Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Automated Continuous SQL Server Replication to MongoDB
Use CData Sync for automated, continuous, customizable SQL Server replication to MongoDB.
Always-on applications rely on automatic failover capabilities and real-time data access. CData Sync integrates live SQL Server data into your MongoDB instance, allowing you to consolidate all of your data into a single location for archiving, reporting, analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence and more.
Configure MongoDB as a Replication Destination
Using CData Sync, you can replicate SQL Server data to MongoDB. To add a replication destination, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click Add Connection.
- Select MongoDB as a destination.
![Configure a Destination connection to MongoDB.]()
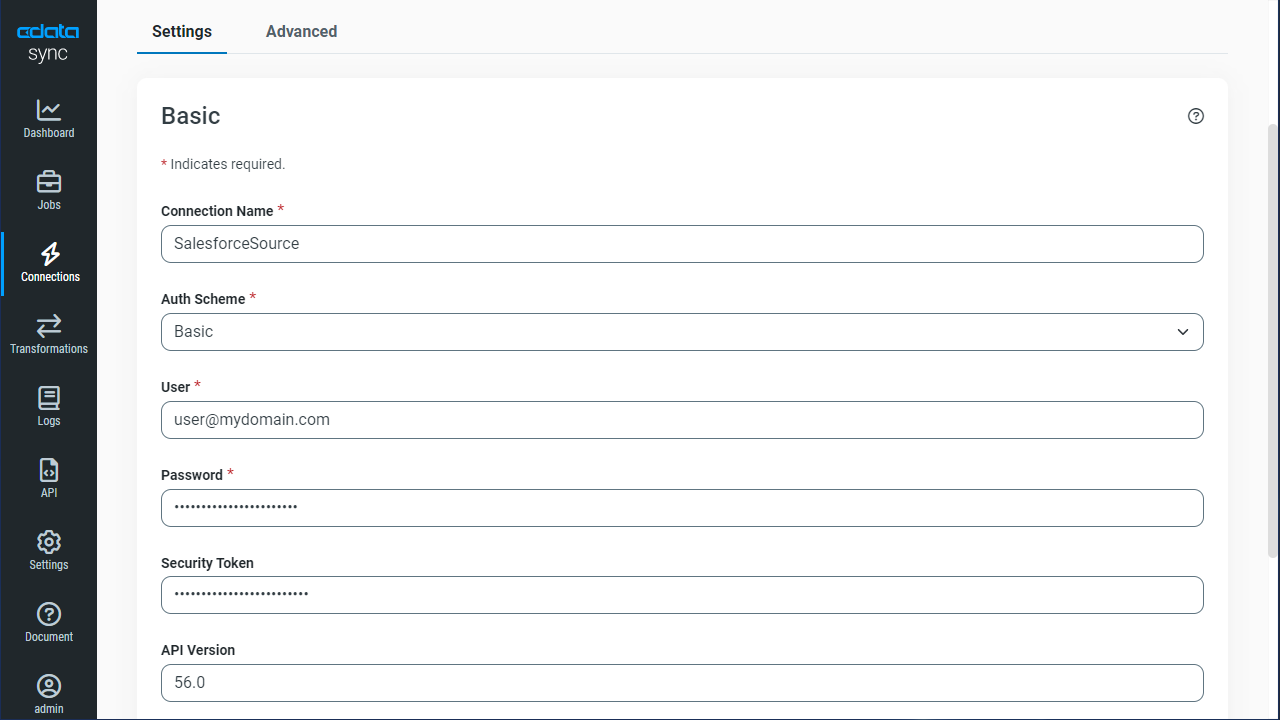
- Enter the necessary connection properties. To connect to MongoDB, set the following:
- Server: Set this to the name or address of the server where your MongoDB instance is running. You can specify the port here or in Port.
- Database: Set this to the database you want to read from and write to.
Connecting to CosmosDB with the MongoDB API
To obtain the connection string needed to connect to a Cosmos DB account using the MongoDB API, log in to the Azure Portal, select Azure Cosmos DB, and select your account. In the Settings section, click Connection String and set the following values.
- Server: Set this to the Host value, the FQDN of the server provisioned for your account. You can also specify the port here or in Port.
- Port: Set this to the port.
- Database: Set this to the database you want to read from and write to.
- User: Set this to the database user.
- Password: Set this to the user's password.
- Click Test Connection to ensure that the connection is configured properly.
![Configure a Destination connection.]()
- Click Save Changes.
Configure the SQL Server Connection
You can configure a connection to SQL Server from the Connections tab. To add a connection to your SQL Server account, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click Add Connection.
- Select a source (SQL Server).
- Configure the connection properties.
Connecting to Microsoft SQL Server
Connect to Microsoft SQL Server using the following properties:
- Server: The name of the server running SQL Server.
- User: The username provided for authentication with SQL Server.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the SQL Server database.
Connecting to Azure SQL Server and Azure Data Warehouse
You can authenticate to Azure SQL Server or Azure Data Warehouse by setting the following connection properties:
- Server: The server running Azure. You can find this by logging into the Azure portal and navigating to "SQL databases" (or "SQL data warehouses") -> "Select your database" -> "Overview" -> "Server name."
- User: The name of the user authenticating to Azure.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the database, as seen in the Azure portal on the SQL databases (or SQL warehouses) page.
![Configure a Source connection (Salesforce is shown).]()
- Click Connect to ensure that the connection is configured properly.
- Click Save Changes.
Configure Replication Queries
CData Sync enables you to control replication with a point-and-click interface and with SQL queries. For each replication you wish to configure, navigate to the Jobs tab and click Add Job. Select the Source and Destination for your replication.
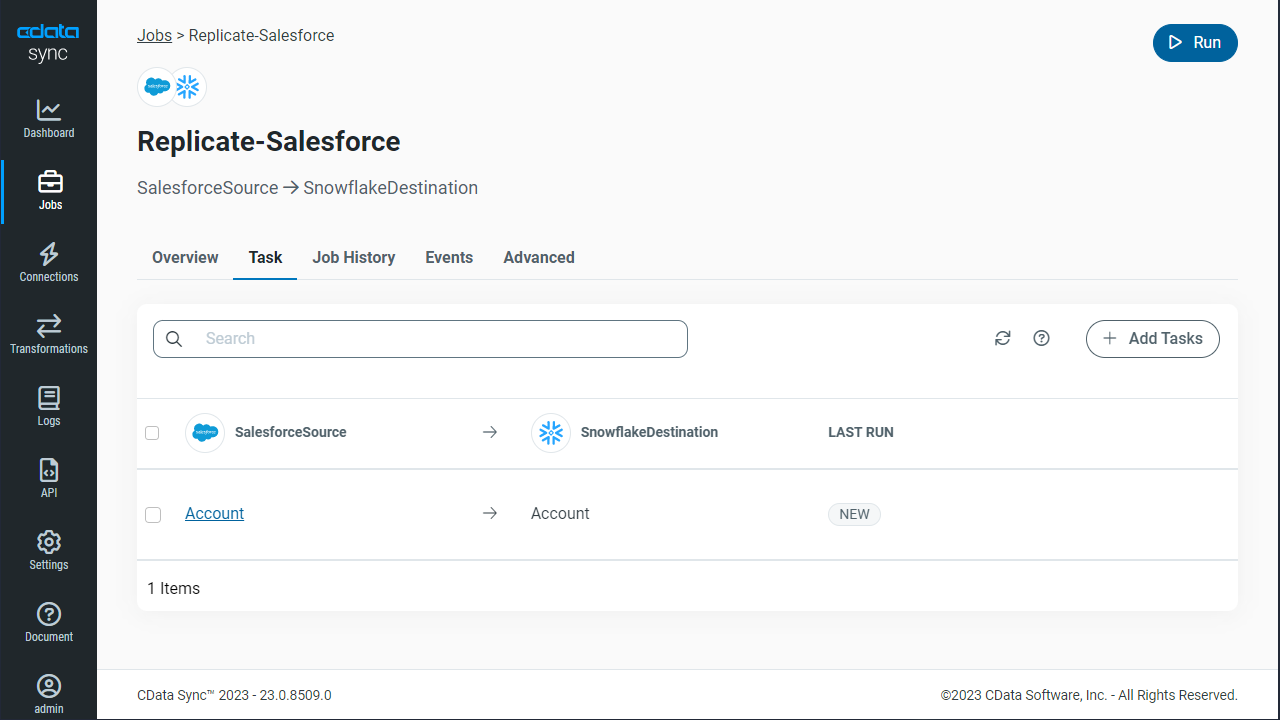
Replicate Entire Tables
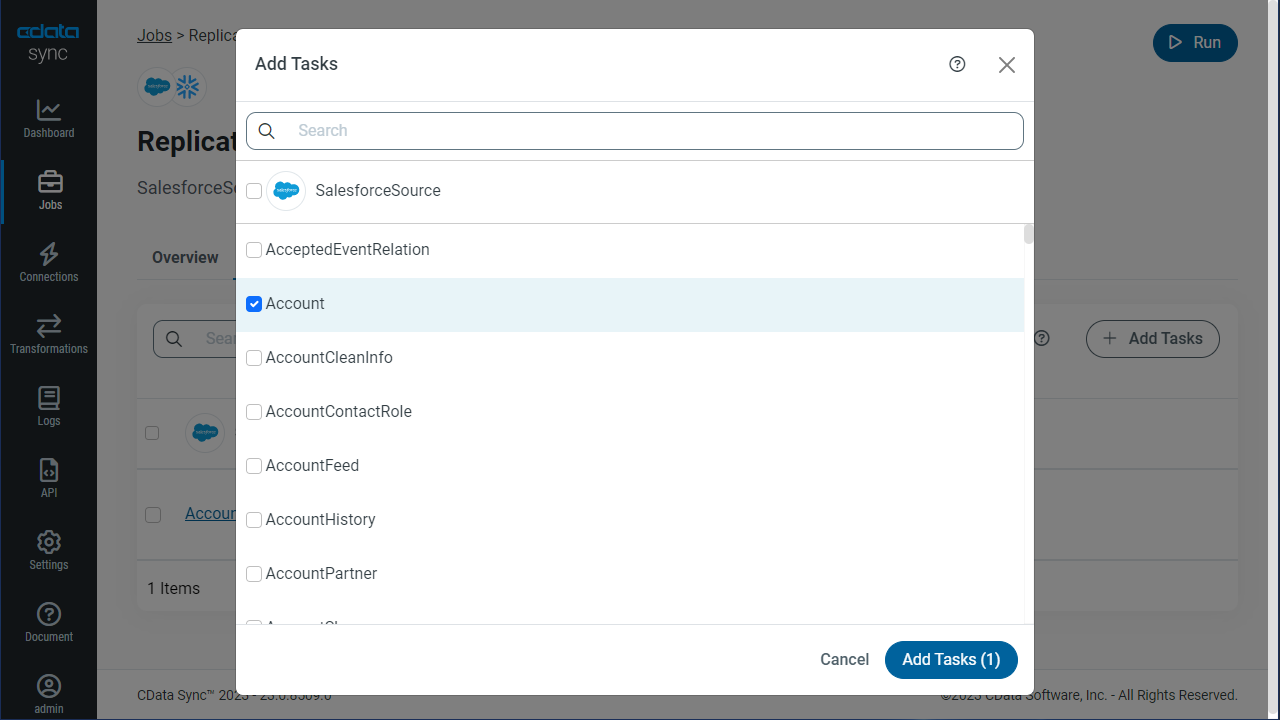
To replicate an entire table, click Add Tables in the Tables section, choose the table(s) you wish to replicate, and click Add Selected Tables.
Customize Your Replication
You can use the Columns and Query tabs of a task to customize your replication. The Columns tab allows you to specify which columns to replicate, rename the columns at the destination, and even perform operations on the source data before replicating. The Query tab allows you to add filters, grouping, and sorting to the replication.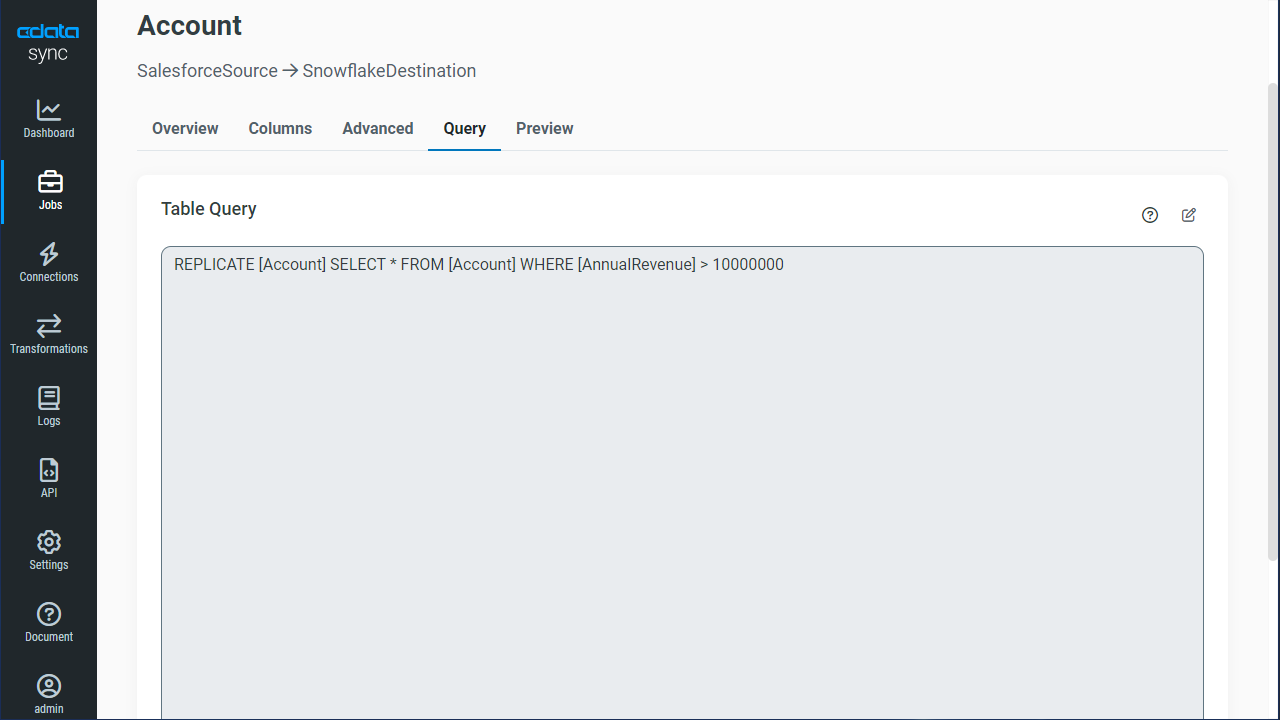
Schedule Your Replication
In the Schedule section, you can schedule a job to run automatically, configuring the job to run after specified intervals ranging from once every 10 minutes to once every month.
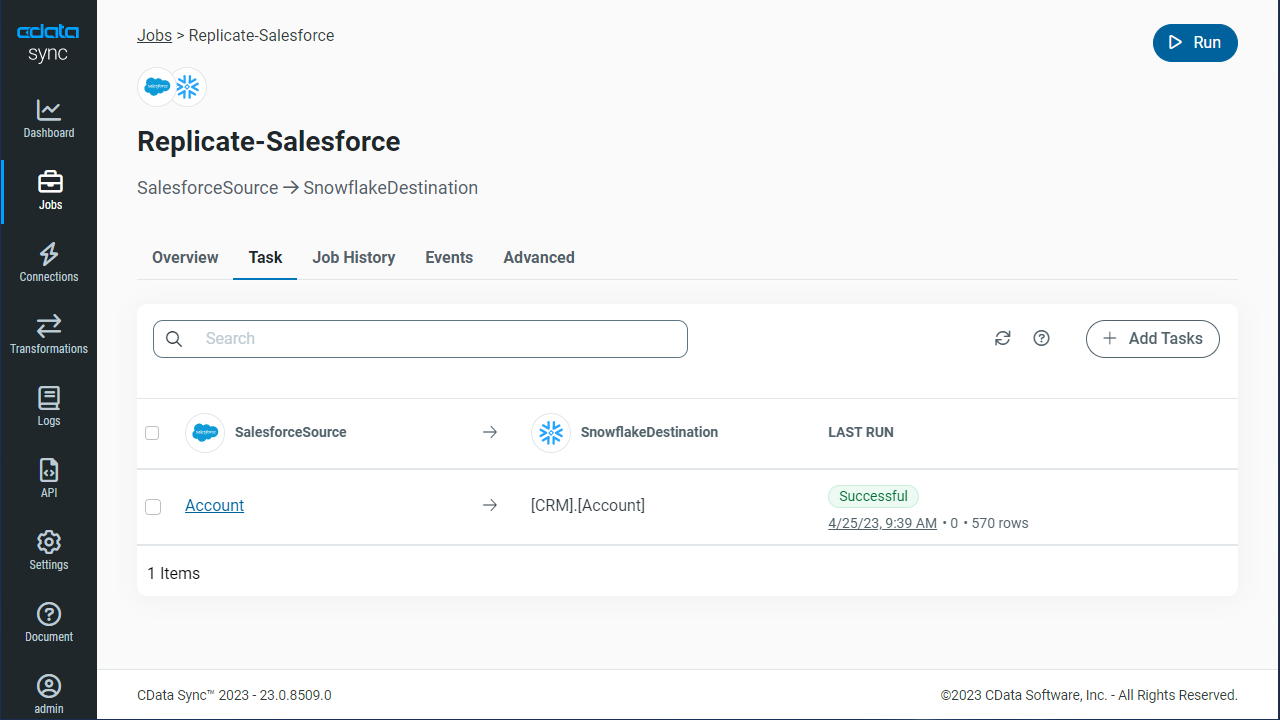
Once you have configured the replication job, click Save Changes. You can configure any number of jobs to manage the replication of your SQL Server data to MongoDB.