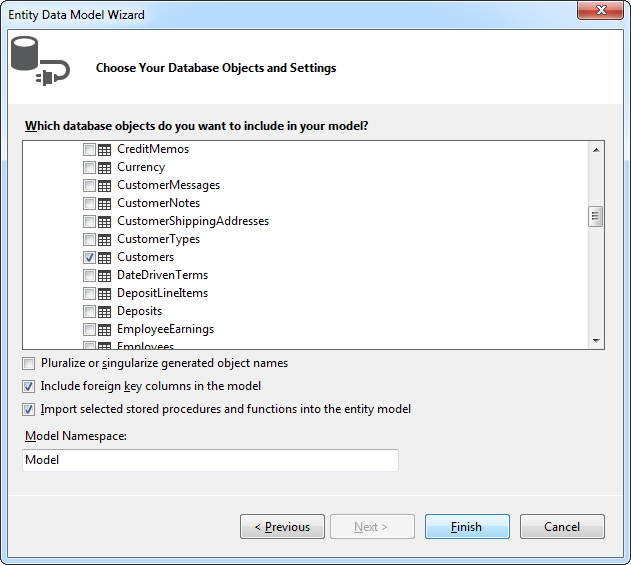
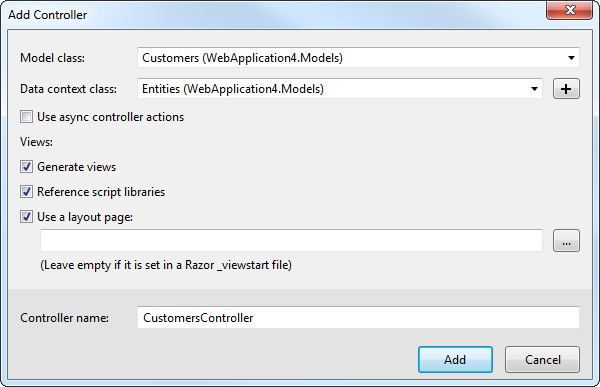
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the controllers folder and click Add -> Controller. Select MVC 5 Controller with views, using Entity Framework.
- In the Add Controller dialog that is then displayed, select the following options:
- Model class: Select a table you imported; for example, Workers.
- Data context class: Select your context class.
-
Leave the default values for the other fields.
![Creating a new controller from an existing entity data model in the Add Controller dialog in MVC 5. (QuickBooks is shown.)]()