Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Stream AlloyDB Data into Apache Kafka Topics
Access and stream AlloyDB data in Apache Kafka using the CData JDBC Driver and the Kafka Connect JDBC connector.
Apache Kafka is an open-source stream processing platform that is primarily used for building real-time data pipelines and event-driven applications. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB, Kafka can work with live AlloyDB data. This article describes how to connect, access and stream AlloyDB data into Apache Kafka Topics and to start Confluent Control Center to help users secure, manage, and monitor the AlloyDB data received using Kafka infrastructure in the Confluent Platform.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live AlloyDB data. When you issue complex SQL queries to AlloyDB, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to AlloyDB and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze AlloyDB data using native data types.
Prerequisites
Before connecting the CData JDBC Driver for streaming AlloyDB data in Apache Kafka Topics, install and configure the following in the client Linux-based system.
- Confluent Platform for Apache Kafka
- Confluent Hub CLI Installation
- Self-Managed Kafka JDBC Source Connector for Confluent Platform
Define a New JDBC Connection to AlloyDB data
- Download CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB on a Linux-based system
- Follow the given instructions to create a new directory extract all the driver contents into it:
- Create a new directory named AlloyDB
mkdir AlloyDB - Move the downloaded driver file (.zip) into this new directory
mv AlloyDBJDBCDriver.zip AlloyDB/ - Unzip the CData AlloyDBJDBCDriver contents into this new directory
unzip AlloyDBJDBCDriver.zip
- Create a new directory named AlloyDB
- Open the AlloyDB directory and navigate to the lib folder
ls cd lib/ - Copy the contents of the lib folder of AlloyDB into the lib folder of Kafka Connect JDBC. Check the Kafka Connect JDBC folder contents to confirm that the cdata.jdbc.alloydb.jar file is successfully copied into the lib folder
cp * ../../confluent-7.5.0/share/confluent-hub-components/confluentinc-kafka-connect-jdbc/lib/ cd ../../confluent-7.5.0/share/confluent-hub-components/confluentinc-kafka-connect-jdbc/lib/ - Install the CData AlloyDB JDBC driver license using the given command, followed by your Name and Email ID
java -jar cdata.jdbc.alloydb.jar -l - Enter the product key or "TRIAL" (In the scenarios of license expiry, please contact our CData Support team)
- Start the Confluent local services using the command:
confluent local services startThis starts all the Confluent Services like Zookeeper, Kafka, Schema Registry, Kafka REST, Kafka CONNECT, ksqlDB and Control Center. You are now ready to use the CData JDBC driver for AlloyDB to stream messages using Kafka Connect Driver into Kafka Topics on ksqlDB.
![Start the Confluent local services Start the Confluent local services]()
- Create the Kafka topics manually using a POST HTTP API Request:
curl --location 'server_address:8083/connectors' --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --data '{ "name": "jdbc_source_cdata_alloydb_01", "config": { "connector.class": "io.confluent.connect.jdbc.JdbcSourceConnector", "connection.url": "jdbc:alloydb:User=alloydb;Password=admin;Database=alloydb;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432", "topic.prefix": "alloydb-01-", "mode": "bulk" } }'Let us understand the fields used in the HTTP POST body (shown above):
- connector.class: Specifies the Java class of the Kafka Connect connector to be used.
- connection.url: The JDBC connection URL to connect with AlloyDB data.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the AlloyDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.alloydb.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.) Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- topic.prefix: A prefix that will be added to the Kafka topics created by the connector. It's set to "alloydb-01-".
- mode: Specifies the mode in which the connector operates. In this case, it's set to "bulk", which suggests that the connector is configured to perform bulk data transfer.
This request adds all the tables/contents from AlloyDB as Kafka Topics.
Note: The IP Address (server) to POST the request (shown above) is the Linux Network IP Address.
- Run ksqlDB and list the topics. Use the commands:
ksql list topics;![List the Kafka Topics (BigCommerce is shown) List the Kafka Topics (BigCommerce is shown)]()
- To view the data inside the topics, type the SQL Statement:
PRINT topic FROM BEGINNING;
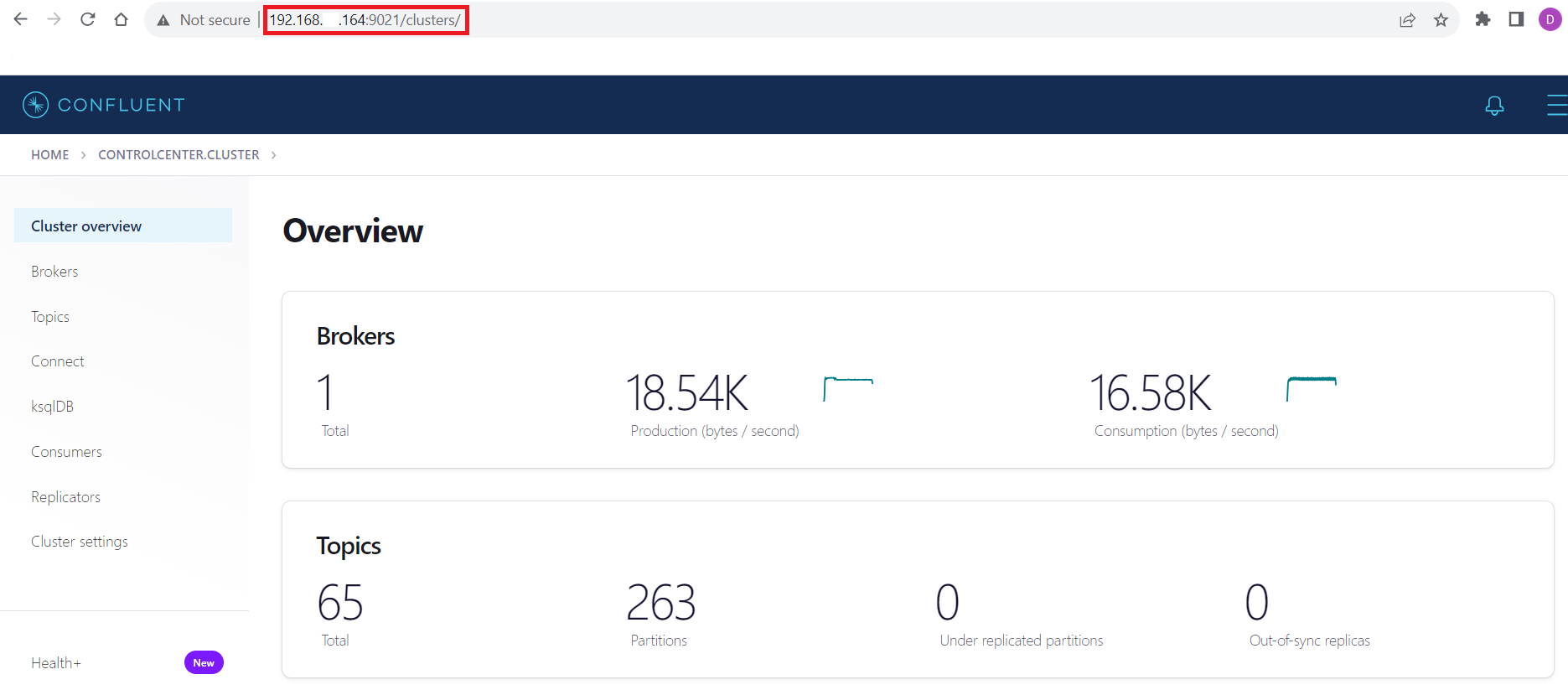
Connecting with the Confluent Control Center
To access the Confluent Control Center user interface, ensure to run the "confluent local services" as described in the above section and type http://<server address>:9021/clusters/ on your local browser.
Get Started Today
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB and start streaming AlloyDB data into Apache Kafka. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.









