Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Use the CData ODBC Driver for TaxJar in SAS JMP
You can use the CData ODBC Driver to integrate TaxJar data into the statistical analysis tools available in SAS JMP. This article shows how to use TaxJar data in the Graph Builder and Query Builder.
You can use the CData ODBC Driver for TaxJar to integrate live data into your statistical analysis with SAS JMP. The driver proxies your queries directly to the TaxJar API, ensuring that your analysis reflects any changes to the data. The CData ODBC Driver supports the standard SQL used by JMP in the background as you design reports.
The TaxJar API supports bidirectional access. This article shows how to access TaxJar data into a report and create data visualization. It also shows how to use SQL to query and manipulate TaxJar data from the JMP Query Builder.
Access TaxJar Data as an ODBC Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
To authenticate to the TaxJar API, you will need to first obtain the API Key from the TaxJar UI.
NOTE: the API is available only for Professional and Premium TaxJar plans.
If you already have a Professional or Premium plan you can find the API Key by logging in the TaxJar UI and navigating to Account -> TaxJar API. After obtaining the API Key, you can set it in the APIKey connection property.
Additional Notes
- By default, the CData connector will retrieve data of the last 3 months in cases where the entity support date range filtering. You can set StartDate to specify the minimum creation date of the data retrieved.
- If the API Key has been created for a sandbox API account please set UseSandbox to true, but not all endpoints will work as expected. For more information, refer to the TaxJar developer documentation.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Import TaxJar Data with the Query Builder
After you have created the TaxJar DSN, you can use SQL to invoke the capabilities of the TaxJar API. Follow the steps below to execute some supported queries in the Query Builder:
- In SAS JMP, click File -> Database -> Query Builder. The Select Database Connection dialog is displayed.
- Click New Connection.
- On the Machine Data Source tab, select the DSN. In the next step, the Select Tables for Query dialog is displayed.
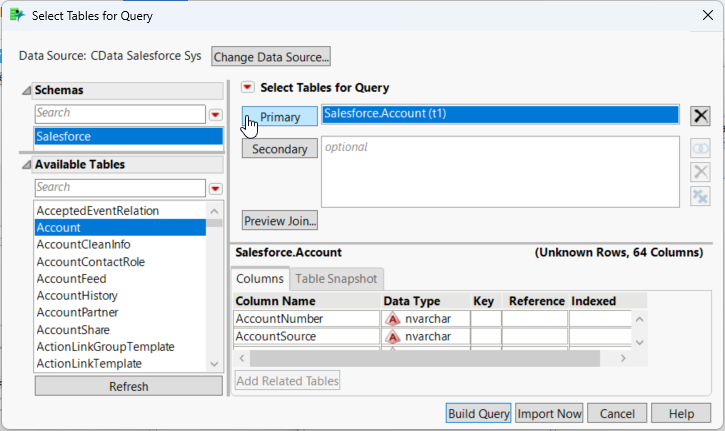
- In the Available Tables section, select a table and click Primary.
- As you drag Available Columns to the Included Columns tab, the underlying SQL query is updated.
![The generated query in the Query Builder. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
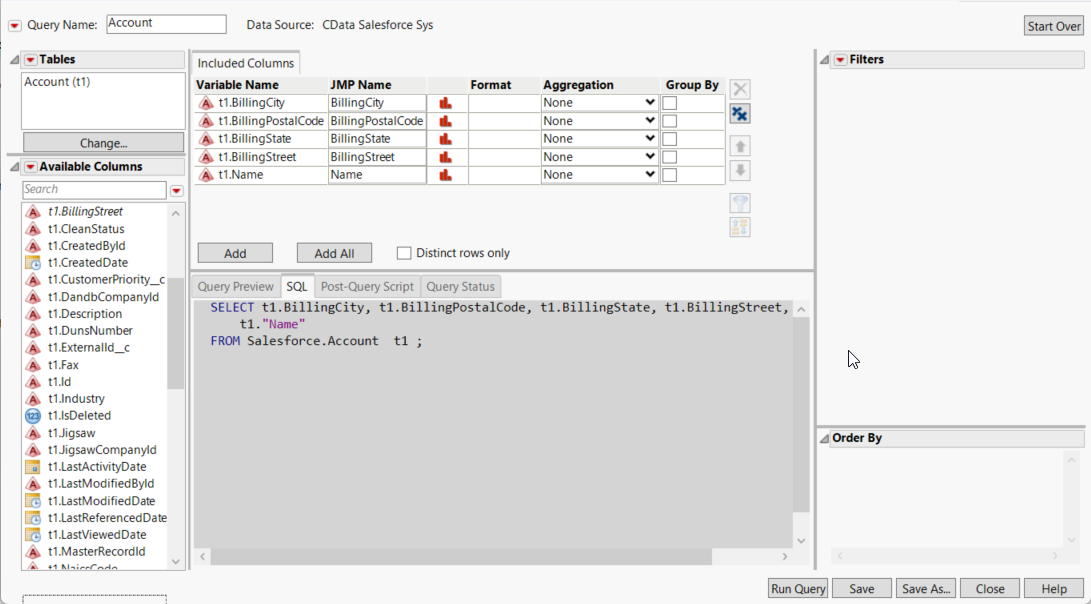
- Click Run Query to display the data.
![The results of a query in the Query Builder. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- To refresh the results with the current data, right-click Update from Database and click Run Script.
Manipulate TaxJar Data
You can execute data manipulation queries from JSL scripts such as the one below. To execute a script, click New Script in the toolbar. To connect, specify the DSN. You can then use the standard SQL syntax:
Open Database( "DSN=CData TaxJar Source;",
"INSERT INTO Orders
(TransactionID)
VALUES ('123');");
Visualize TaxJar Data
After importing, you can use the Graph Builder to create graphs visually. To open the Graph Builder, click the Graph Builder button in the toolbar.
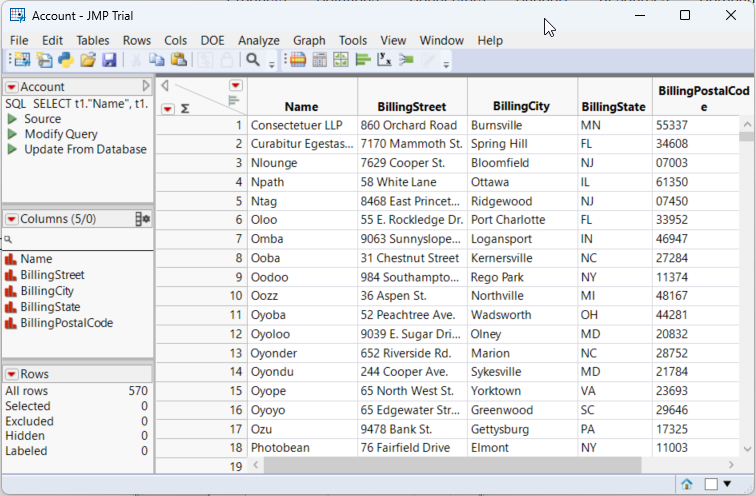
- Drag a dimension column onto the x axis. For example, TransactionID.
- Drag a measure column onto the y axis. For example, UserID.
- Select a chart type. For example, a bar chart.
![Configuration of a basic chart. (Salesforce is shown.)]()