Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Integrate with JSON Services in JReport Designer
Create charts and reports based on JSON services in JReport Designer.
The CData JDBC Driver for JSON services enables access to live data from dashboards and reports as if JSON were a relational database, allowing you to query JSON services using familiar SQL queries. This article shows how to connect to JSON services as a JDBC data source and create reports based on JSON services in JReport Designer.
Connect to JSON Services
- Edit C:\JReport\Designer\bin\setenv.bat to add the location of the JAR file to the ADDCLASSPATH variable:
... set ADDCLASSPATH=%JAVAHOME%\lib\tools.jar;C:\Program Files\CData\CData JDBC Driver for JSON 2016\lib\cdata.jdbc.json.jar; ...
- Create a new data source by clicking File New Data Source.
- In the resulting dialog, create a name for the data source (CData JDBC Driver for JSON), select JDBC, and click OK.
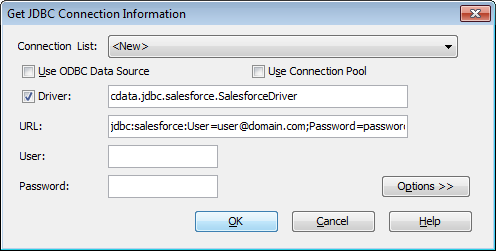
- In the Get JDBC Connection Information dialog you will configure your connection to the JDBC driver:
- Driver: Be sure that the Driver box is checked and fill in the name of the class for the driver:
cdata.jdbc.json.JSONDriver - URL: Enter the JDBC URL. This starts with jdbc:json: and is followed by a semicolon-separated list of connection properties.
See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation to authenticate to your data source: The data provider models JSON APIs as bidirectional database tables and JSON files as read-only views (local files, files stored on popular cloud services, and FTP servers). The major authentication schemes are supported, including HTTP Basic, Digest, NTLM, OAuth, and FTP. See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation for authentication guides.
After setting the URI and providing any authentication values, set DataModel to more closely match the data representation to the structure of your data.
The DataModel property is the controlling property over how your data is represented into tables and toggles the following basic configurations.
- Document (default): Model a top-level, document view of your JSON data. The data provider returns nested elements as aggregates of data.
- FlattenedDocuments: Implicitly join nested documents and their parents into a single table.
- Relational: Return individual, related tables from hierarchical data. The tables contain a primary key and a foreign key that links to the parent document.
See the Modeling JSON Data chapter for more information on configuring the relational representation. You will also find the sample data used in the following examples. The data includes entries for people, the cars they own, and various maintenance services performed on those cars.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the JSON JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.json.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Below is a typical JDBC URL:
jdbc:json:URI=C:/people.json;DataModel=Relational; - User: The username to authenticate with; typically left blank.
- Password: The password to authenticate with; typically left blank.
![Configuring the connection to the JDBC Driver (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Driver: Be sure that the Driver box is checked and fill in the name of the class for the driver:
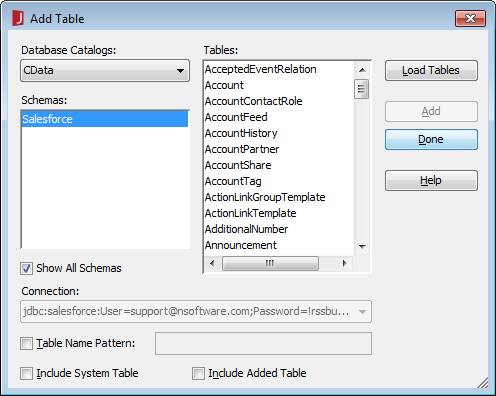
In the Add Table dialog, select the tables you wish to include in your report (or in future reports using this data source) and click Add.
![Adding Tables. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Click Done once the dialog has completed loading the tables.
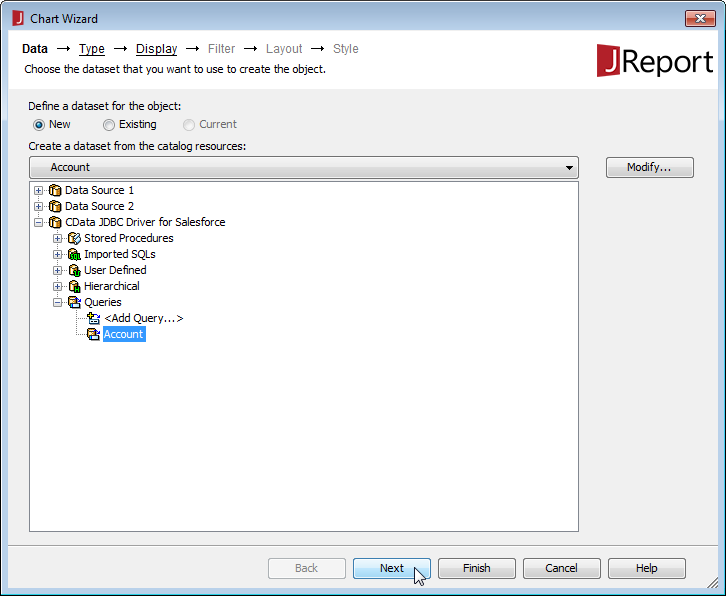
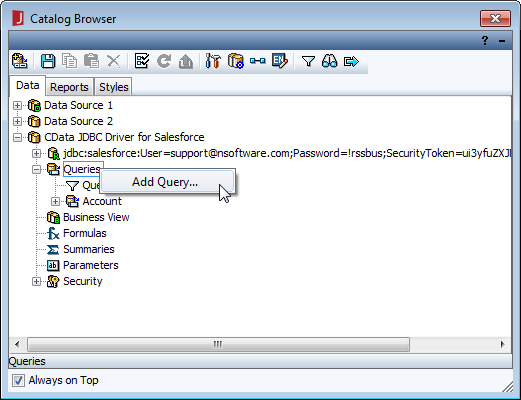
- In the Catalog Browser, you can create the queries that you will use to populate your reports. You can do this now, or after you create your report. In either case, expand () the data source (CData JDBC Driver for JSON), right-click on Queries, and select Add Query.
![Adding a query for data to be used in the report. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
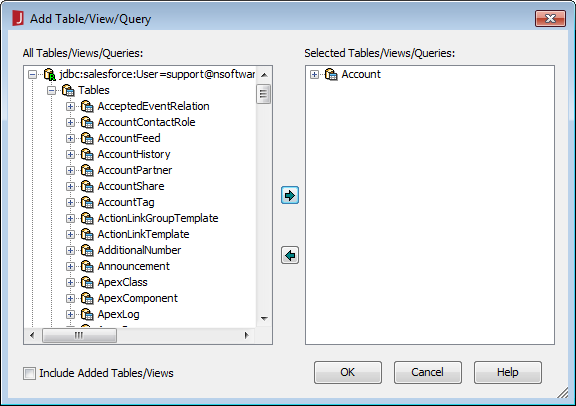
- In the Add Table/View/Query dialog, expand () the JDBC URL and Tables and select the table(s) you wish to use in the query and click OK.
![Selecting a table for the query. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
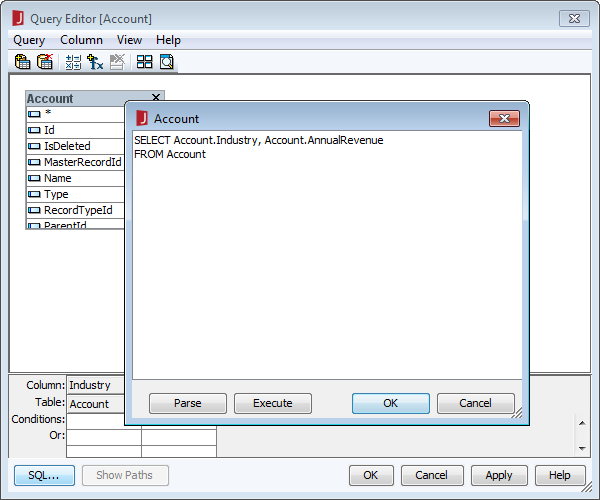
- In the Query Editor dialog, you can select the columns you wish to include or simply click the SQL button and manually input your own query. For example:
SELECT [people].[personal.age] AS age, [people].[personal.gender] AS gender, [people].[personal.name.first] AS first_name, [people].[personal.name.last] AS last_name, [vehicles].[model], FROM [people] JOIN [vehicles] ON [people].[_id] = [vehicles].[people_id]
![Editing the query. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
With the query built, click OK to close the Query Editor dialog. At this point you are ready to add JSON services to a new or existing report.
NOTE: Now that the query is built, you can create a Business View based on the query. With a Business View, you can create Web reports or library components based on the query. For more information on this, refer to the JReport tutorials.
Add JSON Services to a Report
You are now ready to create a report with JSON services.
- Create a new report (File New Page Report) or open the Chart Wizard for an existing report.
- Select the Query (or create a new one; see above).
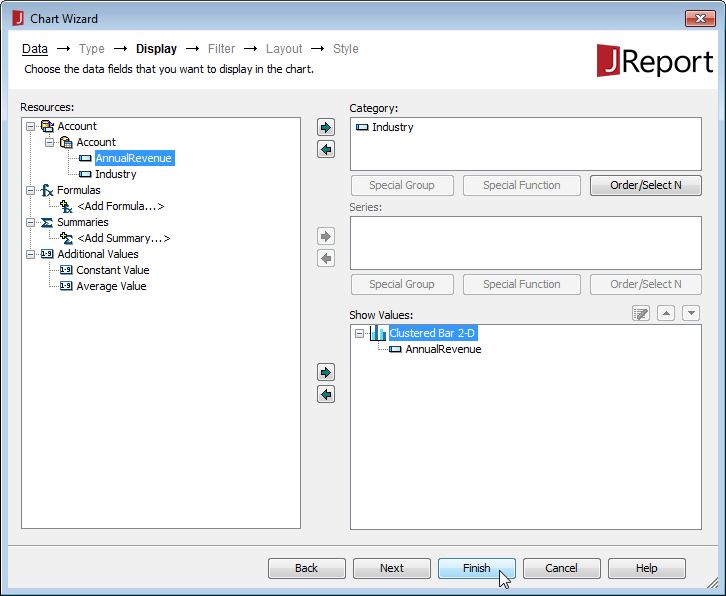
- Assign a Category and Value for the chart from the columns in your Query and click Finish.
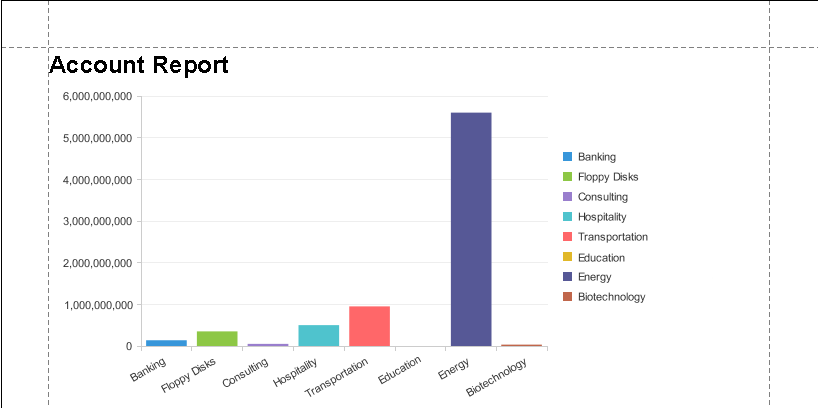
- Click the View tab for your report to see the chart.