Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Integrate Azure Active Directory Data into Power Automate Desktop using CData Connect
CData Connect for Azure Active Directory Data enables you to integrate Azure Active Directory data into workflows built using Microsoft Power Automate Desktop.
CData Connect enables you to access live Azure Active Directory data in workflow automation tools like Power Automate. This article shows how to integrate Azure Active Directory data into a simple workflow, saving Azure Active Directory data into a CSV file.
CData Connect provides a live interface for Azure Active Directory, allowing you to integrate with live Azure Active Directory data in Power Automate — without replicating the data. Connect uses optimized data processing out of the box to push all supported SQL operations (filters, JOINs, etc) directly to Azure Active Directory, leveraging server-side processing to quickly return Azure Active Directory data.
Configure Azure Active Directory Connectivity for Power Automate
Connectivity to Azure Active Directory from Power Automate is made possible through CData Connect Cloud. To work with Azure Active Directory data from Power Automate, we start by creating and configuring a Azure Active Directory connection.
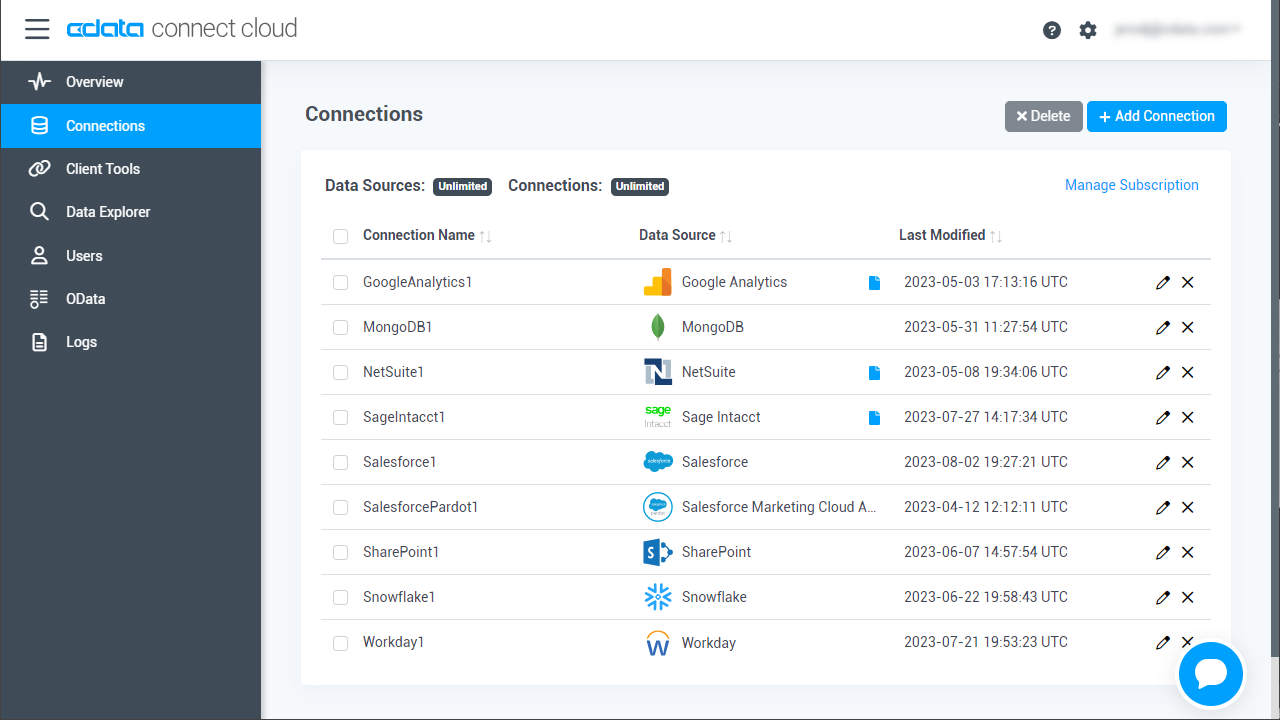
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Connections and click Add Connection
![Adding a Connection]()
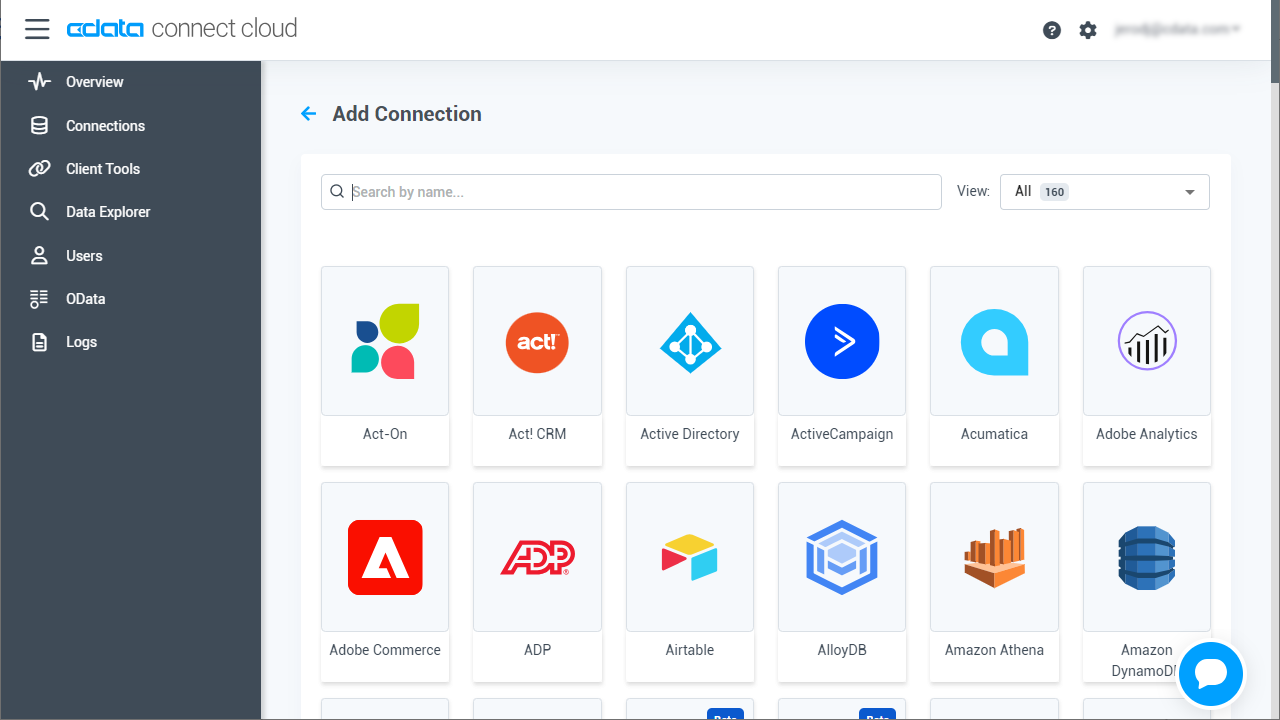
- Select "Azure Active Directory" from the Add Connection panel
![Selecting a data source]()
-
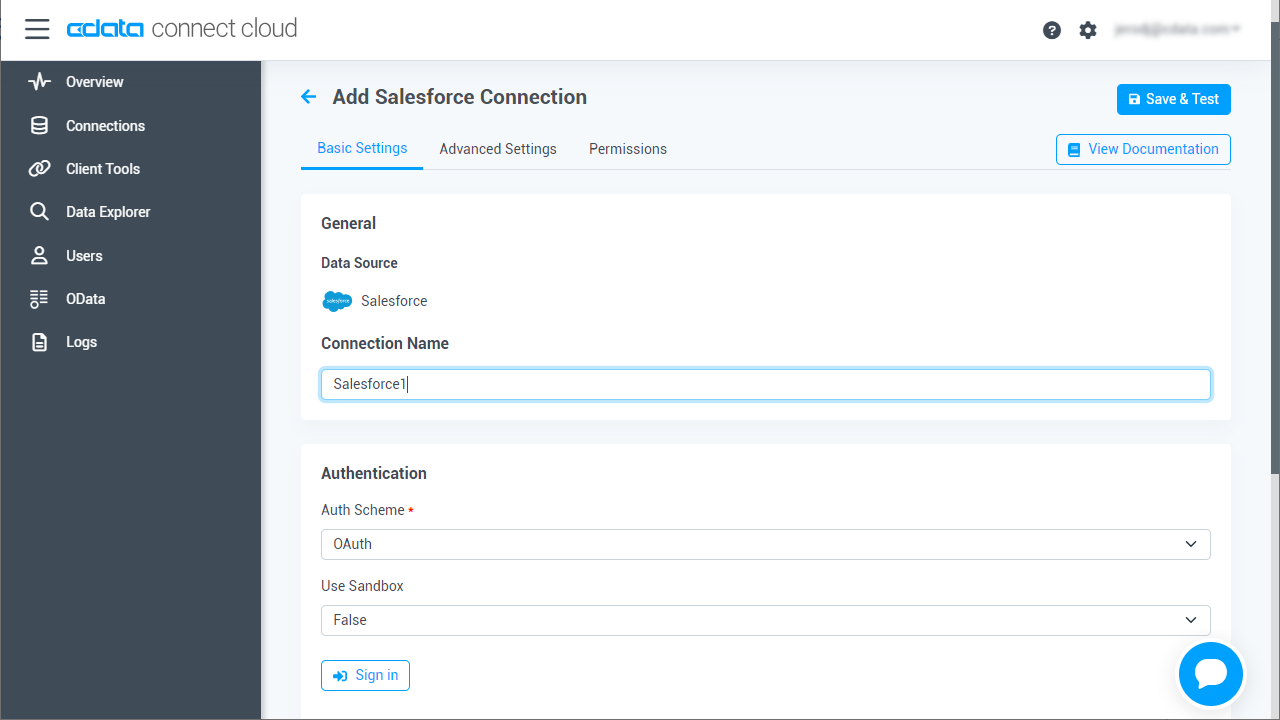
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Azure Active Directory.
Azure Active Directory uses the OAuth authentication standard. To authenticate using OAuth, you will need to create an app to obtain the OAuthClientId, OAuthClientSecret, and CallbackURL connection properties. See the OAuth section in the Help documentation for an authentication guide.
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown)]()
- Click Create & Test
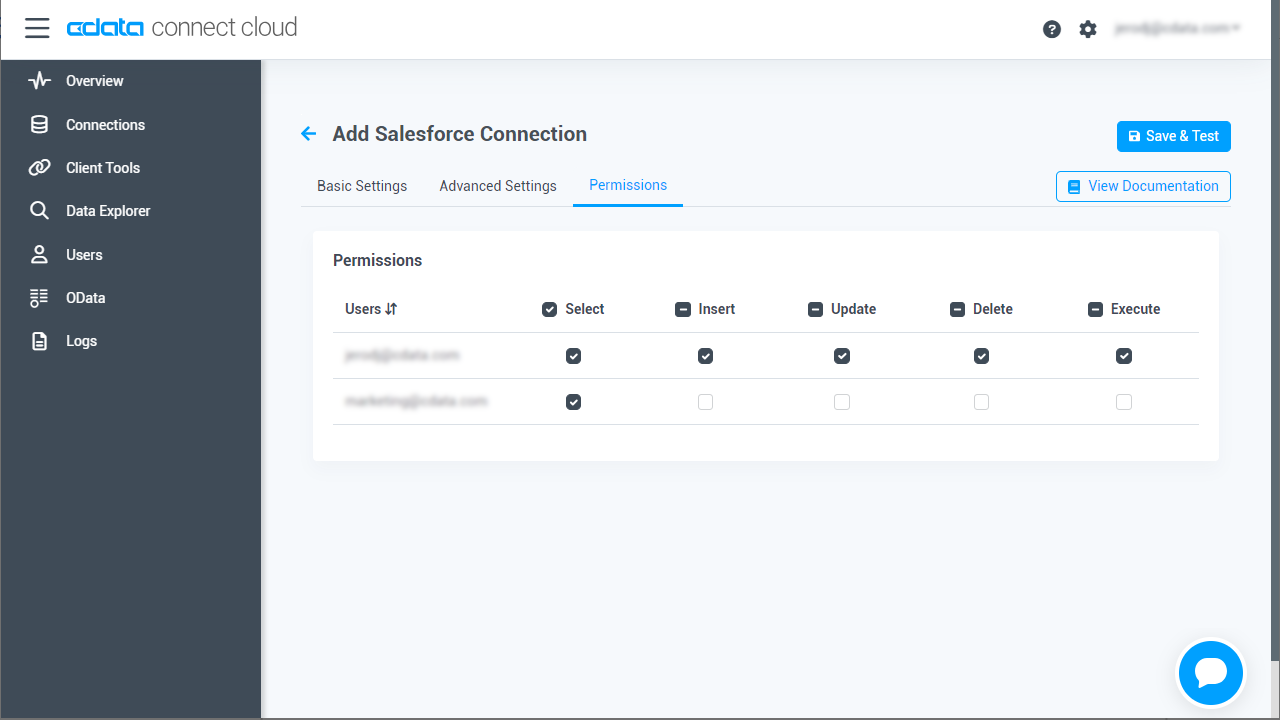
- Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add Azure Active Directory Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
![Updating permissions]()
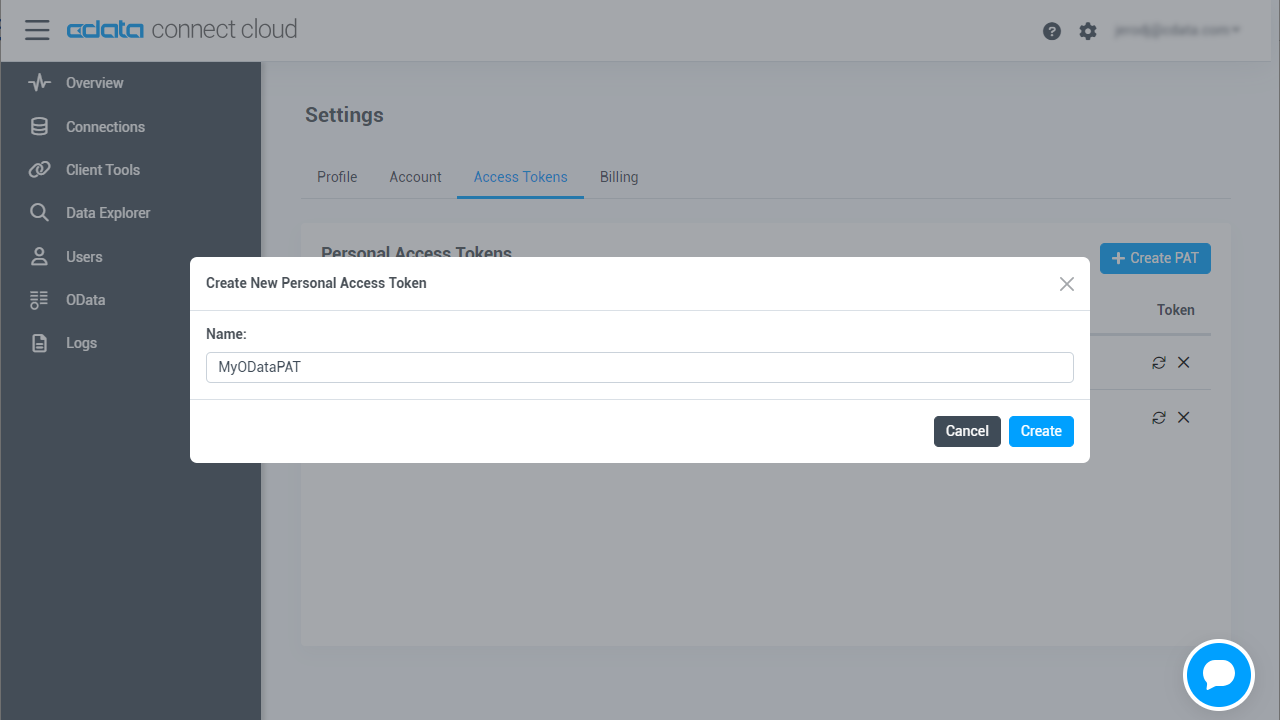
Add a Personal Access Token
If you are connecting from a service, application, platform, or framework that does not support OAuth authentication, you can create a Personal Access Token (PAT) to use for authentication. Best practices would dictate that you create a separate PAT for each service, to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on your username at the top right of the Connect Cloud app and click User Profile.
- On the User Profile page, scroll down to the Personal Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
- Give your PAT a name and click Create.
![Creating a new PAT]()
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured, you are ready to connect to Azure Active Directory data from Power Automate Desktop.
Integrate Azure Active Directory Data into Power Automate Workflows
After configuring CData Connect with Azure Active Directory, you are ready to integrate Azure Active Directory data into your Power Automate workflows. Open Microsoft Power Automate, add a new flow, and name the flow.
In the flow editor, you can add the options to connect to Azure Active Directory, query Azure Active Directory using SQL, and write the query results to a CSV document.
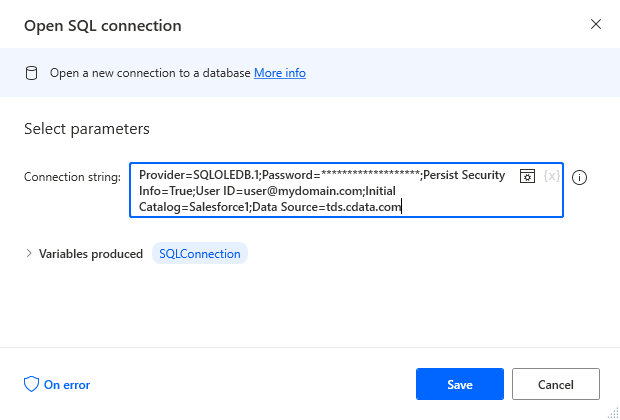
Add an Open SQL Connection Action
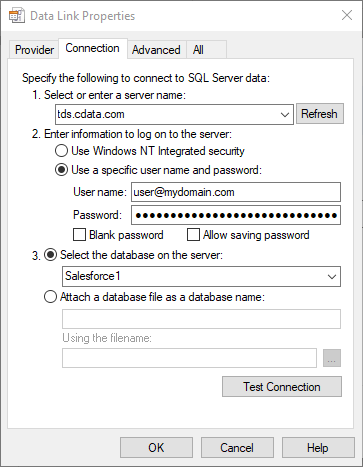
Add an "Open SQL connection" action (Action -> Database) and click the option to build the Connection string. In the Data Link Properties wizard:
- On the Provider tab: select Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server
- On the Connection tab:
- Select or enter a server name: set to tds.cdata.com,14333
- Enter information to lag onto the server: select "Use a specific username and password"
- Set User name to your CData Connect Cloud user name (e.g. user@mydomain.com)
- Set Password to your PAT
- Select the database: use the database configured above (e.g. AzureAD1)
- Click "Test Connection" to ensure the connection is configured properly
- Click "OK"
![A configured connection to CData Connect]()
After building the connection string in the Data Link Properties wizard, save the action.
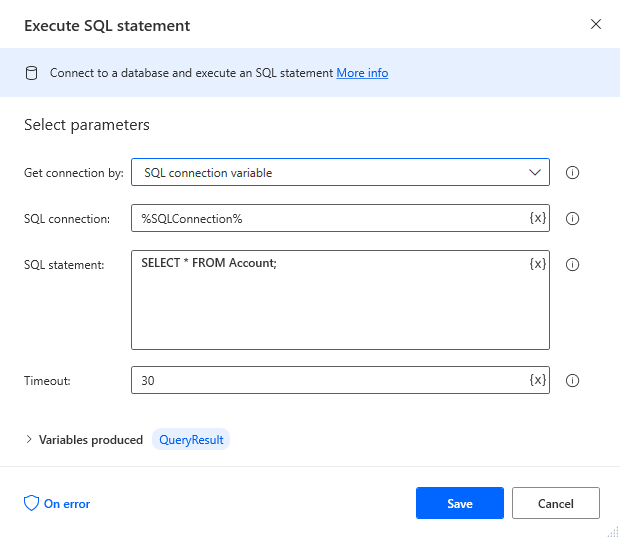
Add an Execute SQL Statement Action
Add an "Execute SQL statement" action (Action -> Database) and configure the properties.
- Get connection by: SQL connection variable
- SQL connection: %SQLConnection% (the variable from the "Open SQL connection" action above)
- SQL statement: SELECT * FROM Domains
After configuring the properties, save the action.
Add a Write to CSV File Action
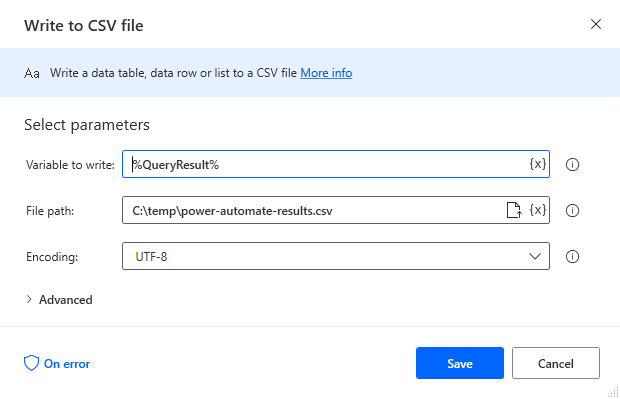
Add a "Write to CSV file" action (Action -> File) and configure the properties.
- Variable to write to: %QueryResult% (the variable from the "Execute SQL statement" action above)
- File path: set to a file on disk
- Configure Advanced settings as needed.
After configuring the properties, save the action.
Add a Close SQL Connection Action
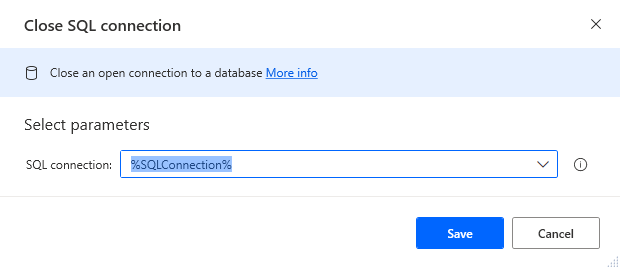
Add a "Close SQL connection" action (Action -> Database) and configure the properties.
- SQL Connection: %SQLConnection% (the variable from the "Open SQL connection" action above)
After configuring the properties, save the action.
Save & Run the Flow
Once you have configured all the options for the flow, click the disk icon to save the flow. Click the play icon to run the flow.
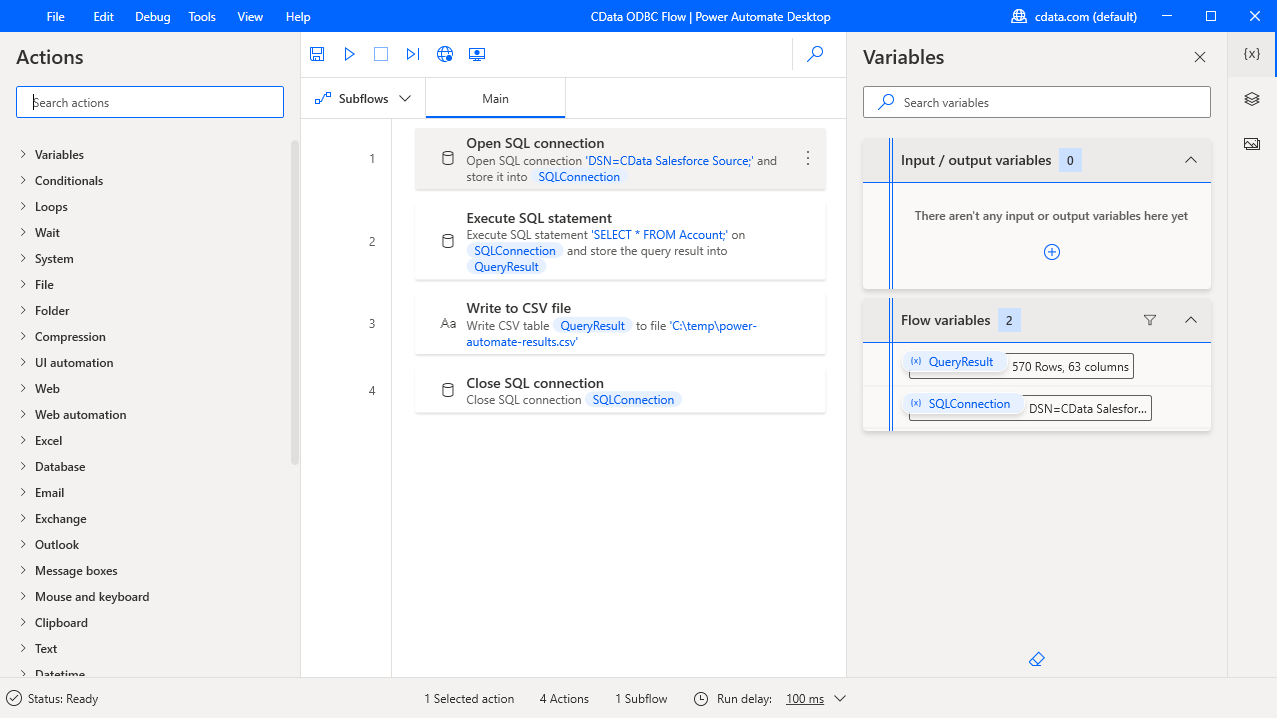
Now you have a workflow to save Azure Active Directory data into a CSV file.
With CData Connect Cloud, you get live connectivity to Azure Active Directory data within your Microsoft Power Automate workflows.
SQL Access to Azure Active Directory Data from Cloud Applications
Now you have a direct connection to live Azure Active Directory data from Power Automate tasks. You can create more connections and workflows to drive business — all without replicating Azure Active Directory data.
To get SQL data access to 100+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your cloud applications, sign up for a free trial of CData Connect Cloud.
Related Power Automate Articles
This article walks through using CData Connect Cloud with Power Automate Desktop. Check out our other articles for more ways to work with Power Automate (Desktop & Online):