Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to Amazon Athena Data as a Linked Server
Use the SQL Gateway and the ODBC Driver to set up a linked server for Amazon Athena data.
You can use the SQL Gateway to configure a TDS (SQL Server) remoting service and set up a linked server for Amazon Athena data. After you have started the service, you can use the UI in SQL Server Management Studio or call stored procedures to create the linked server. You can then work with Amazon Athena data just as you would a linked SQL Server instance.
Connect to Amazon Athena as an ODBC Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
Authenticating to Amazon Athena
To authorize Amazon Athena requests, provide the credentials for an administrator account or for an IAM user with custom permissions: Set AccessKey to the access key Id. Set SecretKey to the secret access key.
Note: Though you can connect as the AWS account administrator, it is recommended to use IAM user credentials to access AWS services.
Obtaining the Access Key
To obtain the credentials for an IAM user, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the IAM console.
- In the navigation pane, select Users.
- To create or manage the access keys for a user, select the user and then select the Security Credentials tab.
To obtain the credentials for your AWS root account, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the AWS Management console with the credentials for your root account.
- Select your account name or number and select My Security Credentials in the menu that is displayed.
- Click Continue to Security Credentials and expand the Access Keys section to manage or create root account access keys.
Authenticating from an EC2 Instance
If you are using the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 from an EC2 Instance and have an IAM Role assigned to the instance, you can use the IAM Role to authenticate. To do so, set UseEC2Roles to true and leave AccessKey and SecretKey empty. The CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 will automatically obtain your IAM Role credentials and authenticate with them.
Authenticating as an AWS Role
In many situations it may be preferable to use an IAM role for authentication instead of the direct security credentials of an AWS root user. An AWS role may be used instead by specifying the RoleARN. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to attempt to retrieve credentials for the specified role. If you are connecting to AWS (instead of already being connected such as on an EC2 instance), you must additionally specify the AccessKey and SecretKey of an IAM user to assume the role for. Roles may not be used when specifying the AccessKey and SecretKey of an AWS root user.
Authenticating with MFA
For users and roles that require Multi-factor Authentication, specify the MFASerialNumber and MFAToken connection properties. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to submit the MFA credentials in a request to retrieve temporary authentication credentials. Note that the duration of the temporary credentials may be controlled via the TemporaryTokenDuration (default 3600 seconds).
Connecting to Amazon Athena
In addition to the AccessKey and SecretKey properties, specify Database, S3StagingDirectory and Region. Set Region to the region where your Amazon Athena data is hosted. Set S3StagingDirectory to a folder in S3 where you would like to store the results of queries.
If Database is not set in the connection, the data provider connects to the default database set in Amazon Athena.
Configure the TDS Remoting Service
See the SQL Gateway Overview for a guide to configure a TDS remoting service in the SQL Gateway UI. The TDS remoting service is a daemon process that listens for TDS requests from clients.
Create a Linked Server for Amazon Athena Data
After you have configured and started the daemon, create the linked server and connect. You can use the UI in SQL Server Management Studio or call stored procedures.
Create a Linked Server from the UI
Follow the steps below to create a linked server from the Object Explorer.
- Open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to an instance of SQL Server.
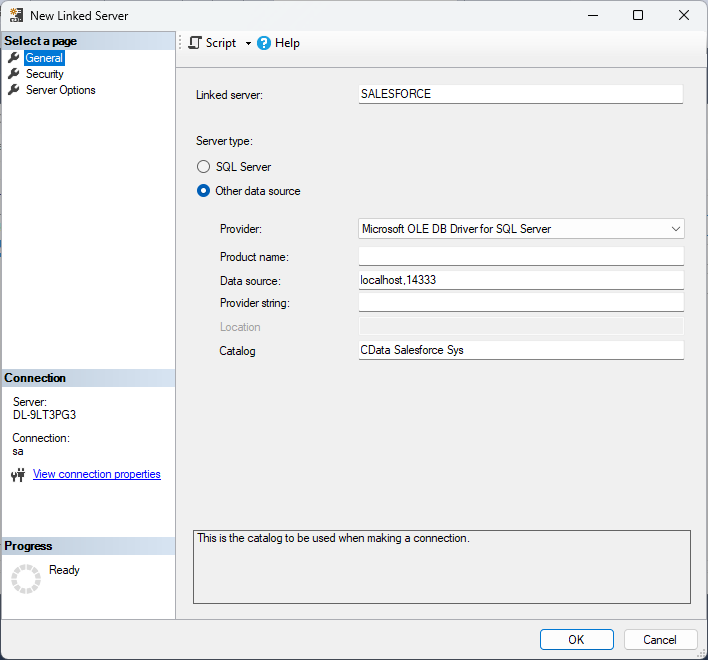
- In the Object Explorer, expand the node for the SQL Server database. In the Server Objects node, right-click Linked Servers and click New Linked Server. The New Linked Server dialog is displayed.
- In the General section, click the Other Data Source option and enter the following information after naming the linked server:
- Provider: Select the SQL Server Native Client Provider that corresponds to your version of SQL Server. For example, SQL Server Native Client 11.0.
Data Source: Enter the host and port the TDS remoting service is running on, separated by a comma.
Note that a value of "localhost" in this input refers to the machine where SQL Server is running so be careful when creating a linked server in Management Studio when not running on the same machine as SQL Server.
- Catalog: Enter the CData system DSN, CData AmazonAthena Sys.
![Linked Server properties. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
-
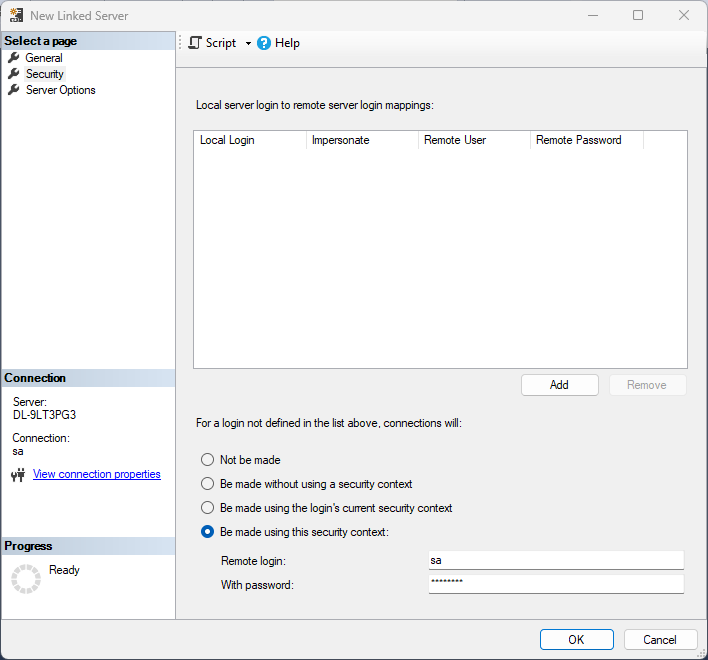
In the Security section, select the option to have the connection "made using this security context" and enter the username and password of a user you created in the Users tab of the SQL Gateway.
![A user known to the daemon in the Linked Server security properties.]()
Create a Linked Server Programmatically
In addition to using the SQL Server Management Studio UI to create a linked server, you can use stored procedures. The following inputs are required:
- server: The linked server name.
- provider: Enter "SQLNCLI", for the SQL Server Native Client Provider.
datasrc: The host and port the service is running on, separated by a comma.
Note that a value of "localhost" in the datasrc input refers to the machine where SQL Server is running, so be careful when creating a linked server in Management Studio when not running on the same machine as SQL Server.
- catalog: Enter the system DSN configured for the service.
- srvproduct: Enter the product name of the data source; this can be an arbitrary value, such as "CData SQL Gateway" or an empty string.
-
Call sp_addlinkedserver to create the linked server:
EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server='AmazonAthena', @provider='SQLNCLI', @datasrc='< MachineIPAddress >,1434', @catalog='CData AmazonAthena Sys', @srvproduct=''; GO -
Call the sp_addlinkedsrvlogin stored procedure to allow SQL Server users to connect with the credentials of an authorized user of the service. Note that the credentials you use to connect to the service must specify a user you configured on the Users tab of the SQL Gateway.
EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname='AmazonAthena', @rmtuser='admin', @rmtpassword='test', @useself='FALSE', @locallogin=NULL; GO
Connect from SQL Server Management Studio
SQL Server Management Studio uses the SQL Server Client OLE DB provider, which requires the ODBC driver to be used inprocess. You must enable the "Allow inprocess" option for the SQL Server Native Client Provider in Management Studio to query the linked server from SQL Server Management Studio. To do this, open the properties for the provider you are using under Server Objects -> Linked Servers -> Providers. Check the "Allow inprocess" option and save the changes.
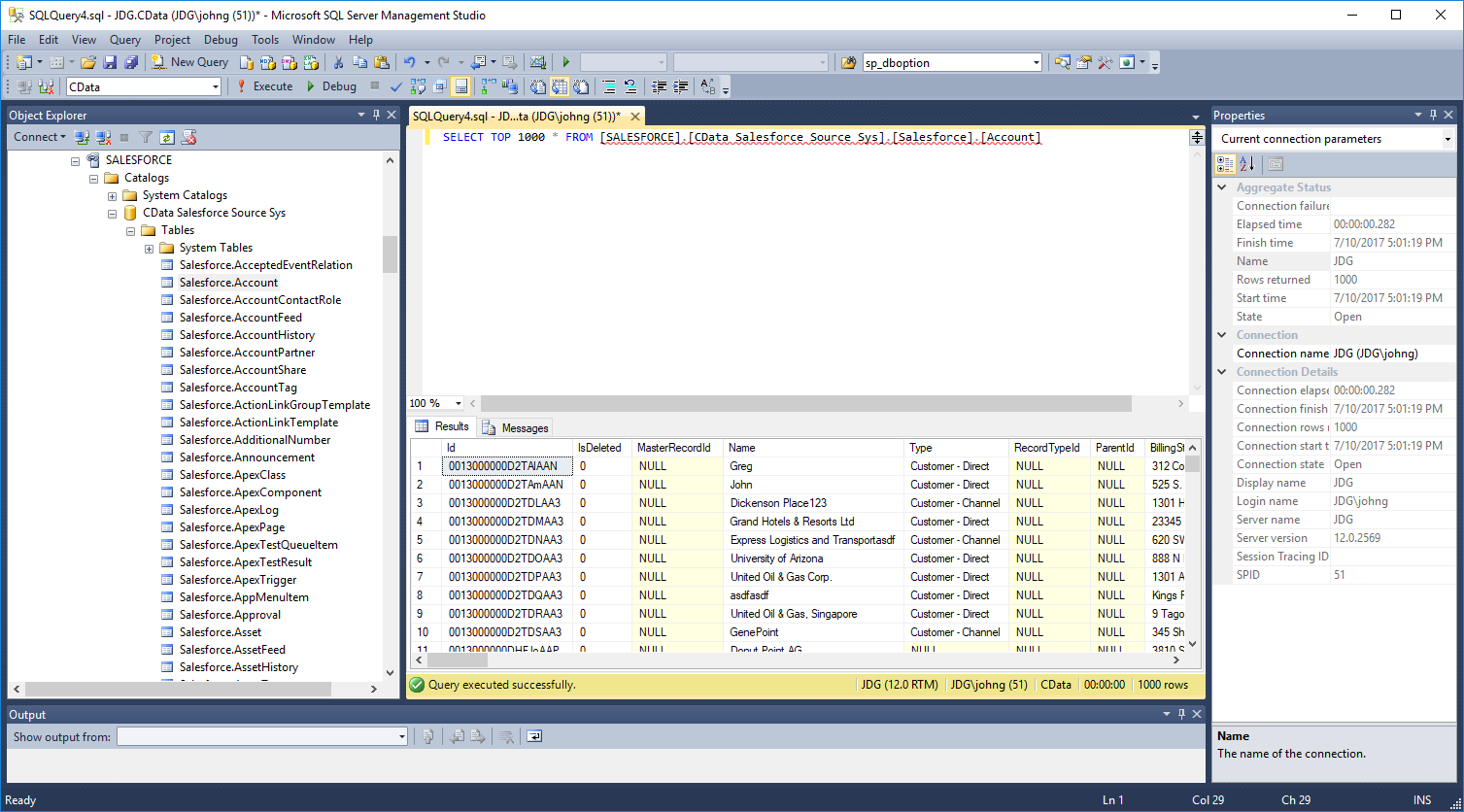
Execute Queries
You can now execute queries to the Amazon Athena linked server from any tool that can connect to SQL Server. Set the table name accordingly:
SELECT * FROM [linked server name].[CData AmazonAthena Sys].[AmazonAthena].[Customers]