Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Automated Continuous AlloyDB Replication to SingleStore
Use CData Sync for automated, continuous, customizable AlloyDB replication to SingleStore.
Always-on applications rely on automatic failover capabilities and real-time data access. CData Sync integrates live AlloyDB data into your SingleStore instance, allowing you to consolidate all of your data into a single location for archiving, reporting, analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence and more.
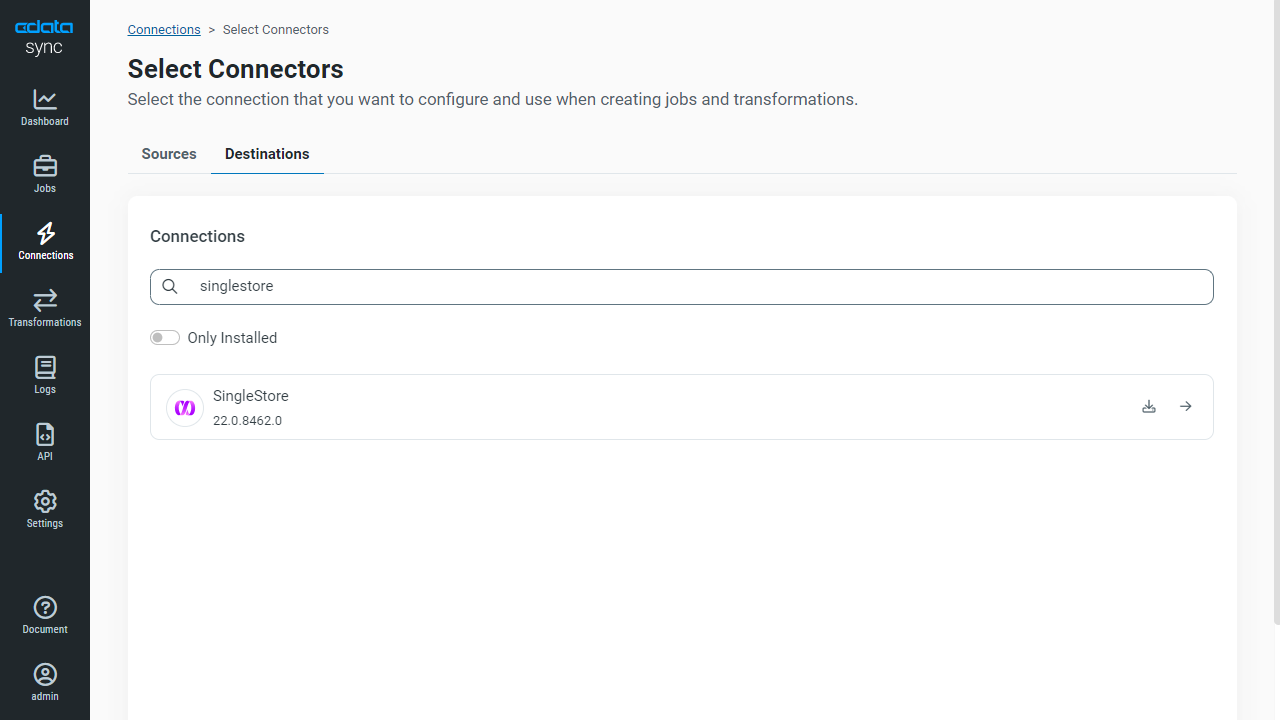
Configure SingleStore as a Replication Destination
Using CData Sync, you can replicate AlloyDB data to SingleStore. To add a replication destination, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click Add Connection.
- Select SingleStore as a destination.
![Configure a Destination connection to SingleStore.]()
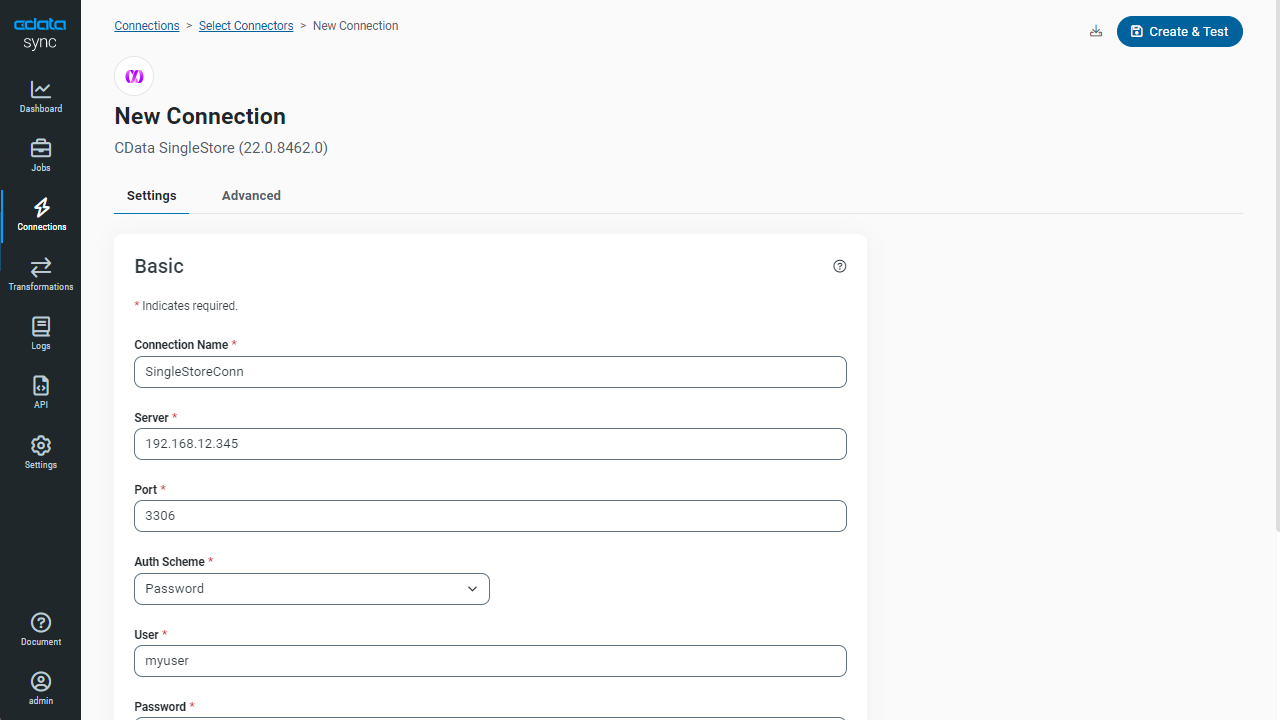
- Enter the required connection properties and select an authentication scheme (see below):
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Database (Optional): The default database to connect to when connecting to the SingleStore Server. If this is not set, tables from all databases will be available.
Connect Using Standard Authentication
To authenticate using standard authentication, set the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
Connect Using Integrated Security
As an alternative to providing the standard username and password, you can set IntegratedSecurity to True to authenticate trusted users to the server via Windows Authentication.
Connect Using SSL Authentication
You can leverage SSL authentication to connect to SingleStore data via a secure session. Configure the following connection properties to connect to data:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate. Used in the case of 2-way SSL, where truststore and keystore are kept on both the client and server machines.
- SSLClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSLClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSLClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSLServerCert: The certificate to be accepted from the server.
Connect Using SSH Authentication
Using SSH, you can securely login to a remote machine. To access SingleStore data via SSH, configure the following connection properties:
- SSHClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate.
- SSHClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSHClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSHClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSHPassword: The password that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
- SSHPort: The port used for SSH operations.
- SSHServer: The SSH authentication server you are trying to authenticate against.
- SSHServerFingerPrint: The SSH Server fingerprint used for verification of the host you are connecting to.
- SSHUser: Set this to the username that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
- Click Test Connection to ensure that the connection is configured properly.
![Configure a Destination connection.]()
- Click Save Changes.
Configure the AlloyDB Connection
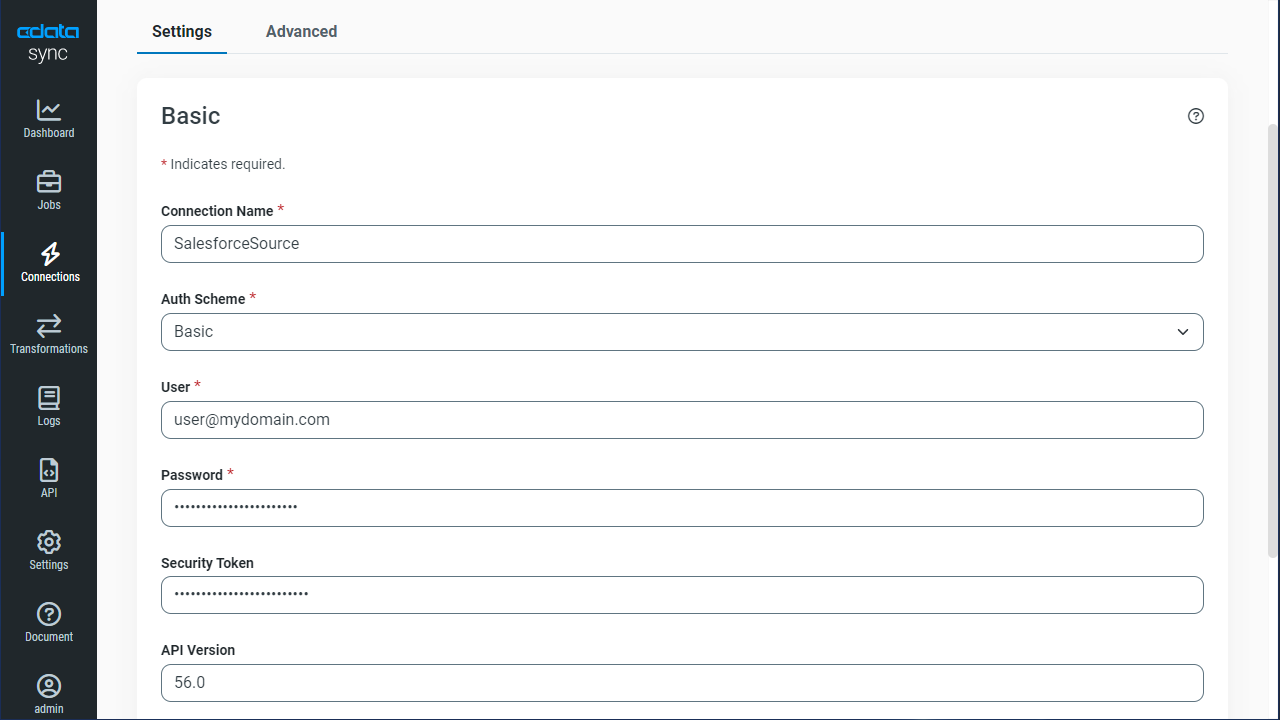
You can configure a connection to AlloyDB from the Connections tab. To add a connection to your AlloyDB account, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click Add Connection.
- Select a source (AlloyDB).
- Configure the connection properties.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
![Configure a Source connection (Salesforce is shown).]()
- Click Connect to ensure that the connection is configured properly.
- Click Save Changes.
Configure Replication Queries
CData Sync enables you to control replication with a point-and-click interface and with SQL queries. For each replication you wish to configure, navigate to the Jobs tab and click Add Job. Select the Source and Destination for your replication.
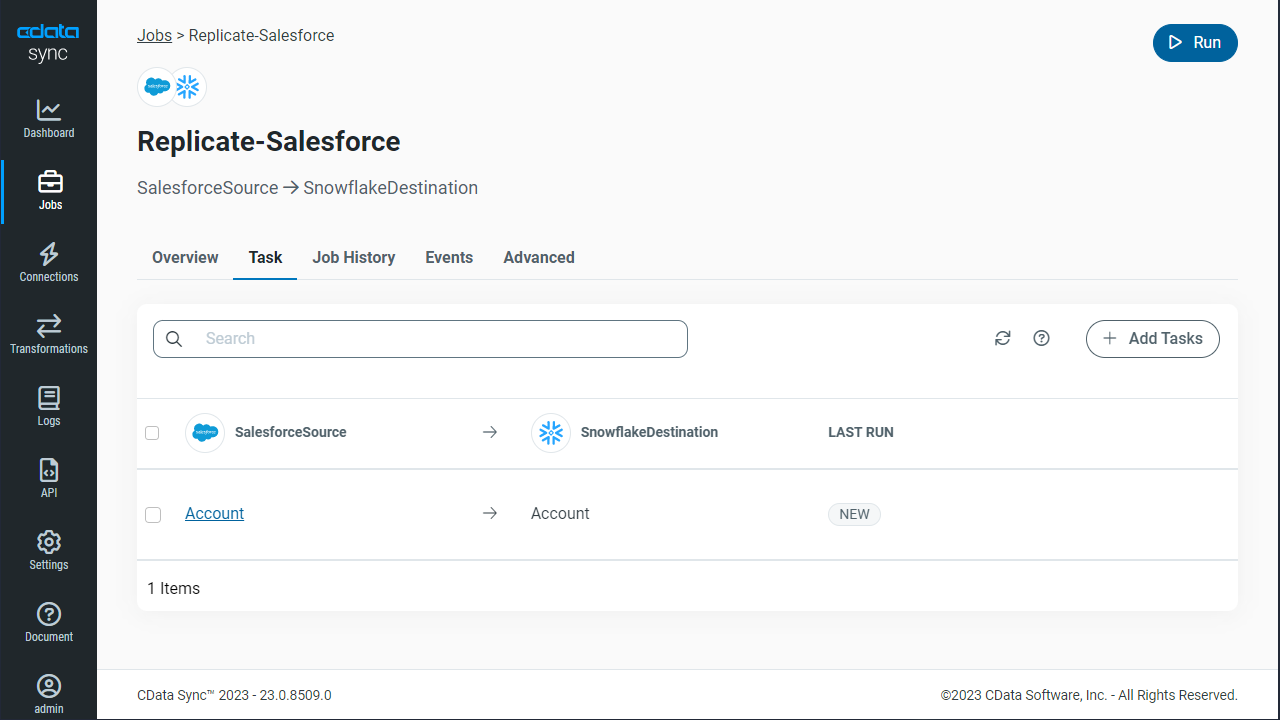
Replicate Entire Tables
To replicate an entire table, click Add Tables in the Tables section, choose the table(s) you wish to replicate, and click Add Selected Tables.
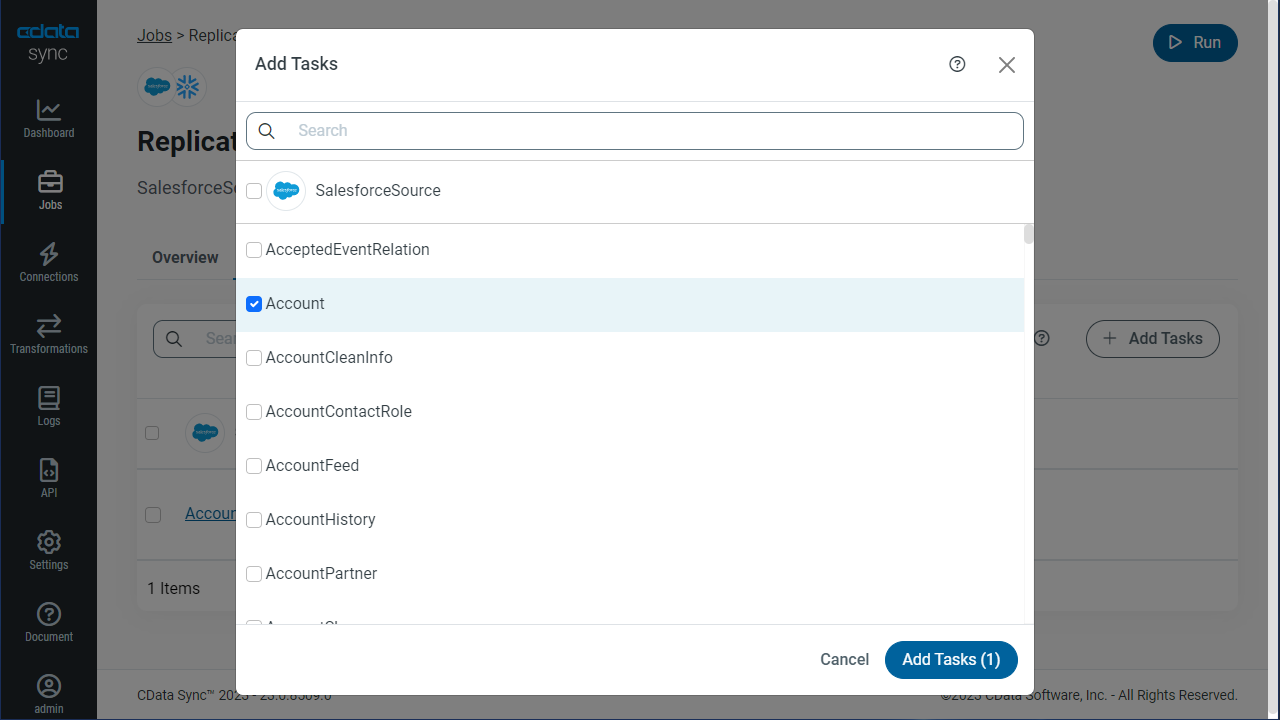
Customize Your Replication
You can use the Columns and Query tabs of a task to customize your replication. The Columns tab allows you to specify which columns to replicate, rename the columns at the destination, and even perform operations on the source data before replicating. The Query tab allows you to add filters, grouping, and sorting to the replication.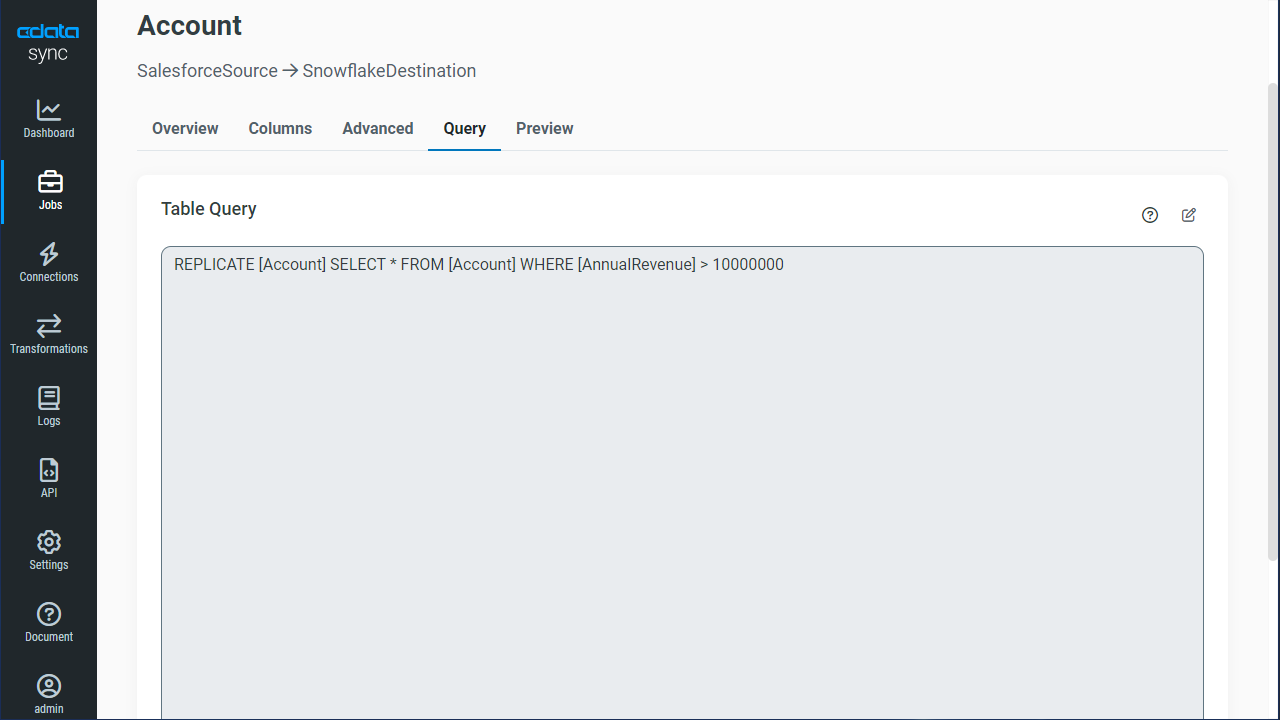
Schedule Your Replication
In the Schedule section, you can schedule a job to run automatically, configuring the job to run after specified intervals ranging from once every 10 minutes to once every month.
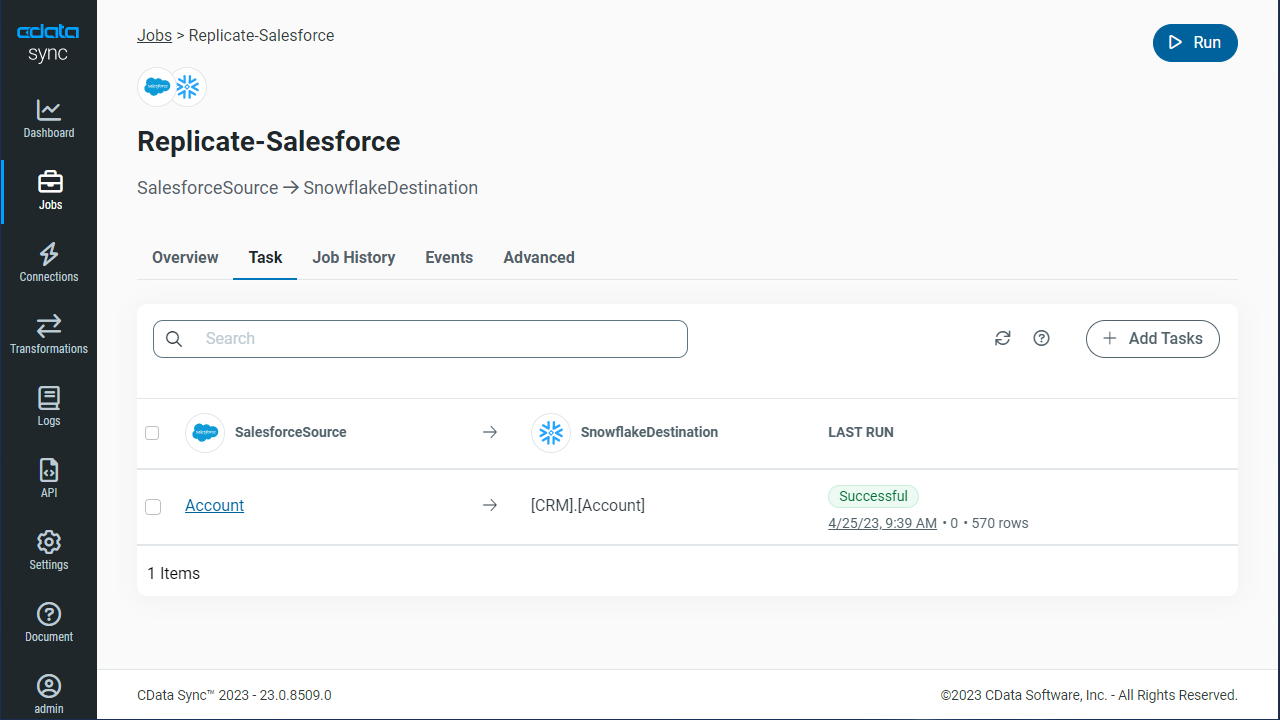
Once you have configured the replication job, click Save Changes. You can configure any number of jobs to manage the replication of your AlloyDB data to SingleStore.