Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Use the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB in MicroStrategy
Connect to AlloyDB data in MicroStrategy Developer using the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB.
MicroStrategy is an analytics and mobility platform that enables data-driven innovation. When you pair MicroStrategy with the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB, you gain database-like access to live AlloyDB data from MicroStrategy, expanding your reporting and analytics capabilities. In this article, we walk through creating a database instance for AlloyDB in MicroStrategy Developer and create a Warehouse Catalog for the AlloyDB data.
The CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live AlloyDB data in MicroStrategy due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries from MicroStrategy to AlloyDB, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to AlloyDB and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can visualize and analyze AlloyDB data using native MicroStrategy data types.
Connect to AlloyDB in MicroStrategy Developer
You can connect to AlloyDB in MicroStrategy Developer by adding a database instance based on the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB.* Before you begin, you will need to install the JDBC Driver for AlloyDB on the machine hosting the MicroStrategy Intelligence Server that your instance of MicroStrategy Developer is connected to.
- Open MicroStrategy Developer and select a Project Source.
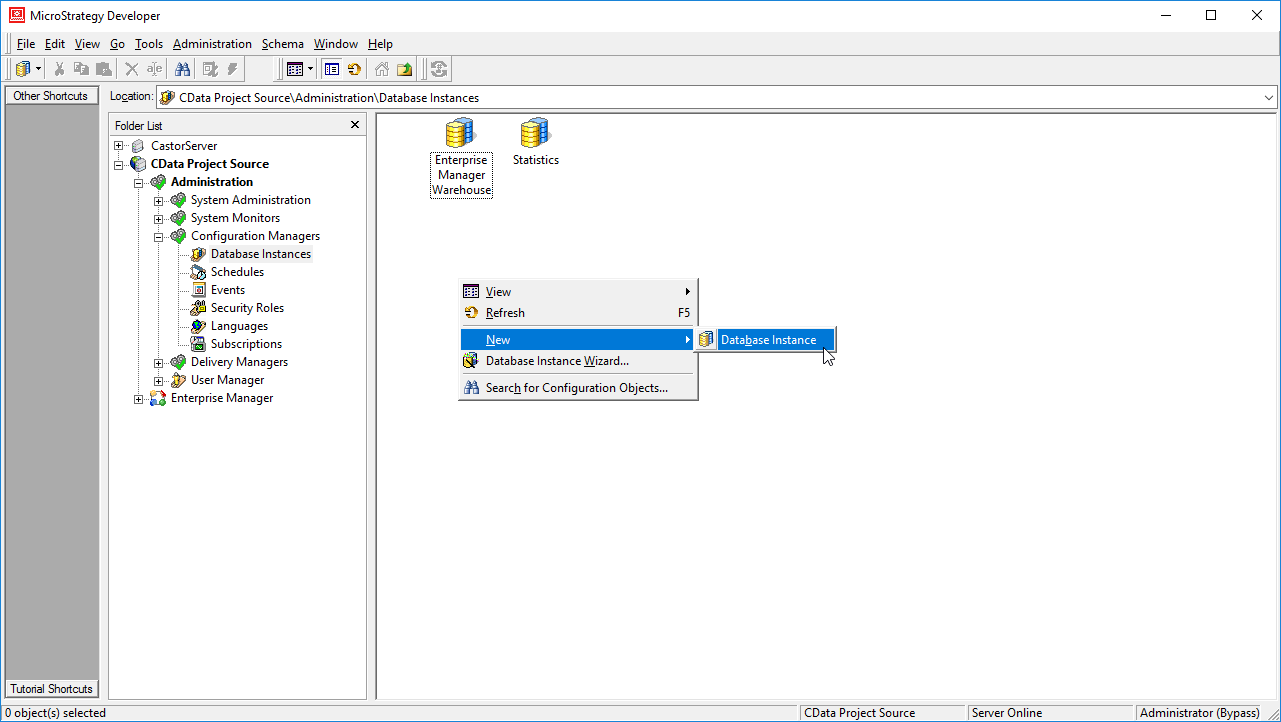
- Navigate to Administration -> Configuration Managers -> Database Instances and right-click to add a new instance.
![Create a new Database Instance]()
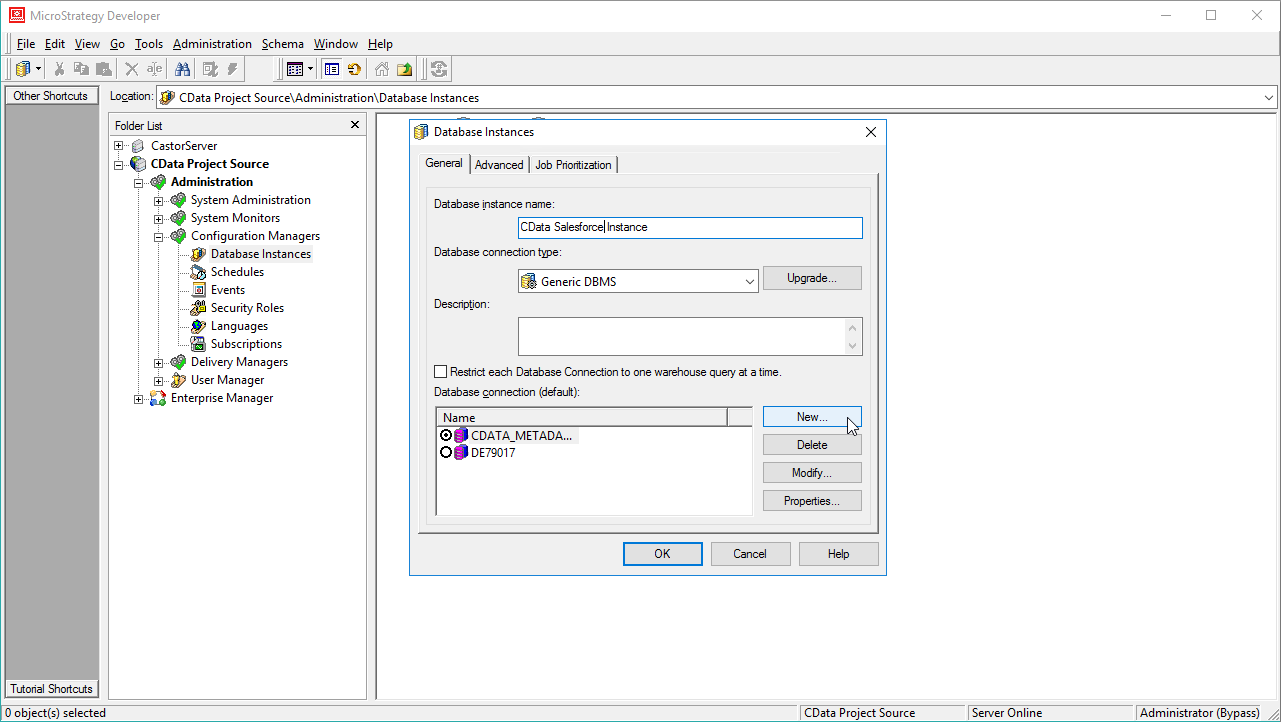
- Name the instance, select Generic DBMS as the database connection type, and create a new database connection.
![Create a new database connection.]()
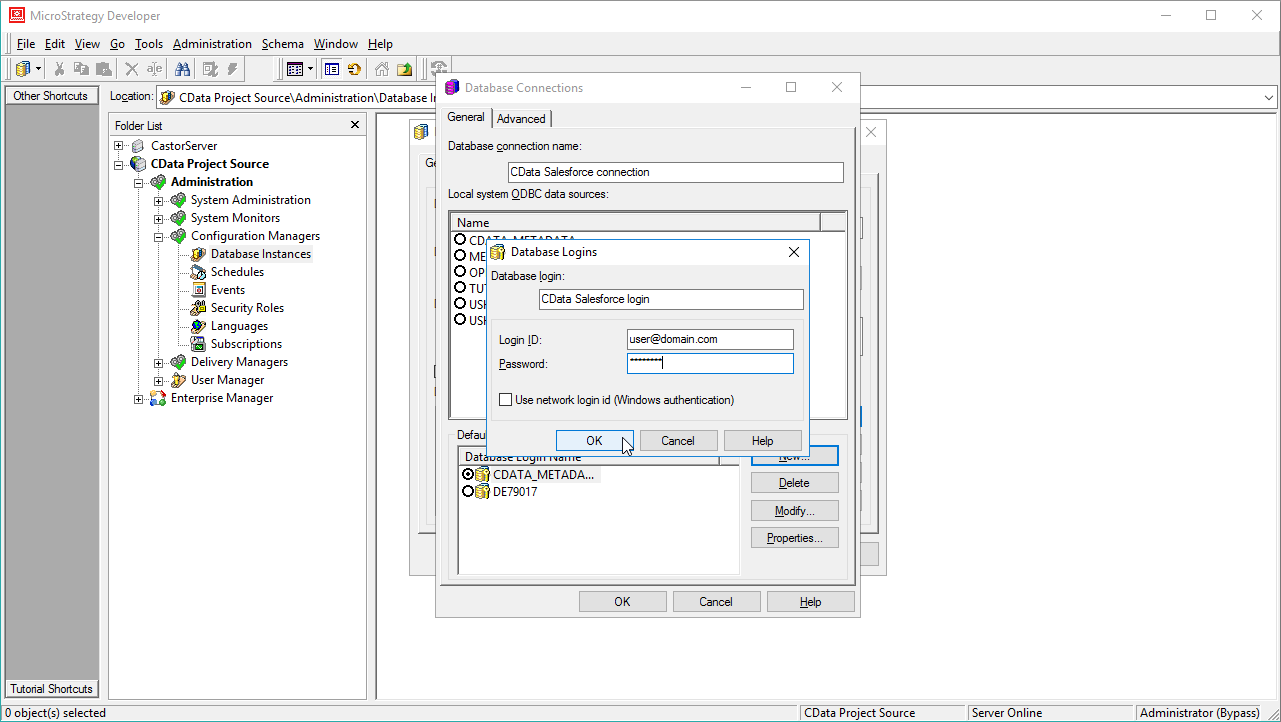
- In the database connection wizard, name the connection and create a new Database Login name, setting the user and password for AlloyDB.
![Create a new database login.]()
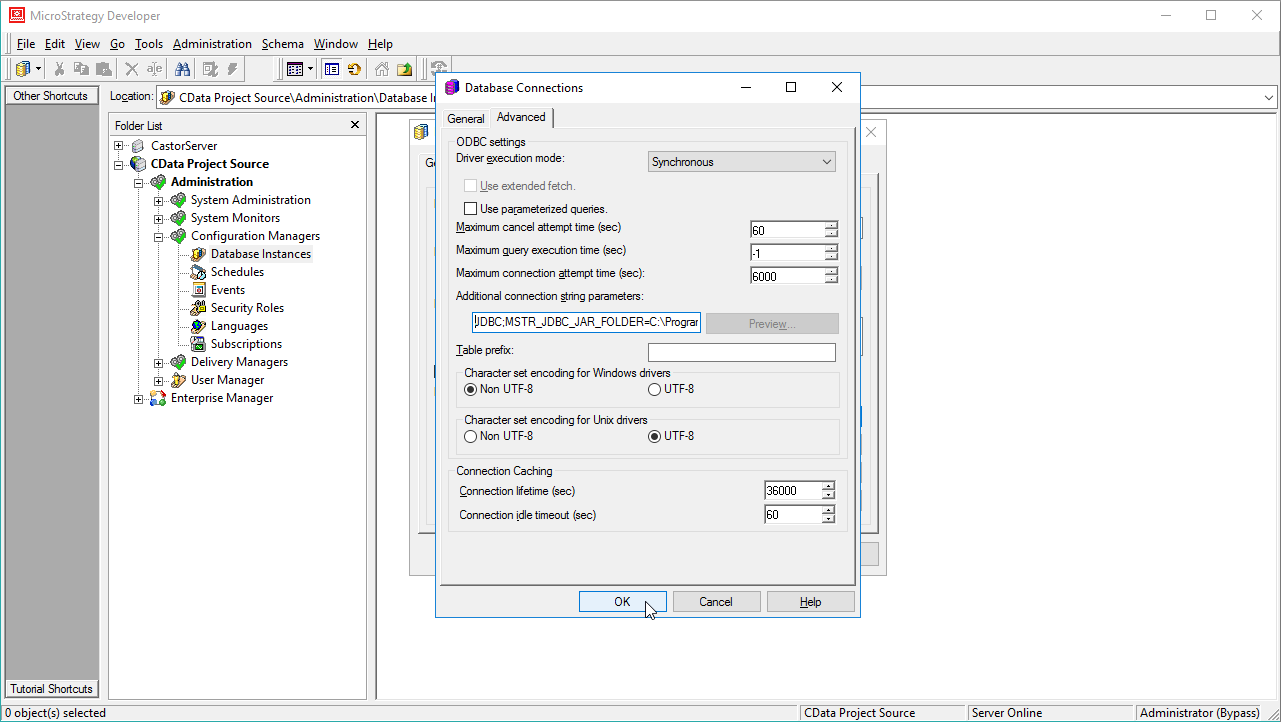
- On the Advanced tab for the connection wizard, set the additional connection string parameters as follows.
- Add the JDBC keyword to the connection string.
- Set MSTR_JDBC_JAR_FOLDER to the path of the directory containing the JAR file for the JDBC driver. (C:\Program Files\CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB\lib\ on Windows.)
- Set DRIVER to cdata.jdbc.alloydb.AlloyDBDriver, the driver class.
- Set URL to the JDBC URL for the AlloyDB driver, which contains the necessary connection properties.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the AlloyDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.alloydb.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Typical additional connection string properties follow:
JDBC;MSTR_JDBC_JAR_FOLDER=PATH\TO\JAR\;DRIVER=cdata.jdbc.alloydb.AlloyDBDriver;URL={jdbc:alloydb:User=alloydb;Password=admin;Database=alloydb;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432};![Configuring the connection to AlloyDB data using JDBC.]()
- Ensure that you have not selected an ODBC data source (this will trigger MicroStrategy to use the additional connection string parameters to build the database instance) and click OK.
- Click OK to close the database instance wizard.
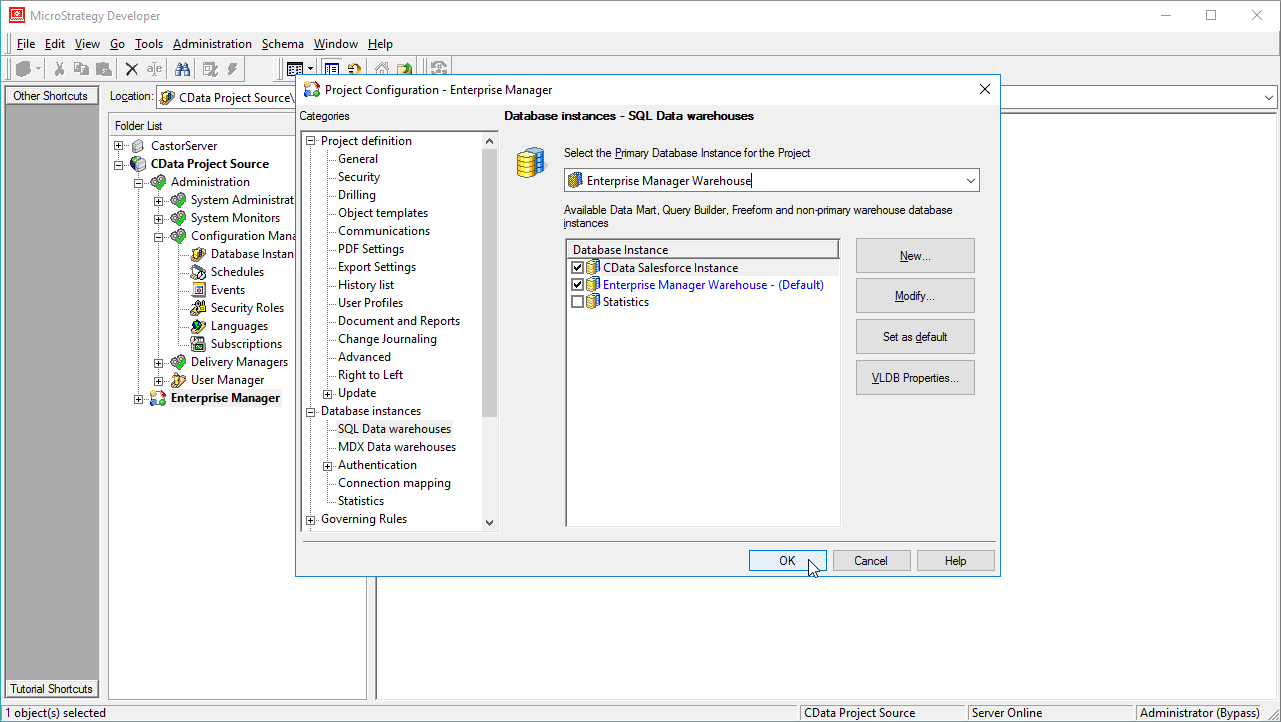
- In the Project Source, right-click the project and open the Project configuration.
- Navigate to Database Instances, select the newly created database instance, and click OK.
![Adding the new database instance to the project.]()
- Close MicroStrategy Developer and restart the connected MicroStrategy Intelligence Server to complete the database instance creation.
With the database instance configured, you will now be able to connect to AlloyDB data from the Warehouse Catalog and Data Import.
Connect to AlloyDB Data from the Warehouse Catalog
Once you have created a database instance based on the JDBC Driver for AlloyDB, you can connect to data from the Warehouse Catalog.
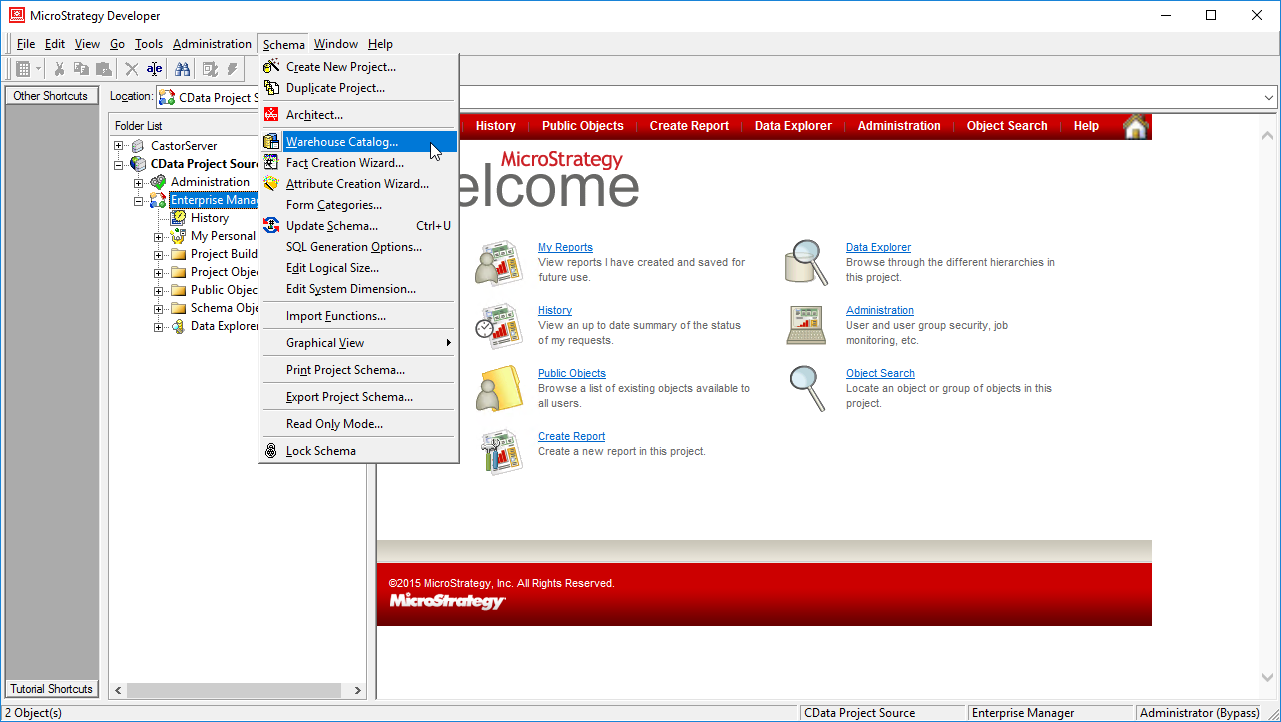
- Select your project and click Schema -> Warehouse Catalog.
![Creating the Warehouse Catalog]()
- In the Read Settings for the Catalog, click Settings and set the queries to retrieve the schema:
- To retrieve the list of tables, use the following query:
SELECT * FROM SYS_TABLES - To retrieve the list of columns for selected tables, use the following query:
SELECT DISTINCT CatalogName NAME_SPACE, TableName TAB_NAME, ColumnName COL_NAME, DataTypeName DATA_TYPE, Length DATA_LEN, NumericPrecision DATA_PREC, NumericScale DATA_SCALE FROM SYS_TABLECOLUMNS WHERE TableName IN (#TABLE_LIST#) ORDER BY 1,2,3
![Custom metadata queries.]()
- To retrieve the list of tables, use the following query:
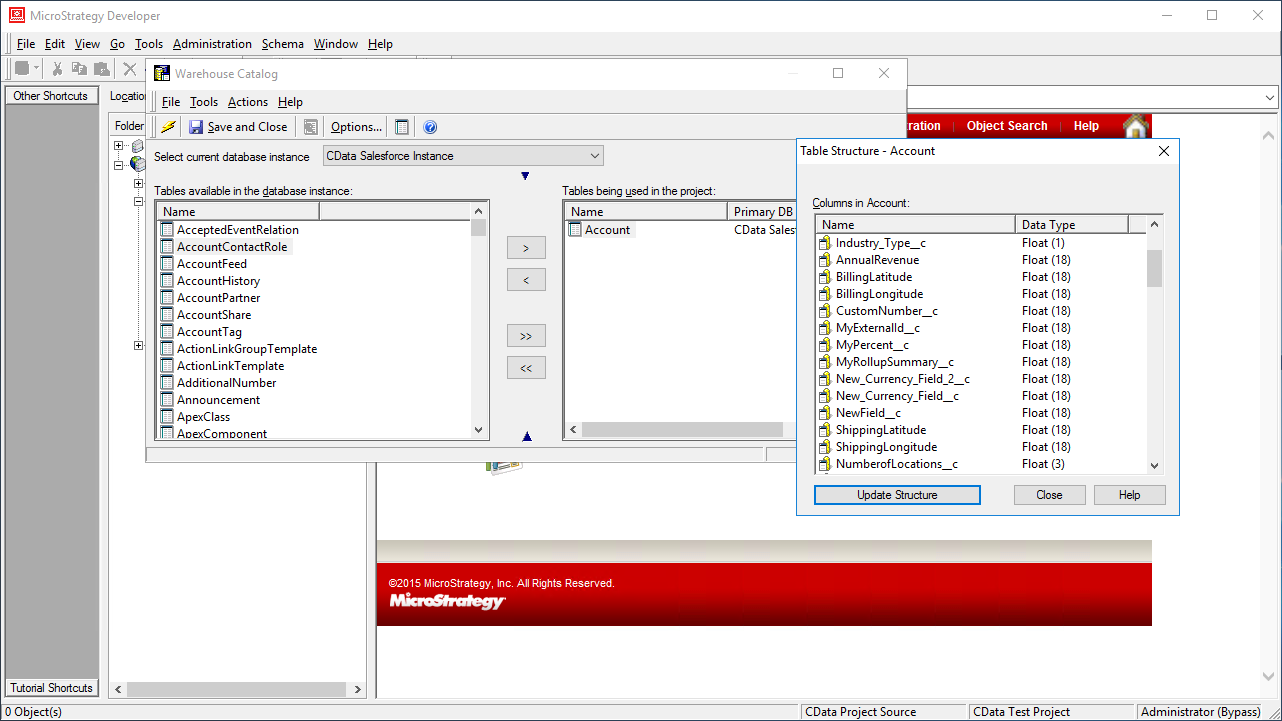
- Select tables to be used in the project.
![Selecting tables to be used in the project.]()
Using the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB in MicroStrategy, you can easily create robust visualizations and reports on AlloyDB data. Read our other articles on connecting to AlloyDB in MictroStrategy Web and connecting to AlloyDB in MicroStrategy Desktop for more information.
Note: Connecting using a JDBC Driver requires a 3- or 4-Tier Architecture.