Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Create Informatica Mappings From/To an ODBC Data Source for Azure Data Lake Storage
Create an ODBC connection to Azure Data Lake Storage in Informatica and browse and transfer Azure Data Lake Storage data.
Informatica provides a powerful, elegant means of transporting and transforming your data. By utilizing the CData ODBC Driver for Azure Data Lake Storage, you are gaining access to a driver based on industry-proven standards that integrates seamlessly with Informatica's powerful data transportation and manipulation features. This tutorial shows how to transfer and browse Azure Data Lake Storage data in Informatica PowerCenter.
Connect to Azure Data Lake Storage as an ODBC Data Source
Information for connecting to Azure Data Lake Storage follows, along with different instructions for configuring a DSN in Windows and Linux environments.
Authenticating to a Gen 1 DataLakeStore Account
Gen 1 uses OAuth 2.0 in Azure AD for authentication.
For this, an Active Directory web application is required. You can create one as follows:
To authenticate against a Gen 1 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen1.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- OAuthClientId: Set this to the application Id of the app you created.
- OAuthClientSecret: Set this to the key generated for the app you created.
- TenantId: Set this to the tenant Id. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
Authenticating to a Gen 2 DataLakeStore Account
To authenticate against a Gen 2 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen2.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- FileSystem: Set this to the file system which will be used for this account.
- AccessKey: Set this to the access key which will be used to authenticate the calls to the API. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
Windows
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
Linux
If you are installing the CData ODBC Driver for Azure Data Lake Storage in a Linux environment, the driver installation predefines a system DSN. You can modify the DSN by editing the system data sources file (/etc/odbc.ini) and defining the required connection properties.
/etc/odbc.ini
[CData ADLS Source]
Driver = CData ODBC Driver for Azure Data Lake Storage
Description = My Description
Schema = ADLSGen2
Account = myAccount
FileSystem = myFileSystem
AccessKey = myAccessKey
For specific information on using these configuration files, please refer to the help documentation (installed and found online).
Create a Linked Table to Resources Data
Follow the steps below to create a linked table, which enables you to access live Resources data.
Create the ODBC Connection
Follow the steps below to connect to Azure Data Lake Storage in Informatica PowerCenter:
- In the Informatica Developer tool connect to your repository and create a project.
- In the Connection Explorer pane, right-click and click Create a Connection.
- In the New Database Connection wizard that is displayed, enter a name and Id for the connection and in the Type menu select ODBC.
- In the Connection String property, enter the DSN.
NOTE: If you are working in a Linux operating system, set the Driver Manager for Linux property to unixODBC 2.3.x.
Create the Azure Data Lake Storage Data Object
After you have created an ODBC connection to Azure Data Lake Storage, you can now access Azure Data Lake Storage entities in Informatica. Follow the steps below to add Resources entities to your project.
- In the Object Explorer, right-click your project and then click New -> Data Object.
- In the wizard that is displayed, select the Relational Data Object option.
- Click the Browse button next to the Connection box and select the ODBC connection you created in the previous step.
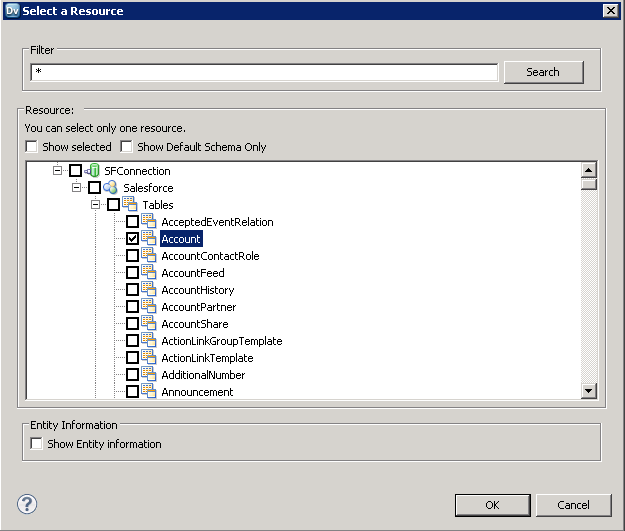
- Select the option to create a data object from an existing resource and click the Browse button next to the Resource box.
- In the dialog that is displayed, clear the Show Default Schema Only option and expand the node for the ODBC connection. Select the entity that you want.
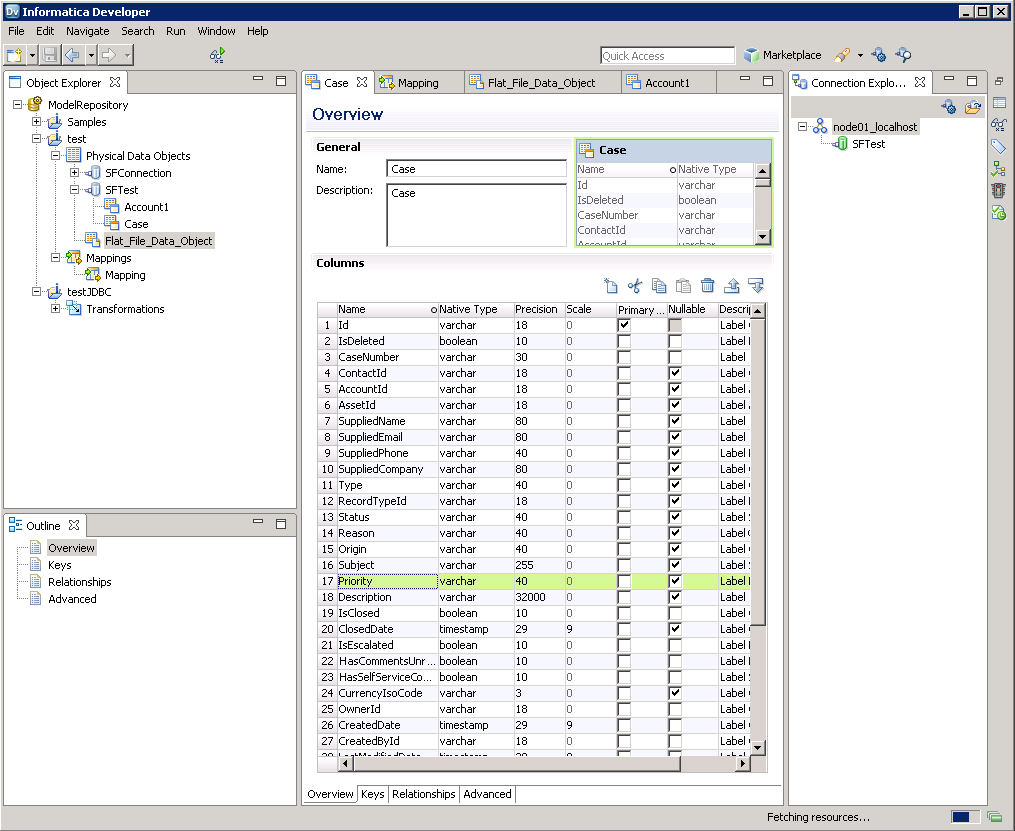
![The driver models Azure Data Lake Storage entities as relational tables. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
You can now browse the table in the Data Viewer: Right-click the node for the table and then click Open. On the Data Viewer view, click Run.
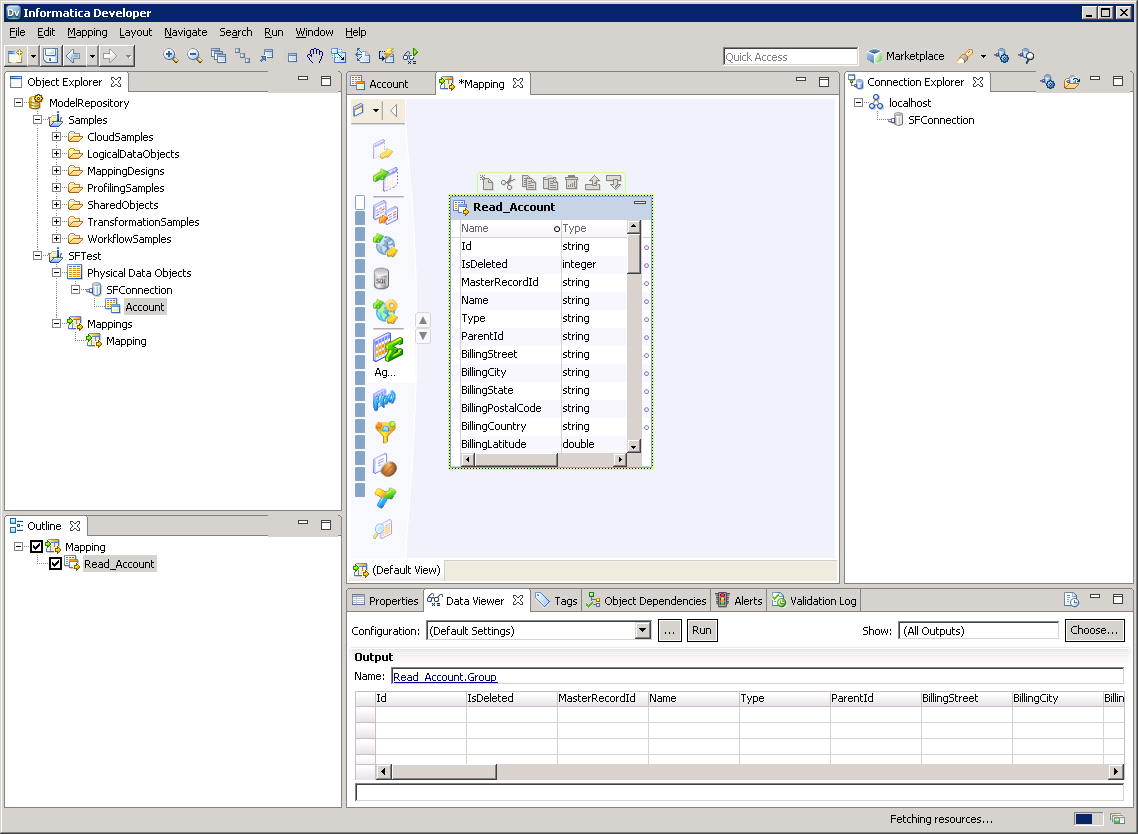
Create the Mapping
Follow the steps below to add the Azure Data Lake Storage source to a mapping:
- In the Object Explorer, right-click your project and then click New -> Mapping.
- Expand the node for the Azure Data Lake Storage connection and then drag the data object for the table onto the editor.
- In the dialog that appears, select the Read option.
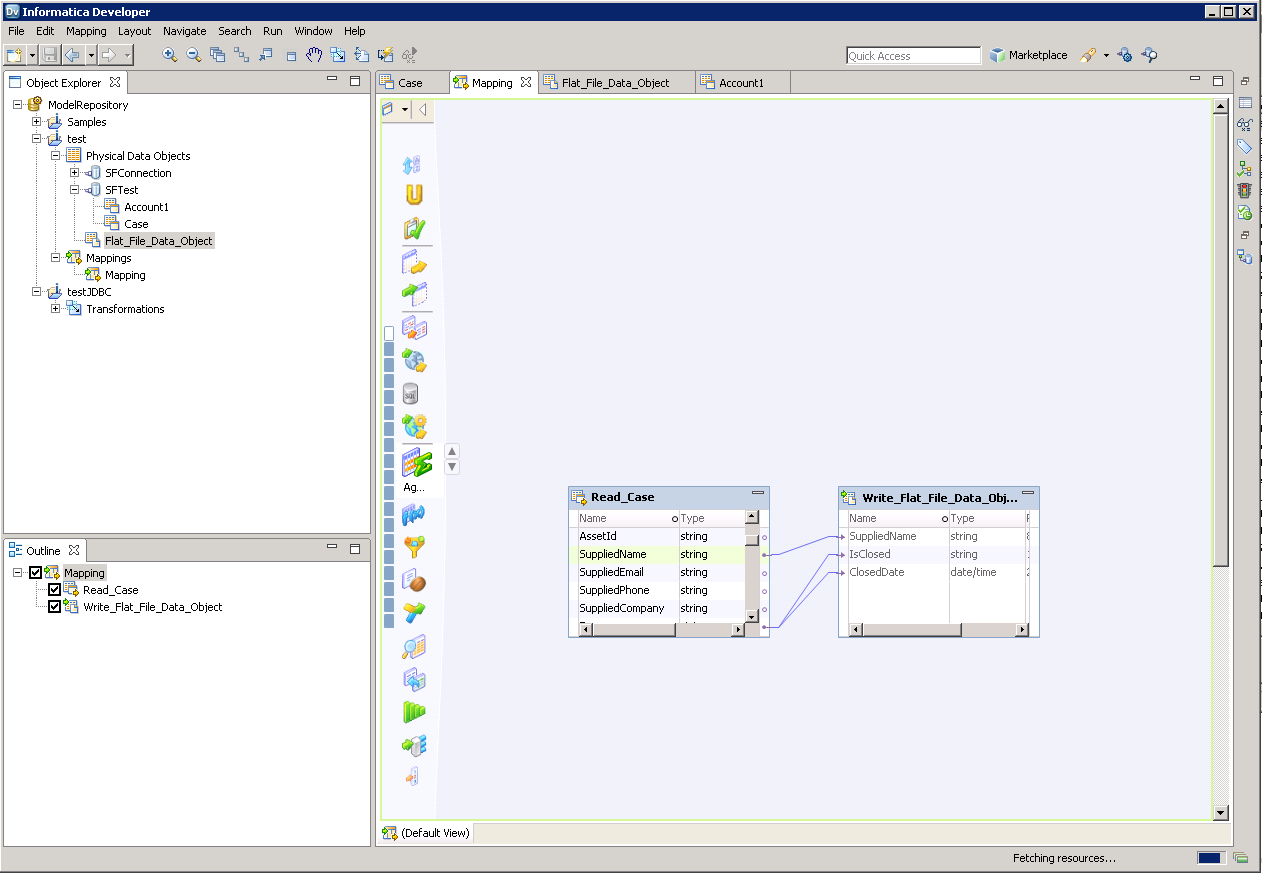
Follow the steps below to map Azure Data Lake Storage columns to a flat file:
- In the Object Explorer, right-click your project and then click New -> Data Object.
- Select Flat File Data Object -> Create as Empty -> Fixed Width.
- In the properties for the Azure Data Lake Storage object, select the rows you want, right-click, and then click copy. Paste the rows into the flat file properties.
- Drag the flat file data object onto the mapping. In the dialog that appears, select the Write option.
- Click and drag to connect columns.
To transfer Azure Data Lake Storage data, right-click in the workspace and then click Run Mapping.