Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Visualize Live Azure Data Lake Storage Data in the Power BI Service
Use CData Connect Server to create a virtual SQL Server database for Azure Data Lake Storage data and create custom reports in the Power BI Service.
Power BI transforms your company's data into rich visuals for you to collect and organize so you can focus on what matters to you. When paired with CData Connect Server, you get instant access to Azure Data Lake Storage data for visualizations, dashboards, and more. This article shows how to build and publish a dataset from Azure Data Lake Storage data in Power BI and then create reports on Azure Data Lake Storage data in the Power BI service.
CData Connect Server provides a pure SQL interface for Azure Data Lake Storage, allowing you to easily build reports from live Azure Data Lake Storage data in Power BI — with no need to replicate the data. As you build visualizations, Power BI generates SQL queries to gather data. Using optimized data processing out of the box, CData Connect Server pushes all supported SQL operations (filters, JOINs, etc) directly to Azure Data Lake Storage, leveraging server-side processing to quickly return Azure Data Lake Storage data.
NOTE: You can also import Azure Data Lake Storage data into Power BI through Connect Server (instead of using the on-premise gateway). Read how in the related Knowledge Base article.
Create a Virtual SQL Database for Azure Data Lake Storage Data
CData Connect Server uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to data sources and generate APIs.
- Login to Connect Server and click Connections.
![Adding a connection]()
- Select "Azure Data Lake Storage" from Available Data Sources.
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Azure Data Lake Storage.
Authenticating to a Gen 1 DataLakeStore Account
Gen 1 uses OAuth 2.0 in Azure AD for authentication.
For this, an Active Directory web application is required. You can create one as follows:
To authenticate against a Gen 1 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen1.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- OAuthClientId: Set this to the application Id of the app you created.
- OAuthClientSecret: Set this to the key generated for the app you created.
- TenantId: Set this to the tenant Id. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
Authenticating to a Gen 2 DataLakeStore Account
To authenticate against a Gen 2 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen2.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- FileSystem: Set this to the file system which will be used for this account.
- AccessKey: Set this to the access key which will be used to authenticate the calls to the API. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
![Configuring a connection (SQL Server is shown).]()
- Click Save Changes
- Click Privileges -> Add and add the new user (or an existing user) with the appropriate permissions.
Connecting to Connect Server from Power BI
To connect to and visualize live Azure Data Lake Storage data in the Power BI service), install the on-premises data gateway, add a data source to the gateway from the Power BI service, and publish a dataset from Power BI Desktop to the service.
Install the On-Premises Data Gateway
The Microsoft on-premises data gateway provides secure data transfer between connected data sources and various cloud-based Microsoft tools and platforms. You can read more about the gateway in the Microsoft documentation.
You can download and install the gateway from the Power BI service:
- Log in to PowerBI.com.
- Click the Download menu and click Data Gateway.
![Download the Data Gateway]()
- Follow the instructions for installation, making note of the name of the gateway.
Add Azure Data Lake Storage as a Data Source to the Power BI Service
Once you have installed the data gateway, you add Connect Server as a data source to the Power BI service:
- Log in to PowerBI.com.
- Click the Settings menu and click "Manage gateways."
![Settings -> Manage gateways]()
- Click "ADD DATA SOURCE" and configure the connection to Connect Server:
- Set Data Source Name Connect_ADLS.
- Choose SQL Server as the Data Source Type.
- Set Server to the address of your Connect Server instance (i.e.: connect_server_url).
- Set Database to the name of your virtual Azure Data Lake Storage database (i.e.: ADLS1).
- Set Authentication Method to Basic.
- Set Username and Password to Connect Server credentials.
Publish a Dataset from Power BI Desktop
With the gateway installed and Connect Server added as a datasource to the Power BI service, you can publish a dataset from Power BI Desktop to the service.
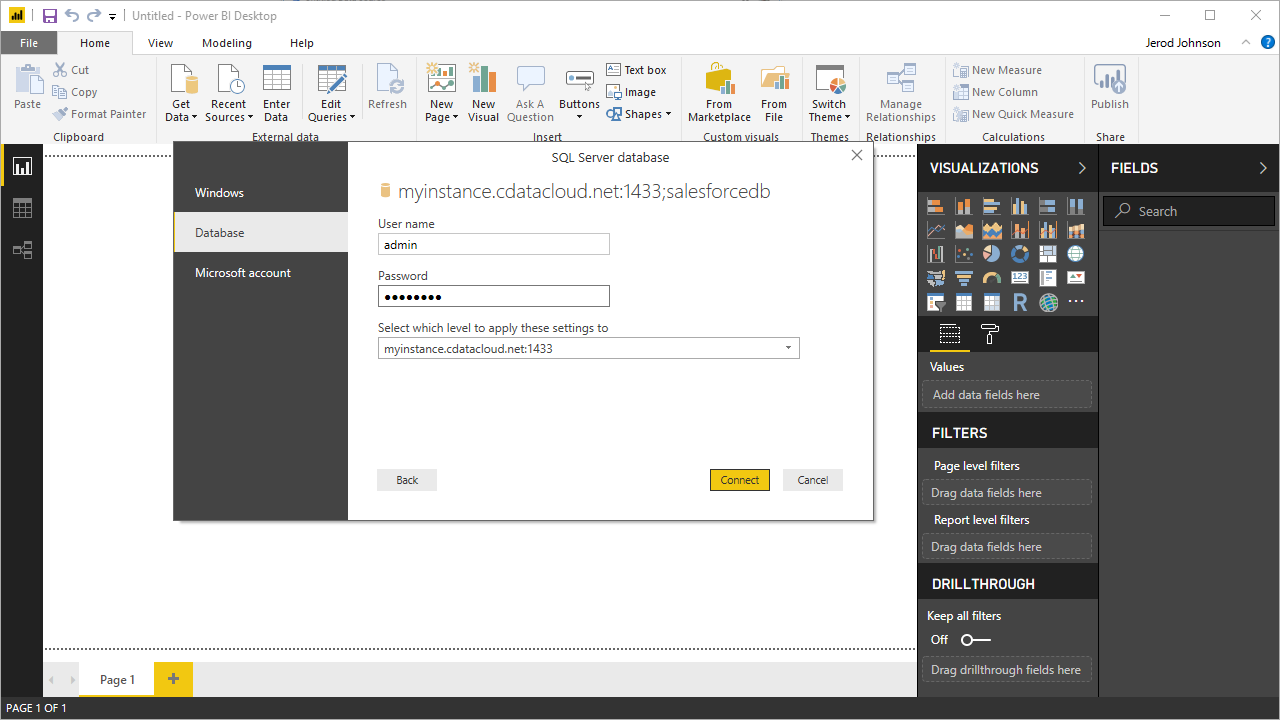
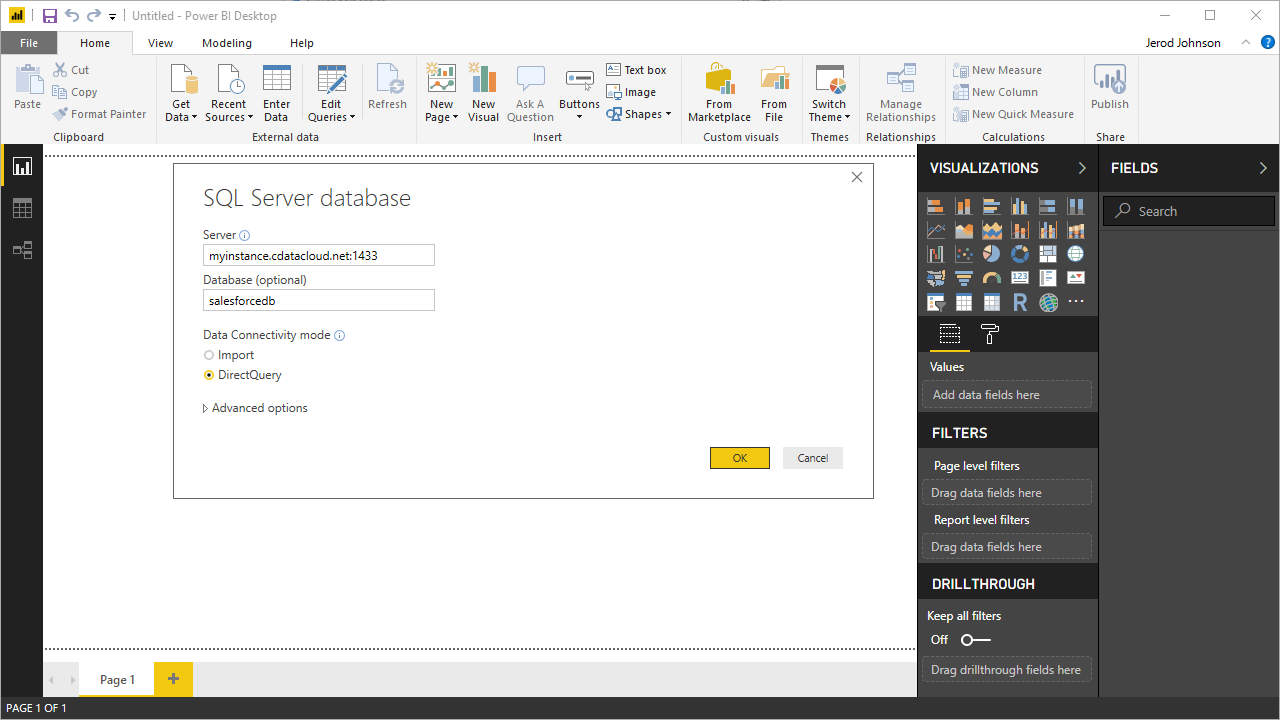
- Open Power BI, click Get Data -> More, then select SQL Server database, and click Connect.
- Set the connection properties and click OK.
- Set Server to the address of your Connect Server instance (i.e.: connect_server_url).
- Set Database to the name of your virtual Azure Data Lake Storage database (i.e.: ADLS1).
- Set Data Connectivity mode to DirectQuery*.
![Connect to CData Connect Server instance]() * DirectQuery enables live query processing and real-time visualizations of Azure Data Lake Storage data.
* DirectQuery enables live query processing and real-time visualizations of Azure Data Lake Storage data.
- In the authentication wizard, select Database, set the User name and Password properties, and click Connect.
- Select the table(s) to visualize in the Navigator dialog.
In the Query Editor, you can customize your dataset by filtering, sorting, and summarizing Azure Data Lake Storage columns. Click Edit to open the query editor. Right-click a row to filter the rows. Right-click a column header to perform actions like the following:
- Change column data types
- Remove a column
- Group by columns
Power BI detects each column's data type from the Azure Data Lake Storage metadata reported by Connect Server.
Power BI records your modifications to the query in the Applied Steps section, adjusting the underlying data retrieval query that is executed to the remote Azure Data Lake Storage data. When you click Close and Apply, Power BI executes the data retrieval query.
Otherwise, click Load to pull the data into Power BI.
- Define any relationships between the selected entities on the Relationships tab.
- Click Publish (from the Home menu) and select a Workspace.
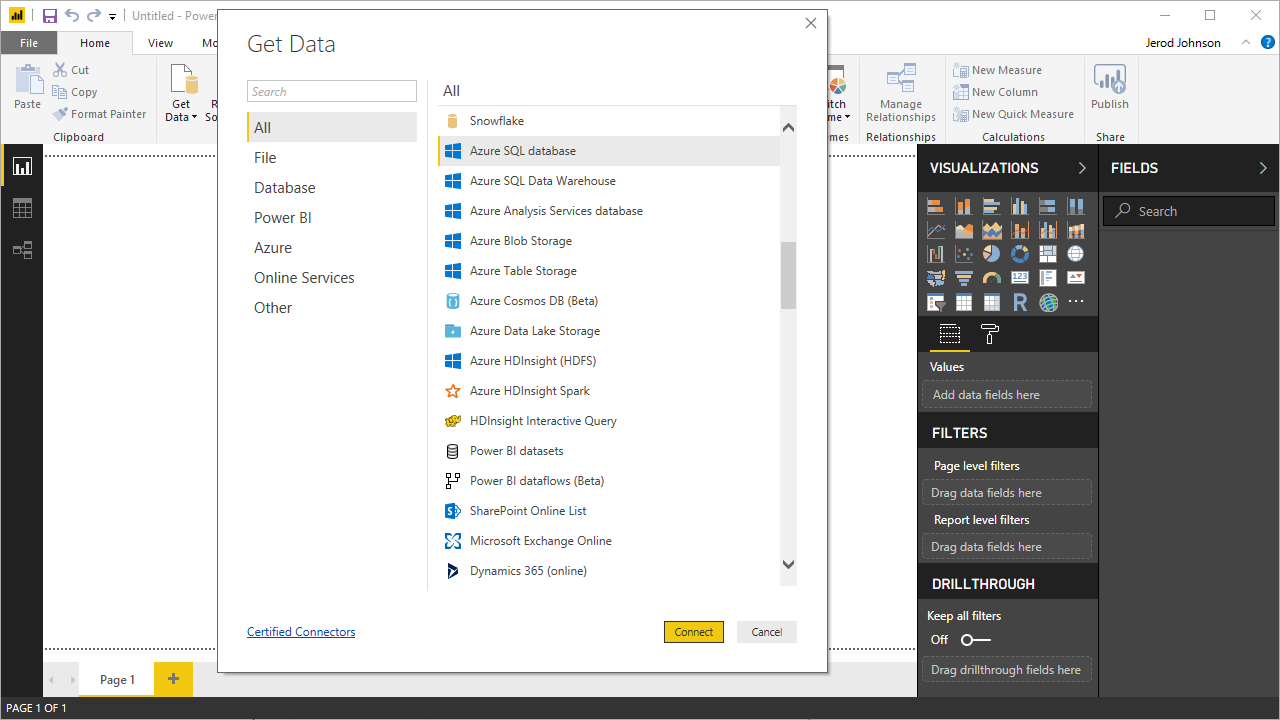
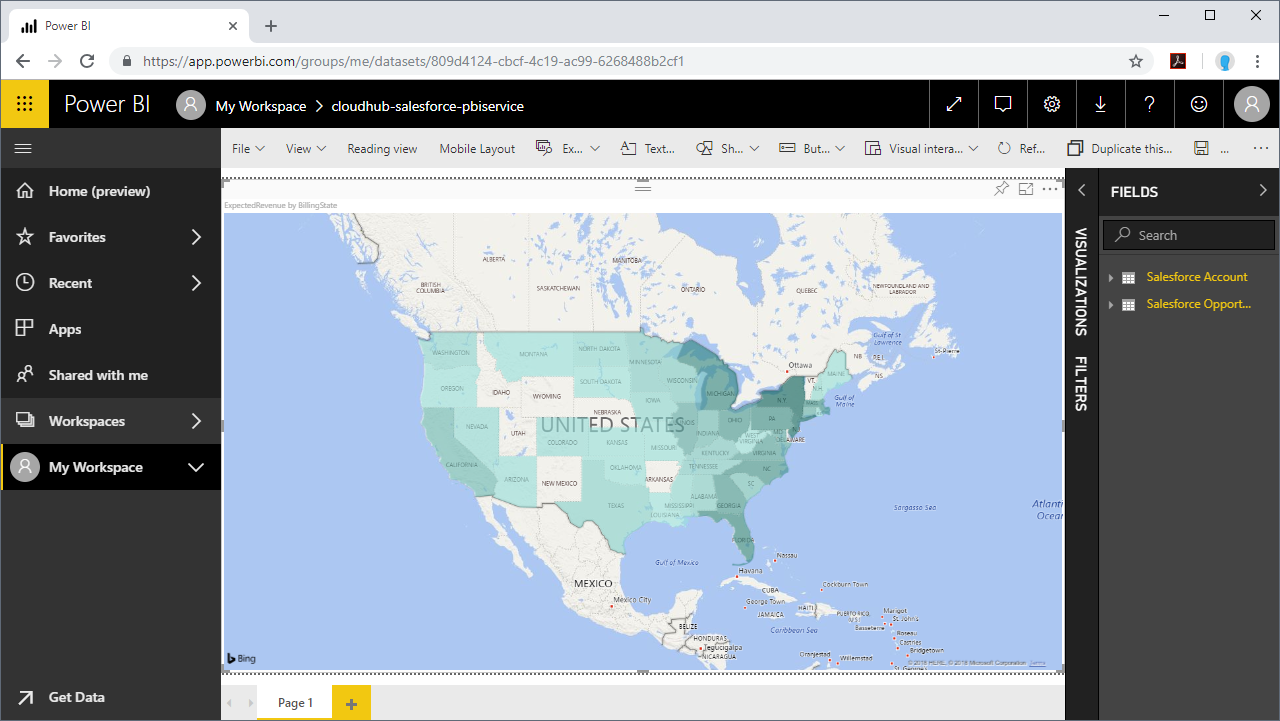
Build Reports and Dashboards on Azure Data Lake Storage Data in the Power BI Service
Now that you have published a dataset to the Power BI service, you can create new reports and dashboards based on the published data:
- Log in to PowerBI.com.
- Click Workspaces and select a workspace.
- Click Create and select Report.
- Select the published dataset for the report.
![Select a dataset]()
- Choose fields and visualizations to add to your report.
![Visualizing Azure Data Lake Storage data in the Power BI service]()
SQL Access to Azure Data Lake Storage Data from Cloud Applications
Now you have a direct connection to live Azure Data Lake Storage data from the Power BI service. You can create more data sources and new visualizations, build reports, and more — all without replicating Azure Data Lake Storage data.
To get SQL data access to 200+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your cloud applications, see the CData Connect Server.







 * DirectQuery enables live query processing and real-time visualizations of Azure Data Lake Storage data.
* DirectQuery enables live query processing and real-time visualizations of Azure Data Lake Storage data.