Developer Guide - Build AI-Powered Data Assistants with OpenAI Python SDK
Build intelligent data assistants that can query your live data sources using natural language. This guide walks you through creating a Python application that combines OpenAI's GPT models with CData Connect AI to enable conversational access to your data.
NOTE: While this guide uses Google Sheets as the data source, the same principles apply to any of the 350+ data sources CData Connect AI supports.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a working Python application that can:
- Connect to any of 350+ data sources through CData Connect AI
- Discover available databases, schemas, and tables automatically
- Execute SQL queries using natural language
- Maintain multi-turn conversations with context
- Stream responses in real-time
Architecture Overview
The application uses the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to bridge OpenAI's GPT models with your data sources:
┌─────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ Your Python │---->│ CData Connect │---->│ Data Sources │
│ Application │ │ AI MCP Server │ │ (300+ types) │
│ │<----│ │<----│ │
└─────────────────┘ └──────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
| |
| Tool Discovery |
| & Execution |
v |
┌─────────────────┐ |
│ │ |
│ OpenAI API │--------------┘
│ (GPT-4, etc.) │ Natural Language
│ │ to SQL Translation
└─────────────────┘
How it works:
- Your Python application connects to CData Connect AI's MCP server
- The MCP server exposes tools for data discovery and querying
- OpenAI's GPT models use these tools to translate natural language into SQL
- Queries are executed against your live data sources
- Results are returned and interpreted by the AI
Prerequisites
This guide requires the following:
- Python 3.9+ installed on your system
- An OpenAI API key (requires a paid account)
- A CData Connect AI account (free trial available)
- A Google account for the sample Google Sheets data
Getting Started
Overview
Here's a quick overview of the steps:
- Set up sample data in Google Sheets
- Configure CData Connect AI and create a Personal Access Token
- Set up the Python project and install dependencies
- Build and run the chat application
STEP 1: Set Up Sample Data in Google Sheets
We'll use a sample Google Sheet containing customer data to demonstrate the capabilities. This dataset includes accounts, sales opportunities, support tickets, and usage metrics.
- Navigate to the sample customer health spreadsheet
- Click File > Make a copy to save it to your Google Drive
- Give it a memorable name (e.g., "demo_organization") - you'll need this later
The spreadsheet contains four sheets:
- account: Company information (name, industry, revenue, employees)
- opportunity: Sales pipeline data (stage, amount, probability)
- tickets: Support tickets (priority, status, description)
- usage: Product usage metrics (job runs, records processed)
STEP 2: Configure CData Connect AI
2.1 Sign Up or Log In
- Navigate to https://www.cdata.com/ai/signup/ to create a new account, or https://cloud.cdata.com/ to log in
- Complete the registration process if creating a new account
2.2 Add a Google Sheets Connection
-
Once logged in, click Sources in the left navigation menu and click Add Connection
-
Select Google Sheets from the Add Connection panel
-
Configure the connection:
- Set the Spreadsheet property to the name of your copied sheet (e.g., "demo_organization")
- Click Sign in to authenticate with Google OAuth
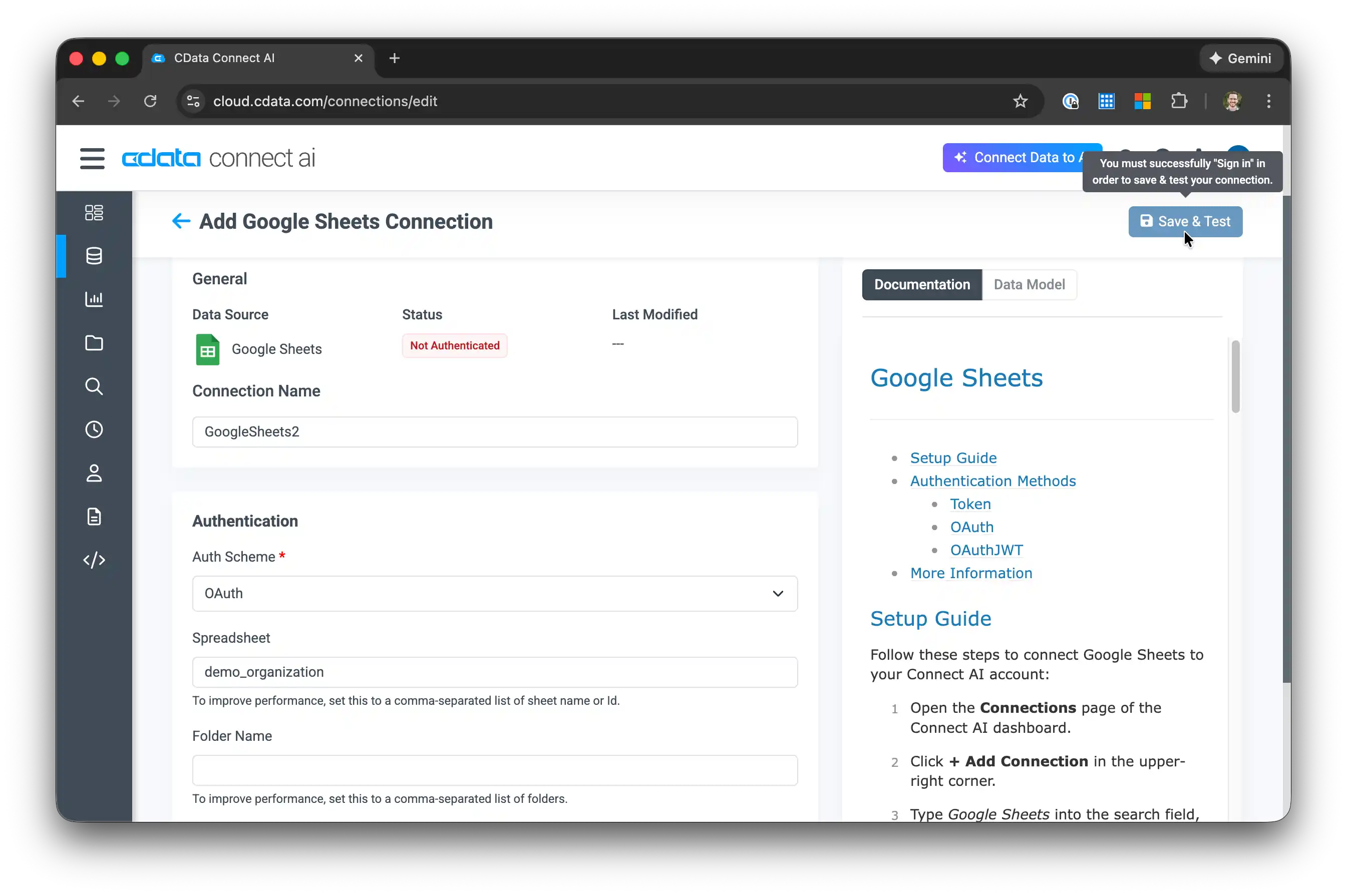
-
After authentication, navigate to the Permissions tab and verify your user has access
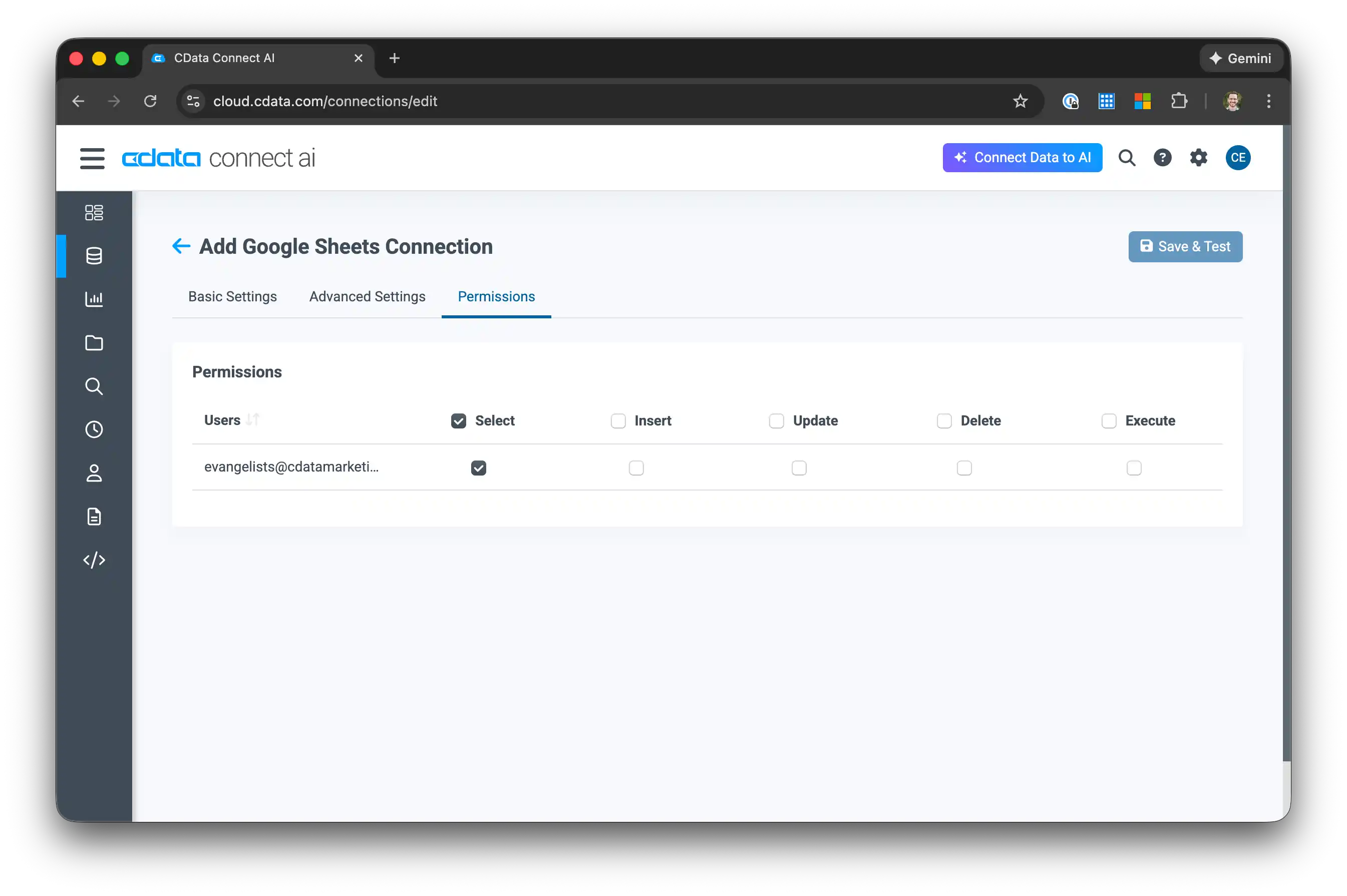
2.3 Create a Personal Access Token
Your Python application will use a Personal Access Token (PAT) to authenticate with Connect AI.
- Click the Gear icon in the top right to open Settings
- Go to the Access Tokens section
- Click Create PAT
-
Give the token a name (e.g., "OpenAI Python App") and click Create
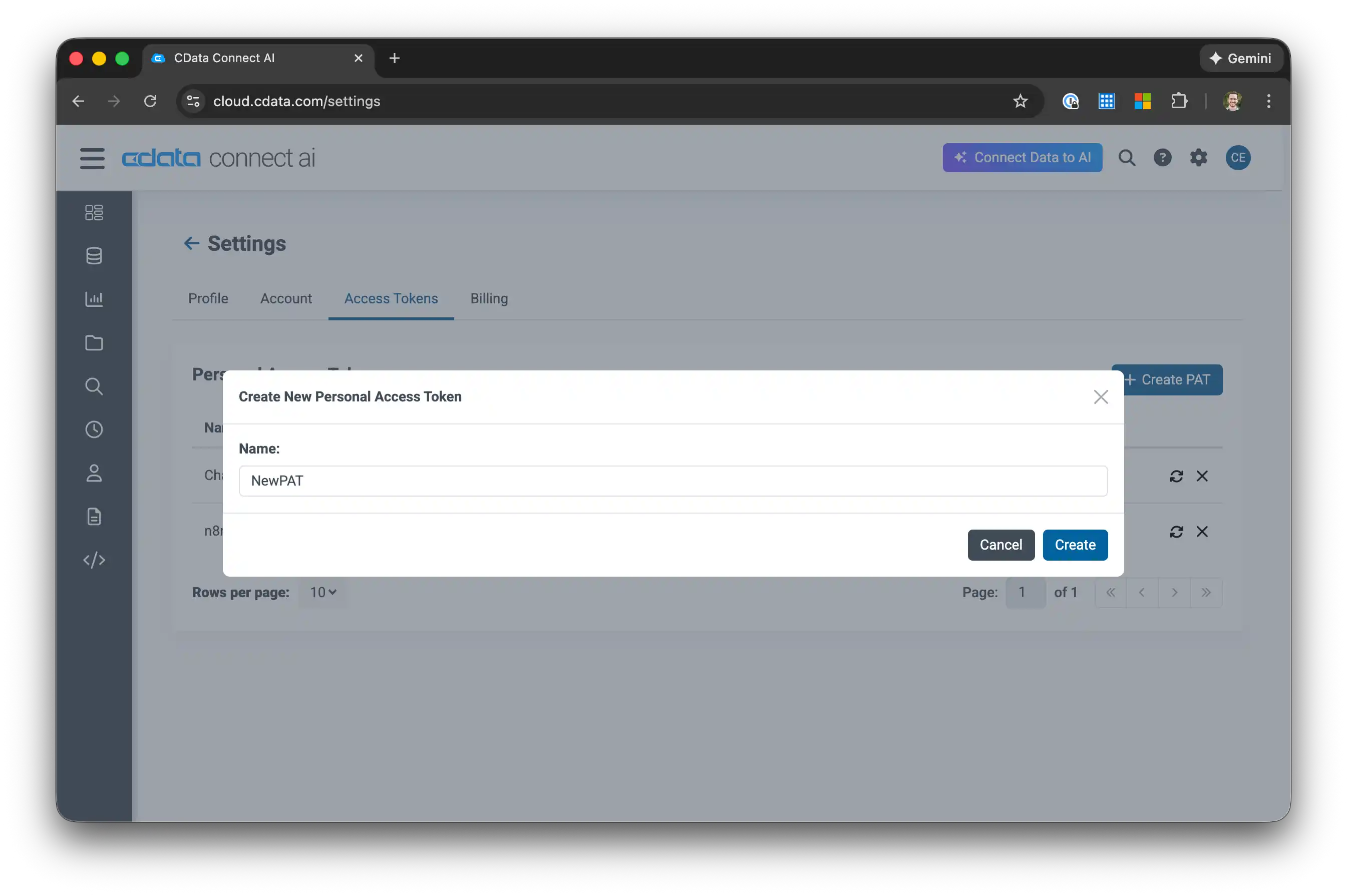
- Important: Copy the token immediately - it's only shown once!
STEP 3: Set Up the Python Project
3.1 Clone from GitHub (Recommended)
Clone the complete project with all examples:
git clone https://github.com/CDataSoftware/connectai-openai-agent.git
cd connectai-openai-agent
pip install -r requirements.txt
3.2 Alternative: Create from Scratch
Create a new project directory and install dependencies:
mkdir connectai-openai-agent
cd connectai-openai-agent
pip install openai httpx python-dotenv
3.3 Configure Environment Variables
Create a .env file in your project root:
# OpenAI Configuration
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-your-openai-api-key-here
OPENAI_MODEL=gpt-4o
# CData Connect AI Configuration
[email protected]
CDATA_PAT=your-personal-access-token-here
MCP_SERVER_URL=https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp
Replace the placeholder values with your actual credentials.
STEP 4: Understanding the Code Architecture
The project consists of three main components:
4.1 Config Class
Handles configuration and credential management:
from dataclasses import dataclass
import os
import base64
@dataclass
class Config:
"""Configuration for the Connect AI OpenAI Agent."""
openai_api_key: str
cdata_email: str
cdata_pat: str
openai_model: str = "gpt-4o"
mcp_server_url: str = "https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp"
@classmethod
def from_env(cls) -> "Config":
"""Create configuration from environment variables."""
return cls(
openai_api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
cdata_email=os.getenv("CDATA_EMAIL"),
cdata_pat=os.getenv("CDATA_PAT"),
openai_model=os.getenv("OPENAI_MODEL", "gpt-4o"),
mcp_server_url=os.getenv("MCP_SERVER_URL", "https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp"),
)
def get_auth_header(self) -> str:
"""Generate Base64 authentication header."""
credentials = f"{self.cdata_email}:{self.cdata_pat}"
return base64.b64encode(credentials.encode()).decode()
4.2 MCPClient Class
Handles HTTP communication with the CData Connect AI MCP server:
import json
import sys
import httpx
class MCPClient:
"""HTTP client for CData Connect AI MCP server."""
def __init__(self, config: Config):
self.config = config
self._client = httpx.Client(
headers={
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Accept": "application/json, text/event-stream",
"Authorization": f"Basic {config.get_auth_header()}",
"User-Agent": f"CDataConnectAI-OpenAIAgent (Python/{sys.version_info.major}.{sys.version_info.minor})",
},
timeout=60.0,
)
def _parse_sse_response(self, response_text: str) -> dict:
"""Parse Server-Sent Events response."""
for line in response_text.split("
"):
if line.startswith("data: "):
return json.loads(line[6:])
raise ValueError("No data found in SSE response")
def list_tools(self) -> list:
"""Discover available tools from the MCP server."""
response = self._client.post(
self.config.mcp_server_url,
json={"jsonrpc": "2.0", "method": "tools/list", "params": {}, "id": 1},
)
result = self._parse_sse_response(response.text)
return result.get("result", {}).get("tools", [])
def call_tool(self, tool_name: str, arguments: dict) -> dict:
"""Execute a tool on the MCP server."""
response = self._client.post(
self.config.mcp_server_url,
json={
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {"name": tool_name, "arguments": arguments},
"id": 2,
},
)
result = self._parse_sse_response(response.text)
return result.get("result", \{})
4.3 MCPAgent Class
The AI agent that combines OpenAI with MCP tools:
from openai import OpenAI
class MCPAgent:
"""AI Agent using OpenAI with CData Connect AI MCP tools."""
def __init__(self, config: Config):
self.config = config
self.mcp_client = MCPClient(config)
self.openai_client = OpenAI(api_key=config.openai_api_key)
self.conversation_history = []
self._tools_cache = []
def _get_openai_tools(self) -> list:
"""Convert MCP tools to OpenAI function format."""
if not self._tools_cache:
mcp_tools = self.mcp_client.list_tools()
for tool in mcp_tools:
self._tools_cache.append({
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": tool.get("name"),
"description": tool.get("description", ""),
"parameters": tool.get("inputSchema", {}),
},
})
return self._tools_cache
def chat(self, message: str) -> str:
"""Send a message and get a response."""
self.conversation_history.append({"role": "user", "content": message})
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a data assistant..."},
*self.conversation_history,
]
tools = self._get_openai_tools()
# Process until we get a final response
for _ in range(10):
response = self.openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model=self.config.openai_model,
messages=messages,
tools=tools if tools else None,
)
assistant_message = response.choices[0].message
if assistant_message.tool_calls:
messages.append(assistant_message.model_dump())
for tool_call in assistant_message.tool_calls:
result = self.mcp_client.call_tool(
tool_call.function.name,
json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
)
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": json.dumps(result),
})
else:
content = assistant_message.content or ""
self.conversation_history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": content})
return content
return "Max iterations reached."
STEP 5: Build the Chat Application
Create an interactive chat application:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""Interactive chat application for querying data with AI."""
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from src.connectai_openai import Config, MCPAgent
load_dotenv()
def main():
print("=" * 60)
print("CData Connect AI - OpenAI Chat Assistant")
print("=" * 60)
# Initialize
config = Config.from_env()
agent = MCPAgent(config)
tools = agent._get_openai_tools()
print(f"
Connected! {len(tools)} tools available.")
print("
Chat with your data! Type 'quit' to exit.
")
while True:
user_input = input("You: ").strip()
if user_input.lower() in ("quit", "exit"):
print("Goodbye!")
break
response = agent.chat(user_input)
print(f"
Assistant: {response}
")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
STEP 6: Run Your Application
With everything configured, run your chat application:
python examples/basic_chat.py
You should see output like:
============================================================ CData Connect AI - OpenAI Chat Assistant ============================================================ Connected! 8 tools available. Chat with your data! Type 'quit' to exit. You: What data sources do I have? Assistant: You have the following data sources connected: 1. **demo_organization** (Google Sheets) - Tables: account, opportunity, tickets, usage Would you like me to explore any of these in more detail?
STEP 7: Example Queries
Here are some example prompts to try with your data assistant:
Data Discovery
- "What data sources do I have connected?"
- "Show me all the tables in demo_organization"
- "What columns are in the account table?"
Basic Queries
- "Query the top 5 accounts by annual_revenue"
- "How many support tickets are there by priority?"
- "Show me all open opportunities"
Analysis
- "Which accounts have the most critical support tickets?"
- "Summarize the health of Aurora Healthcare Systems"
- "Find accounts with high revenue but low product usage"
STEP 8: Available MCP Tools
Your AI agent has access to these CData Connect AI tools:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| getCatalogs | List available data source connections |
| getSchemas | Get schemas for a specific catalog |
| getTables | Get tables in a schema |
| getColumns | Get column metadata for a table |
| queryData | Execute SQL queries |
| getProcedures | List stored procedures |
| getProcedureParameters | Get procedure parameter details |
| executeProcedure | Execute stored procedures |
STEP 9: SQL Query Format
When the AI generates SQL queries, it uses fully qualified table names:
SELECT [column1], [column2]
FROM [CatalogName].[SchemaName].[TableName]
WHERE [column1] = 'value'
ORDER BY [column2]
LIMIT 100
For example, to query the account table from your Google Sheets:
SELECT [name], [annual_revenue], [industry]
FROM [demo_organization].[GoogleSheets].[account]
ORDER BY [annual_revenue] DESC
LIMIT 10
Troubleshooting
Authentication Errors
- Verify your CData email and PAT are correct in .env
- Ensure the PAT has not expired
- Check that your Connect AI account is active
No Tools Available
- Confirm you have at least one data source connected in Connect AI
- Check that your user has permissions to access the connection
Query Errors
- Use fully qualified table names: [Catalog].[Schema].[Table]
- Verify column names exist using the getColumns tool
- Check SQL syntax (Connect AI uses SQL-92 standard)
What's Next?
Now that you have a working AI data assistant, you can:
- Connect more data sources: Add Salesforce, Snowflake, or any of 350+ supported sources to expand your data access.
- Customize the agent: Modify the system instructions for your specific use case and domain.
- Build production applications: Integrate the agent into web apps, Slack bots, or other interfaces.
- Add streaming: Use chat_stream() for real-time response streaming.
- Explore the examples: Check out the additional examples in the GitHub repository for data analysis workflows, multi-source queries, and more.
Resources
- GitHub Repository - Complete source code and examples
- CData Connect AI Documentation
- CData Prompt Library - Example prompts for various use cases
- OpenAI API Documentation
- Model Context Protocol
Get Started with CData Connect AI
Ready to build AI-powered data applications? CData Connect AI provides live data access to 350+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your AI applications.
Sign up for a free trial and start building intelligent data assistants today!





