Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Trigger Amazon Athena IFTTT Flows in Azure App Service
This article shows how to automate IFTTT (if-this-then-that) workflows with standard wizards in Logic Apps.
Through standards-based interfaces like OData and Swagger, the CData API Server, when paired with the ADO.NET Provider for Amazon Athena (or any of 200+ other ADO.NET Providers), provides a native experience in Logic Apps and Power Automate with Amazon Athena. OData enables real-time connectivity to data; Swagger enables scaffolding, or code generation, of wizards in Logic Apps and Power Automate, as well as scaffolding Power Apps. This article shows how to add Amazon Athena to an IFTTT (if-this-then-that) workflow in a Logic App.
Set Up the API Server
Follow the steps below to begin producing secure and Swagger-enabled Amazon Athena APIs:
Deploy
The API Server runs on your own server. On Windows, you can deploy using the stand-alone server or IIS. On a Java servlet container, drop in the API Server WAR file. See the help documentation for more information and how-tos.
The API Server is also easy to deploy on Microsoft Azure, Amazon EC2, and Heroku.
Connect to Amazon Athena
After you deploy the API Server and the ADO.NET Provider for Amazon Athena, provide authentication values and other connection properties by clicking Settings -> Connections and adding a new connection in the API Server administration console. You can then choose the entities you want to allow the API Server access to by clicking Settings -> Resources.
Authenticating to Amazon Athena
To authorize Amazon Athena requests, provide the credentials for an administrator account or for an IAM user with custom permissions: Set AccessKey to the access key Id. Set SecretKey to the secret access key.
Note: Though you can connect as the AWS account administrator, it is recommended to use IAM user credentials to access AWS services.
Obtaining the Access Key
To obtain the credentials for an IAM user, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the IAM console.
- In the navigation pane, select Users.
- To create or manage the access keys for a user, select the user and then select the Security Credentials tab.
To obtain the credentials for your AWS root account, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the AWS Management console with the credentials for your root account.
- Select your account name or number and select My Security Credentials in the menu that is displayed.
- Click Continue to Security Credentials and expand the Access Keys section to manage or create root account access keys.
Authenticating from an EC2 Instance
If you are using the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 from an EC2 Instance and have an IAM Role assigned to the instance, you can use the IAM Role to authenticate. To do so, set UseEC2Roles to true and leave AccessKey and SecretKey empty. The CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 will automatically obtain your IAM Role credentials and authenticate with them.
Authenticating as an AWS Role
In many situations it may be preferable to use an IAM role for authentication instead of the direct security credentials of an AWS root user. An AWS role may be used instead by specifying the RoleARN. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to attempt to retrieve credentials for the specified role. If you are connecting to AWS (instead of already being connected such as on an EC2 instance), you must additionally specify the AccessKey and SecretKey of an IAM user to assume the role for. Roles may not be used when specifying the AccessKey and SecretKey of an AWS root user.
Authenticating with MFA
For users and roles that require Multi-factor Authentication, specify the MFASerialNumber and MFAToken connection properties. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to submit the MFA credentials in a request to retrieve temporary authentication credentials. Note that the duration of the temporary credentials may be controlled via the TemporaryTokenDuration (default 3600 seconds).
Connecting to Amazon Athena
In addition to the AccessKey and SecretKey properties, specify Database, S3StagingDirectory and Region. Set Region to the region where your Amazon Athena data is hosted. Set S3StagingDirectory to a folder in S3 where you would like to store the results of queries.
If Database is not set in the connection, the data provider connects to the default database set in Amazon Athena.
You will also need to enable CORS and define the following sections on the Settings -> Server page. As an alternative, you can select the option to allow all domains without '*'.
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin: Set this to a value of '*'. An Access-Control-Allow-Origin header value of '*' is required to use the API Server in the Logic Apps Designer.
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods: Set this to a value of "GET,PUT,POST,OPTIONS".
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Set this to "x-ms-client-request-id, authorization, content-type".
Authorize API Server Users
After determining the OData services you want to produce, authorize users by clicking Settings -> Users. The API Server uses authtoken-based authentication and supports the major authentication schemes. You can authenticate as well as encrypt connections with SSL. Access can also be restricted by IP address; access is restricted to only the local machine by default.
For simplicity, we will allow the authtoken for API users to be passed in the URL. You will need to add a setting in the Application section of the settings.cfg file, located in the data directory. On Windows, this is the app_data subfolder in the application root. In the Java edition, the location of the data directory depends on your operation system:
- Windows: C:\ProgramData\CData
- Unix or Mac OS X: ~/cdata
[Application]
AllowAuthtokenInURL = true
Access Amazon Athena in a Logic App
You can use the API Server in a Logic App to create process flows around Amazon Athena data. The HTTP + Swagger action provides a wizard to define the operations you want to execute to Amazon Athena. The following steps below show how to retrieve Amazon Athena data in a Logic App.
If your table has a column containing the creation date of a record, you can follow the steps below to write a function to check the column values for any new records. Otherwise, skip to the Create a Logic App section to send out emails to entities that match a filter.
Check for New Amazon Athena Entities
To find new Amazon Athena entities since a certain time, you can write a function that retrieves a datetime value for the start of the interval:
- In the Azure Portal, click New -> Function App -> Create.
- Enter a name and select the subscription, resource group, App Service plan, and storage account.
- Select your Function App and select the Webhook + API scenario.
- Select the language. This article uses JavaScript.
- Add the following code to return the previous hour in a JSON object:
module.exports = function (context, data) { var d = new Date(); d.setHours(d.getHours()-1); // Response of the function to be used later. context.res = { body: { start: d } }; context.done(); };
Add Amazon Athena to a Trigger
Follow the steps below to create a trigger that searches Amazon Athena for results that match a filter. If you created the function above, you can search for objects that were created after the start of the interval returned.
- In the Azure Portal, click New and in the Web + Mobile section select Logic App and select a resource group and App Service plan.
- You can then use the wizards available in the Logic App Designer, which can be accessed from the settings blade for the Logic App. Select the Blank Logic App template.
- Add a Recurrence action that will poll for the Amazon Athena objects. This article polls every hour. Select the timezone -- the default is UTC.
- Add a function action: Expand the menu in the Add Action dialog and select the option to show Azure functions in the same region. Select the Function App you created earlier and select the function that returns the interval start.
- Enter an empty pair of curly brackets, "{}", to pass an empty payload object to the function.
- Add the HTTP + Swagger action and enter the swagger URL of the API Server:
http://MySite:MyPort/api.rsc/@MyAuthtoken/$oas - Select the "Return Customers" operation.
Use the descriptions for each property to specify additional parameters such as the columns to retrieve, filters, etc. Below is an example filter:
CustomerId eq '12345'
The API Server returns the descriptions and other documentation in the swagger document. You can find more information on using the OData API and supported OData in the API Server help documentation.
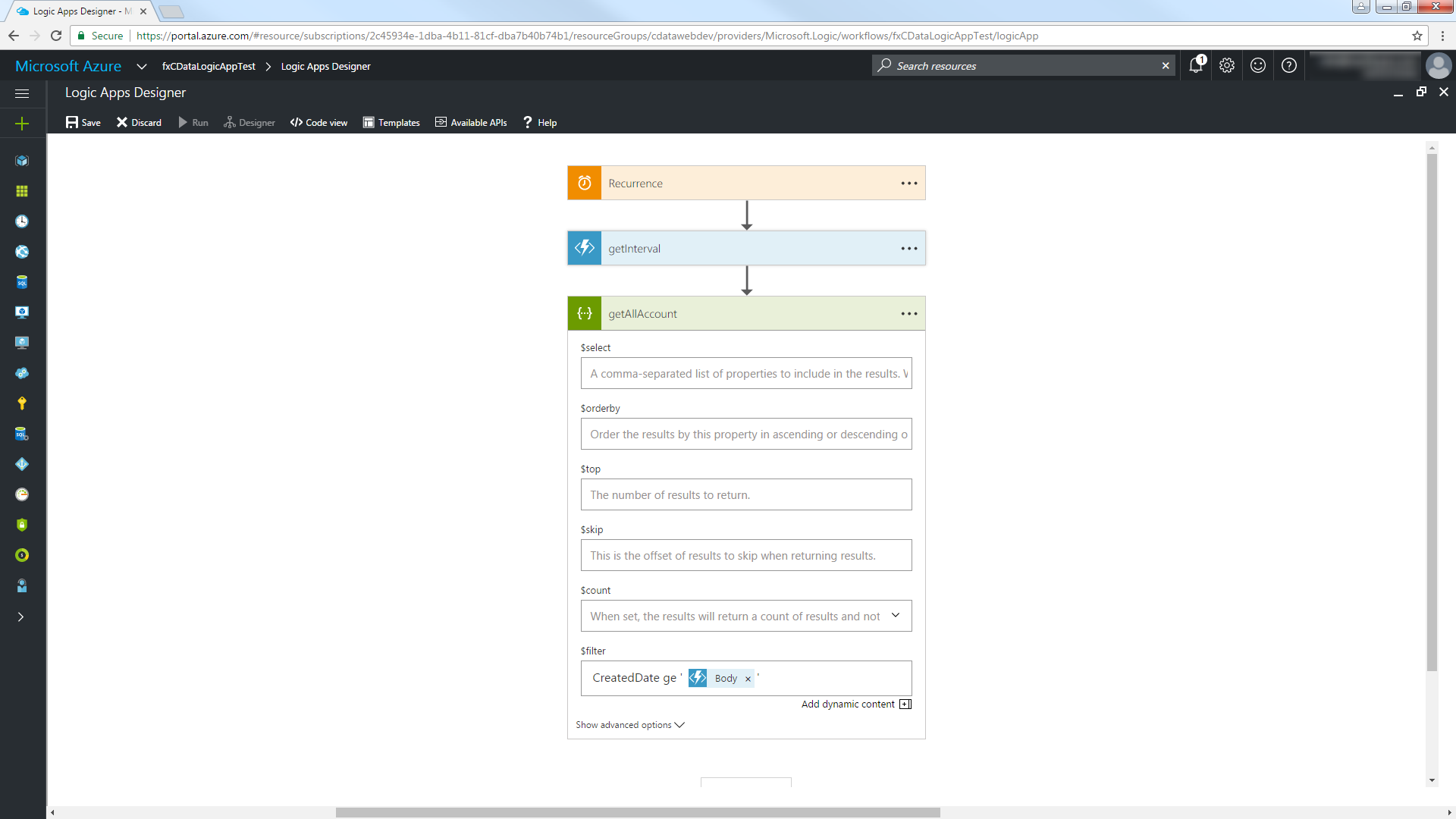
To use the datetime value returned from the getInterval function, use the "ge" operator with a datetime column in the Customers table and select the Body parameter in the dialog. Note that quotes must be used to surround the datetime value.
![An OData filter on the results of an Azure Function App, getToday. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Switch to Code View and modify the $filter expression to extract the property containing the start of the interval. Use the syntax '@{body('MyFunc')['MyProp']'.
"getAllAccount": { "inputs": { "method": "get", "queries": { "$filter": "CreatedDate ge '@{body('getInterval')['start']}'" }, "uri": "https://MySite:MyPort/api.rsc/@MyAuthtoken/Customers" }
You can now access Amazon Athena as data sources and destinations in your workflows.
Email New Records
Follow the steps below to email a report with any new Customers entities.
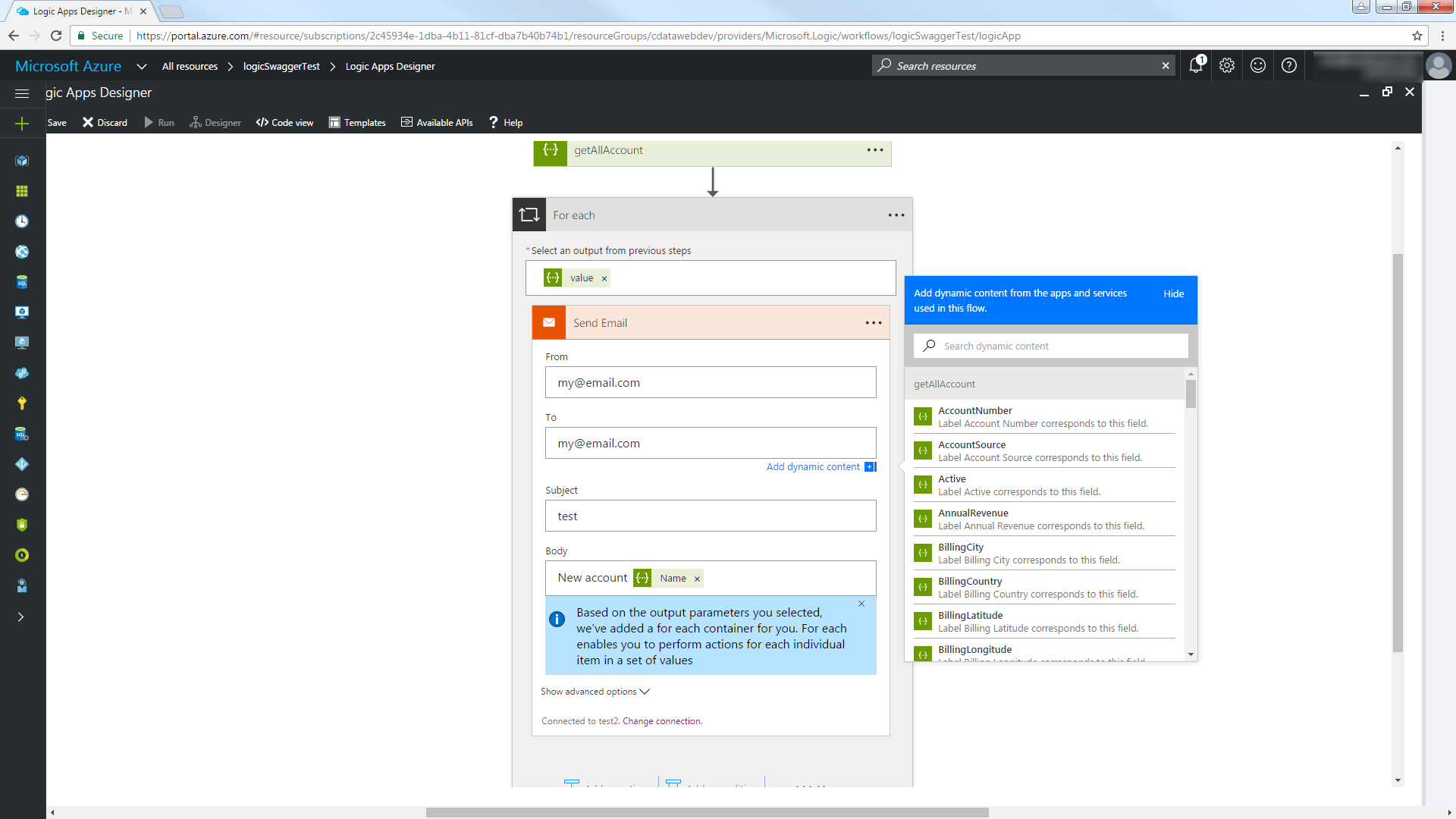
- In the Logic Apps Designer, add an SMTP - Send Email action.
- Configure the necessary information for the SMTP server.
- Configure the From, To, Subject, and Body. You can add parameters from the Amazon Athena columns returned.
Click Save and then click Run to send email notifications on any Amazon Athena records created in the last hour.