Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Create Informatica Mappings From/To a JDBC Data Source for Redshift
Create Redshift data objects in Informatica using the standard JDBC connection process: Copy the JAR and then connect.
Informatica provides a powerful, elegant means of transporting and transforming your data. By utilizing the CData JDBC Driver for Redshift, you are gaining access to a driver based on industry-proven standards that integrates seamlessly with Informatica's powerful data transportation and manipulation features. This tutorial shows how to transfer and browse Redshift data in Informatica PowerCenter.
Deploy the Driver
To deploy the driver to the Informatica PowerCenter server, copy the CData JAR and .lic file, located in the lib subfolder in the installation directory, to the following folder: Informatica-installation-directory\services\shared\jars\thirdparty.
To work with Redshift data in the Developer tool, you will need to copy the CData JAR and .lic file, located in the lib subfolder in the installation directory, into the following folders:
- Informatica-installation-directory\client\externaljdbcjars
- Informatica-installation-directory\externaljdbcjars
Create the JDBC Connection
Follow the steps below to connect from Informatica Developer:
- In the Connection Explorer pane, right-click your domain and click Create a Connection.
- In the New Database Connection wizard that is displayed, enter a name and Id for the connection and in the Type menu select JDBC.
- In the JDBC Driver Class Name property, enter:
cdata.jdbc.redshift.RedshiftDriver - In the Connection String property, enter the JDBC URL, using the connection properties for Redshift.
To connect to Redshift, set the following:
- Server: Set this to the host name or IP address of the cluster hosting the Database you want to connect to.
- Port: Set this to the port of the cluster.
- Database: Set this to the name of the database. Or, leave this blank to use the default database of the authenticated user.
- User: Set this to the username you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
- Password: Set this to the password you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
You can obtain the Server and Port values in the AWS Management Console:
- Open the Amazon Redshift console (http://console.aws.amazon.com/redshift).
- On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster.
- On the Configuration tab for the cluster, copy the cluster URL from the connection strings displayed.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Redshift JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.redshift.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical connection string is below:
jdbc:redshift:User=admin;Password=admin;Database=dev;Server=examplecluster.my.us-west-2.redshift.amazonaws.com;Port=5439;
Browse Redshift Tables
After you have added the driver JAR to the classpath and created a JDBC connection, you can now access Redshift entities in Informatica. Follow the steps below to connect to Redshift and browse Redshift tables:
- Connect to your repository.
- In the Connection Explorer, right-click the connection and click Connect.
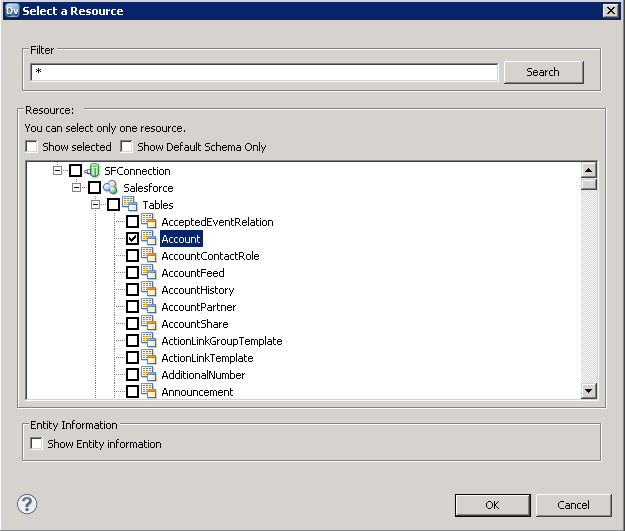
- Clear the Show Default Schema Only option.
![The driver models Redshift entities as relational tables. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
You can now browse Redshift tables in the Data Viewer: Right-click the node for the table and then click Open. On the Data Viewer view, click Run.
Create Redshift Data Objects
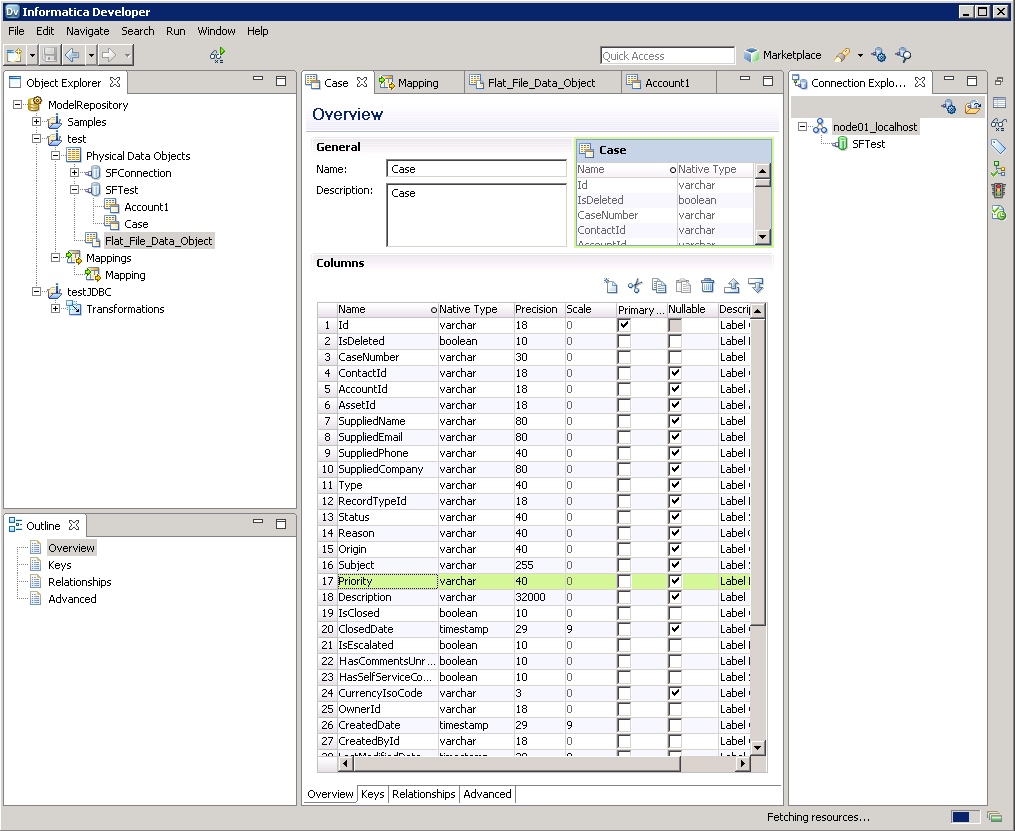
Follow the steps below to add Redshift tables to your project:
- Select tables in Redshift, then right-click a table in Redshift, and click Add to Project.
- In the resulting dialog, select the option to create a data object for each resource.
- In the Select Location dialog, select your project.
Create a Mapping
Follow the steps below to add the Redshift source to a mapping:
- In the Object Explorer, right-click your project and then click New -> Mapping.
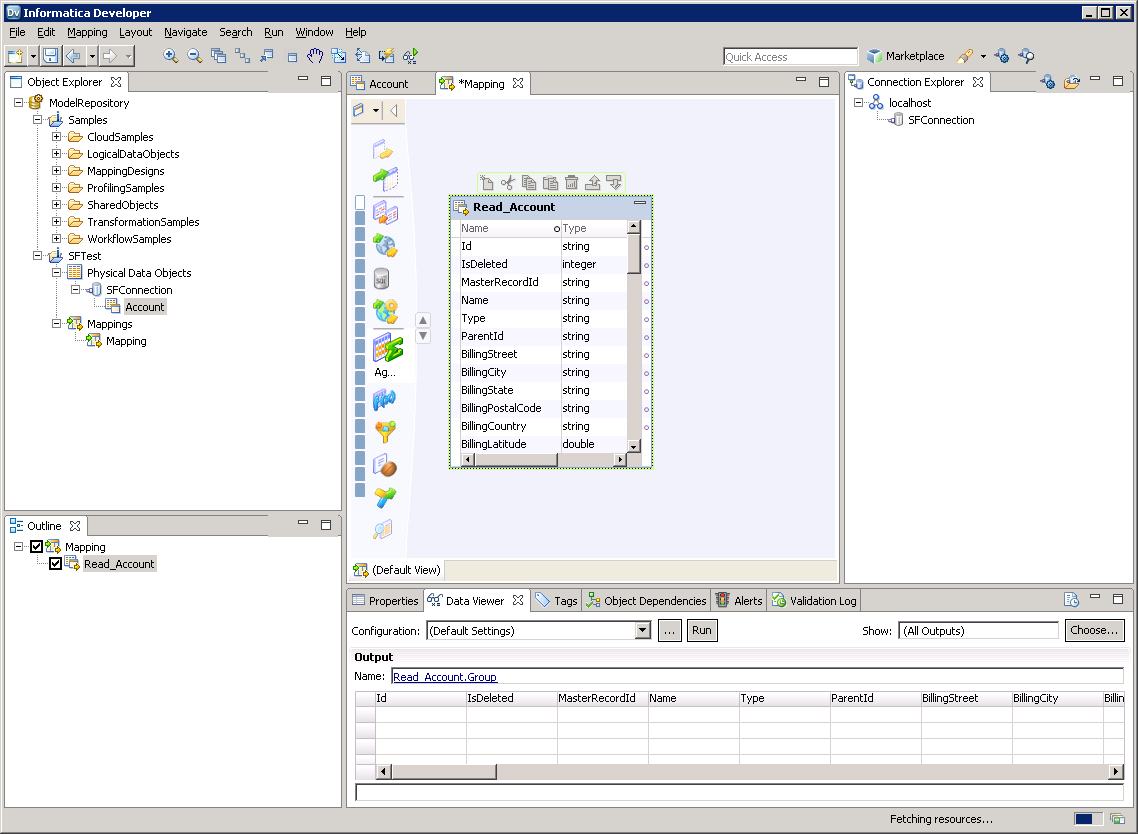
- Expand the node for the Redshift connection and then drag the data object for the table onto the editor.
- In the dialog that appears, select the Read option.
![The source Redshift table in the mapping. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Follow the steps below to map Redshift columns to a flat file:
- In the Object Explorer, right-click your project and then click New -> Data Object.
- Select Flat File Data Object -> Create as Empty -> Fixed Width.
- In the properties for the Redshift object, select the rows you want, right-click, and then click copy. Paste the rows into the flat file properties.
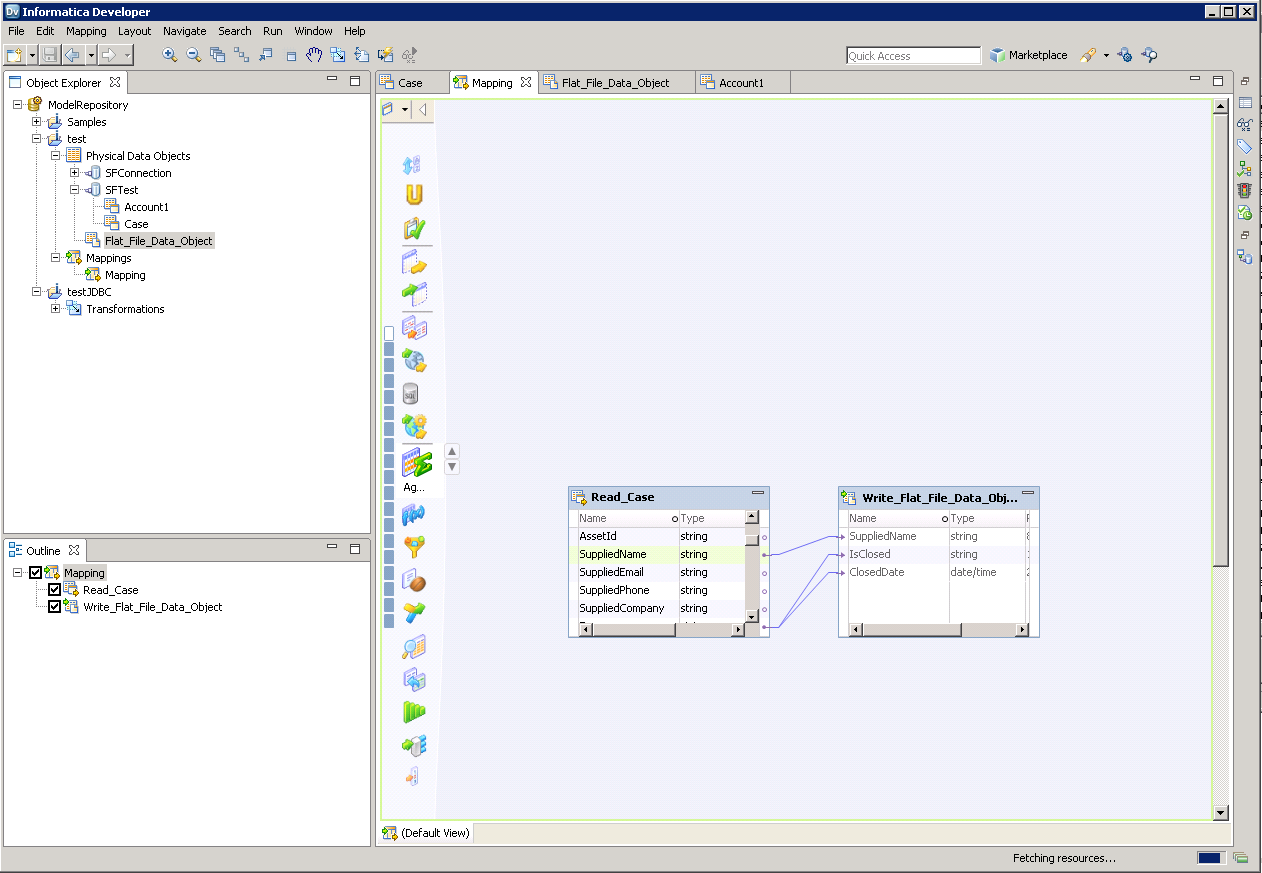
- Drag the flat file data object onto the mapping. In the dialog that appears, select the Write option.
- Click and drag to connect columns.
To transfer Redshift data, right-click in the workspace and then click Run Mapping.
![The completed mapping. (Salesforce is shown.)]()