Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Model AlloyDB Data Using Azure Analysis Services
Leverage CData Connect Cloud to establish a connection between Azure Analysis Services and AlloyDB, enabling the direct import of real-time AlloyDB data.
Microsoft Azure Analysis Services (AAS) is a fully-managed platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offering that delivers enterprise-grade data models in the cloud. When combined with CData Connect Cloud, AAS facilitates immediate cloud-to-cloud access to AlloyDB data for applications. This article outlines the process of connecting to AlloyDB via Connect Cloud and importing AlloyDB data into Visual Studio using an AAS extension.
CData Connect Cloud offers a seamless cloud-to-cloud interface tailored for AlloyDB, enabling you to create live models of AlloyDB data in Azure Analysis Services without the need to replicate data to a natively supported database. While constructing high-quality semantic data models for business reports and client applications, Azure Analysis Services formulates SQL queries to retrieve data. CData Connect Cloud is equipped with optimized data processing capabilities right from the start, directing all supported SQL operations, including filters and JOINs, directly to AlloyDB. This leverages server-side processing for swift retrieval of the requested AlloyDB data.
Configure AlloyDB Connectivity for AAS
Connectivity to AlloyDB from Azure Analysis Services is made possible through CData Connect Cloud. To work with AlloyDB data from Azure Analysis Services, we start by creating and configuring a AlloyDB connection.
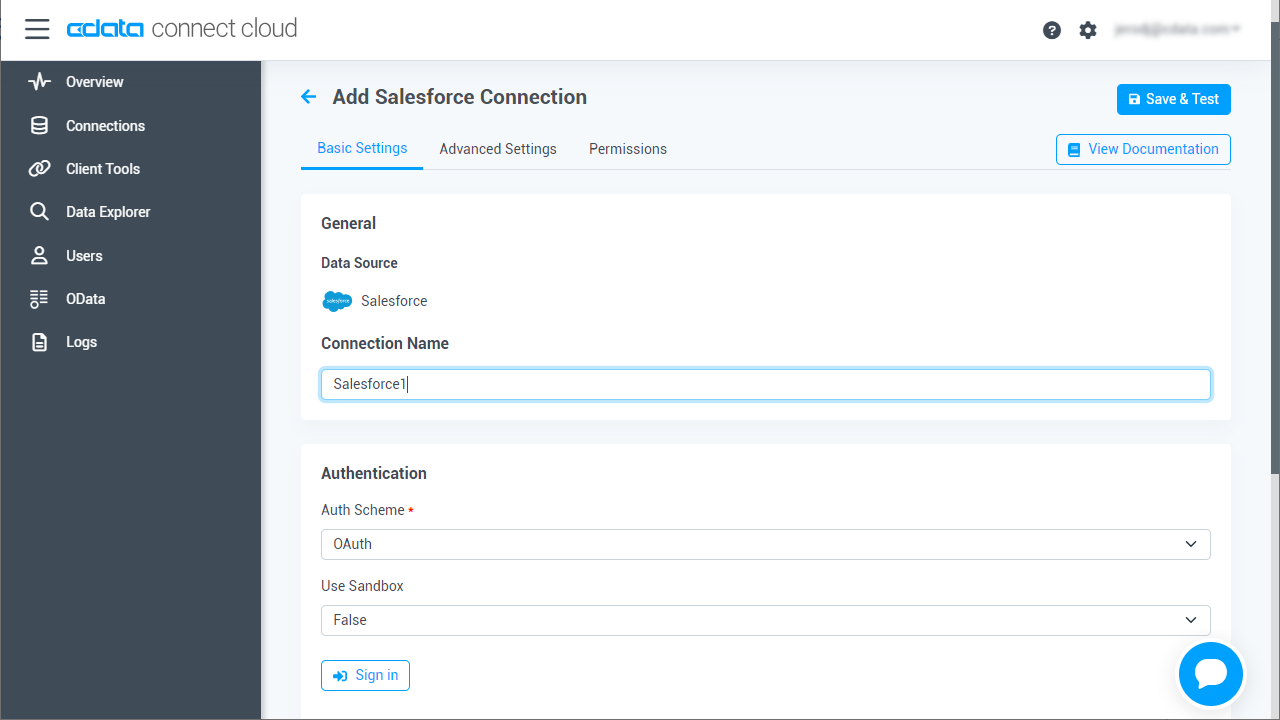
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Connections and click Add Connection
- Select "AlloyDB" from the Add Connection panel
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to AlloyDB.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown)]()
- Click Create & Test
-
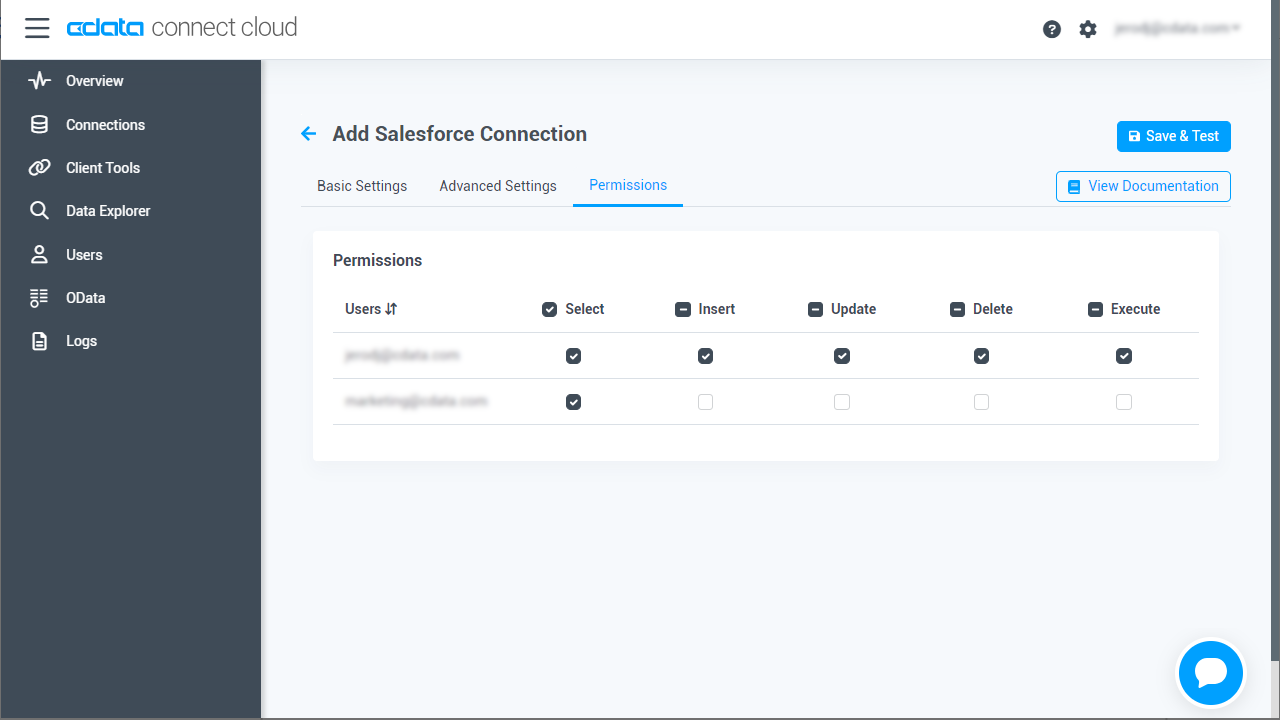
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add AlloyDB Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
![Updating permissions]()
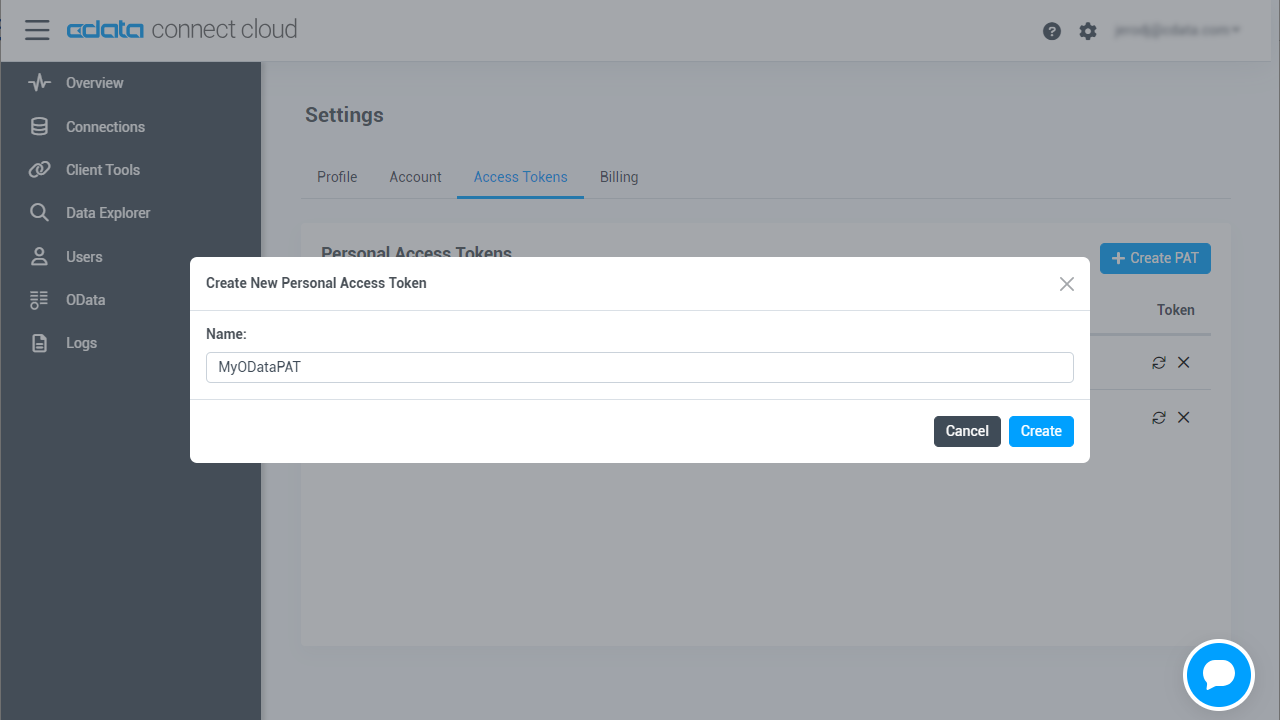
Add a Personal Access Token
If you are connecting from a service, application, platform, or framework that lacks support for OAuth authentication, you have the option to generate a Personal Access Token (PAT) for authentication purposes. It's advisable to follow best practices by creating a distinct PAT for each service to uphold access granularity.
- Click on your username at the top right of the Connect Cloud app and click User Profile.
- On the User Profile page, scroll down to the Personal Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
- Give your PAT a name and click Create.
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured, you are ready to connect to AlloyDB data from Visual Studio using Azure Analysis Services.
Connect to AlloyDB in Visual Studio Using AAS
The steps below outline connecting to CData Connect Cloud from Azure Analysis Services to create a new AlloyDB data source. You will need the Microsoft Analysis Services Project Extension installed to continue.
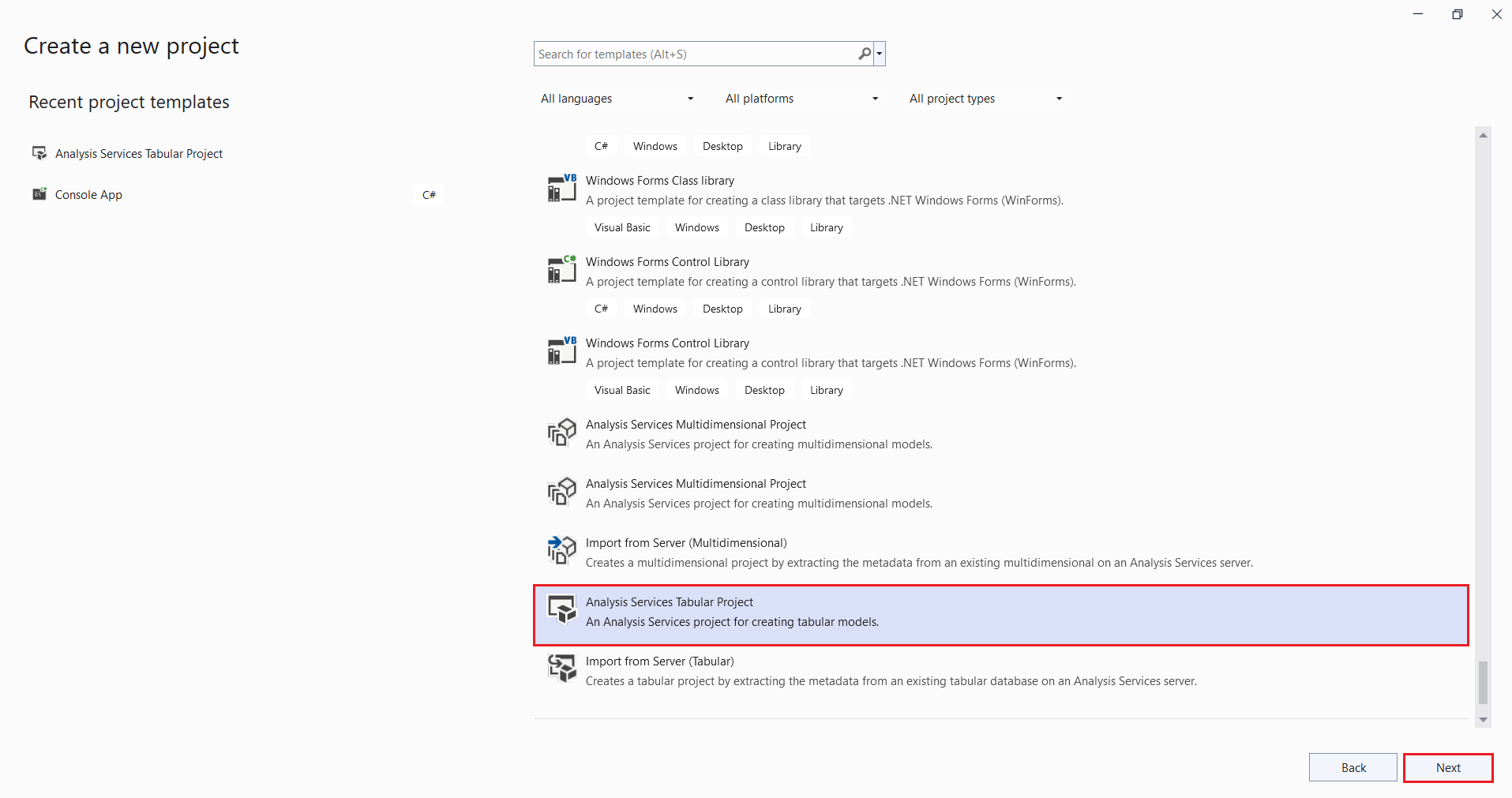
- In Visual Studio, create a new project. Select Analysis Services Tabular Project.
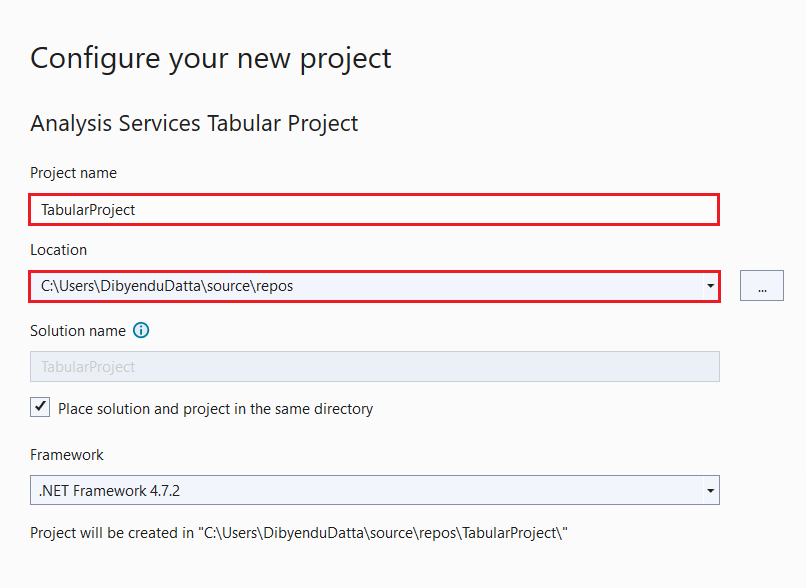
- In the Configure your new project dialog, enter a name for your project in the Project name field. Fill in the rest of the fields.
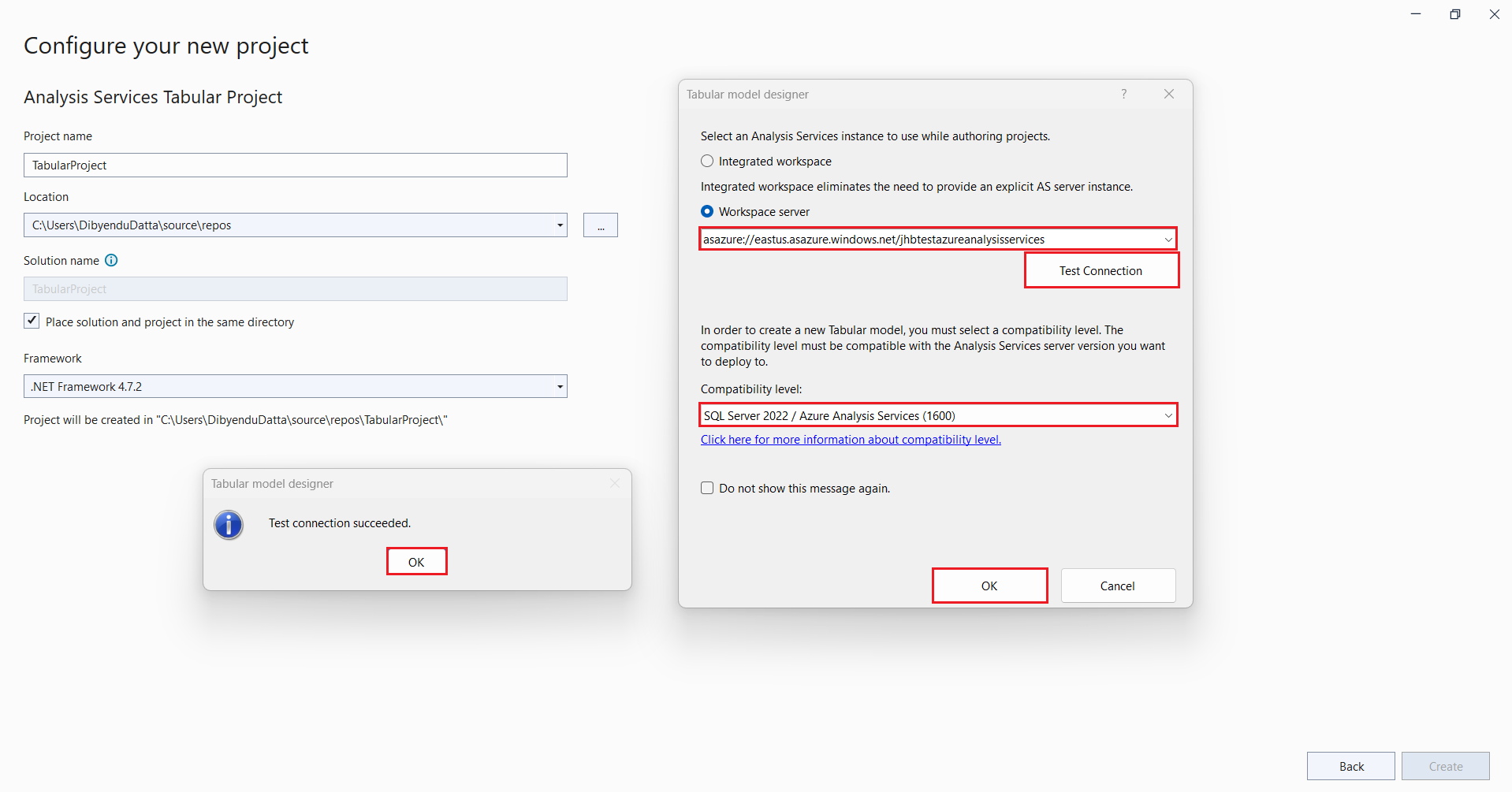
- Click Create. The Tabular model designer dialog box opens. Select Workspace server and enter the address of your Azure Analysis Services server (for example, asazure://eastus.azure.windows.net/myAzureServer). Click Test Connection and sign in to your server.
- Click OK to create the project. Your Visual Studio window should resemble the following screenshot:
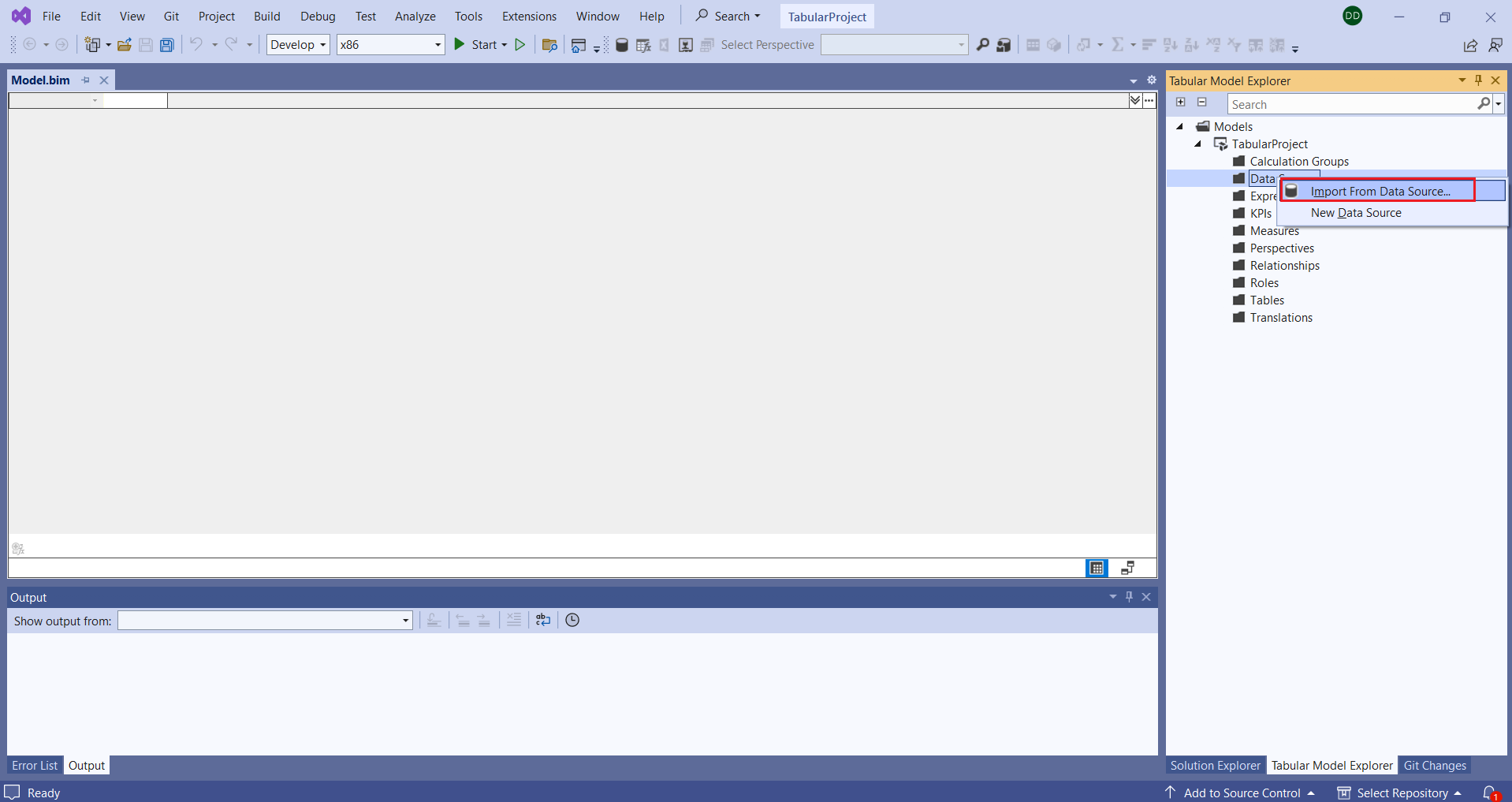
- In Visual Studio, in Tabular model Explorer, right-click Data Sources and select Import From Data Source.
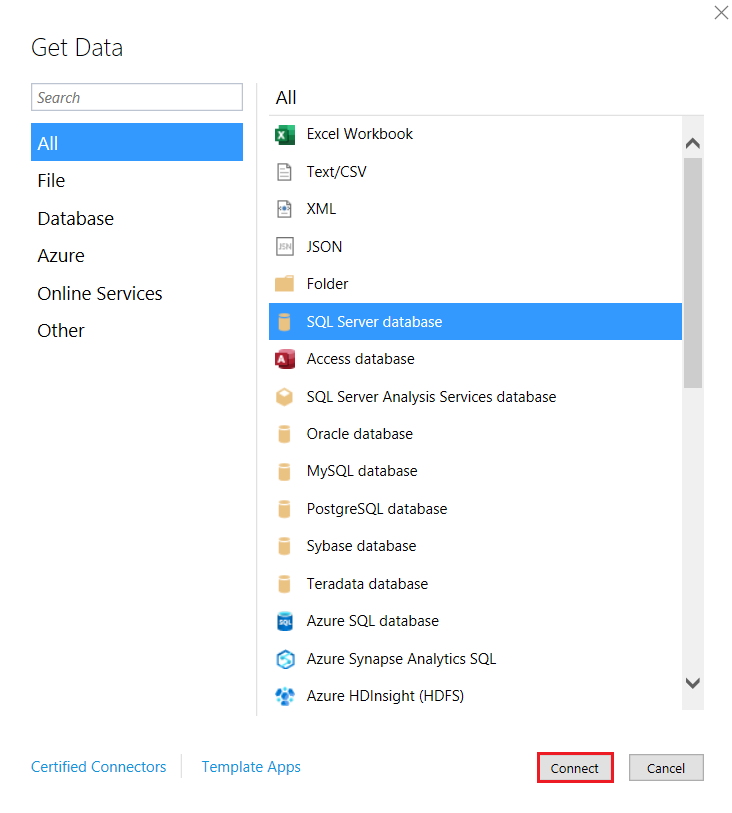
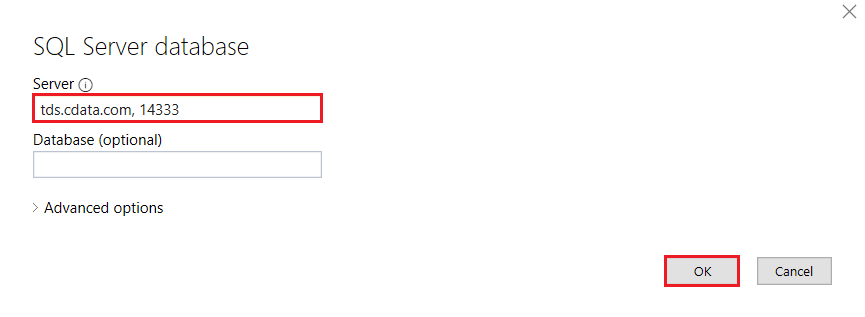
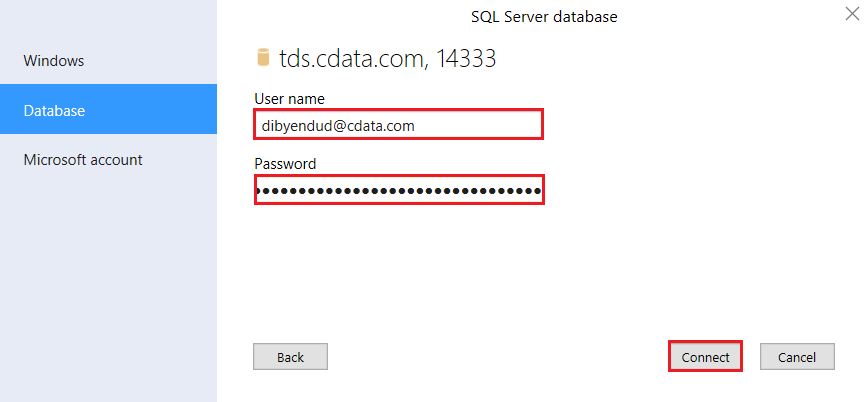
- In the Table Import Wizard, select SQL Server database and click Connect. In the Server field, enter the Virtual SQL Server endpoint and port separated by a comma: e.g., tds.cdata.com,14333
-
Click SQL Server Authentication and enter the following information:
- User name: Enter your CData Connect Cloud username. This is displayed in the top-right corner of the CData Connect Cloud interface. For example, test@cdata.com.
- Password: Enter the PAT you generated on the Settings page.
- On the next screen, select Current User and click Next.
- Now, select the first option and click Next.
- On the next screen, select a table from the list and click Preview & Filter.
- You should now see the table from AlloyDB populated with data.

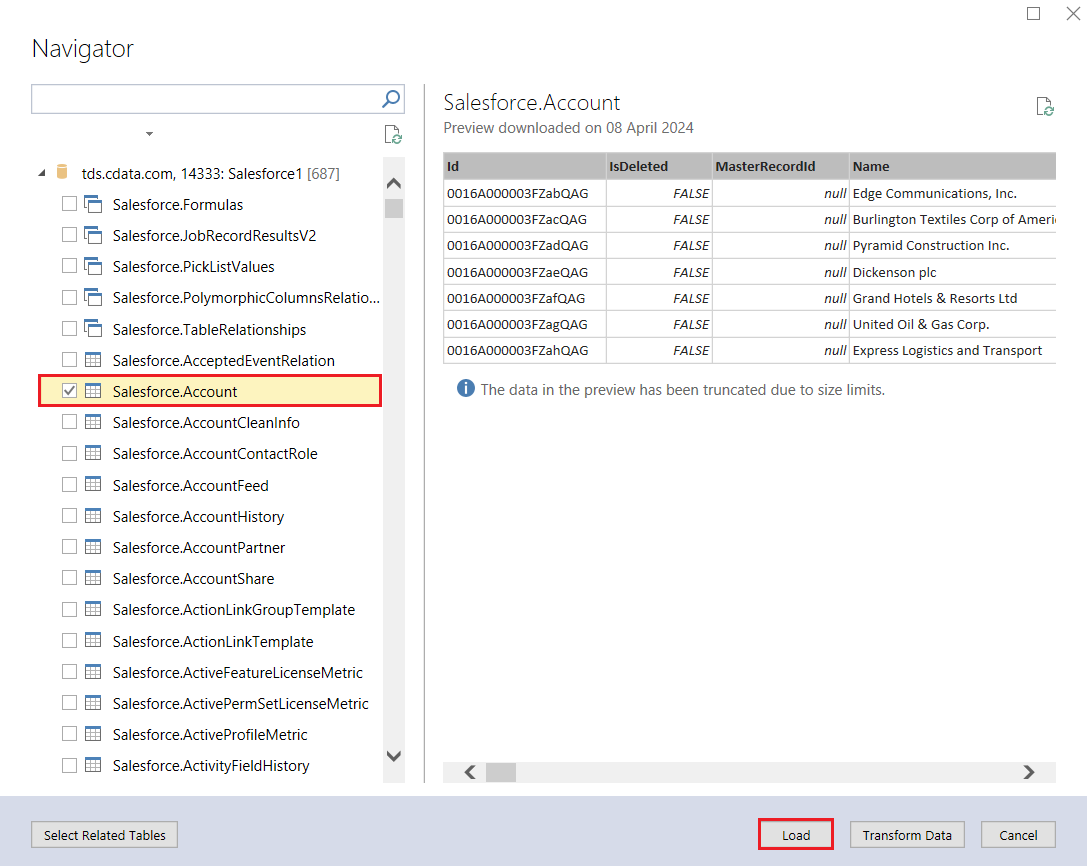
Now that you have imported the AlloyDB data into your data model, you are ready to deploy the project to Azure Analysis Services for use in business reports, client applications, and more.
Get CData Connect Cloud
To get live data access to 100+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your cloud applications, try CData Connect Cloud today!