Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Access Live Gmail Data in TIBCO Data Virtualization
Use the CData TIBCO DV Adapter for Gmail to create a Gmail data source in TIBCO Data Virtualization Studio and gain access to live Gmail data from your TDV Server.
TIBCO Data Virtualization (TDV) is an enterprise data virtualization solution that orchestrates access to multiple and varied data sources. When paired with the CData TIBCO DV Adapter for Gmail, you get federated access to live Gmail data directly within TIBCO Data Virtualization. This article walks through deploying an adapter and creating a new data source based on Gmail.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData TIBCO DV Adapter offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Gmail data. When you issue complex SQL queries to Gmail, the adapter pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Gmail. Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze Gmail data using native data types.
Deploy the Gmail TIBCO DV Adapter
In a console, navigate to the bin folder in the TDV Server installation directory. If there is a current version of the adapter installed, you will need to undeploy it.
.\server_util.bat -server localhost -user admin -password ******** -undeploy -version 1 -name Gmail
Extract the CData TIBCO DV Adapter to a local folder and deploy the JAR file (tdv.gmail.jar) to the server from the extract location.
.\server_util.bat -server localhost -user admin -password ******** -deploy -package /PATH/TO/tdv.gmail.jar
You may need to restart the server to ensure the new JAR file is loaded properly, which can be accomplished by running the composite.bat script located at: C:\Program Files\TIBCO\TDV Server <version>\bin. Note that reauthenticating to the TDV Studio is required after restarting the server.
Sample Restart Call
.\composite.bat monitor restartOnce you deploy the adapter, you can create a new data source in TDV Studio for Gmail.
Create a Gmail Data Source in TDV Studio
With the CData TIBCO DV Adapter for Gmail, you can easily create a data source for Gmail and introspect the data source to add resources to TDV.
Create the Data Source
- Right-click on the folder you wish to add the data source to and select New -> New Data Source.
- Scroll until you find the adapter (e.g. Gmail) and click Next.
- Name the data source (e.g. CData Gmail Source).
Fill in the required connection properties.
There are two ways to authenticate to Gmail. Before selecting one, first ensure that you have enabled IMAP access in your Gmail account settings. See the "Connecting to Gmail" section under "Getting Started" in the installed documentation for a guide.
The User and Password properties, under the Authentication section, can be set to valid Gmail user credentials.
Alternatively, instead of providing the Password, you can use the OAuth authentication standard. To access Google APIs on behalf on individual users, you can use the embedded credentials or you can register your own OAuth app.
OAuth also enables you to use a service account to connect on behalf of users in a Google Apps domain. To authenticate with a service account, you will need to register an application to obtain the OAuth JWT values.
In addition to the OAuth values, you will need to provide the User. See the "Getting Started" chapter in the help documentation for a guide to using OAuth.
![Filling in Connection Information (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Click Create & Close.
Introspect the Data Source
Once the data source is created, you can introspect the data source by right-clicking and selecting Open. In the dashboard, click Add/Remove Resources and select the Tables, Views, and Stored Procedures to include as part of the data source. Click Next and Finish to add the selected Gmail tables, views, and stored procedures as resources.
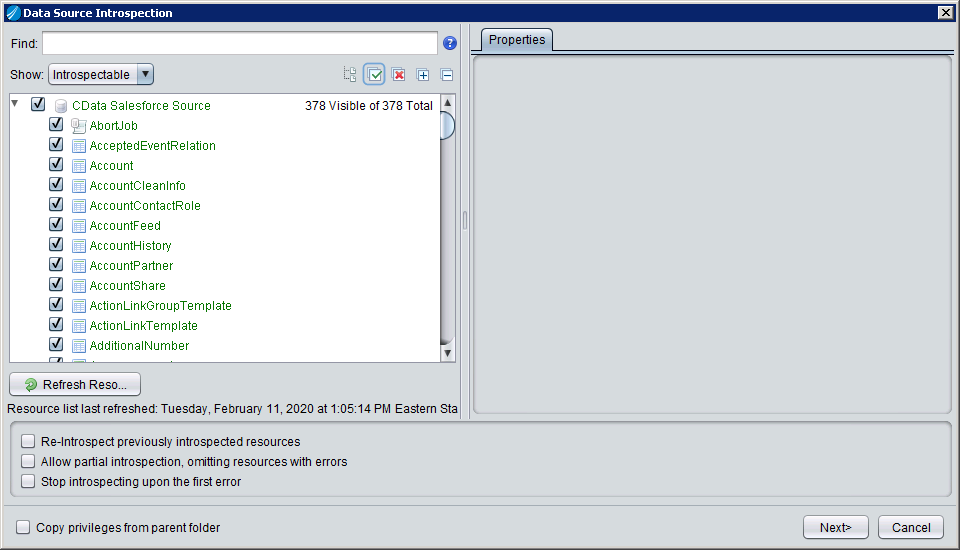
After creating and introspecting the data source, you are ready to work with Gmail data in TIBCO Data Virtualization just like you would any other relational data source. You can create views, query using SQL, publish the data source, and more.







