Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Access Azure Data Lake Storage Data in PHP through Connect Server
Connect to Azure Data Lake Storage through the standard SQL Server libraries in PHP.
You can use CData Connect Server to access Azure Data Lake Storage data from SQL Server clients, without needing to perform an ETL or cache data. Follow the steps below to create a virtual SQL Server database for Azure Data Lake Storage and connect to Azure Data Lake Storage data in real time through PHP's standard SQL Server interface, i.e. sqlsrv_connect.
CData Connect Server provides a pure SQL Server interface for Azure Data Lake Storage, allowing you to easily build reports from live Azure Data Lake Storage data in PHP — without replicating the data to a natively supported database. As you build visualizations, PHP generates SQL queries to gather data. Using optimized data processing out of the box, CData Connect Server pushes all supported SQL operations (filters, JOINs, etc) directly to Azure Data Lake Storage, leveraging server-side processing to quickly return the requested Azure Data Lake Storage data.
Create a Virtual SQL Server Database for Azure Data Lake Storage Data
CData Connect Server uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to data sources and generate APIs.
-
Login to Connect Server and click Connections.
![Adding a connection]()
- Select "Azure Data Lake Storage" from Available Data Sources.
-
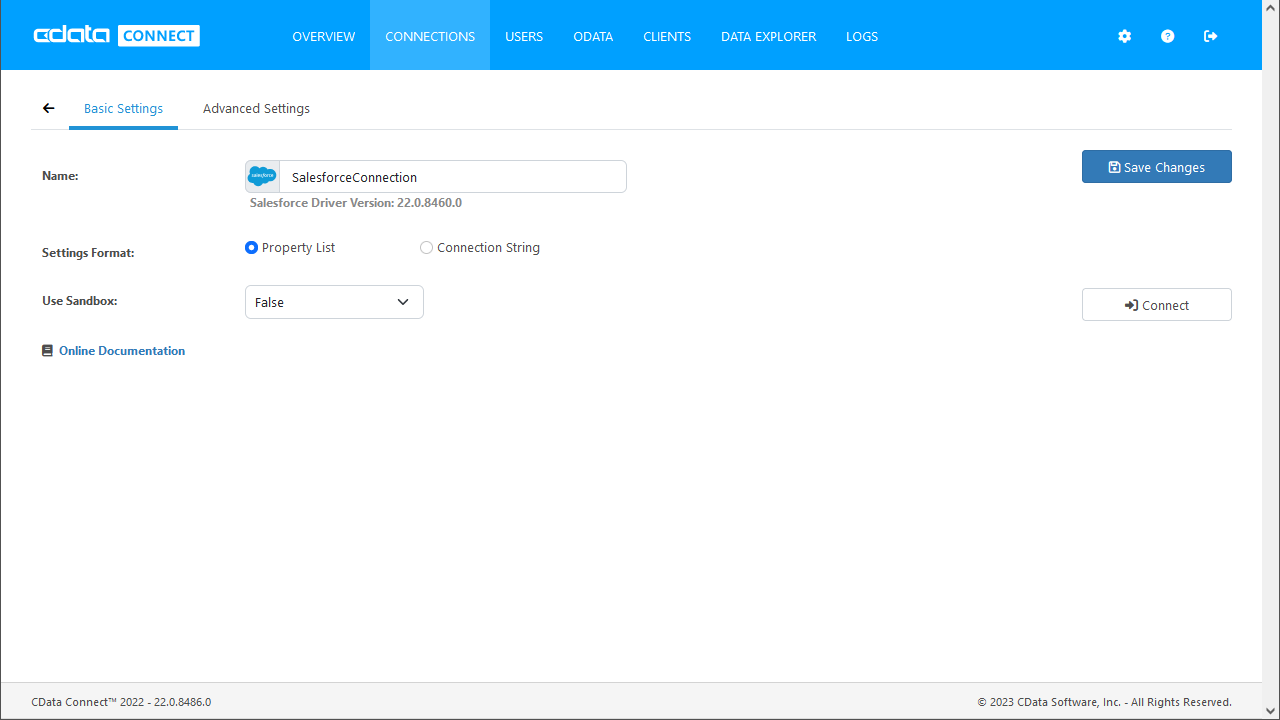
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Azure Data Lake Storage.
Authenticating to a Gen 1 DataLakeStore Account
Gen 1 uses OAuth 2.0 in Azure AD for authentication.
For this, an Active Directory web application is required. You can create one as follows:
To authenticate against a Gen 1 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen1.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- OAuthClientId: Set this to the application Id of the app you created.
- OAuthClientSecret: Set this to the key generated for the app you created.
- TenantId: Set this to the tenant Id. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
Authenticating to a Gen 2 DataLakeStore Account
To authenticate against a Gen 2 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen2.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- FileSystem: Set this to the file system which will be used for this account.
- AccessKey: Set this to the access key which will be used to authenticate the calls to the API. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
![Configuring a connection (SQL Server is shown).]()
- Click Save Changes
- Click Privileges -> Add and add the new user (or an existing user) with the appropriate permissions.
With the virtual database created, you are ready to connect to Azure Data Lake Storage data from PHP.
Connect in PHP
The following examples show how to use object-oriented interfaces to connect and execute queries. Initialize the connection object with the following parameters to connect to the virtual SQL Server database:
- Server name/Host: Specify the remote host location where the service is running.
- Username: Specify the username for a user you authorized in Connect Server.
- Password: Specify the password for the authorized user account.
- Database Name: Specify the name of the virtual database you created for Azure Data Lake Storage.
- Port: Specify the port the service is running on, port 1433 in this example.
sqlsrv_connect
<?php
$serverName = "connect_server_url, 1433"; //Connect Server Address, portNumber (default is 1433)
$connectionInfo = array( "Database"=>"ADLS1", "UID"=>"userName", "PWD"=>"password");
$conn = sqlsrv_connect( $serverName, $connectionInfo);
if( $conn ) {
echo "Connection established.<br>";
}else{
echo "Connection could not be established.<br>";
die( print_r( sqlsrv_errors(), true));
}
?>
PDO
<?php
<?php
$user = my_connect_user
$pass = my_connect_pass
$pdo = new PDO("sqlsrv:Server=connect_server_url,1433;Database=ADLS1", $user , $pass);
?>
Query in PHP
With the connection established, you can then access tables. The following steps walk through the example:
- Query the table; for example, Resources. The results will be stored as an associative array in the $result object.
- Iterate over each row and column, printing the values to display in the PHP page.
- Close the connection.
sqlsrv_connect
$result = $sqlsrv_connect->query("SELECT FullPath, Permission FROM Resources WHERE Type = 'FILE'");
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
foreach ($row as $k=>$v) {
echo "$k : $v";
echo "<br>";
}
}
$sqlsrv_connect->close();
PDO
$result = $pdo->query("SELECT FullPath, Permission FROM Resources WHERE Type = 'FILE'");
while($row = $result->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)) {
foreach ($row as $k=>$v) {
echo "$k : $v";
echo "<br>";
}
}
$result = null;
$pdo = null;
SQL Server Access to Azure Data Lake Storage Data using PHP
You have retrieved live Azure Data Lake Storage Data using PHP. Now, you can easily access data sources and more — all without replicating Azure Data Lake Storage data.
To get SQL data access to 200+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your applications, try CData Connect Server.