Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →DataBind Redshift Data to the DevExpress Data Grid
Use the CData ADO.NET Provider for Redshift with the DevExpress Windows Forms and Web controls to provide Redshift data to a chart.
The ADO.NET Provider for Redshift by CData incorporates conventional ADO.NET data access components compatible with third-party controls. You can adhere to the standard ADO.NET data binding procedures to establish two-way access to real-time data through UI controls. This article will demonstrate the utilization of CData components for data binding with DevExpress UI Controls (Windows Forms and Web controls), specifically binding to a chart that visualizes live data.
To connect to Redshift, set the following:
- Server: Set this to the host name or IP address of the cluster hosting the Database you want to connect to.
- Port: Set this to the port of the cluster.
- Database: Set this to the name of the database. Or, leave this blank to use the default database of the authenticated user.
- User: Set this to the username you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
- Password: Set this to the password you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
You can obtain the Server and Port values in the AWS Management Console:
- Open the Amazon Redshift console (http://console.aws.amazon.com/redshift).
- On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster.
- On the Configuration tab for the cluster, copy the cluster URL from the connection strings displayed.
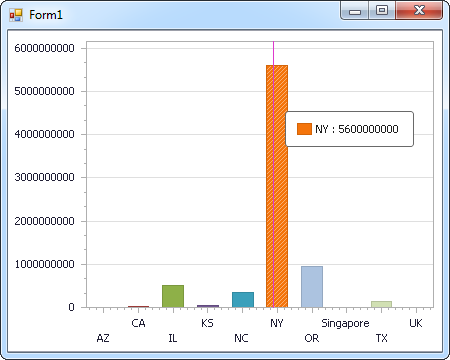
Windows Forms Controls
The code below shows how to populate a DevExpress chart with Redshift data. The RedshiftDataAdapter binds to the Series property of the chart control. The Diagram property of the control defines the x- and y-axes as the column names.
using (RedshiftConnection connection = new RedshiftConnection(
"User=admin;Password=admin;Database=dev;Server=examplecluster.my.us-west-2.redshift.amazonaws.com;Port=5439;")) {
RedshiftDataAdapter dataAdapter = new RedshiftDataAdapter(
"SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM Orders", connection);
DataTable table = new DataTable();
dataAdapter.Fill(table);
DevExpress.XtraCharts.Series series = new DevExpress.XtraCharts.Series();
chartControl1.Series.Add(series);
series.DataSource = table;
series.ValueDataMembers.AddRange(new string[] { "ShipCity" });
series.ArgumentScaleType = DevExpress.XtraCharts.ScaleType.Qualitative;
series.ArgumentDataMember = "ShipName";
series.ValueScaleType = DevExpress.XtraCharts.ScaleType.Numerical;
chartControl1.Legend.Visibility = DevExpress.Utils.DefaultBoolean.False;
((DevExpress.XtraCharts.SideBySideBarSeriesView)series.View).ColorEach = true;
}
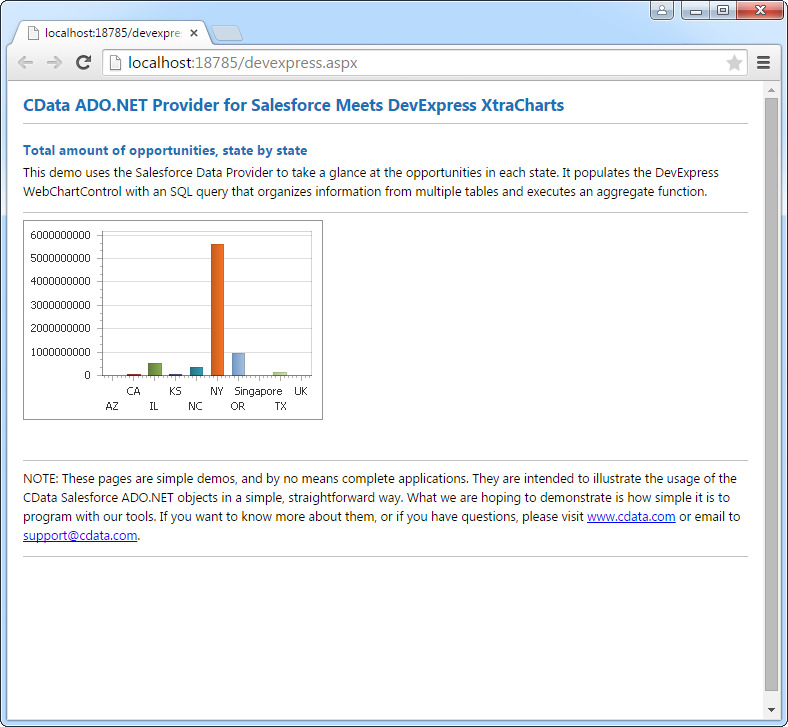
Web Controls
The code below shows how to populate a DevExpress Web control with Redshift data. The RedshiftDataAdapter binds to the Series property of the chart; the Diagram property defines the x- and y-axes as the column names.
using DevExpress.XtraCharts;
using (RedshiftConnection connection = new RedshiftConnection(
"User=admin;Password=admin;Database=dev;Server=examplecluster.my.us-west-2.redshift.amazonaws.com;Port=5439;"))
{
RedshiftDataAdapter RedshiftDataAdapter1 = new RedshiftDataAdapter("SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM Orders", connection);
DataTable table = new DataTable();
RedshiftDataAdapter1.Fill(table);
DevExpress.XtraCharts.Series series = new Series("Series1", ViewType.Bar);
WebChartControl1.Series.Add(series);
series.DataSource = table;
series.ValueDataMembers.AddRange(new string[] { "ShipCity" });
series.ArgumentScaleType = ScaleType.Qualitative;
series.ArgumentDataMember = "ShipName";
series.ValueScaleType = ScaleType.Numerical;
((DevExpress.XtraCharts.SideBySideBarSeriesView)series.View).ColorEach = true;
}