Build a Salesforce Integration with Java and Code Assist MCP
Building code to connect different software systems used to be a slow and complex process. Developers had to invest significant time understanding how each system worked, reviewing documentation, and conducting thorough testing. Today, things have improved considerably. With AI coding assistants like Cursor and straightforward integrations from CData Code Assist MCP and drivers, creating data-driven applications has become much faster and more accessible.
The following tutorial details the process for creating a Java application that supports bi-directional CRUD operations. Rapid development is possible by connecting CData Code Assist MCP for Salesforce with Cursor and utilizing the CData Salesforce JDBC Driver in the application.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, ensure the following components are installed and ready:
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 8 or higher
- Apache Maven 3.6+
- CData Code Assist MCP for Salesforce
- CData Salesforce JDBC Driver with valid license
- Cursor IDE
Configure CData Code Assist MCP
Proper setup of the Salesforce MCP connection is essential for efficient Cursor development.
- Download and install the CData Code Assist MCP for Salesforce
- Open CData Code Assist MCP for Salesforce and launch the application which opens the Configuration dialog
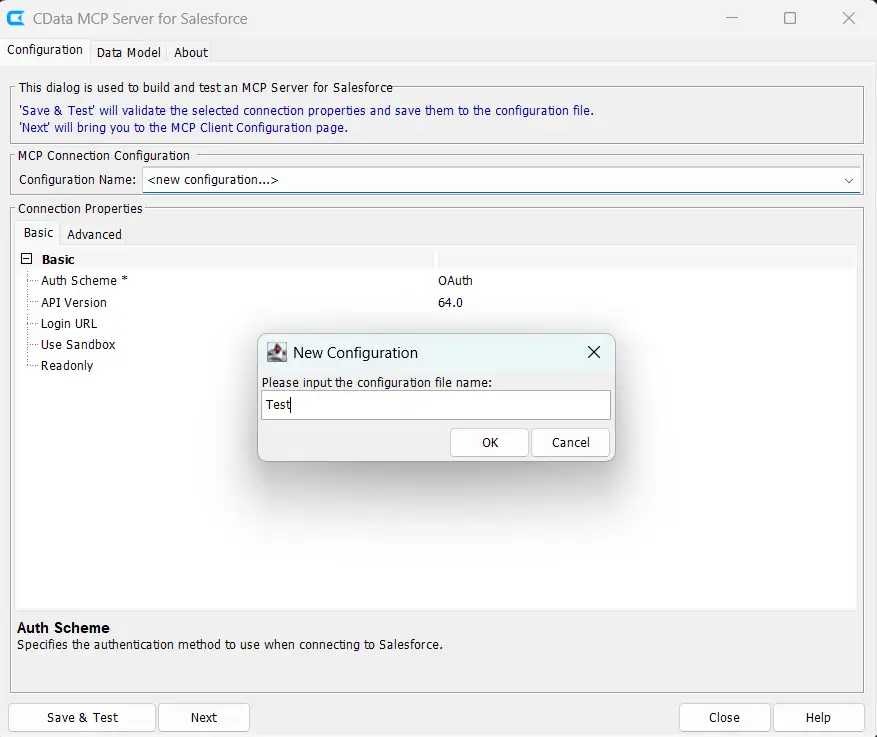
- Create a New Configuration
- Enter configuration name
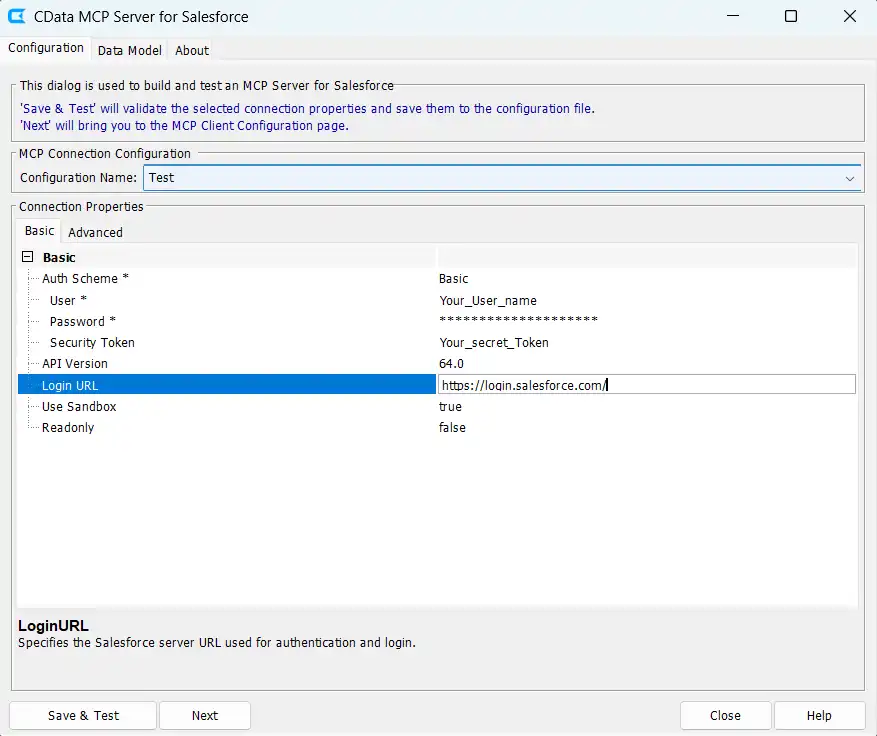
- Configure Connection Properties:
- Auth Scheme: Use Basic or OAuth as per the requirement
- Username: Enter your Salesforce username
- Password: Enter your Salesforce account password
- Login URL: Specify your Salesforce server URL (use sandbox URL for non-production environments)
- Use Sandbox: Enable when connecting to a sandbox environment
- Readonly: Set to false to enable write operations for full CRUD functionality
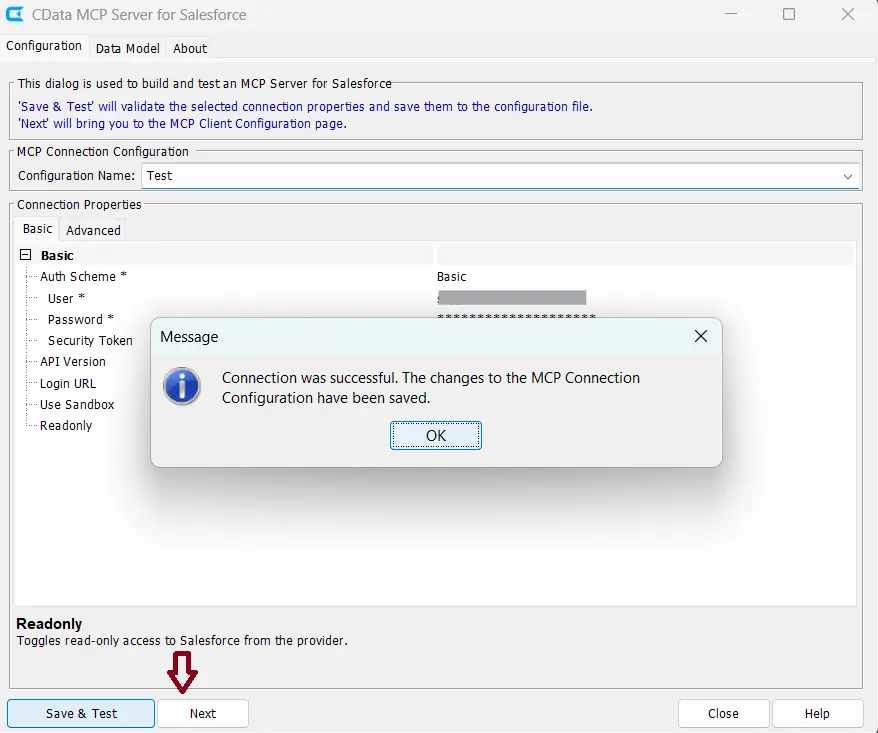
- Click Save & Test
Connecting with Cursor
After the test connection is successful, click Next to navigate to the MCP Client Configuration page. This screen allows you to configure how Cursor connects to the Salesforce MCP server
- Select Cursor from the dropdown menu to display Cursor-specific configuration options
- Click on Copy JSON
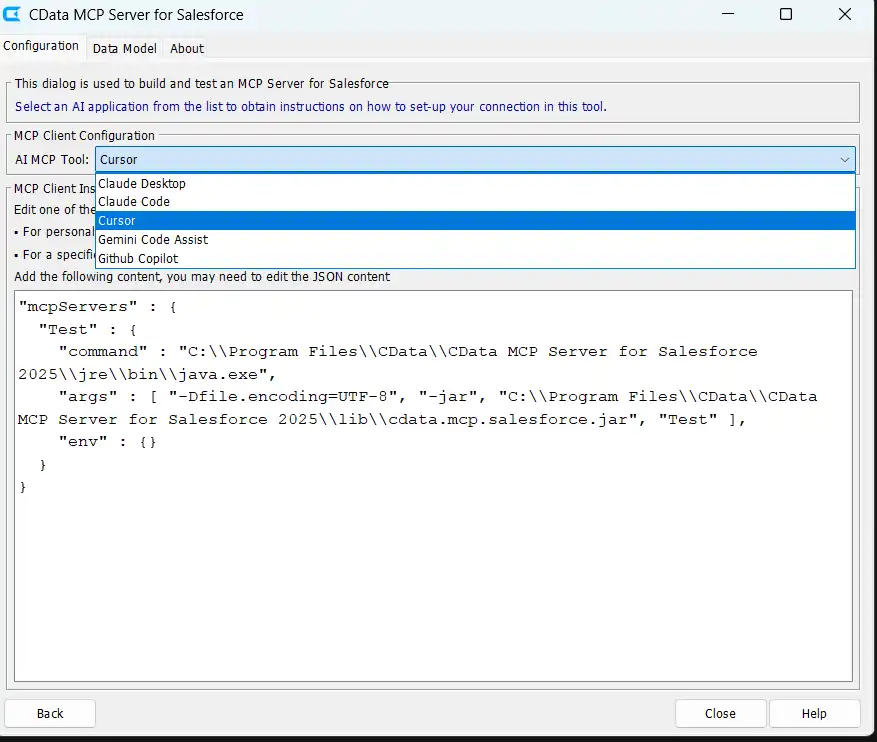
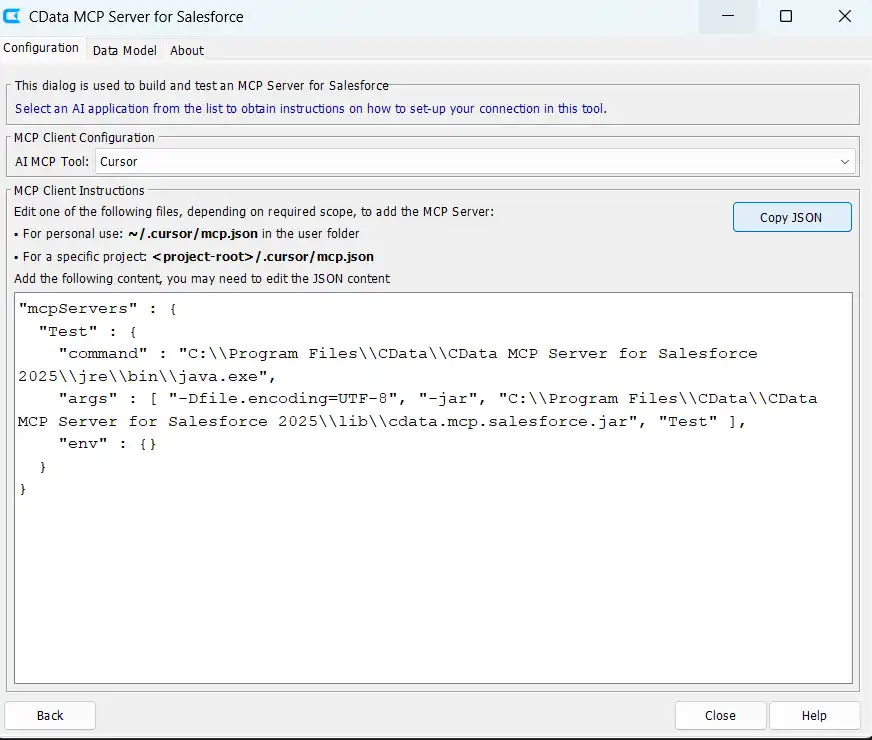
Cursor supports two configuration scopes for MCP servers: global scope and project scope. The difference lies in where the mcp.json file is stored. For this tutorial, the project scope is recommended as it keeps the configuration contained within the application directory
Follow these steps to configure the MCP server directly from Cursor IDE:
- Start the Cursor IDE and open the settings
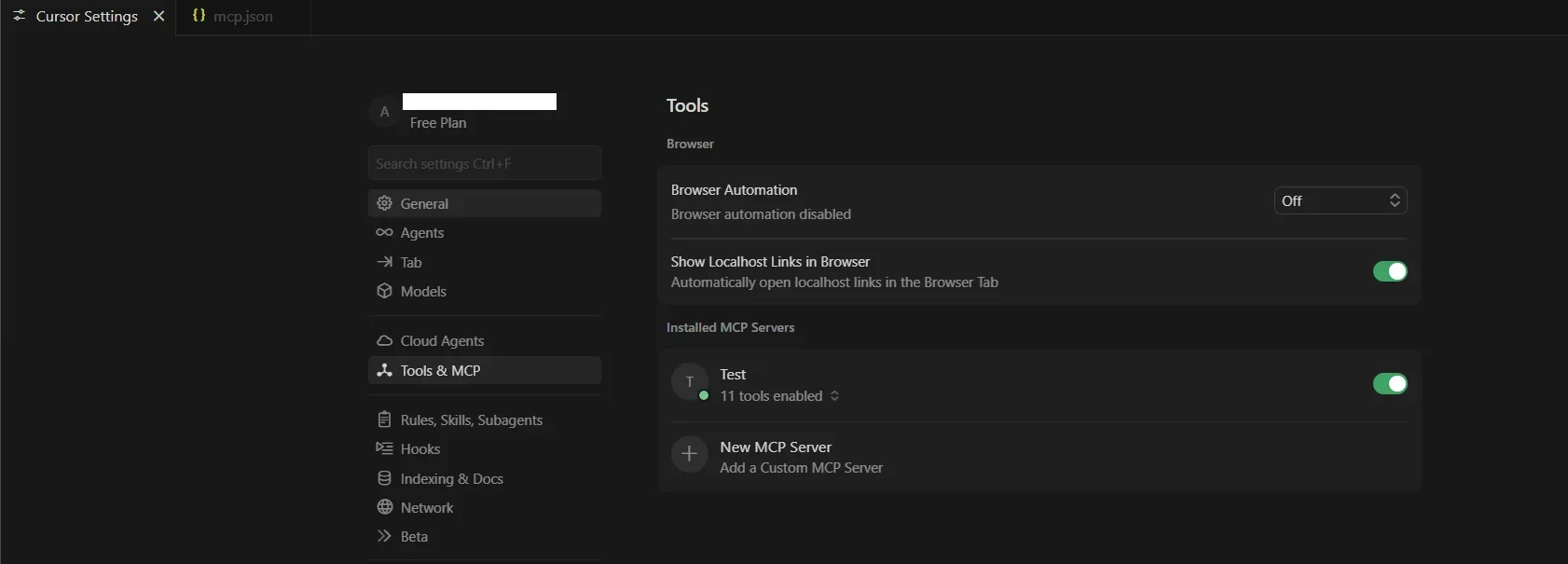
- Navigate to Tools & MCP
- Under Installed MCP Servers, select New MCP Server
- This action creates a new empty mcp.json file in the .cursor directory
- Paste the JSON configuration copied from the CData Code Assist wizard into the file
- Save the mcp.json file
- If the connection is successful, the configuration name and the list of connected tools will appear in the MCP Servers section
Alternatively, user can also use project root directory to configure the MCP server using the steps mentioned below:
- Navigate to the project root directory using a file explorer or terminal
- Create a .cursor directory if it does not already exist in the project root
- Create a new file named mcp.json inside the .cursor directory
- Click the Copy JSON button in the CData Code Assist MCP interface and paste the copied content into the mcp.json file
- Save the mcp.json file and close it
- Restart the Cursor IDE to load the new MCP configuration
Vibe coding with Cursor
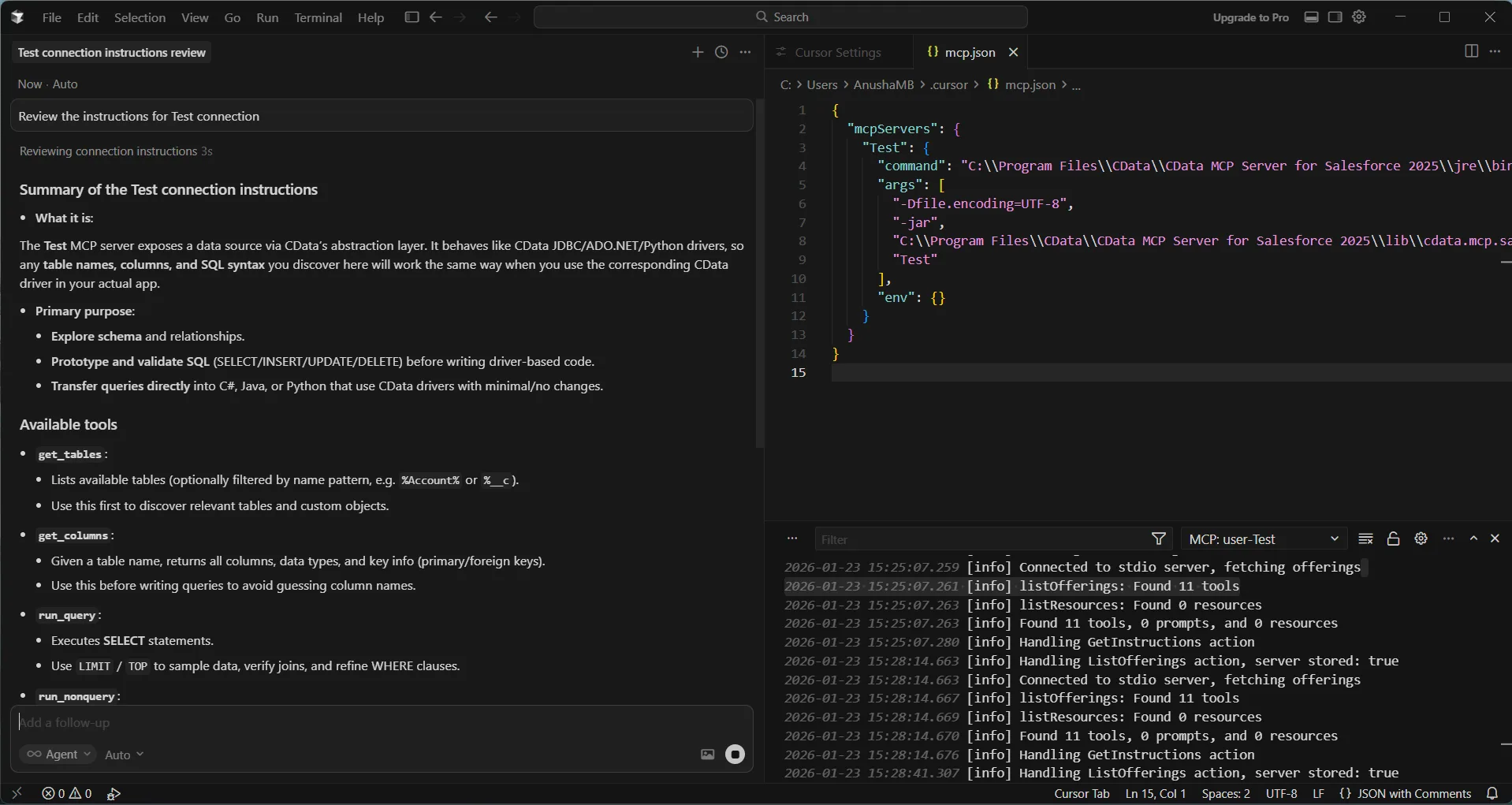
Start a new agent chat in Cursor and prompt it to review the MCP connection instructions using the prompt below:
"Review the instruction for the "Your_Configuration_name" Connection"This ensures Cursor has the necessary context before generating code.
Use the following prompt to create the application:
"Build a Java application that has a bi-directional integration with Salesforce. Add support for Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations. Add a GUI for the user.For authentication,I would like to use the connection string that can be generated from the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce. Review the "Your_Configuration_name" connection instructions before getting started."
Cursor will create a project plan and generate the application automatically.
For authentication, specify the connection string generated from the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce as mentioned in the prompt earlier. Ensure both the Driver JAR file and License file are included in the project. The MCP connection instructions provide Cursor with the correct file paths for smooth execution.
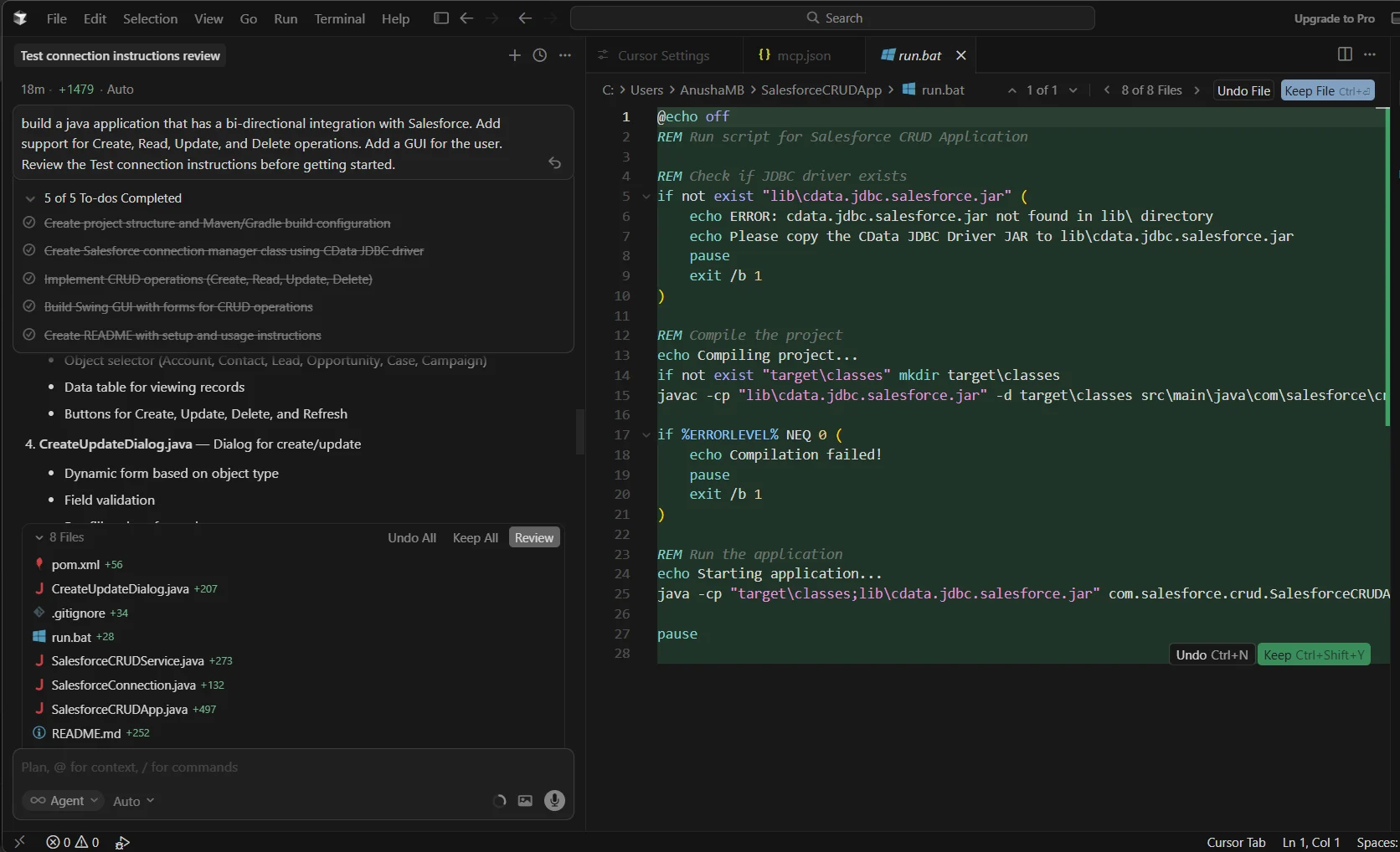
After launching the application and providing the connection string, the application successfully connects to Salesforce.The GUI will pop up and enables full CRUD operations against your Salesforce data.
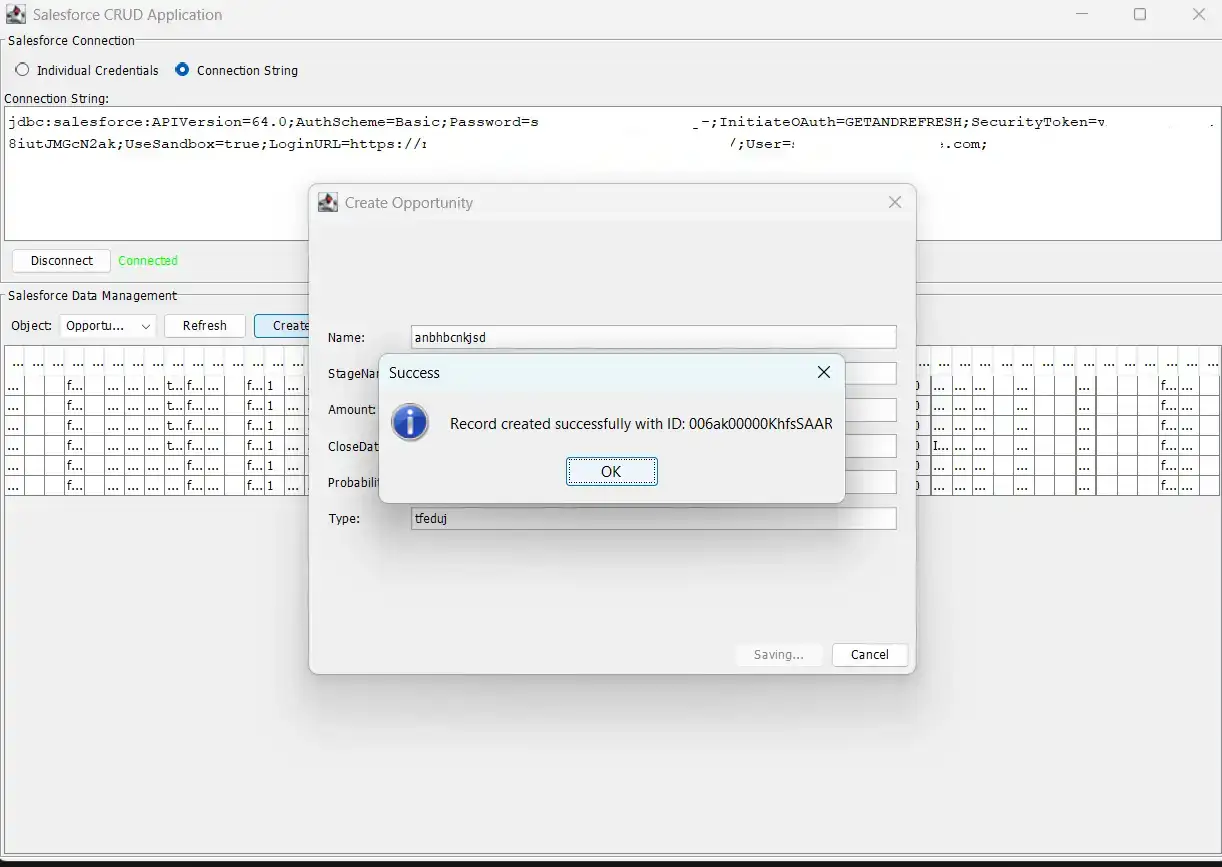
The combination of AI coding tools with CData Code Assist MCP and CData drivers accelerates development and simplifies the transition from testing to production with identical data models and queries.
Get Started Today
Start your 30-day free trial with CData Code Assist MCP and CData JDBC Driver to build integrations faster with AI-powered development. Need assistance? Contact our support team.





