Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Analyze ADP Data with Power Pivot
This article walks you through the process of using the CData ODBC Driver for ADP from Power Pivot. You will use the Table Import Wizard to load ADP data. You can visually build the import query or use any SQL supported by the driver.
The ODBC protocol is used by a wide variety of Business Intelligence (BI) and reporting tools to get access to different databases. The CData ODBC Driver for ADP brings the same power and ease of use to ADP data. This article uses the driver to import ADP data into Power Pivot.
Connect to ADP as an ODBC Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
Connect to ADP by specifying the following properties:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the certificate provided during registration.
- SSLClientCertPassword: Set this to the password of the certificate.
- UseUAT: The connector makes requests to the production environment by default. If using a developer account, set UseUAT = true.
- RowScanDepth: The maximum number of rows to scan for the custom fields columns available in the table. The default value will be set to 100. Setting a high value may decrease performance.
The connector uses OAuth to authenticate with ADP. OAuth requires the authenticating user to interact with ADP using the browser. For more information, refer to the OAuth section in the Help documentation.
Connect from Power Pivot
Follow the steps below to connect to the DSN in Power Pivot.
- In Excel, click the Power Pivot Window icon on the Power Pivot tab to open Power Pivot.
- Launch the Table Import Wizard: Click the Get External Data from Other Data Sources button.
- Select the OLEDB/ODBC source option.
- Click Build to open the Data Link Properties dialog.
- In the Provider tab, select the Microsoft OLEDB Provider for ODBC Drivers option.
- In the Connection tab, select the Use Data Source Name option and then select the ADP DSN in the menu.
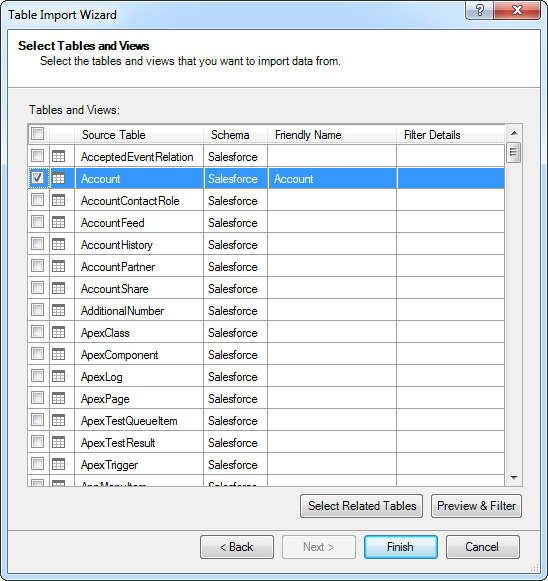
Select and Filter Tables and Views
Follow the steps below to use the wizard to import ADP tables. As you use the wizard to select, filter, and sort columns of ADP tables, Power Pivot generates the query to be executed.
-
After selecting the DSN in the Table Import Wizard, select the option to select from a list of tables.
Click Preview & Filter to select specific columns, sort data, and visually build filters. To include or exclude columns, select and clear the option next to the column name.
To filter based on column values, click the down arrow button next to the column name. In the resulting dialog, select or clear the column values you want to filter. Alternatively, click Number Filters or Text Filters and then select a comparison operator. In the resulting dialog, build the filter criteria.
- Return to the Select Tables and Views page of the wizard. You can access filters by clicking the Applied Filters link in the Filter Details column.

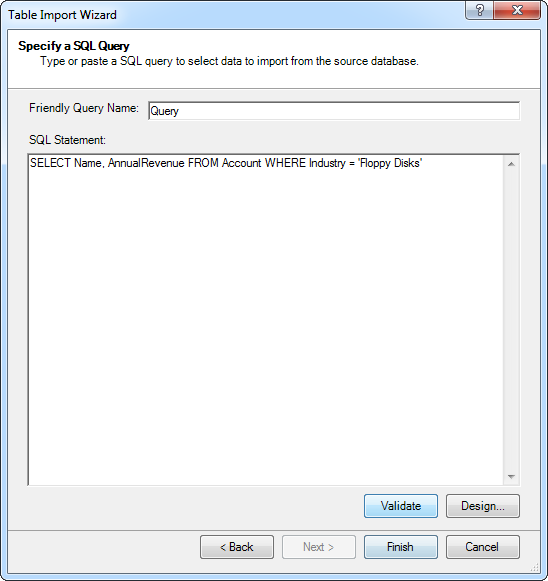
Import and Filter with SQL
You can also import with an SQL query. The driver supports the standard SQL, allowing Excel to communicate with ADP APIs.
- After selecting the DSN in the Table Import Wizard, select the option to write a query.
In the SQL Statement box, enter the query. Click Validate to check that the syntax of the query is valid. Click Design to preview the results and adjust the query before import.
![The query to be used to import the data.]()
- Finish the wizard to import the data for your chosen query.
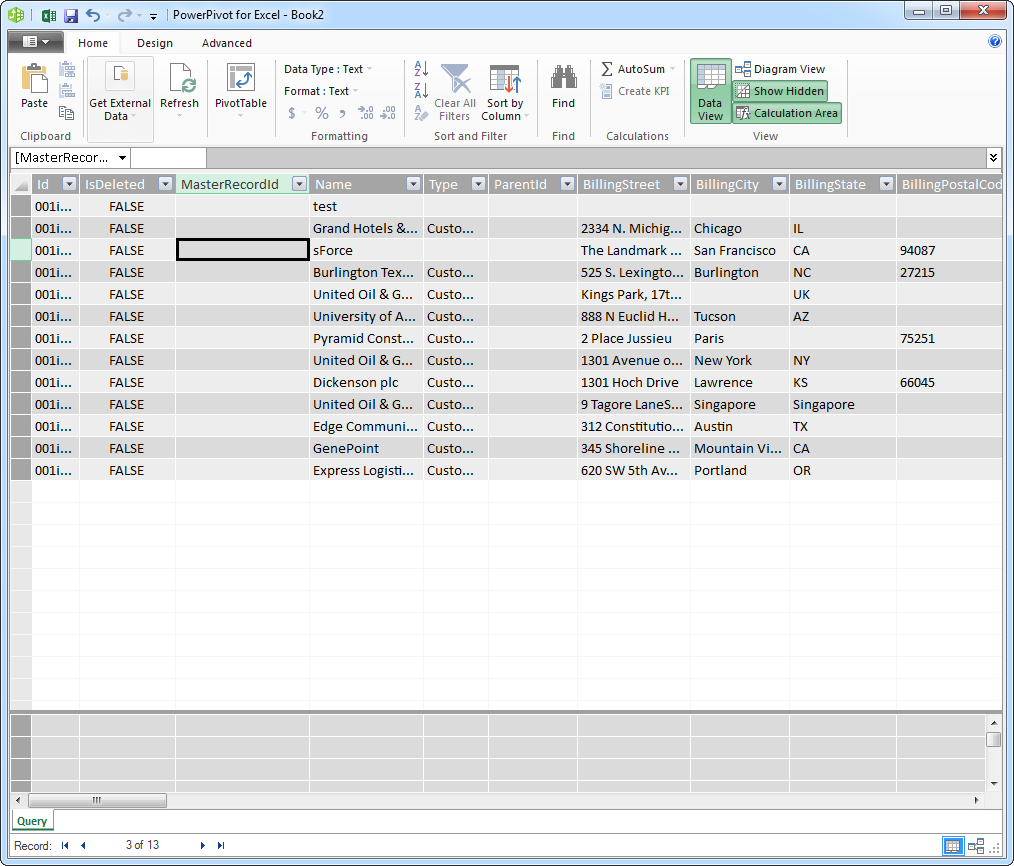
Refresh On Demand
Connectivity to ADP APIs enables real-time analysis. To immediately update your workbook with any changes, click Refresh.