Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Publish Crystal Reports on Azure Data Lake Storage Data
Use the Report Wizard and standard ADO.NET to design a report based on up-to-date Azure Data Lake Storage data.
The CData ADO.NET Provider for Azure Data Lake Storage is fully integrated into the SAP Crystal Reports for Visual Studio development environment. You can employ standard ADO.NET components to construct reports, much like you would with SQL Server, but with the added advantage of real-time connectivity to Azure Data Lake Storage. This article will guide you through the essential three steps to incorporate Azure Data Lake Storage data into a report that refreshes upon opening.
Note: You will need to install SAP Crystal Reports, developer version for Visual Studio to follow this tutorial.
Create a Crystal Reports Application
To follow this article, you will also need a Visual Studio Crystal Reports project. This article will add a report to a WPF application. You can create one by clicking File -> New Project and then selecting the Crystal Reports WPF Application template. In the resulting wizard, select the option to create a blank report.
Connect to Azure Data Lake Storage
Creating an ADO.NET data source for Azure Data Lake Storage from Server Explorer makes it easy to create a DataSet that can be used in Crystal Reports wizards and the Crystal Reports Designer. You can find a guide to working with Azure Data Lake Storage data in Server Explorer in the "Getting Started" chapter of the help documentation.
Authenticating to a Gen 1 DataLakeStore Account
Gen 1 uses OAuth 2.0 in Azure AD for authentication.
For this, an Active Directory web application is required. You can create one as follows:
To authenticate against a Gen 1 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen1.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- OAuthClientId: Set this to the application Id of the app you created.
- OAuthClientSecret: Set this to the key generated for the app you created.
- TenantId: Set this to the tenant Id. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
Authenticating to a Gen 2 DataLakeStore Account
To authenticate against a Gen 2 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen2.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- FileSystem: Set this to the file system which will be used for this account.
- AccessKey: Set this to the access key which will be used to authenticate the calls to the API. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
When you configure the connection, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Create a DataSet
Follow the steps below to use the Visual Studio ADO.NET DataSet Designer to create an ADO.NET DataSet object. Crystal Reports will bind to the DataSet object, which contains Azure Data Lake Storage table metadata. Note that this approach also adds a connection string to App.config; you will use this connection string later to load data into the report.
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click your project and then click Add -> New Item.
- Select DataSet. The DataSet Designer is then displayed.
- Drag and drop tables from Server Explorer onto the DataSet Designer. This article uses the Resources table.
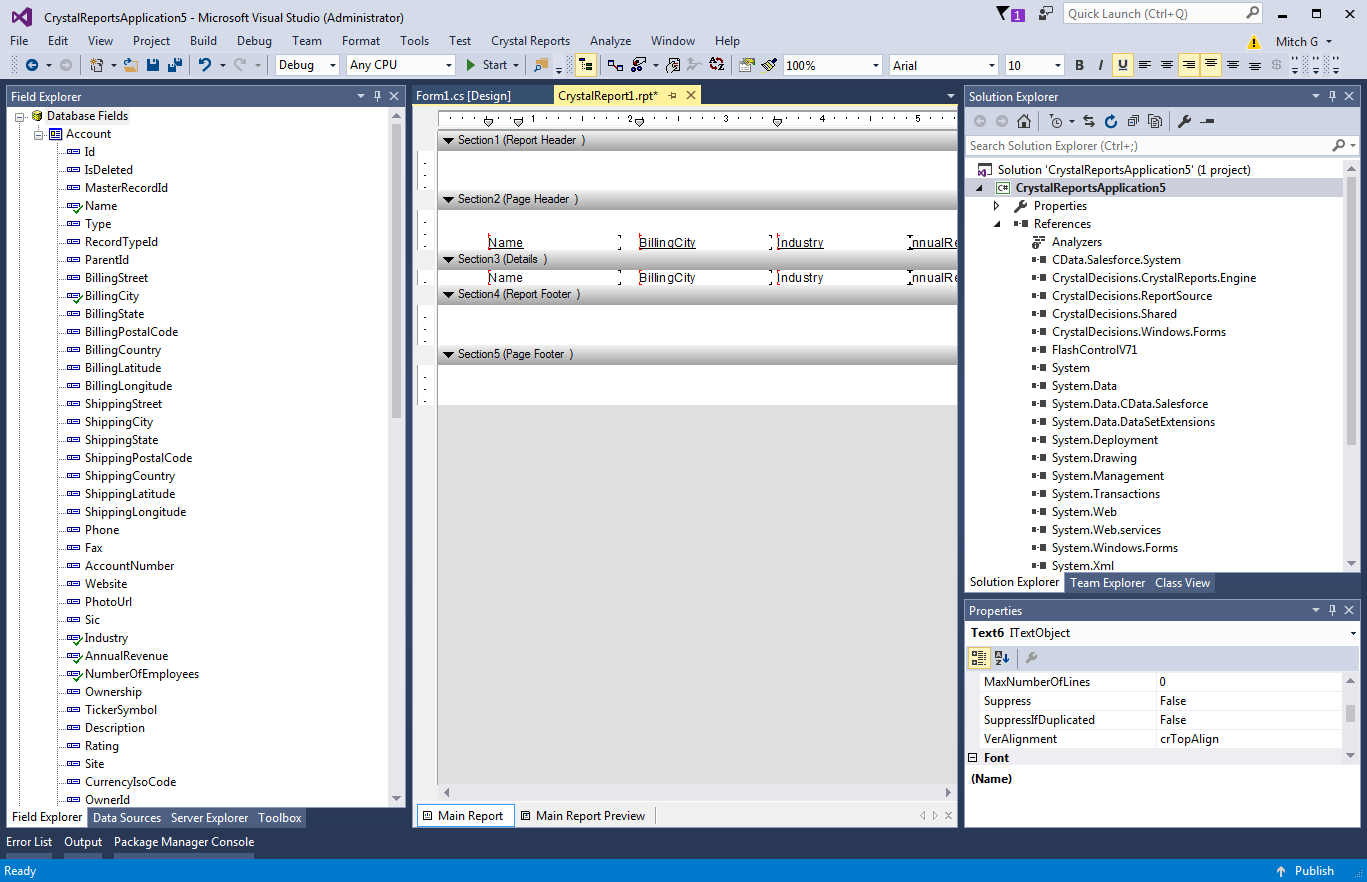
Add Azure Data Lake Storage Fields to the Report
Follow the steps below to add columns from the DataSet to the report:
- Double-click the .rpt file in the Solution Explorer to open the Crystal Reports Designer.
- Right-click the designer and click Database -> Database Expert.
- Expand the Project Folder and ADO.NET DataSets nodes and drag the DataSet you created into the Selected Tables box. The fields are now accessible from the Field Explorer.
- Drag and drop fields from the Field Explorer to the Details section or another section of your report.
Load Data into the Report
Having created the DataSet, which will only contain the metadata, you will now need to create the DataTable containing the actual data. You can use the ADLSDataAdapter to fill a DataTable with the results of an SQL query.
- Add a reference to System.Configuration.dll to your project to be able to use the connection string from App.config.
- In App.config, add the following code to the configuration node for compatibility with Crystal Reports when working with .NET 4.0:
<startup useLegacyV2RuntimeActivationPolicy="true"> <supportedRuntime version="v4.0" sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.0"/> </startup> Add the following references in your Window.xaml.cs file:
using System.Configuration; using CrystalDecisions.CrystalReports.Engine; using CrystalDecisions.Shared; using System.Data.CData.ADLS; using System.Data;
-
Add the following Window_Loaded method in your Window.xaml.cs to execute the SQL query that will return the DataTable. Note that your query needs to select at least the same columns used in your report.
private void Window_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { ReportDocument report = new ReportDocument(); report.Load("../../CrystalReport1.rpt"); var connectionString = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["MyAppConfigConnectionStringName"].ConnectionString; using (ADLSConnection connection = new ADLSConnection(connectionString)) { ADLSDataAdapter dataAdapter = new ADLSDataAdapter( "SELECT FullPath, Permission FROM Resources WHERE Type = 'FILE'", connection); DataSet set = new DataSet("_set"); DataTable table = set.Tables.Add("_table"); dataAdapter.Fill(table); report.SetDataSource(table); } reportViewer.ViewerCore.ReportSource = report; } In the Window.xaml file, add the Loaded event so that your Window tag resembles the following:
<Window x:Class="CrystalReportWpfApplication4.Window1" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:cr="clr-namespace:SAPBusinessObjects.WPF.Viewer;assembly=SAPBusinessObjects.WPF.Viewer" Title="WPF Crystal Report Viewer" Height="600" Width="800" Loaded="Window_Loaded"> ... </Window>- Run the report. When the report is loaded, the provider executes the query to retrieve the current data.
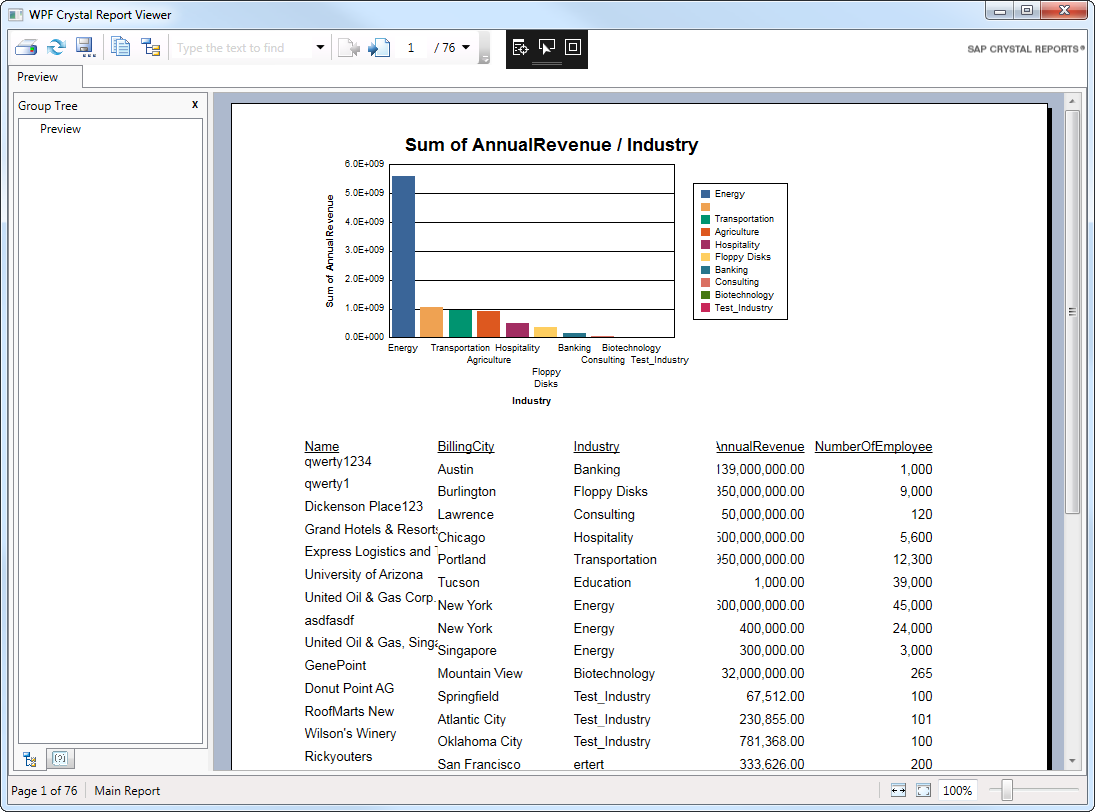
![A report that loads the current data when opened. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Chart Azure Data Lake Storage Data
You can also use the DataSet with experts like the Chart Expert:
- Right-click in the Crystal Reports Designer and click Insert -> Chart.
- Select the Report Header or Report Footer section. The Chart Expert is then displayed.
- On the Type tab, select the chart type. This article uses a side-by-side bar chart.
- On the Data tab, select the column and conditions for the x-axis. For example, drag the FullPath column in the DataSet node onto the box under the On Change Of menu.
- Select the x-axis column and click the TopN and Order buttons to configure sorting and limiting.
- Select the columns and summary operations for the y-axis. For example, drag the Permission column in the DataSet node into the Show Values box.
- Run the report.
Note that Crystal Reports performs the aggregation on the data already loaded into DataTable, instead of, for example, executing a GROUP BY to the Azure Data Lake Storage API. This will also be true for the report creation wizards.
You could gain more control over the queries executed to Azure Data Lake Storage by creating another DataSet and populating it with a different query. See the help documentation for more information on the driver's SQL engine.