Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to connect to XML Data from MS Excel on Mac OS X
Create a Data Source Name in iODBC with the CData ODBC Driver for XML and work with XML data in Microsoft Excel on Mac OS X.
Microsoft Excel features calculations, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language that allows users to work with data in many of the ways that suit their needs, whether on a Windows machine or a Macintosh machine. This article walks through creating a DSN for XML data in iODBC and accessing XML data in Microsoft Excel, all on a machine running Mac OS X.
Installing the CData ODBC Drivers on Mac OS X
The CData ODBC Driver for XML is preconfigured for the iODBC driver manager, as are many other products like Microsoft Excel. This makes the driver easy to use with these tools.
Licensing the Driver
In a terminal run the following commands to license the driver. To activate a trial license, omit the key input.
cd "/Applications/CData ODBC Driver for XML/bin" sudo ./install-license <key>
Defining a DSN for iODBC with odbc.ini
You can define ODBC data sources in sections in the odbc.ini file. User data sources can only be accessed by the user account whose home folder the odbc.ini is located in. System data sources can be accessed by all users. You can find the correct odbc.ini in the following paths:
| Privileges | Path | |
|---|---|---|
| User | /Users/myuser/Library/ODBC/odbc.ini | |
| System | /Library/ODBC/odbc.ini |
Modifying iODBC's system-wide settings requires elevated permissions; to do so, you can use following to open a text editor from the terminal:
sudo nano /Library/ODBC/odbc.ini
See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation to authenticate to your data source: The data provider models XML APIs as bidirectional database tables and XML files as read-only views (local files, files stored on popular cloud services, and FTP servers). The major authentication schemes are supported, including HTTP Basic, Digest, NTLM, OAuth, and FTP. See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation for authentication guides.
After setting the URI and providing any authentication values, set DataModel to more closely match the data representation to the structure of your data.
The DataModel property is the controlling property over how your data is represented into tables and toggles the following basic configurations.
- Document (default): Model a top-level, document view of your XML data. The data provider returns nested elements as aggregates of data.
- FlattenedDocuments: Implicitly join nested documents and their parents into a single table.
- Relational: Return individual, related tables from hierarchical data. The tables contain a primary key and a foreign key that links to the parent document.
See the Modeling XML Data chapter for more information on configuring the relational representation. You will also find the sample data used in the following examples. The data includes entries for people, the cars they own, and various maintenance services performed on those cars.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
In addition to the connection properties required to connect to XML, the Driver property specifies either a driver definition in the odbcinst.ini file or the path to the driver library. Place your connection properties at the beginning of odbc.ini:
[CData XML Sources] Driver = CData ODBC Driver for XML URI = C:/people.xml DataModel = Relational
If you wish to authenticate using OAuth, you will need to add an additional connection property to ensure that the OAuth flow can execute properly:
Other = CheckPromptMode=False
Mac OS validates our drivers separately so you need to copy the license file to the appropriate path as well. After you have configured odbc.ini, run the following command.
sudo cp /Applications/CData ODBC Driver for XML/lib/CData.ODBC.XML.lic /Users/<YOUR_USER>/Library/Containers/com.microsoft.Excel/Data/.cdata/
Additionally, in the ODBC Data Sources section, the DSN must be set to a driver defined in the odbcinst.ini file. For example, below is the entry for the DSN created during the driver install:
[ODBC Data Sources]
CData XML Source = CData ODBC Driver for XML
Registering a DSN for iODBC with odbcinst.ini
You may need to modify the installed driver definition if you change the path to the driver library. To register an ODBC driver, modify the odbcinst.ini file. With iODBC, drivers can be available to only one user account or drivers can be available system wide. You can find the correct odbcinst.ini in the following paths:
| Privileges | Path | |
|---|---|---|
| User | /Users/myuser/Library/ODBC/odbcinst.ini | |
| System | /Library/ODBC/odbcinst.ini |
Drivers are defined in sections in the odbcinst.ini file. The section name specifies the name of the driver. In this section, the Driver property specifies the path to the driver library. The driver library is the .dylib file located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory, by default in /Applications/CData ODBC Driver for XML.
[CData ODBC Driver for XML]
Driver = /Applications/CData ODBC Driver for XML/lib/libxml.odbc.dylib
The ODBC Drivers section must also contain a property with the driver name, set to "Installed".
[ODBC Drivers]
CData ODBC Driver for XML = Installed
Testing the Connection
You can test your connection using the iODBC administrator.
- Open a terminal and enter the following command to start the iODBC Administrator with the necessary permissions:
sudo /Applications/iODBC/iODBC\ Administrator64.app/Contents/MacOS/iODBC\ Administrator64
- On the Users tab, select CData XML Source.
- Click the Test button.
Accessing XML Data from Microsoft Excel
You can use the DSN configured above to access XML data from Microsoft Excel.
- Open Microsoft Excel and open a spreadsheet (new or existing).
- Navigate to the data ribbon and select New Database Query From Database
- Select the User or System DSN that you previously configured and click OK.
![Choosing the DSN (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Build your SQL query in the Microsoft Query wizard:
![Querying for data (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Click Return Data to execute the query and pull data into Excel.
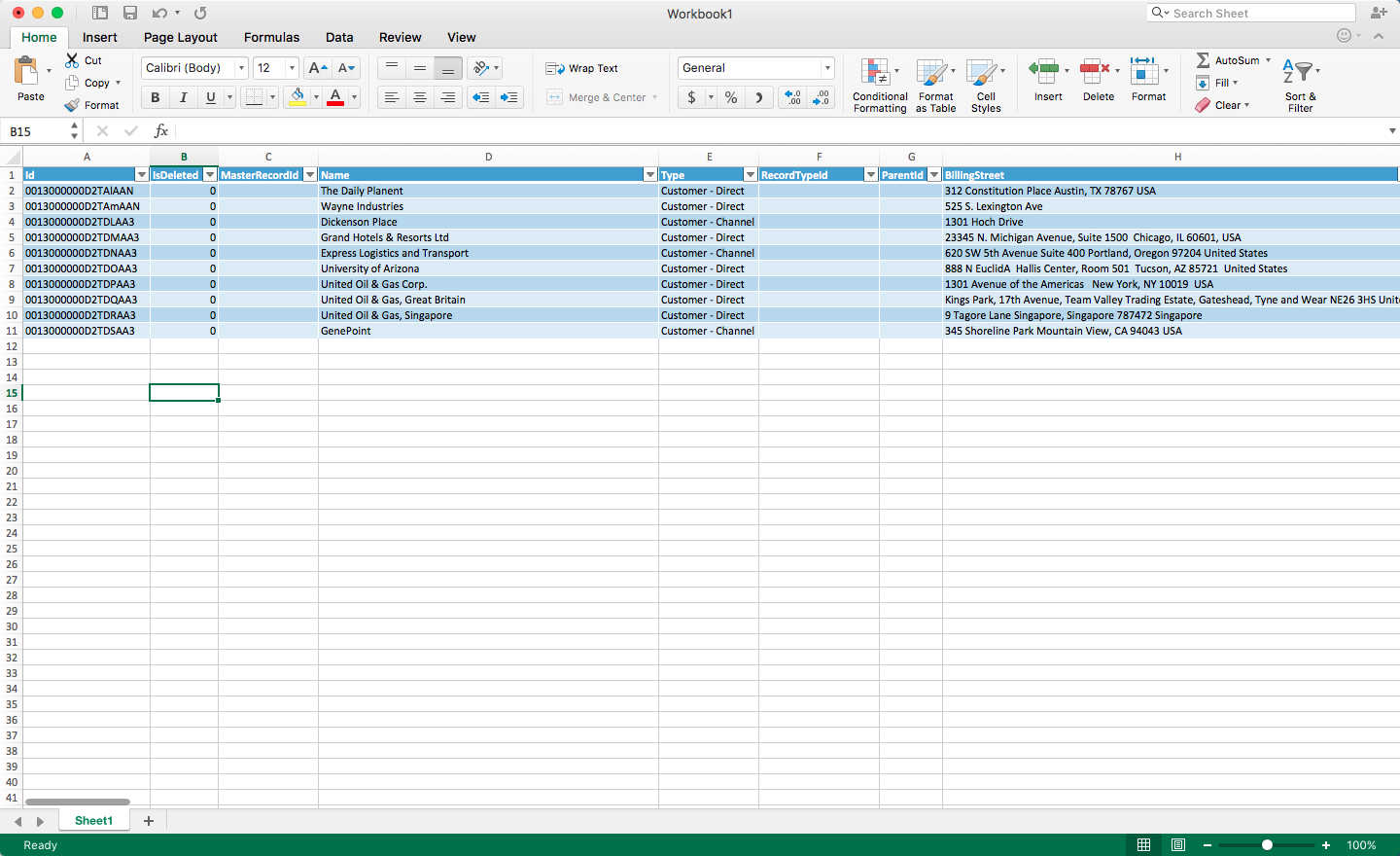
Using the CData ODBC Driver for XML, you can easily pull your XML data directly into Excel. Once there, you can leverage all of the powerful features native to Excel to analyze, report, transform your XML data, and more!