Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Excel Spreadsheet Automation with the QUERY Formula
Pull data, automate spreadsheets, and more with the QUERY formula.
The CData Excel Add-In for MySQL provides formulas that can edit, save, and delete MySQL data. The following three steps show how you can automate the following task: Search MySQL data for a user-specified value and then organize the results into an Excel spreadsheet.
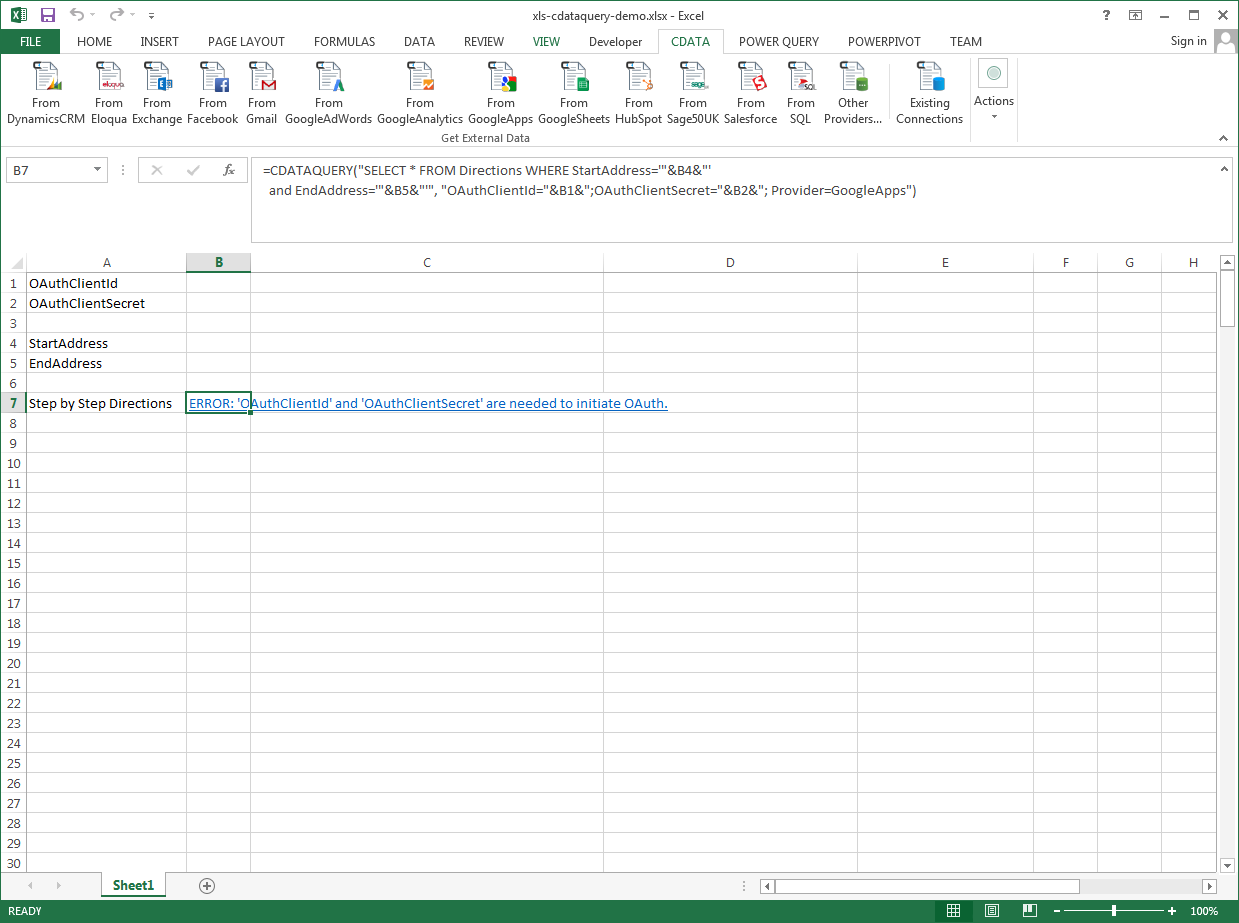
The syntax of the CDATAQUERY formula is the following:
=CDATAQUERY(Query, [Connection], [Parameters], [ResultLocation]);
This formula requires three inputs:
- Query: The declaration of the MySQL data records you want to retrieve or the modifications to be made, written in standard SQL.
Connection: Either the connection name, such as MySQLConnection1, or a connection string. The connection string consists of the required properties for connecting to MySQL data, separated by semicolons.
The Server and Port properties must be set to a MySQL server. If IntegratedSecurity is set to false, then User and Password must be set to valid user credentials. Optionally, Database can be set to connect to a specific database. If not set, tables from all databases will be returned.
- ResultLocation: The cell that the output of results should start from.
Pass Spreadsheet Cells as Inputs to the Query
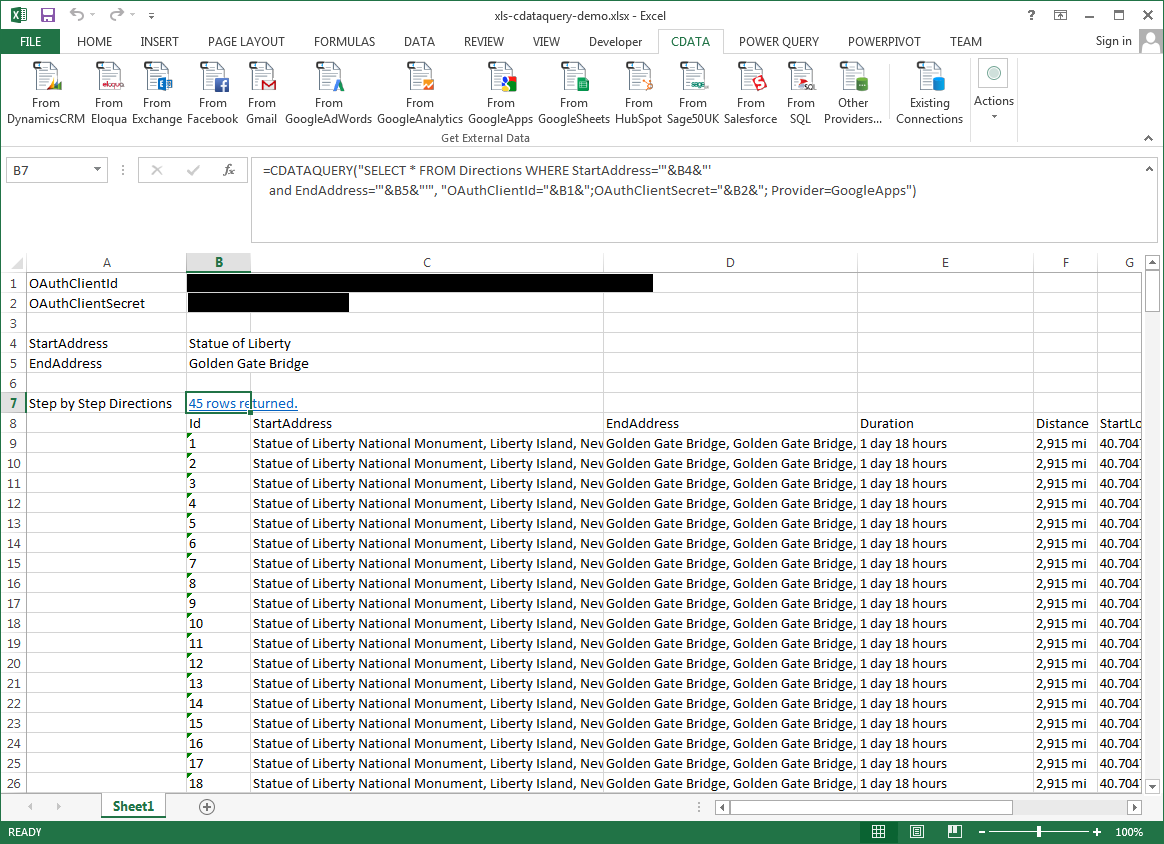
The procedure below results in a spreadsheet that organizes all the formula inputs in the first column.
- Define cells for the formula inputs. In addition to the connection inputs, add another input to define a criterion for a filter to be used to search MySQL data, such as ShipCountry.
- In another cell, write the formula, referencing the cell values from the user input cells defined above. Single quotes are used to enclose values such as addresses that may contain spaces.
- Change the filter to change the data.
![The outputs of the formula. (Google Apps is shown.)]()
=CDATAQUERY("SELECT * FROM Orders WHERE ShipCountry = '"&B6&"'","User="&B1&";Password="&B2&";Database="&B3&";Server="&B4&";Port="&B5&";Provider=MySQL",B7)