Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Query Act CRM Data as a SQL Server Database in Node.js
Execute SQL Server queries against Act CRM data from Node.js.
You can use CData Connect Cloud to query Act CRM data through a SQL Server interface. Follow the procedure below to create a virtual database for Act CRM in Connect Cloud and start querying using Node.js.
CData Connect Cloud provides a pure MySQL, cloud-to-cloud interface for Act CRM, allowing you to easily query live Act CRM data in Node.js — without replicating the data to a natively supported database. As you query data in Node.js, CData Connect Cloud pushes all supported SQL operations (filters, JOINs, etc) directly to Act CRM, leveraging server-side processing to quickly return Act CRM data.
Configure Act CRM Connectivity for NodeJS
Connectivity to Act CRM from NodeJS is made possible through CData Connect Cloud. To work with Act CRM data from NodeJS, we start by creating and configuring a Act CRM connection.
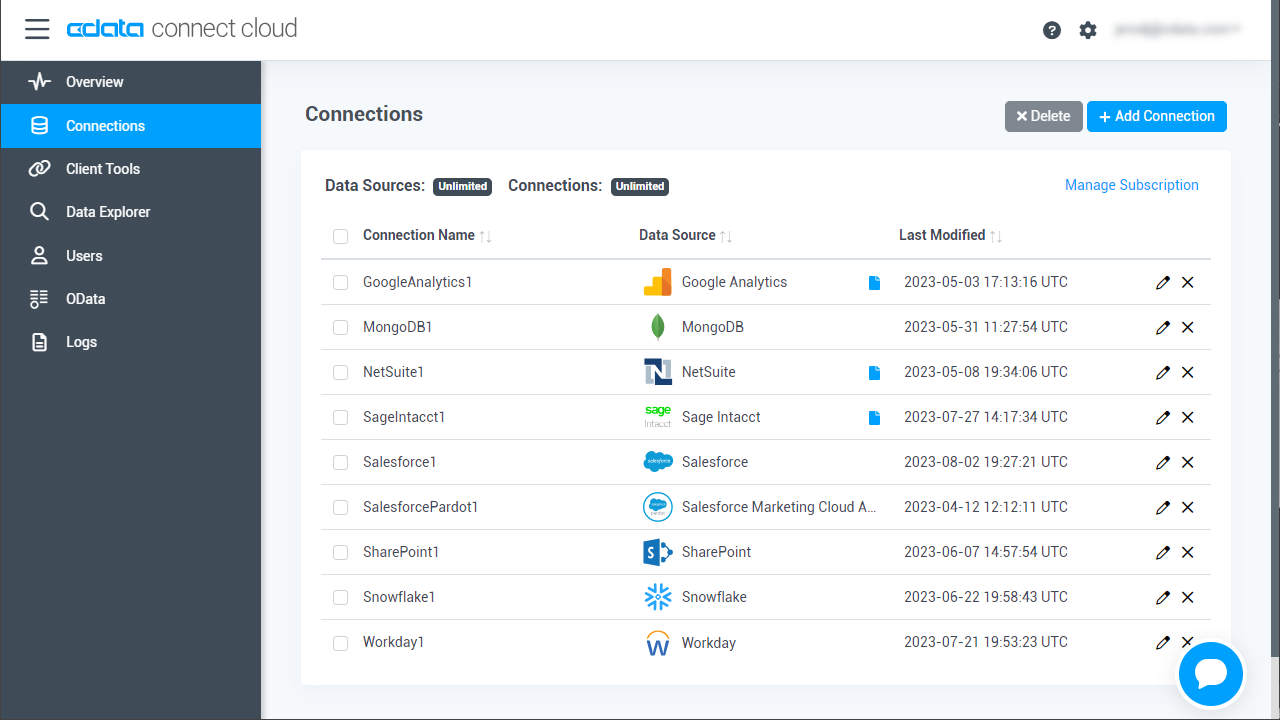
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Connections and click Add Connection
![Adding a Connection]()
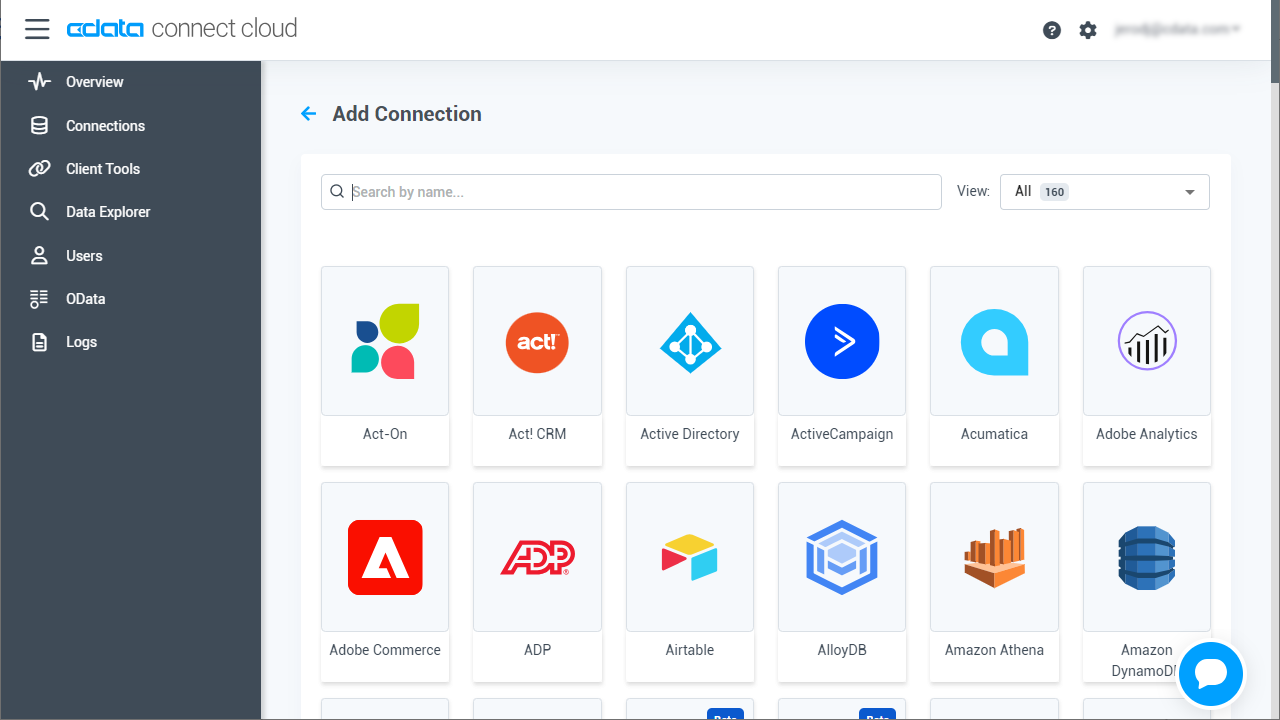
- Select "Act CRM" from the Add Connection panel
![Selecting a data source]()
-
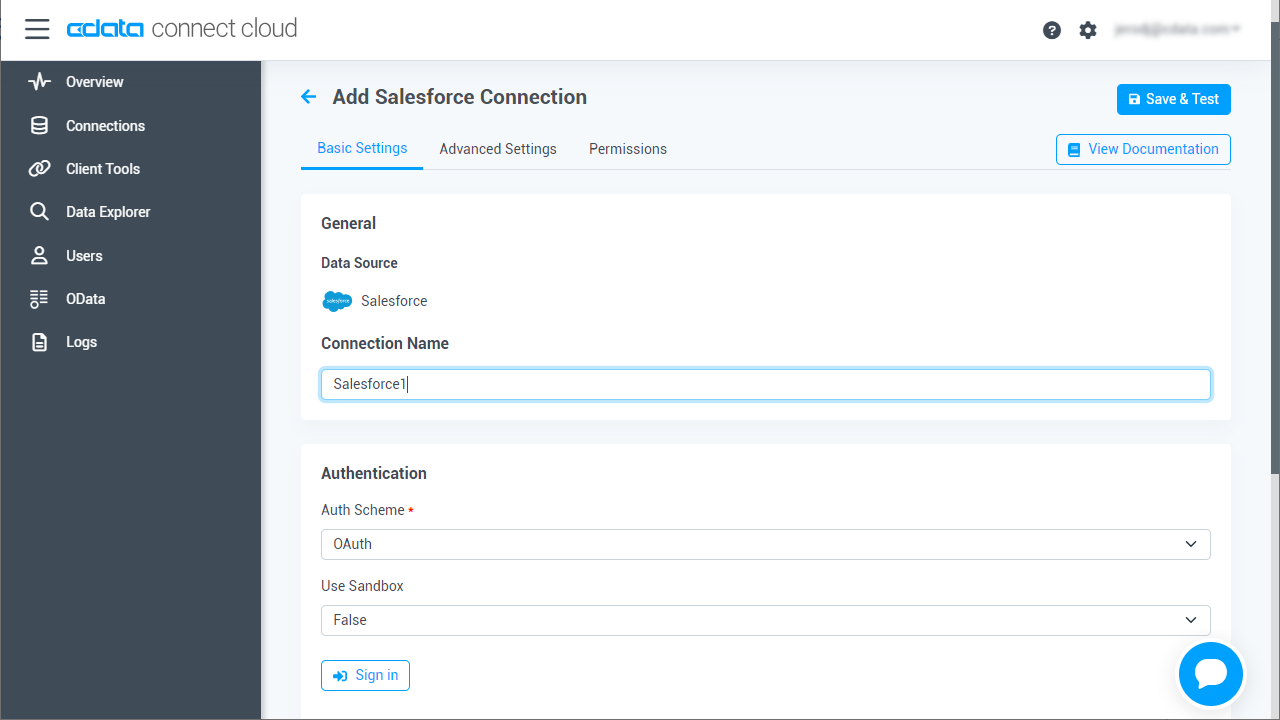
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Act CRM.
The User and Password properties, under the Authentication section, must be set to valid Act! user credentials. In addition to the authentication values, see the following:
-
Connecting to Act! Premium
In addition to the authentication values, the URL to Act! is also required; for example https://eup1-iis-04.eu.hosted.act.com/.
Additionally, you must specify the ActDatabase you will connect to. This is found by going to the About Act! Premium menu of your account, at the top right of the page, in the ? menu. Use the Database Name in the window that appears.
-
Connecting to Act! Premium Cloud
To connect to your Act! Premium Cloud account, you also need to specify the ActCloudName property. This property is found in the URL address of the Cloud account; for example https://eup1-iis-04.eu.hosted.act.com/ActCloudName/.
Note that retrieving ActCRM metadata can be expensive. It is advised that you set the CacheMetadata property to store the metadata locally.
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown)]()
-
- Click Create & Test
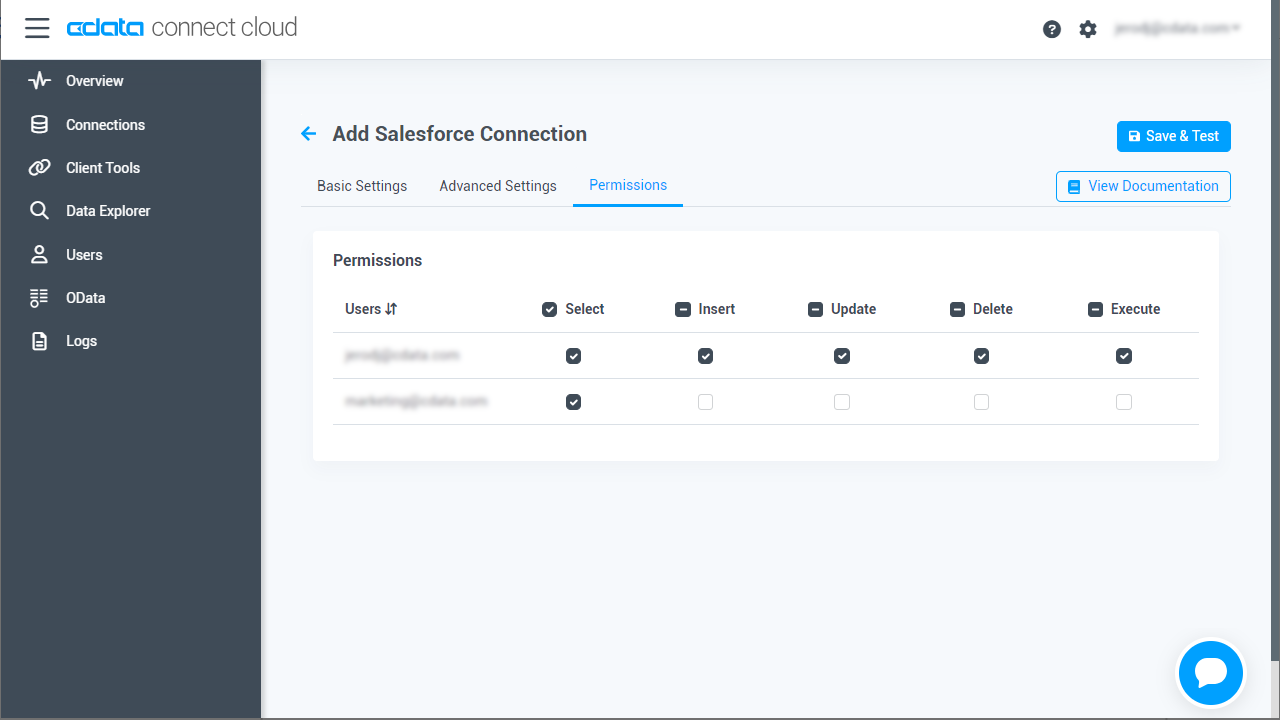
- Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add Act CRM Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
![Updating permissions]()
Add a Personal Access Token
If you are connecting from a service, application, platform, or framework that does not support OAuth authentication, you can create a Personal Access Token (PAT) to use for authentication. Best practices would dictate that you create a separate PAT for each service, to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on your username at the top right of the Connect Cloud app and click User Profile.
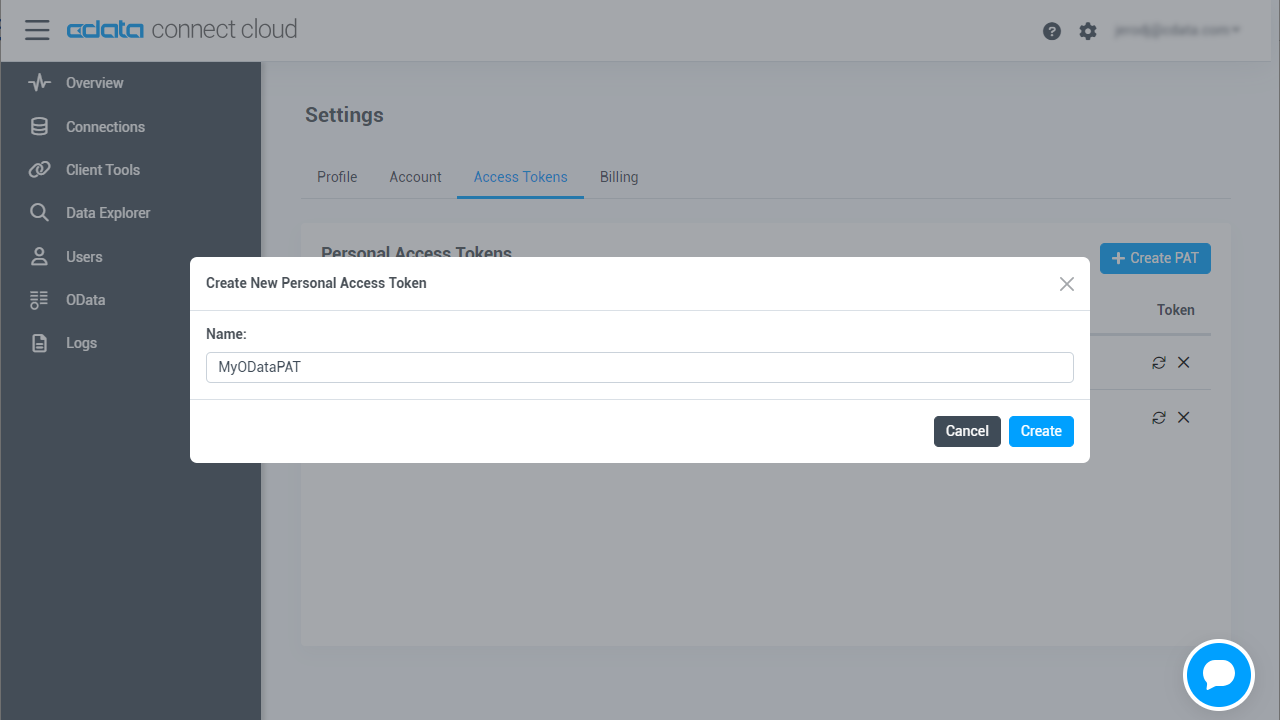
- On the User Profile page, scroll down to the Personal Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
- Give your PAT a name and click Create.
![Creating a new PAT]()
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured, you are ready to connect to Act CRM data from Node.js.
Query Act CRM from Node.js
The following example shows how to define a connection and execute queries to Act CRM with the SQL Server module. You will need the following information:
- server: tds.cdata.com
- port: 14333
- user: a Connect Cloud user (e.g. user@mydomain.com)
- password: the PAT for the above user
- database: The connection you configured for Act CRM (ActCRM1)
Connect to Act CRM data and start executing queries with the code below:
var sql = require('mssql')
var config = {
server: 'tds.cdata.com',
port: 14333,
user: 'user@mydomain.com', //update me
password: 'CONNECT_USER_PAT', //update me
options: {
encrypt: true,
database: 'ActCRM1'
}
}
sql.connect(config, err => {
if(err){
throw err ;
}
new sql.Request().query('SELECT * FROM Activities', (err, result) => {
console.dir(result)
})
});
sql.on('error', err => {
console.log("SQL Error: " ,err);
})