Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to connect to EnterpriseDB Data from IntelliJ
Integrate connectivity to EnterpriseDB data with wizards in IntelliJ.
The CData JDBC Driver for EnterpriseDB enables you to access EnterpriseDB as a JDBC data source, providing integration with rapid development tools in IDEs. This article shows how to use the data source configuration wizard to connect to EnterpriseDB data in IntelliJ.
Create a JBDC Data Source for EnterpriseDB
Follow the steps below to add the driver JAR and define connection properties required to connect to EnterpriseDB data.
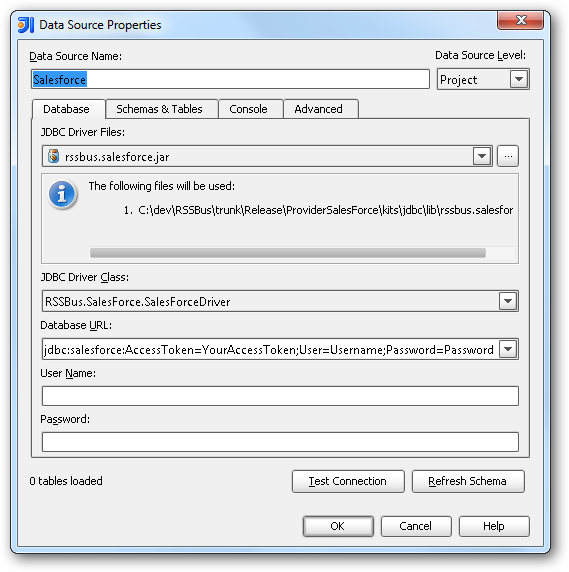
- In the Data Sources window, right-click and then click Add Data Source -> DB Data Source.
In the Data Source Properties dialog that appears, the following properties are required:
- JDBC Driver Files: Click the button next to this menu to add the JDBC Driver file cdata.jdbc.enterprisedb.jar, located in the installation directory.
- JDBC Driver Class: In this menu, select cdata.jdbc.enterprisedb.EnterpriseDBDriver from the list.
Database URL: Enter the connection URL in the JDBC URL property. The URL must start with jdbc:enterprisedb: and includes connection properties separated with semicolons.
The following connection properties are required in order to connect to data.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the EnterpriseDB database.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the EnterpriseDB database.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The default database to connect to when connecting to the EnterpriseDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
Connect Using Standard Authentication
To authenticate using standard authentication, set the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the EnterpriseDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the EnterpriseDB server.
Connect Using SSL Authentication
You can leverage SSL authentication to connect to EnterpriseDB data via a secure session. Configure the following connection properties to connect to data:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate. Used in the case of 2-way SSL, where truststore and keystore are kept on both the client and server machines.
- SSLClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSLClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSLClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSLServerCert: The certificate to be accepted from the server.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the EnterpriseDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.enterprisedb.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical JDBC URL is the following:
jdbc:enterprisedb:User=postgres;Password=admin;Database=postgres;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5444
Edit and Save EnterpriseDB Data
To discover schema information, right-click the data source you just created and click Refresh Tables. To query a table, right-click it and then click Open Tables Editor. You can also modify records in the Table Editor.