Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →ETL Amazon S3 in Oracle Data Integrator
This article shows how to transfer Amazon S3 data into a data warehouse using Oracle Data Integrator.
Leverage existing skills by using the JDBC standard to connect to Amazon S3: Through drop-in integration into ETL tools like Oracle Data Integrator (ODI), the CData JDBC Driver for Amazon S3 connects real-time Amazon S3 data to your data warehouse, business intelligence, and Big Data technologies.
JDBC connectivity enables you to work with Amazon S3 just as you would any other database in ODI. As with an RDBMS, you can use the driver to connect directly to the Amazon S3 APIs in real time instead of working with flat files.
This article walks through a JDBC-based ETL -- Amazon S3 to Oracle. After reverse engineering a data model of Amazon S3 entities, you will create a mapping and select a data loading strategy -- since the driver supports SQL-92, this last step can easily be accomplished by selecting the built-in SQL to SQL Loading Knowledge Module.
Install the Driver
To install the driver, copy the driver JAR and .lic file, located in the installation folder, into the ODI appropriate directory:
- UNIX/Linux without Agent: ~/.odi/oracledi/userlib
- UNIX/Linux with Agent: $ODI_HOME/odi/agent/lib
- Windows without Agent: %APPDATA%\Roaming\odi\oracledi\userlib
- Windows with Agent: %APPDATA%\Roaming\odi\agent\lib
Restart ODI to complete the installation.
Reverse Engineer a Model
Reverse engineering the model retrieves metadata about the driver's relational view of Amazon S3 data. After reverse engineering, you can query real-time Amazon S3 data and create mappings based on Amazon S3 tables.
-
In ODI, connect to your repository and click New -> Model and Topology Objects.
![Create a New Model]()
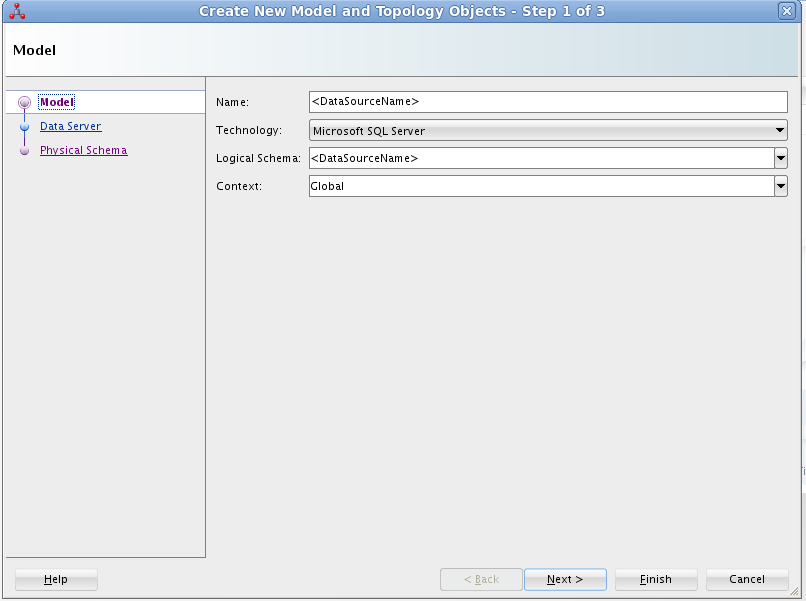
- On the Model screen of the resulting dialog, enter the following information:
- Name: Enter AmazonS3.
- Technology: Select Generic SQL (for ODI Version 12.2+, select Microsoft SQL Server).
- Logical Schema: Enter AmazonS3.
- Context: Select Global.
![Configuring the Model]()
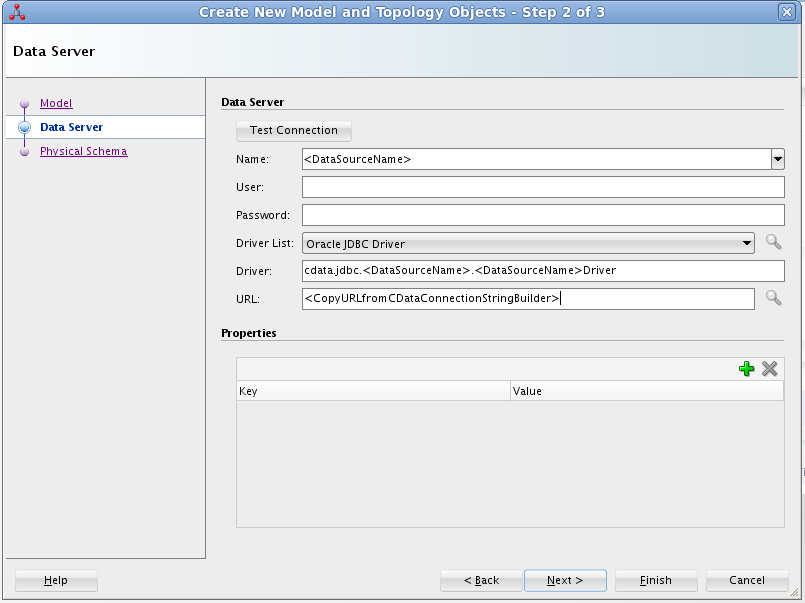
- On the Data Server screen of the resulting dialog, enter the following information:
- Name: Enter AmazonS3.
- Driver List: Select Oracle JDBC Driver.
- Driver: Enter cdata.jdbc.amazons3.AmazonS3Driver
- URL: Enter the JDBC URL containing the connection string.
To authorize Amazon S3 requests, provide the credentials for an administrator account or for an IAM user with custom permissions. Set AccessKey to the access key Id. Set SecretKey to the secret access key.
Note: You can connect as the AWS account administrator, but it is recommended to use IAM user credentials to access AWS services.
For information on obtaining the credentials and other authentication methods, refer to the Getting Started section of the Help documentation.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Amazon S3 JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.amazons3.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Below is a typical connection string:
jdbc:amazons3:AccessKey=a123;SecretKey=s123;
![Configuring the Data Server]()
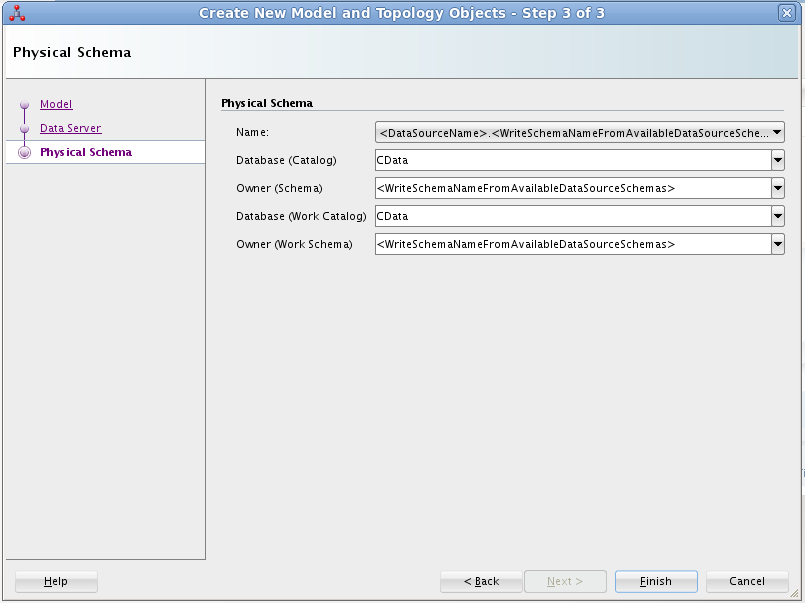
- On the Physical Schema screen, enter the following information:
- Name: Select from the Drop Down menu.
- Database (Catalog): Enter CData.
- Owner (Schema): If you select a Schema for Amazon S3, enter the Schema selected, otherwise enter AmazonS3.
- Database (Work Catalog): Enter CData.
- Owner (Work Schema): If you select a Schema for Amazon S3, enter the Schema selected, otherwise enter AmazonS3.
![Configuring the Physical Schema]()
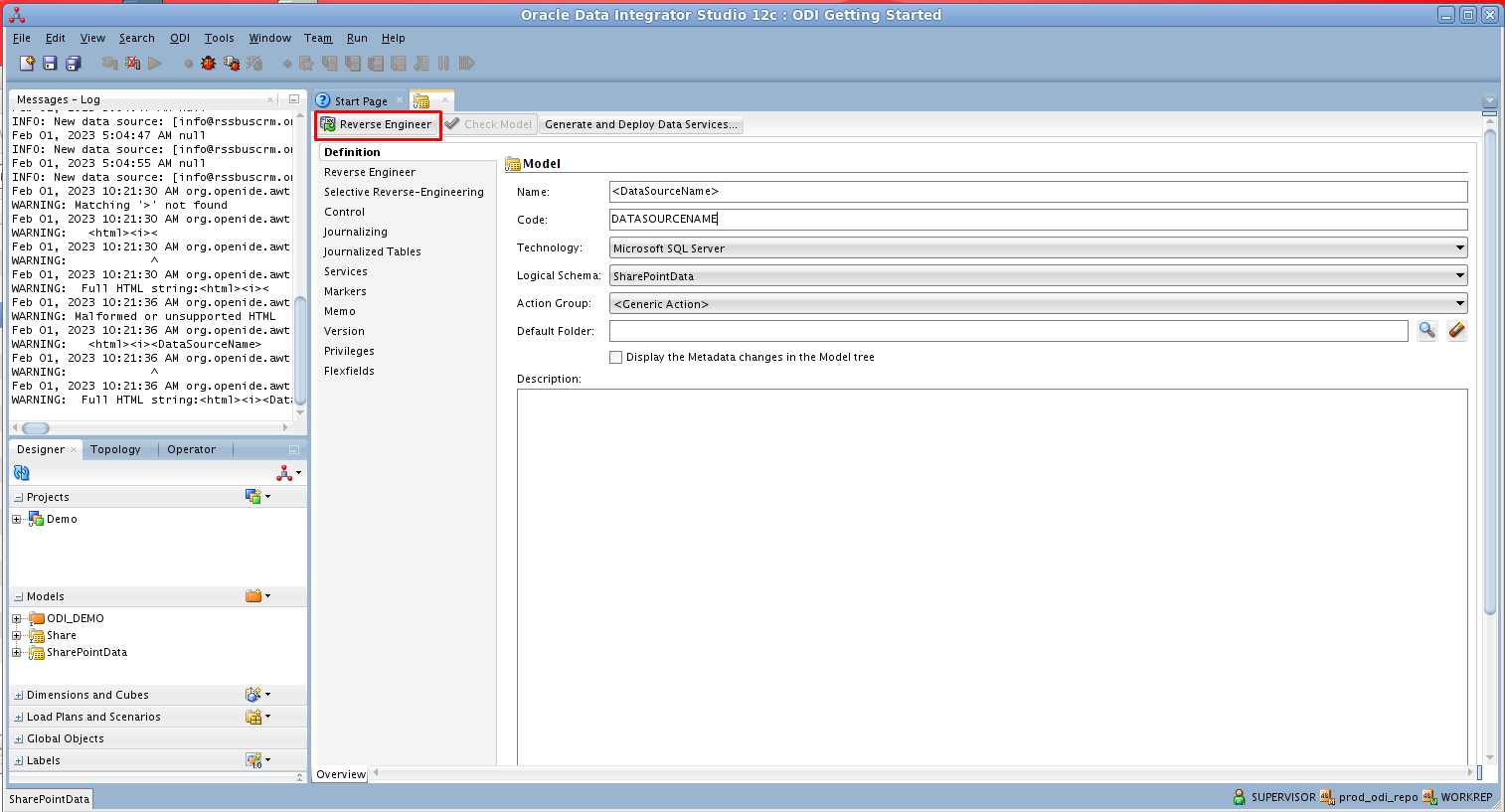
- In the opened model click Reverse Engineer to retrieve the metadata for Amazon S3 tables.
![Reverse Engineer the Model]()
Edit and Save Amazon S3 Data
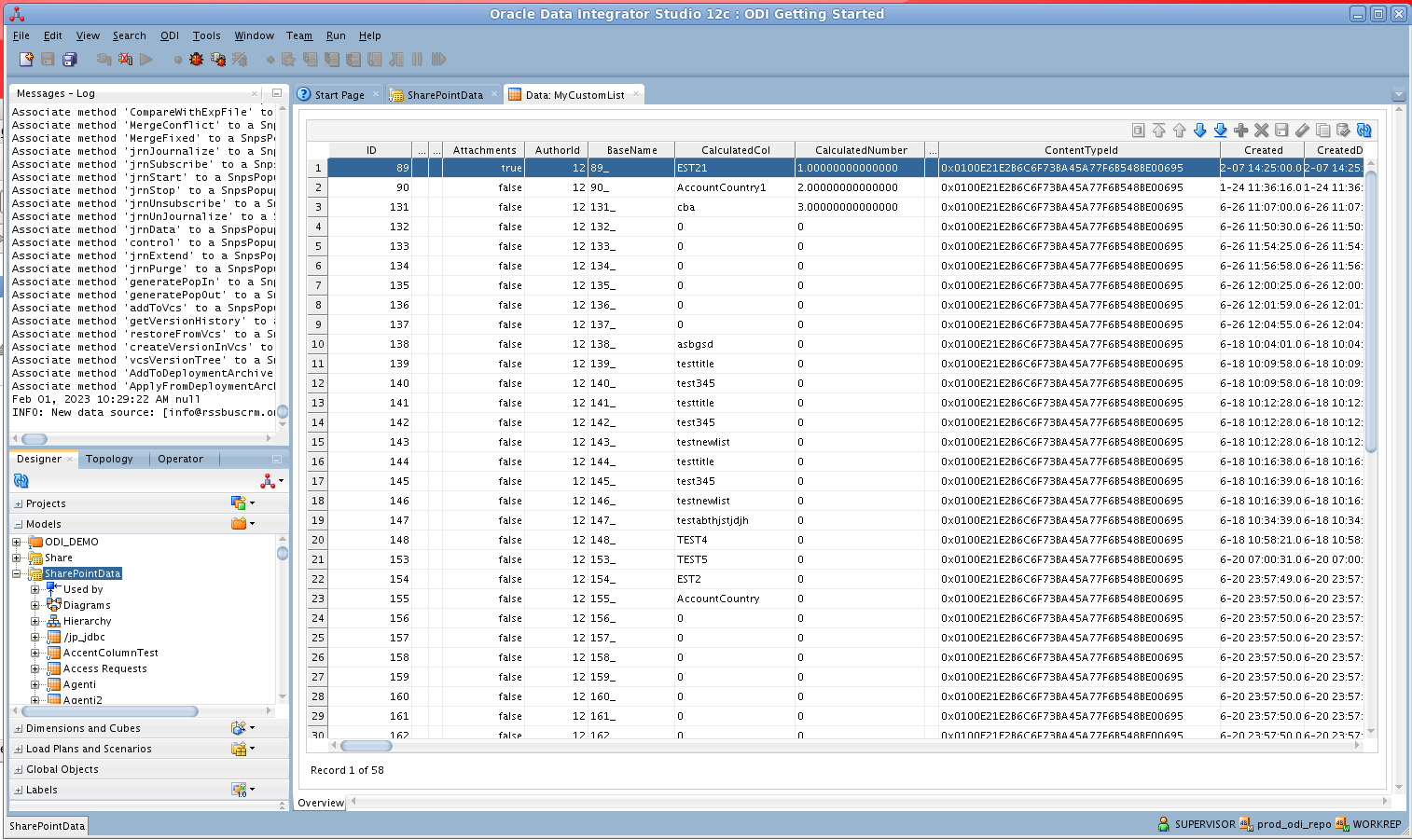
After reverse engineering you can now work with Amazon S3 data in ODI.
To view Amazon S3 data, expand the Models accordion in the Designer navigator, right-click a table, and click View data.
Create an ETL Project
Follow the steps below to create an ETL from Amazon S3. You will load ObjectsACL entities into the sample data warehouse included in the ODI Getting Started VM.
Open SQL Developer and connect to your Oracle database. Right-click the node for your database in the Connections pane and click new SQL Worksheet.
Alternatively you can use SQLPlus. From a command prompt enter the following:
sqlplus / as sysdba- Enter the following query to create a new target table in the sample data warehouse, which is in the ODI_DEMO schema. The following query defines a few columns that match the ObjectsACL table in Amazon S3:
CREATE TABLE ODI_DEMO.TRG_OBJECTSACL (OWNERID NUMBER(20,0),Name VARCHAR2(255)); - In ODI expand the Models accordion in the Designer navigator and double-click the Sales Administration node in the ODI_DEMO folder. The model is opened in the Model Editor.
- Click Reverse Engineer. The TRG_OBJECTSACL table is added to the model.
- Right-click the Mappings node in your project and click New Mapping. Enter a name for the mapping and clear the Create Empty Dataset option. The Mapping Editor is displayed.
- Drag the TRG_OBJECTSACL table from the Sales Administration model onto the mapping.
- Drag the ObjectsACL table from the Amazon S3 model onto the mapping.
- Click the source connector point and drag to the target connector point. The Attribute Matching dialog is displayed. For this example, use the default options. The target expressions are then displayed in the properties for the target columns.
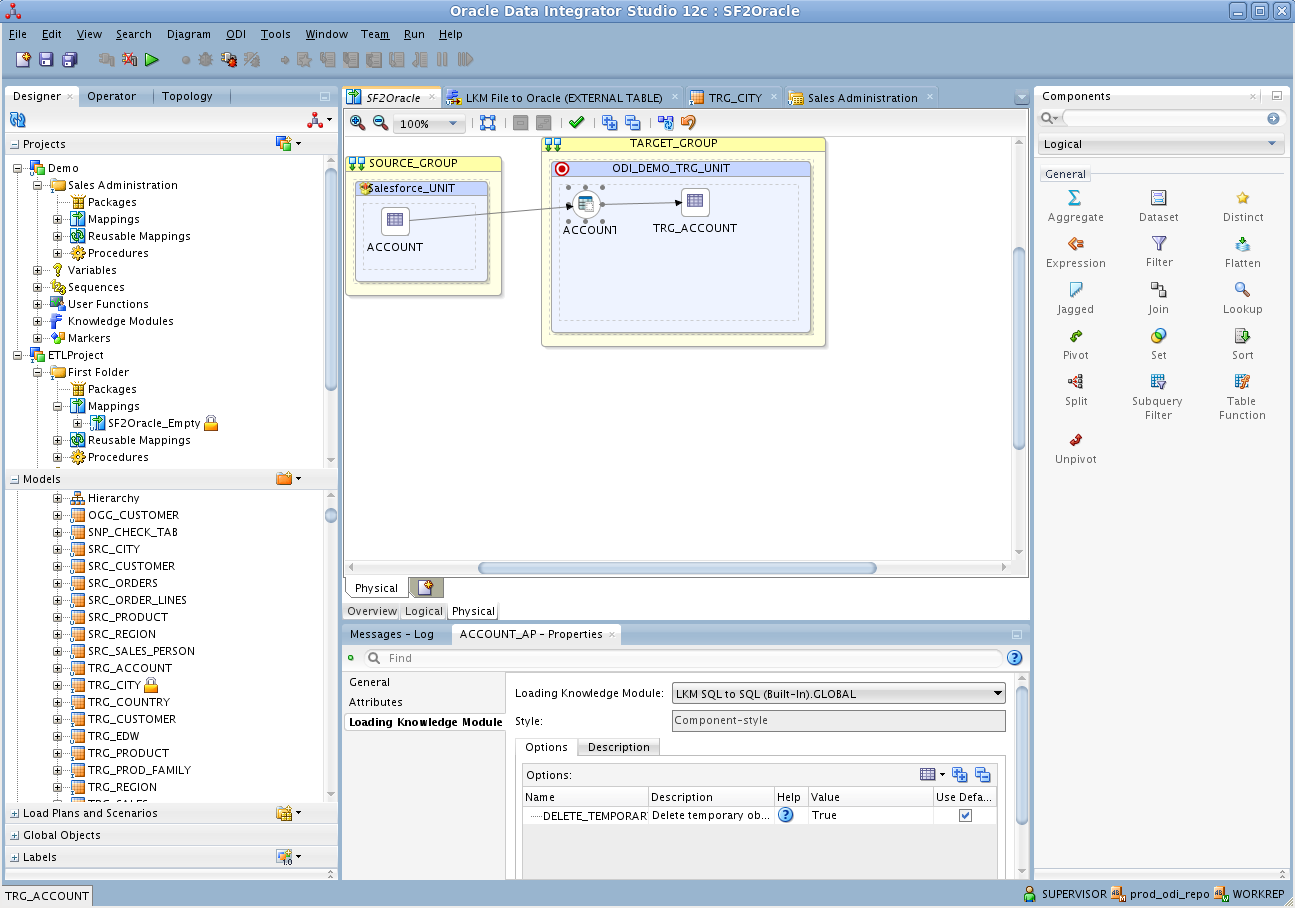
- Open the Physical tab of the Mapping Editor and click OBJECTSACL_AP in TARGET_GROUP.
- In the OBJECTSACL_AP properties, select LKM SQL to SQL (Built-In) on the Loading Knowledge Module tab.
![SQL-based access to Amazon S3 enables you to use standard database-to-database knowledge modules.]()
You can then run the mapping to load Amazon S3 data into Oracle.