Build PingOne-Powered Applications in Claude Code with CData Code Assist MCP
Claude Code is an AI-powered command line tool that enables agentic coding workflows. With support for MCP, Claude Code can connect to local tools and enterprise data sources directly from your terminal, enabling natural language interaction with live systems without switching context.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard for connecting LLM clients to external services through structured tool interfaces. MCP servers expose capabilities such as schema discovery and live querying, allowing AI agents to retrieve and reason over real-time data safely and consistently.
The following steps cover installing the CData Code Assist MCP for PingOne, configuring the connection to PingOne, connecting the Code Assist MCP add-on to Claude Code, and querying live PingOne data from within the terminal.
Step 1: Download and install the CData Code Assist MCP for PingOne
- To begin, download the CData Code Assist MCP for PingOne
- Find and double-click the installer to begin the installation
- Run the installer and follow the prompts to complete the installation
When the installation is complete, you are ready to configure your Code Assist MCP add-on by connecting to PingOne.
Step 2: Configure the connection to PingOne
- After installation, open the CData Code Assist MCP for PingOne configuration wizard
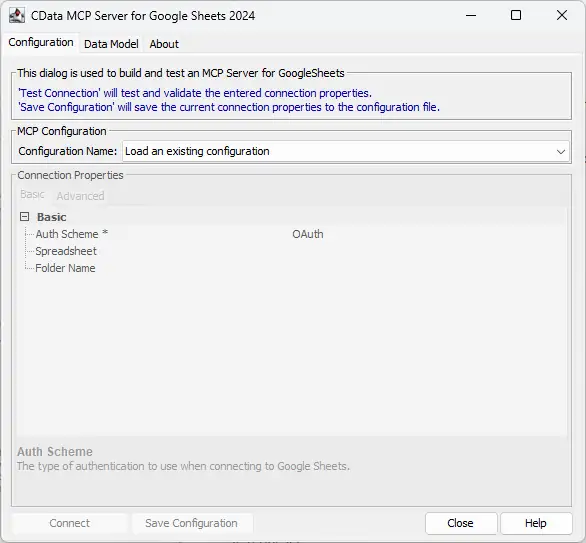
NOTE: If the wizard does not open automatically, search for "CData Code Assist MCP for PingOne" in the Windows search bar and open the application.
- In MCP Configuration > Configuration Name, either select an existing configuration or choose
to create a new one 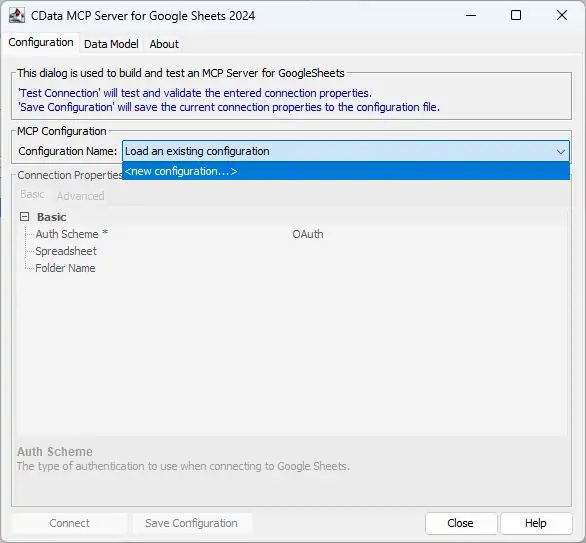
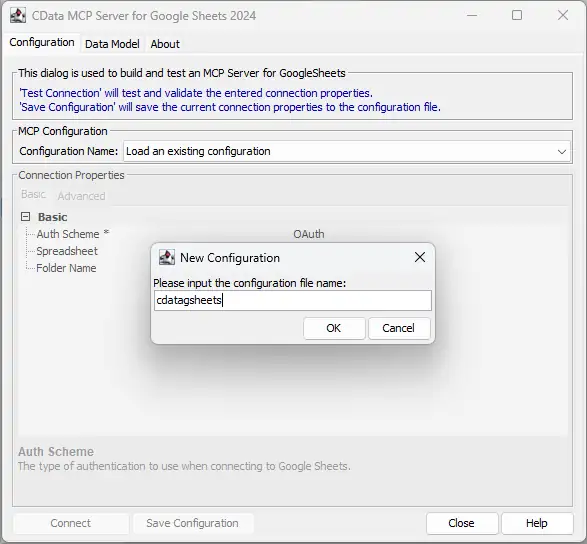
- Name the configuration (e.g. "cdata_pingone") and click OK
-
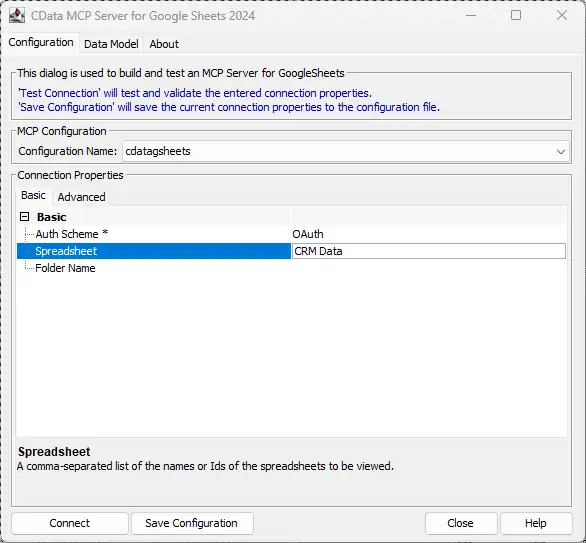
Enter the appropriate connection properties in the configuration wizard
To connect to PingOne, configure these properties:
- Region: The region where the data for your PingOne organization is being hosted.
- AuthScheme: The type of authentication to use when connecting to PingOne.
- Either WorkerAppEnvironmentId (required when using the default PingOne domain) or AuthorizationServerURL, configured as described below.
Configuring WorkerAppEnvironmentId
WorkerAppEnvironmentId is the ID of the PingOne environment in which your Worker application resides. This parameter is used only when the environment is using the default PingOne domain (auth.pingone). It is configured after you have created the custom OAuth application you will use to authenticate to PingOne, as described in Creating a Custom OAuth Application in the Help documentation.
First, find the value for this property:
- From the home page of your PingOne organization, move to the navigation sidebar and click Environments.
- Find the environment in which you have created your custom OAuth/Worker application (usually Administrators), and click Manage Environment. The environment's home page displays.
- In the environment's home page navigation sidebar, click Applications.
- Find your OAuth or Worker application details in the list.
-
Copy the value in the Environment ID field.
It should look similar to:
WorkerAppEnvironmentId='11e96fc7-aa4d-4a60-8196-9acf91424eca'
Now set WorkerAppEnvironmentId to the value of the Environment ID field.
Configuring AuthorizationServerURL
AuthorizationServerURL is the base URL of the PingOne authorization server for the environment where your application is located. This property is only used when you have set up a custom domain for the environment, as described in the PingOne platform API documentation. See Custom Domains.
Authenticating to PingOne with OAuth
PingOne supports both OAuth and OAuthClient authentication. In addition to performing the configuration steps described above, there are two more steps to complete to support OAuth or OAuthCliet authentication:
- Create and configure a custom OAuth application, as described in Creating a Custom OAuth Application in the Help documentation.
- To ensure that the driver can access the entities in Data Model, confirm that you have configured the correct roles for the admin user/worker application you will be using, as described in Administrator Roles in the Help documentation.
- Set the appropriate properties for the authscheme and authflow of your choice, as described in the following subsections.
OAuth (Authorization Code grant)
Set AuthScheme to OAuth.
Desktop Applications
Get and Refresh the OAuth Access Token
After setting the following, you are ready to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: GETANDREFRESH. To avoid the need to repeat the OAuth exchange and manually setting the OAuthAccessToken each time you connect, use InitiateOAuth.
- OAuthClientId: The Client ID you obtained when you created your custom OAuth application.
- OAuthClientSecret: The Client Secret you obtained when you created your custom OAuth application.
- CallbackURL: The redirect URI you defined when you registered your custom OAuth application. For example: https://localhost:3333
When you connect, the driver opens PingOne's OAuth endpoint in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions to the application. The driver then completes the OAuth process:
- The driver obtains an access token from PingOne and uses it to request data.
- The OAuth values are saved in the location specified in OAuthSettingsLocation, to be persisted across connections.
The driver refreshes the access token automatically when it expires.
For other OAuth methods, including Web Applications, Headless Machines, or Client Credentials Grant, refer to the Help documentation.
- Click Connect to authenticate with PingOne through OAuth
- Then, click Save Configuration to save the Code Assist MCP add-on
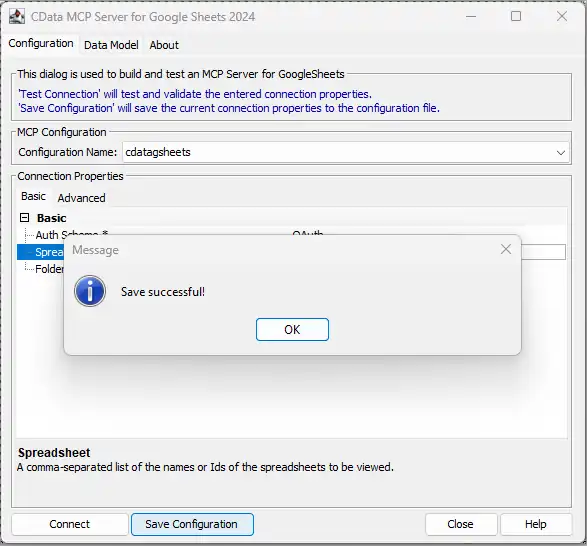
This process creates a .mcp configuration file that Claude Code will reference when launching the Code Assist MCP add-on. Now with your Code Assist MCP add-on configured, you are ready to connect it to Claude Code.
Step 3: Connect the Code Assist MCP add-on to Claude Code
- Install the Claude Code CLI using the terminal
- Open the Claude Code configuration file at ~/.config/claude-code/config.json (or the location shown after initialization)
Option 1: Manually add the MCP configuration
- Open the mcp.json file in your preferred editor
- Add the code shown below
{
"mcpServers" : {
"cdata_pingone" : {
"type" : "stdio",
"command" : "C:\Program Files\CData\CData Code Assist MCP for PingOne\jre\bin\java.exe",
"args" : [ "-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8", "-jar", "C:\Program Files\CData\CData Code Assist MCP for PingOne/lib/cdata.mcp.pingone.jar", "cdata_pingone" ],
"env" : {}
}
}
}
NOTE: The command value should point to your Java 17+ java.exe executable, and the JAR path should point to the installed CData Code Assist MCP add-on .jar file. The final argument must match the MCP configuration name you saved in the CData configuration wizard (e.g. "cdata_pingone").
Option 2: Copy the MCP configuration from the CData Code Assist MCP for PingOne UI
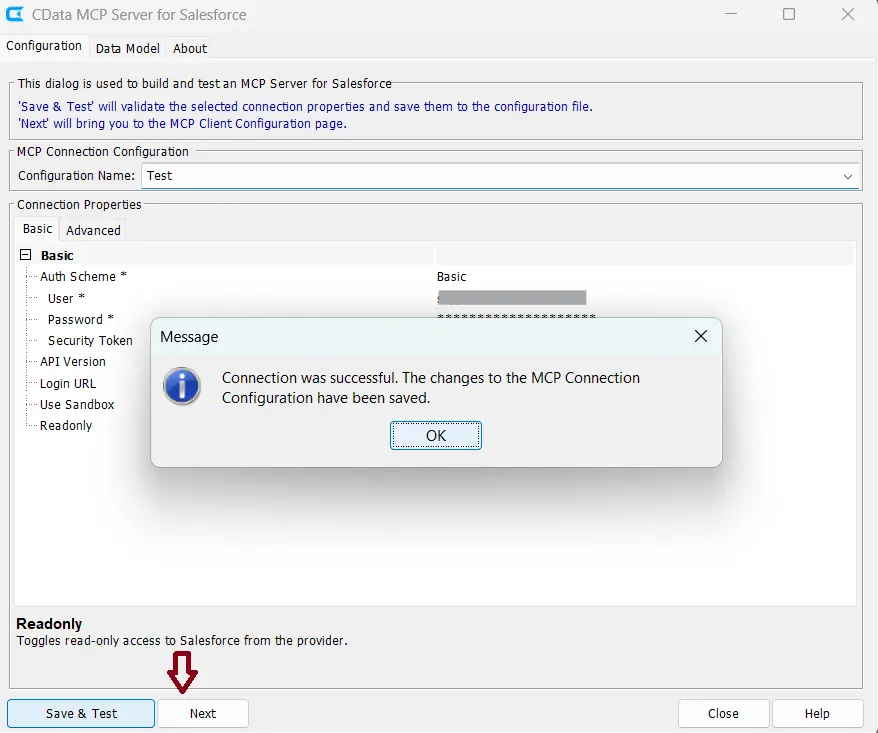
- After saving and testing your connection in the configuration wizard, click Next
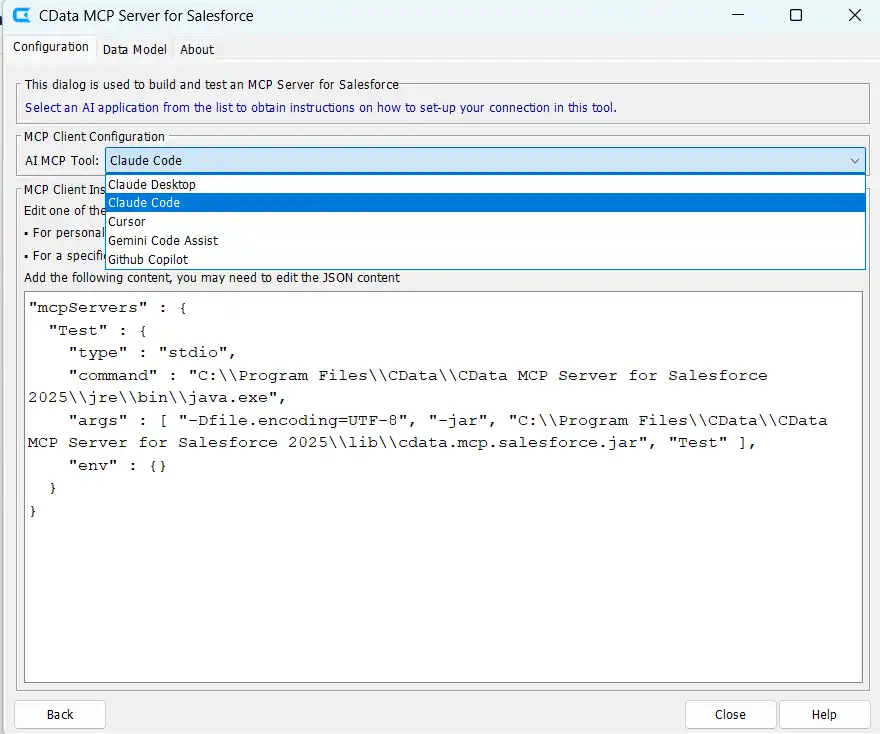
- Select Claude Code from the AI MCP Tool dropdown
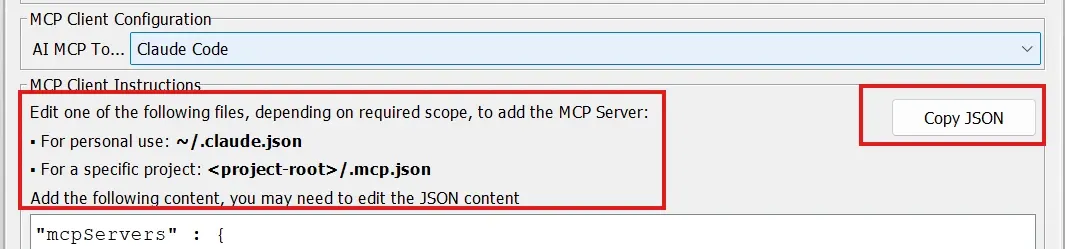
- Click Copy JSON to copy the generated MCP configuration to your clipboard
- Paste the copied JSON into the mcp.json file
Step 4: Verify connection in Claude Code
Claude Code provides tools to verify the connection is active before building.
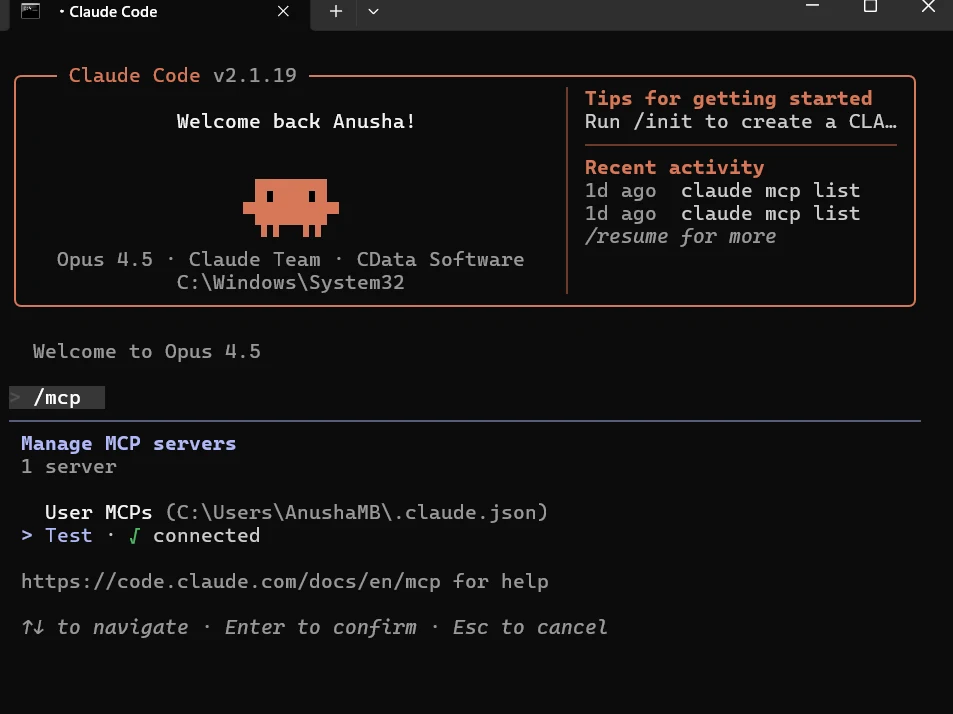
- Open a terminal and navigate to your project directory. Run the command claude mcp list
- Check that your configuration name appears with a Connected status
- Start Claude Code by running claude
- Inside the Claude Code session, type /mcp to view active servers

Step 5: Query live PingOne data in Claude Code
With the connection verified, you can now use natural language prompts to query and work with live PingOne data.
- Prompt Claude Code to review the instructions for your MCP connection to ensure it has all the appropriate context when writing code
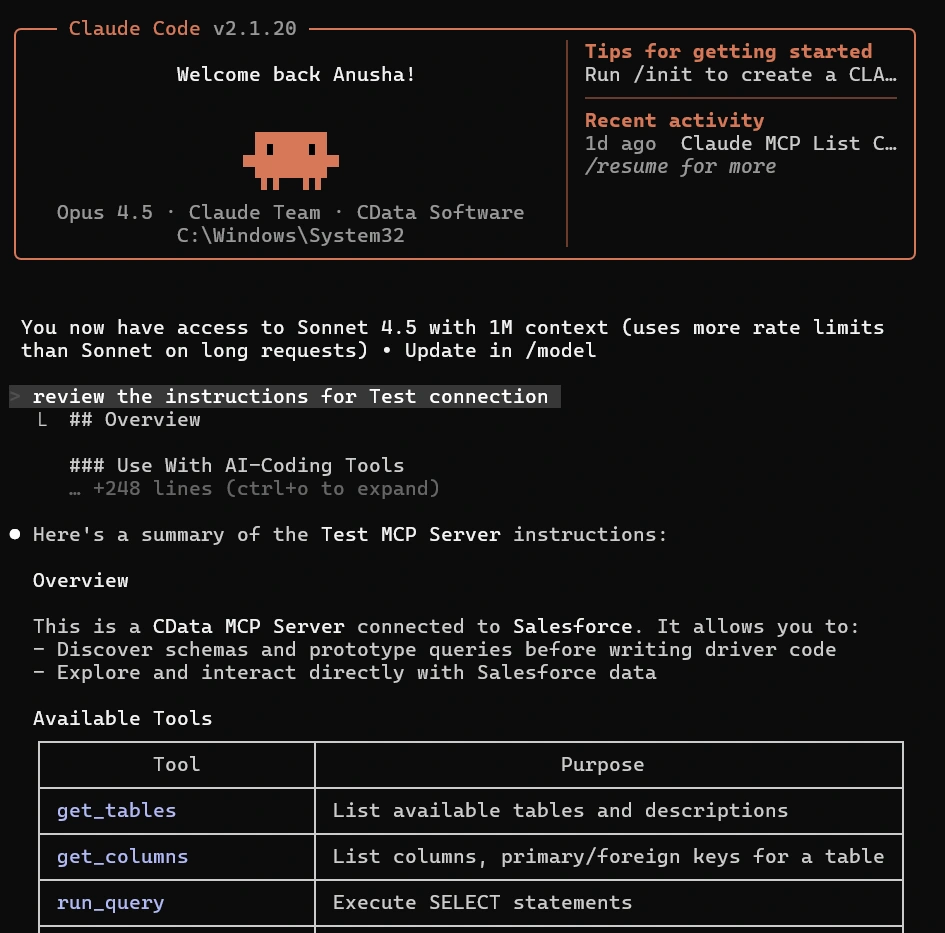
- Start building with natural language prompts! For example:
For my project, data from the [CData].[Administrators].Users is very important. Pull data from the most important columns like Id and Username.
Claude Code will use the MCP add-on to connect to PingOne, retrieve the requested data, and provide results directly in your terminal
Build with Code Assist MCP. Deploy with CData Drivers.
Download Code Assist MCP for free and give your AI tools schema-aware access to live PingOne data during development. When you're ready to move to production, CData PingOne Drivers deliver the same SQL-based access with enterprise-grade performance, security, and reliability.
Visit the CData Community to share insights, ask questions, and explore what's possible with MCP-powered AI workflows.






