The JSON ADO.NET Data Provider enables user to easily connect to JSON services from .NET applications. Rapidly create and deploy powerful .NET applications that integrate with JSON web services.

JSON .NET Connectivity Features
- SQL-92 access to JSON files and JSON Web Services
- Intelligent schema discovery with relational modeling and document flattening
- Connect to live JSON data, for real-time data access with the JSON ODBC Driver
- Full support for data aggregation and complex JOINs in SQL queries
- Secure connectivity through modern cryptography, including TLS 1.2, SHA-256, ECC, etc.
- Generate table schema automatically based on existing JSON data or manually for greater control of the content you need
- Seamless integration with leading BI, reporting, and ETL tools and with custom applications via the JSON Connector.
Target Service, API
The driver provides SQL access to JSON files and JSON APIs. Supports local files, URLs, and REST endpoints returning JSON.
Schema, Data Model
Flexible schema detection from JSON structure. Supports nested objects and arrays with configurable flattening strategies.
Key Objects
JSON documents exposed as tables. Complex JSON structures can be modeled as multiple related tables. Supports JSON Path expressions.
Operations
Read and write operations on JSON data. SQL queries with filtering and projections. Supports both file-based and API-based JSON sources.
Authentication
For APIs: supports various authentication methods. For files: file system permissions. Configurable headers and parameters.
Start a 30-day Free Trial Today
See what you can do with JSON ADO.NET provider
Use JSON from SQL Server Analysis Service (SSAS) multi-dimensional cubes. Keep your analytical data modeling and access to any source including cloud and on-premises.

The JSON ADO.NET Provider allows developers to build applications that connect to JSON using familiar SQL and Entity Framework. Integrate JSON to your mission -critical applications or create easy side-by-side applications.

You can connect from ADO.NET compliant low-code development tools:
You can connect JSON from .NET-based reporting and analytics tools:
Standard ADO.NET Access to JSON
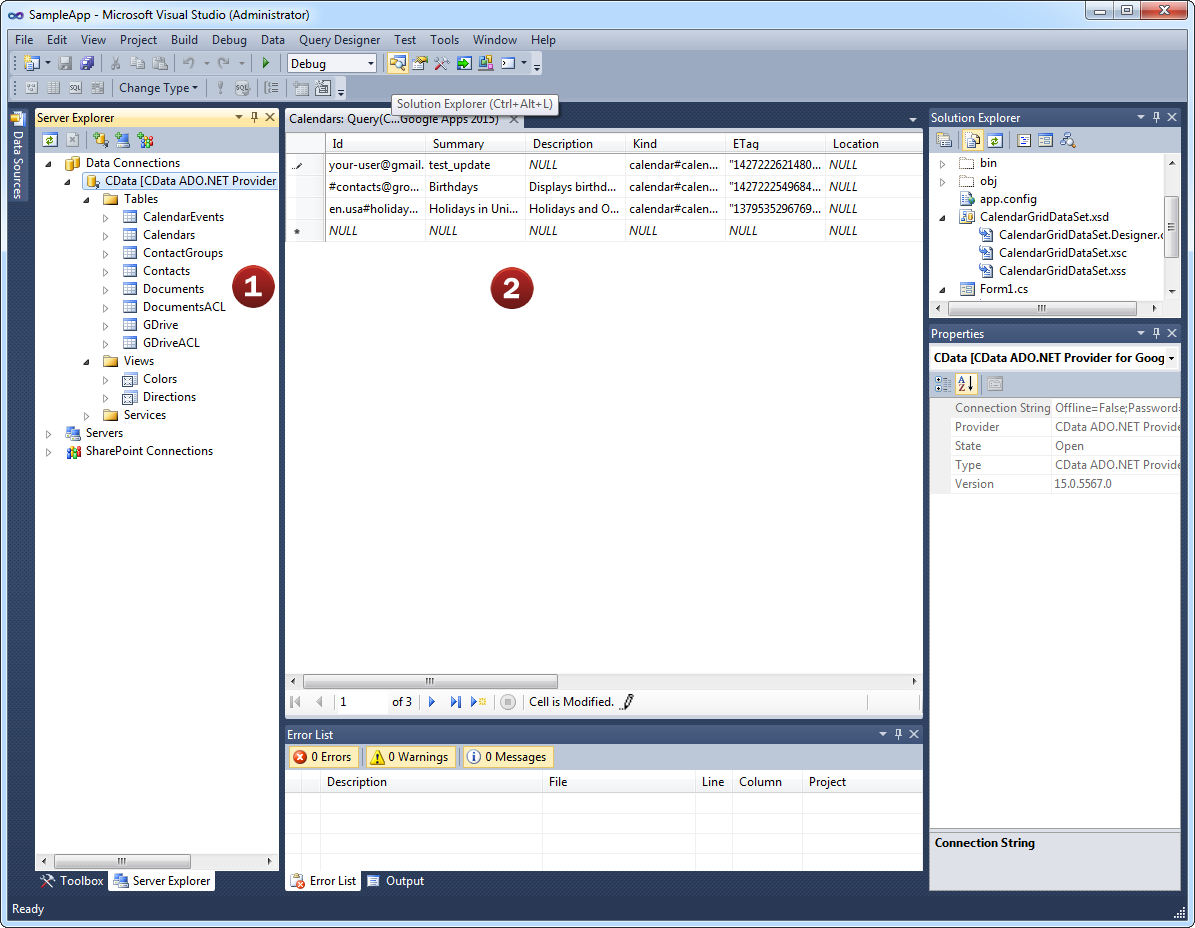
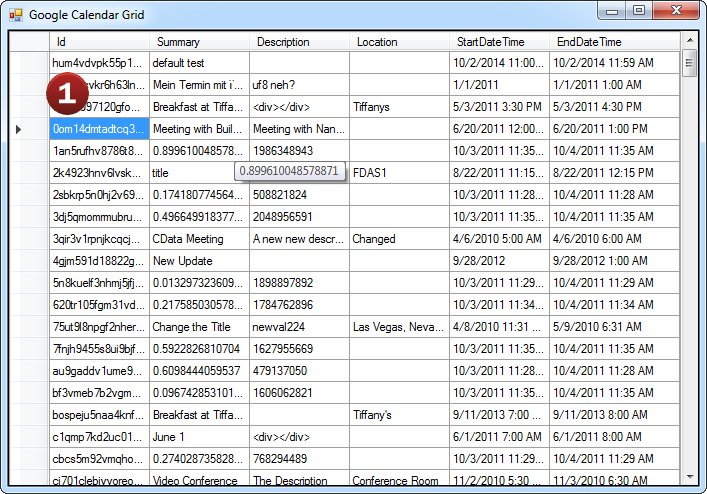
The JSON ADO.NET Provider offers the most natural way to access JSON data from any .NET application. Simply use JSON Data Provider objects to connect and access data just as you would access any traditional database. You will be able to use the JSON Data Provider through Visual Studio Server Explorer, in code through familiar classes, and in data controls like DataGridView, GridView, DataSet, etc.
The CData ADO.NET Provider for JSON hides the complexity of accessing data and provides additional powerful security features, smart caching, batching, socket management, and more.
Working with DataAdapters, DataSets, DataTables, etc.
The JSON Data Provider has the same ADO.NET architecture as the native .NET data providers for SQL Server and OLEDB, including: JSONConnection, JSONCommand, JSONDataAdapter, JSONDataReader, JSONDataSource, JSONParameter, etc. Because of this you can now access JSON data in an easy, familiar way.
For example:
using (JSONConnection conn = new JSONConnection("...")) {
string select = "SELECT * FROM JSONService";
JSONCommand cmd = new JSONCommand(select, conn);
JSONDataAdapter adapter = new JSONDataAdapter(cmd);
using (adapter) {
DataTable table = new DataTable();
adapter.Fill(table);
...
}
}
More Than Read-Only: Full Update/CRUD Support
JSON Data Provider goes beyond read-only functionality to deliver full support for Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations (CRUD). Your end-users can interact with the data presented by the JSON Data Provider as easily as interacting with a database table.
using (JSONConnection connection = new JSONConnection(connectionString)) {
JSONDataAdapter dataAdapter = new JSONDataAdapter(
"SELECT Id, Where FROM JSONService", connection);
dataAdapter.UpdateCommand = new JSONCommand(
"UPDATE JSONService SET Where = @Where " +
"WHERE Id = @ID", connection);
dataAdapter.UpdateCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Where", "Where");
dataAdapter.UpdateCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Id", "80000173-1387137645");
DataTable JSONServiceTable = new DataTable();
dataAdapter.Fill(JSONServiceTable);
DataRow firstrow = JSONServiceTable.Rows[0];
firstrow["Where"] = "New Location";
dataAdapter.Update(JSONServiceTable);
}
ADO.NET Provider Performance
With traditional approaches to remote access, performance bottlenecks can spell disaster for applications. Regardless if an application is created for internal use, a commercial project, web, or mobile application, slow performance can rapidly lead to project failure. Accessing data from any remote source has the potential to create these problems. Common issues include:
- Network Connections - Slow network connections and latency issues are common in mobile applications.
- Service Delays - Delays due to service interruptions, resulting in server hardware or software updates.
- Large Data - Intentional or unintentional requests for large amounts of data.
- Disconnects - Complete loss of network connectivity.
The CData ADO.NET Provider for JSON solves these issues by supporting powerful smart caching technology that can greatly improve the performance and dramatically reduce application bottlenecks.
Smart Caching
Smart caching is a configurable option that works by storing queried data into a local database. Enabling smart caching creates a persistent local cache database that contains a replica of data retrieved from the remote source. The cache database is small, lightweight, blazing-fast, and it can be shared by multiple connections as persistent storage.
Caching with our ADO.NET Providers is highly configurable, including options for:
- Auto Cache - Maintain an automatic local cache of data on all requests. The provider will automatically load data into the cache database each time you execute a SELECT query. Each row returned by the query will be inserted or updated as necessary into the corresponding table in the cache database.
- Explicit Cache - Cache only on demand. Developers decide exactly what data gets stored in the cache and when it is updated. Explicit caching provides full control over the cache contents by using explicit execution of CACHE statements.
- No Cache - All requests access only live data and no local cache file is created.
This powerful caching functionality increases application performance and allows applications to disconnect and continue limited functioning without writing code for additional local storage and/or data serialization/deserialization.
More information about ADO.NET Provider caching and best caching practices is available in the included help files.
Visual Studio Integration & Server Explorer
Working with the new JSON ADO.NET Provider is easy. As a fully-managed .NET Data Provider, the JSON Data Provider integrates seamlessly with the Visual Studio development environment as well as any .NET application.
As an ADO.NET Data Provider, JSON ADO.NET Provider can be used to access and explore JSON data directly from the Visual Studio Server Explorer.
It's easy. As a standard ADO.NET adapter, developers can connect the Server Explorer to JSON ADO.NET Provider just like connecting to any standard database.
- Add a new Data Connection from the Server Explorer and select the JSON Data Source
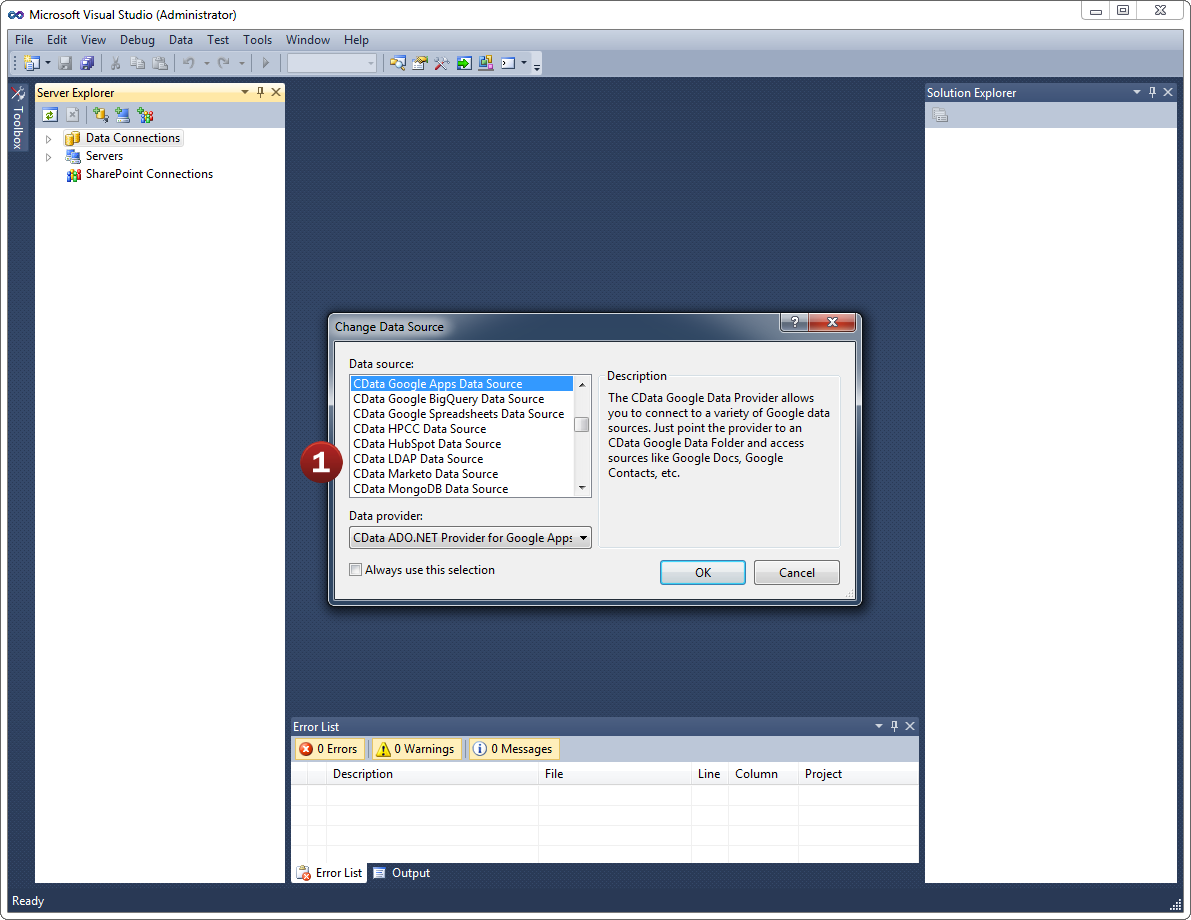
- Configure the basic connection properties to access your JSON account data.
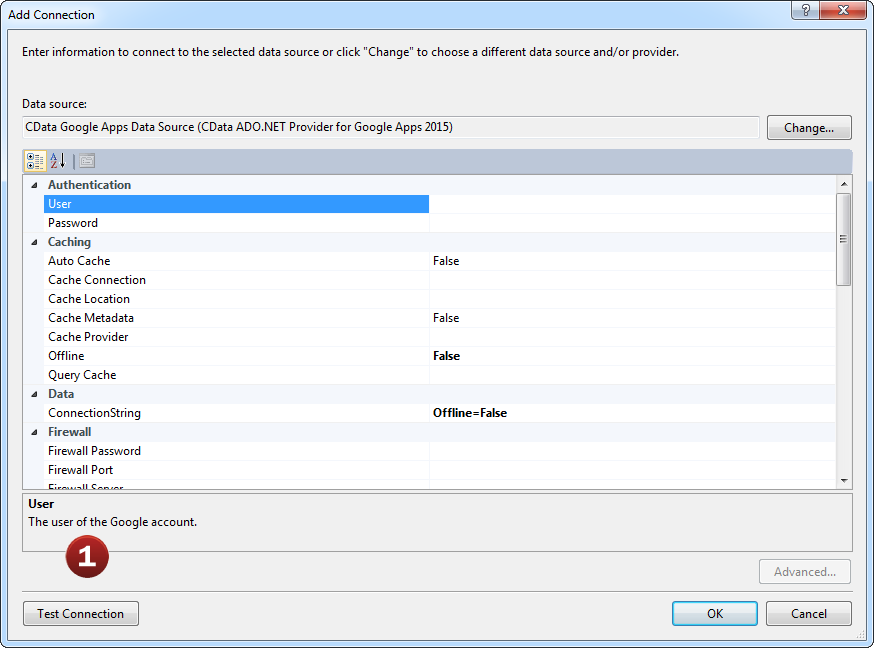
Explore all of the data available! JSON ADO.NET Provider makes it easy to access live JSON data from Visual Studio.
Developer Integration: Databind to JSON
Connecting Web, Desktop, and Mobile .NET applications with JSON is just like working with SQL Server. It is even possible to integrate JSON ADO.NET Provider into applications without writing code.
Developers are free to access the JSON ADO.NET Provider in whatever way they like best. Either visually through the Visual Studio Winforms or Webforms designers, or directly through code.
- Developers can connect the JSON Data Source directly to form components by configuring the object's smart
tags.
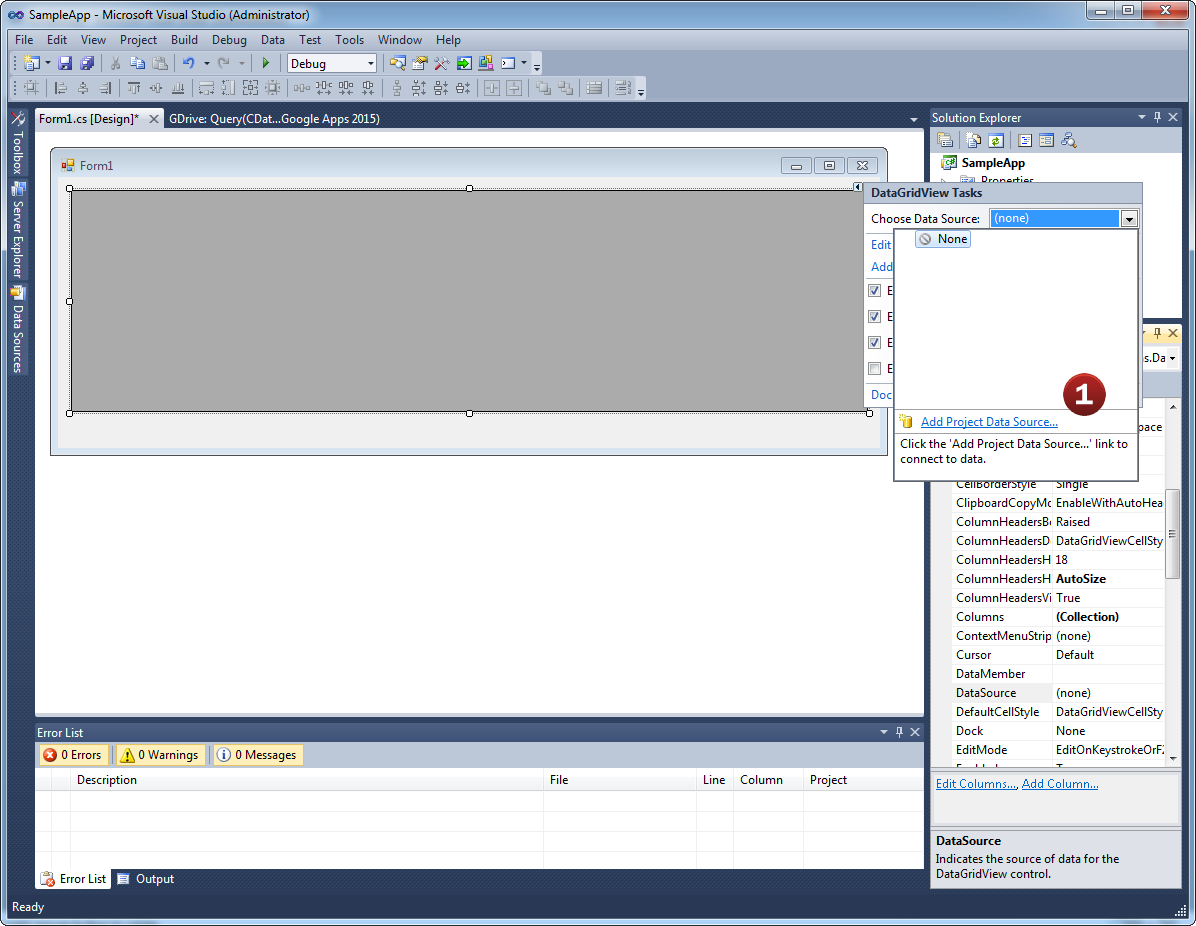
- Add a new Data Connection from the Server Explorer and select the JSON Data Source. Then, select the
feed, view, or services you would like to connect the object to.
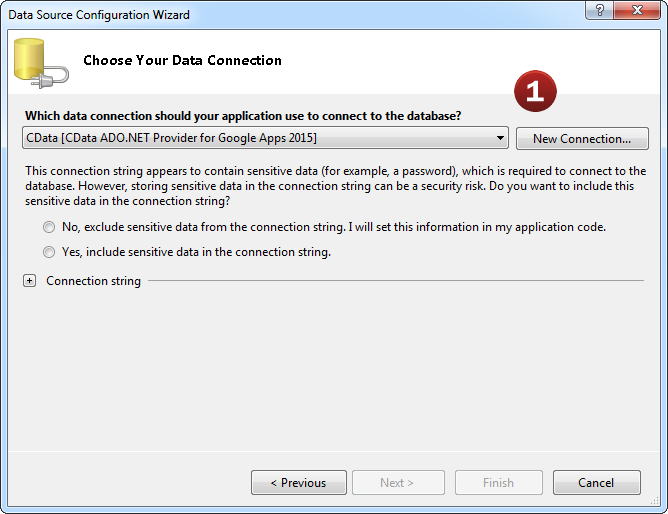
Done! It's just like connecting to SQL Server.
AI-Assisted Development with CData Code Assist MCP
Build JSON integrations faster with AI that understands your schema
Supported AI Coding Tools
Code Assist MCP gives AI coding tools direct access to your JSON schema. No more guessing table names or column types—AI sees the same metadata as your ADO.NET Driver.
Table names, column names, and SQL syntax in Code Assist MCP are identical to this ADO.NET Driver. Queries you validate with AI work directly in your production code.
Stop guessing. Start shipping. Prototype queries in conversation, validate against live data, then deploy with CData ADO.NET Drivers—no rewriting required.
Free for development. No trial period. No credit card required.
Popular ADO Videos: