Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Integrate AlloyDB Data in Your Informatica Cloud Instance
Use CData JDBC drivers with the Informatica Cloud Secure Agent to access live AlloyDB data from Informatica Cloud.
Informatica Cloud allows you to perform extract, transform, and load (ETL) tasks in the cloud. With the Cloud Secure Agent and the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB, you get live access to AlloyDB data, directly within Informatica Cloud. In this article, we will walk through downloading and registering the Cloud Secure Agent, connecting to AlloyDB through the JDBC Driver and generating a mapping that can be used in any Informatica Cloud process.
Informatica Cloud Secure Agent
To work with the AlloyDB data through the JDBC Driver, install the Cloud Secure Agent.
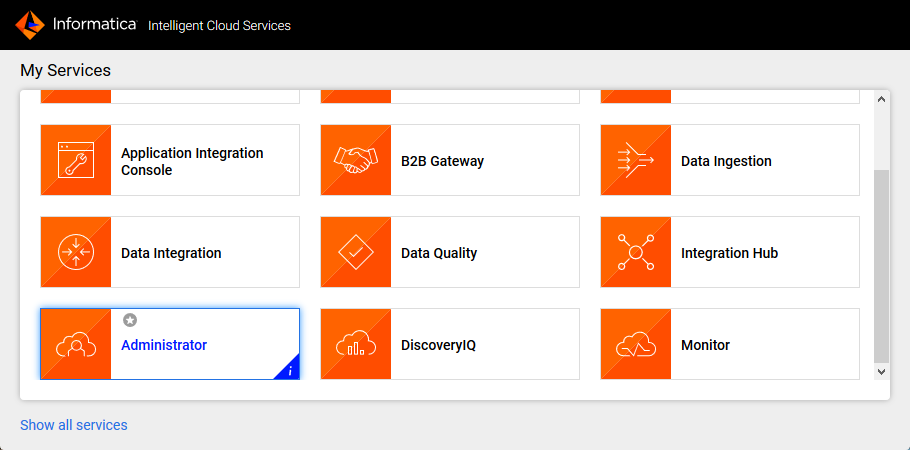
- Navigate to the Administrator page in Informatica Cloud
![]()
- Select the Runtime Environments tab
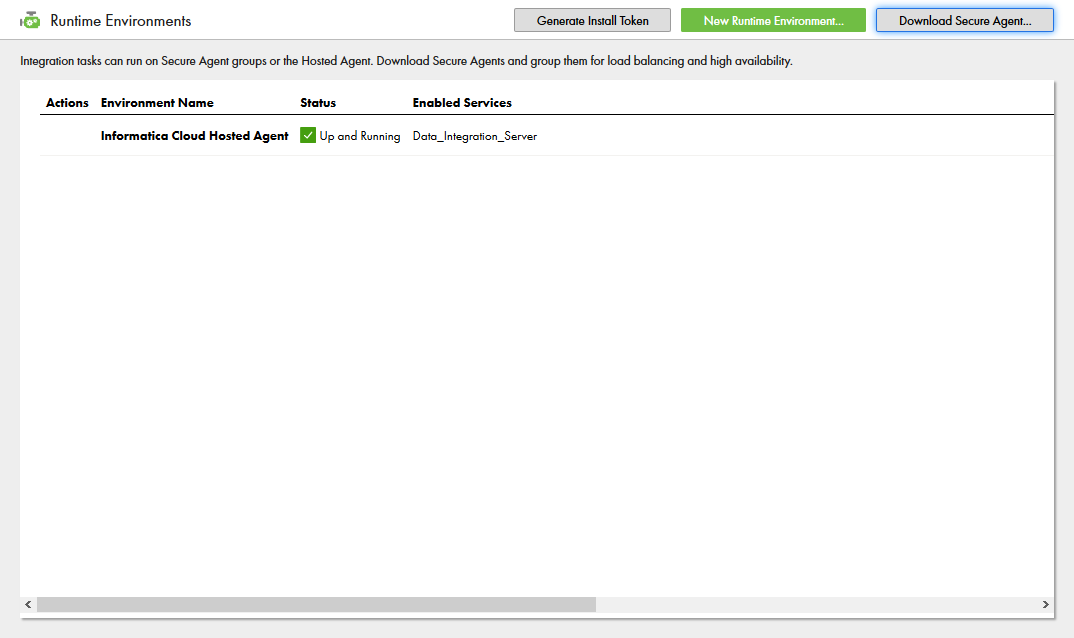
- Click "Download Secure Agent"
![]()
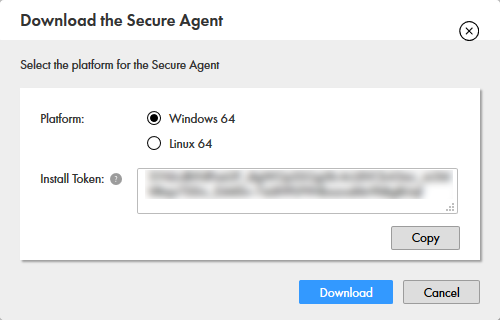
- Make note of the Install Token
![]()
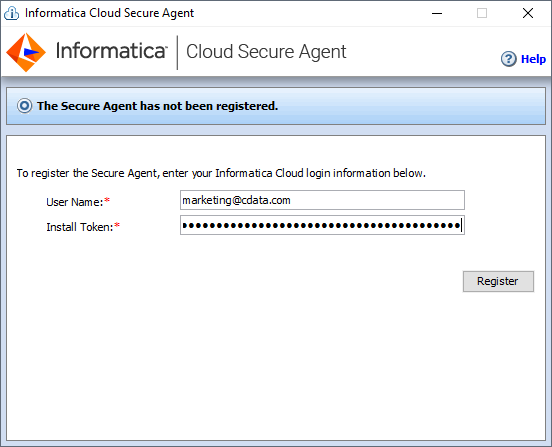
- Run the installer on the client machine and register the Cloud Secure Agent with your username and install token
![]()
NOTE: It may take some time for all of the Cloud Secure Agent services to get up and running.
Connecting to the AlloyDB JDBC Driver
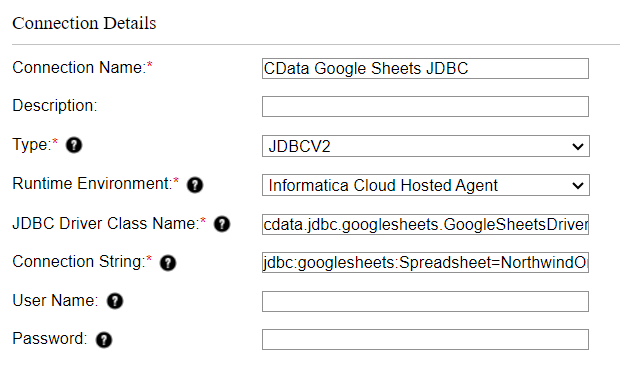
With the Cloud Secure Agent installed and running, you are ready to connect to AlloyDB through the JDBC Driver. Start by clicking the Connections tab and clicking New Connection. Fill in the following properties for the connection:
- Connection Name: Name your connection (i.e.: CData AlloyDB Connection)
- Type: Select "JDBC_IC (Informatica Cloud)"
- Runtime Environment: Select the runtime environment where you installed the Cloud Secure Agent
- JDBC Connection URL: Set this to the JDBC URL for AlloyDB. Your URL will look similar to the following:
jdbc:alloydb:User=alloydb;Password=admin;Database=alloydb;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
Built-In Connection String Designer
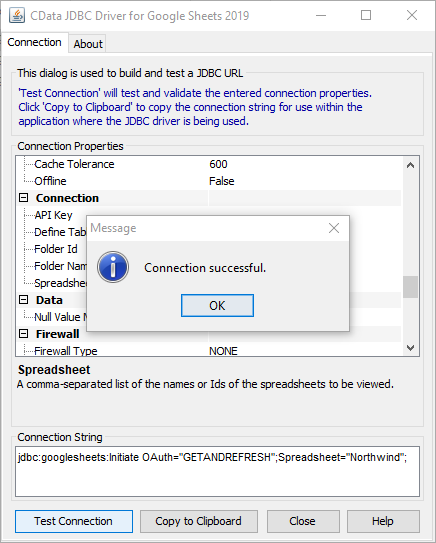
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the AlloyDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the .jar file or execute the .jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.alloydb.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Google Sheets is shown.)]()
- JDBC Jar Directory: Set this to the lib folder in the installation location for the JDBC Driver (on Windows, typically C:\Program Files\CData[product_name]\)
- Driver Class: Set this to cdata.jdbc.alloydb.AlloyDBDriver
- Username: Set this to the username for AlloyDB
- Password: Set this to the password for AlloyDB
Create a Mapping for AlloyDB Data
With the connection to AlloyDB configured, we can now access AlloyDB data in any Informatica process. The steps below walk through creating a mapping for AlloyDB to another data target.
- Navigate to the Data Integration page
![]()
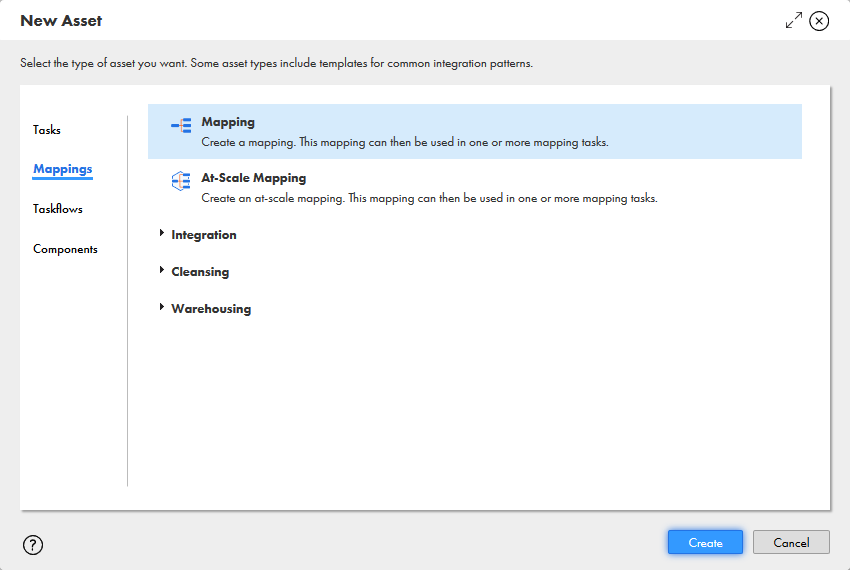
- Click New.. and select Mapping from the Mappings tab
![]()
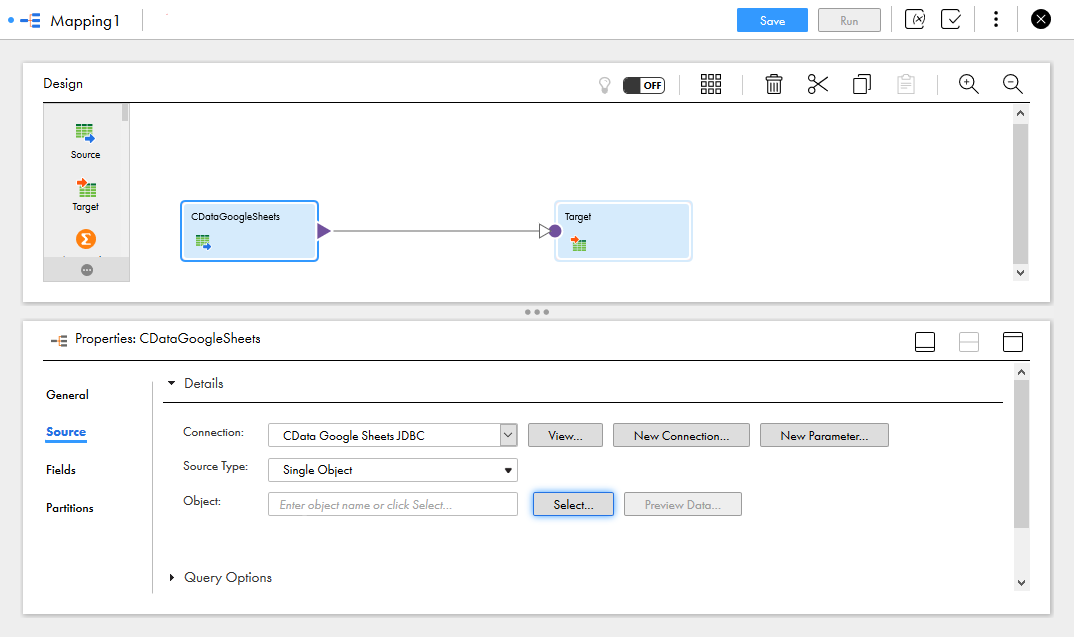
- Click the Source Object and in the Source tab, select the Connection and set the Source Type
![Selecting the Source Connection and Source Type]()
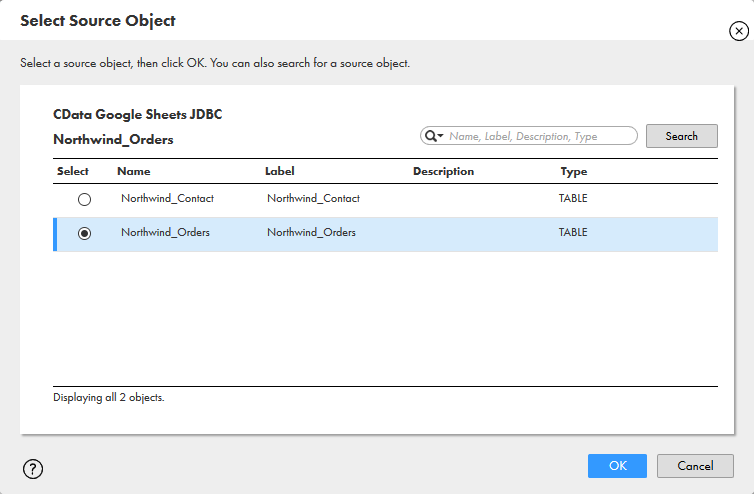
- Click "Select" to choose the table to map
![Selecting the Source Object]()
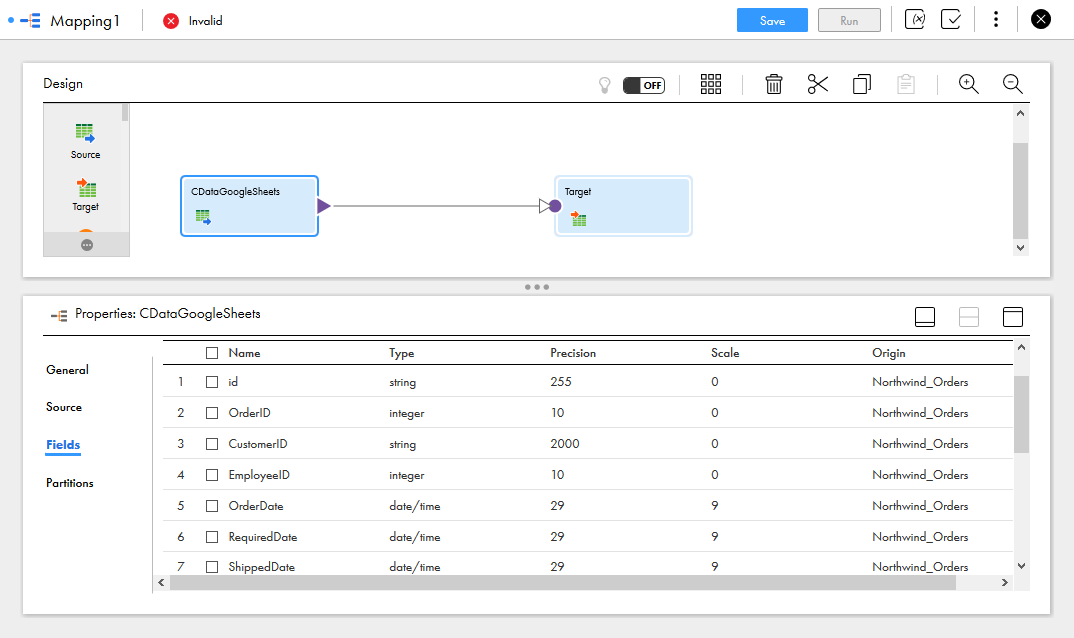
- In the Fields tab, select the fields from the AlloyDB table to map
![Selecting Source Fields to map]()
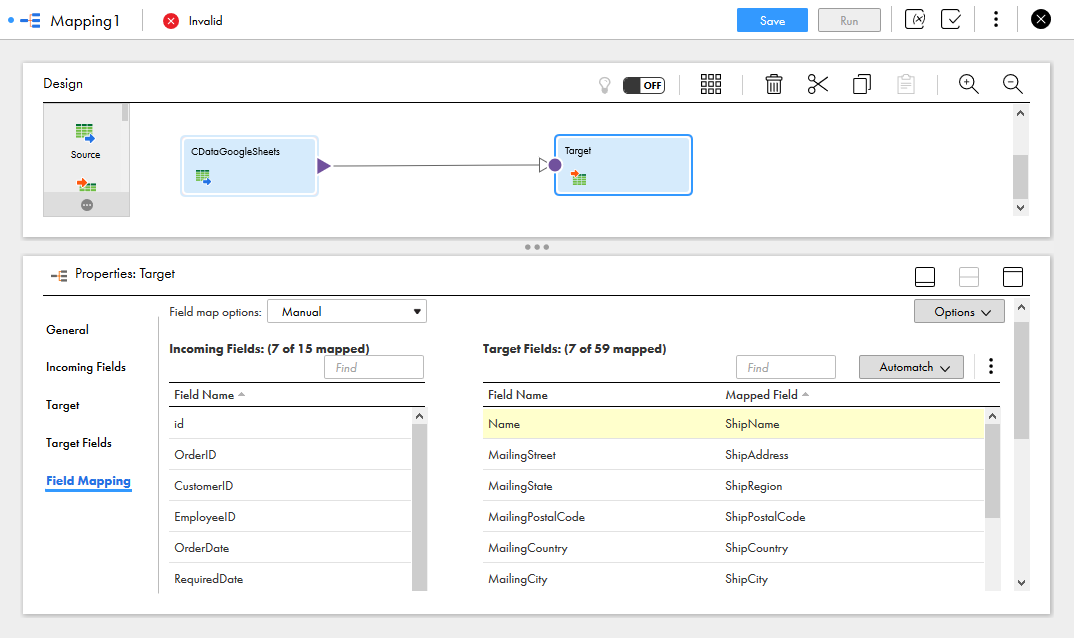
- Click the Target object and configure the Target source, table and fields. In the Field Mapping tab, map the source fields to the target fields.
![Selecting the Target Field Mappings]()
With the mapping configured, you are ready to start integrating live AlloyDB data with any of the supported connections in Informatica Cloud. Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB and start working with your live AlloyDB data in Informatica Cloud today.