Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Export Data from SQL Server to Redshift through SSIS
Easily push SQL Server data to Redshift using the CData SSIS Tasks for Redshift.
SQL Server databases are commonly used to store enterprise records. It is often necessary to move this data to other locations. The CData SSIS Task for Redshift allows you to easily transfer Redshift data. In this article you will export data from SQL Server to Redshift.
Add Source and Destination Components
To get started, add a new ADO.NET Source control and a new Redshift Destination control to the data flow task.
Configure the ADO.NET Source
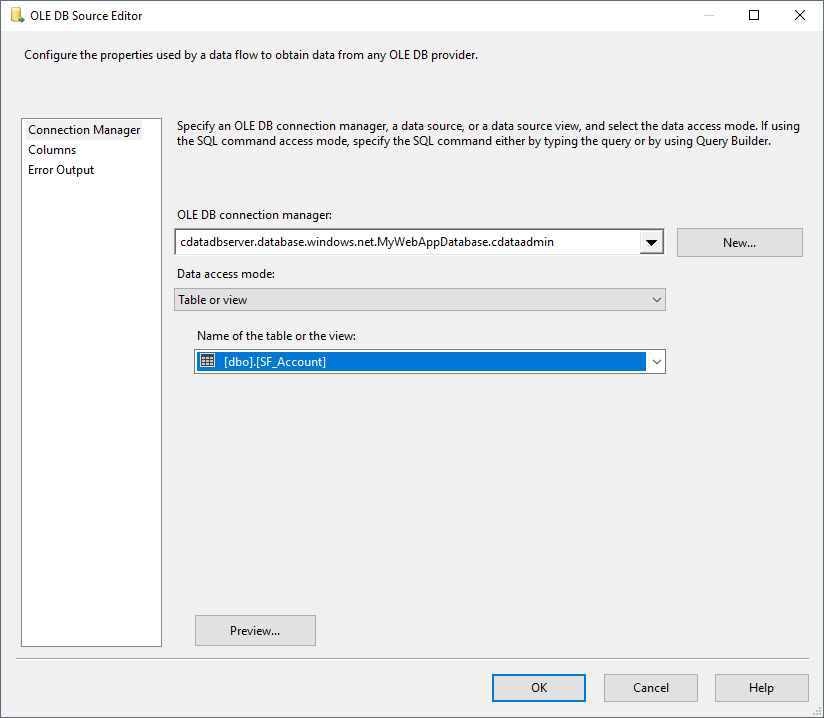
Follow the steps below to specify properties required to connect to the SQL Server instance.
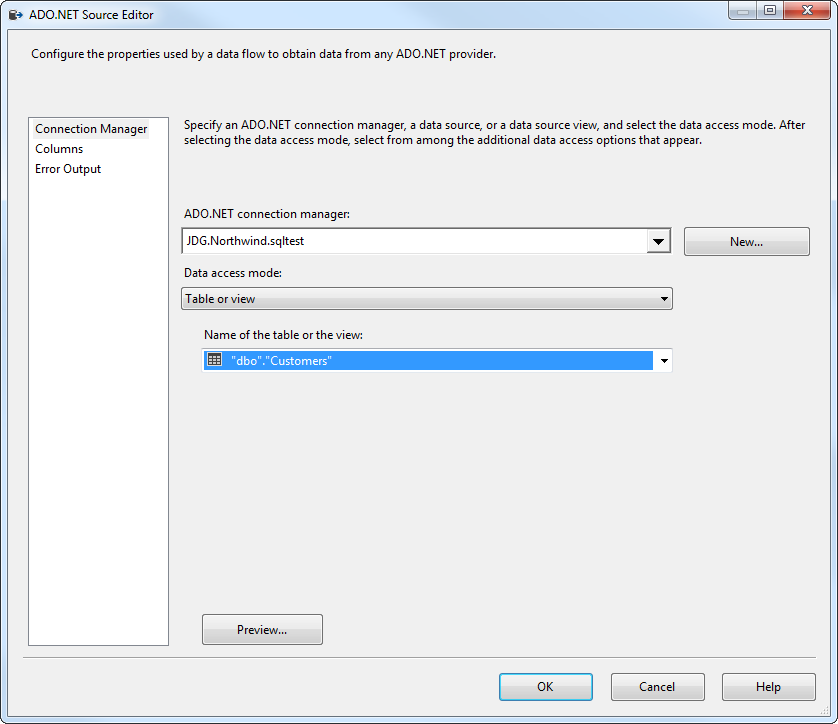
- Open the ADO.NET Source and add a new connection. Enter your server and database information here.
- In the Data access mode menu, select "Table or view" and select the table or view to export into Redshift.
- Close the ADO NET Source wizard and connect it to the destination component.

Create a New Connection Manager for Redshift
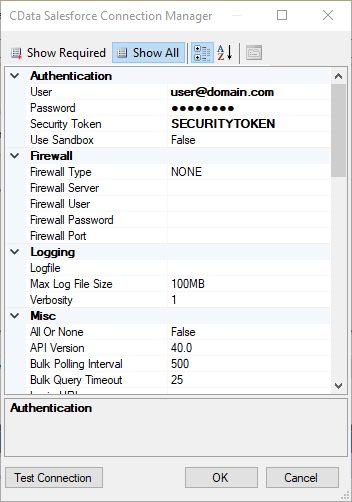
Follow the steps below to set required connection properties in the Connection Manager.
- Create a new connection manager: In the Connection Manager window, right-click and then click New Connection. The Add SSIS Connection Manager dialog is displayed.
- Select CData Redshift Connection Manager in the menu.
-
Configure the connection properties.
To connect to Redshift, set the following:
- Server: Set this to the host name or IP address of the cluster hosting the Database you want to connect to.
- Port: Set this to the port of the cluster.
- Database: Set this to the name of the database. Or, leave this blank to use the default database of the authenticated user.
- User: Set this to the username you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
- Password: Set this to the password you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
You can obtain the Server and Port values in the AWS Management Console:
- Open the Amazon Redshift console (http://console.aws.amazon.com/redshift).
- On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster.
- On the Configuration tab for the cluster, copy the cluster URL from the connection strings displayed.
Configure the Redshift Destination
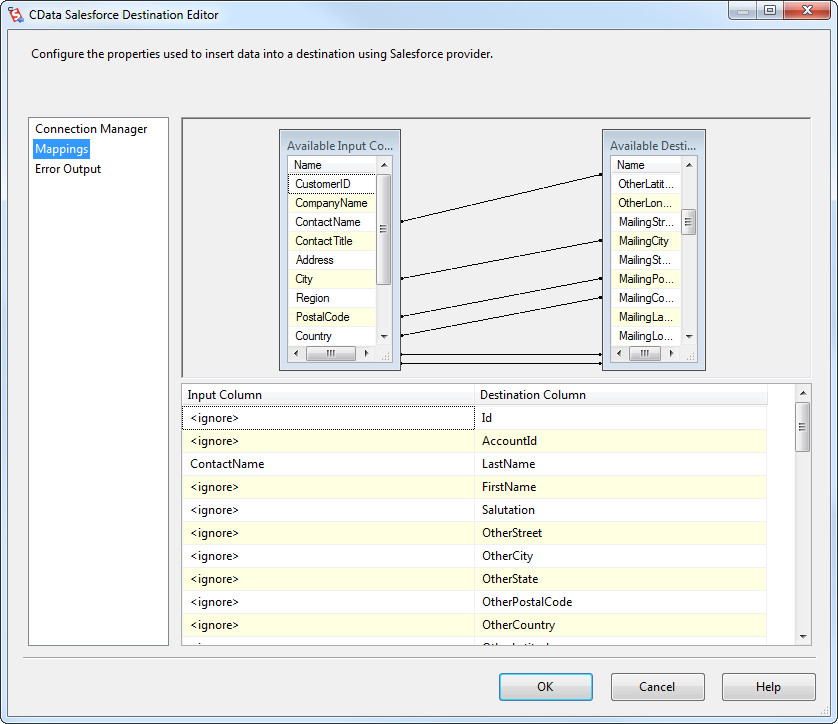
In the destination component Connection Manager, define mappings from the SQL Server source table into the Redshift destination table and the action you want to perform on the Redshift data. In this article, you will insert Orders entities to Redshift.
- Double-click the Redshift destination to open the destination component editor.
- In the Connection Managers tab, select the connection manager previously created.
-
In the Use a Table, menu, select Orders.
In the Action menu, select Insert.
![The destination table and action to be performed.]()
-
On the Column Mappings tab, configure the mappings from the input columns to the destination columns.
![The mappings from the SQL Server source to the SSIS destination component.]()
Run the Project
You can now run the project. After the SSIS Task has finished executing, data from your SQL table will be exported to the chosen table.