Build a Salesforce Integration with C# and Code Assist MCP
Custom code integrations with Salesforce have traditionally required significant developer time and effort. Teams spend hours studying unique schemas, navigating through documentation, and conducting extensive testing cycles. The emergence of AI coding tools like Cursor, combined with CData Code Assist MCP for Salesforce and drivers, has transformed this landscape. Developers can now build sophisticated data-driven applications in a fraction of the time previously required.
This article demonstrates how to create a C# application with full bi-directional CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) capabilities for Salesforce. Developers can accelerate development by connecting CData Code Assist MCP for Salesforce with Cursor while utilizing the CData Salesforce ADO.NET Driver in application runtime.
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure the following components are installed and ready:
- .NET 6.0 or higher
- Visual Studio 2022 or Visual Studio Code with C# extension
- CData Salesforce ADO.NET Driver with valid license
- CData Code Assist MCP for Salesforce
- Cursor IDE
Configure CData Code Assist MCP
Proper setup of the Salesforce MCP connection is essential for efficient Cursor development.
- Download and install the CData Code Assist MCP for Salesforce.
- Open CData Code Assist MCP for Salesforce to launch the Configuration dialog.
- Create a New Configuration.
- Enter a configuration name (for example, "cdata-salesforce").
- Configure Connection Properties:
- Auth Scheme: Use Basic or OAuth as per the requirement.
- Username: Enter your Salesforce username.
- Password: Enter your Salesforce account password.
- Login URL: Specify your Salesforce server URL (use sandbox URL for non-production environments).
- Use Sandbox: Enable when connecting to a sandbox environment.
- Readonly: Set to false to enable write operations for full CRUD functionality.
- Click Save & Test.
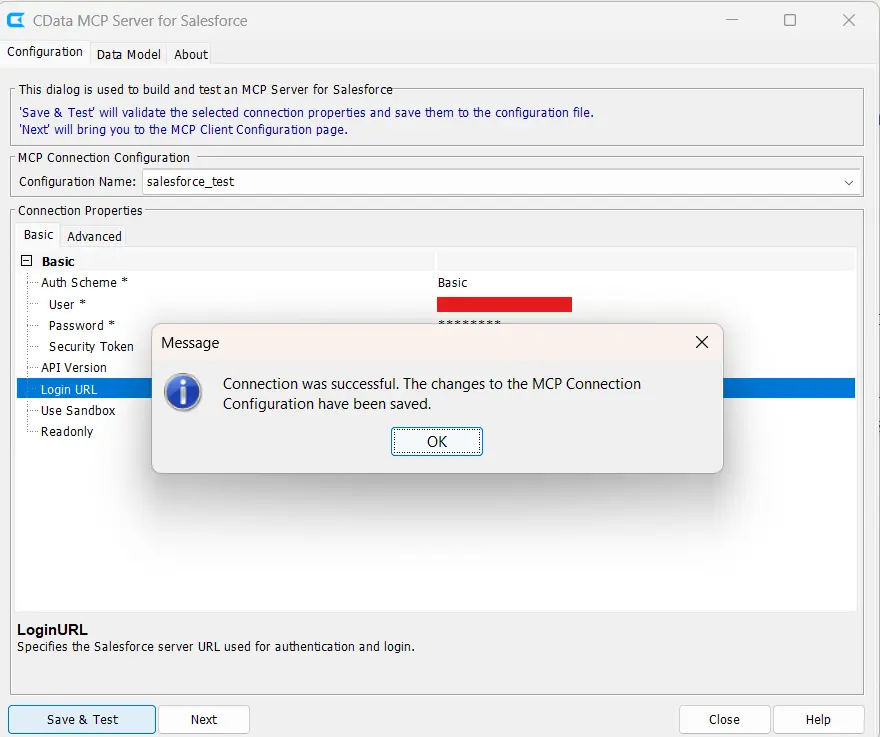
Connecting with Cursor
Follow these steps to complete the Cursor configuration:
- Click Next to navigate to the MCP Client Configuration Page. This screen allows configuration of how Cursor connects to the Salesforce Code Assist MCP add-on.
- Select Cursor from the dropdown menu to display Cursor-specific configuration options. Cursor supports two configuration scopes for MCP add-ons: global scope and project scope. The difference lies in where the mcp.json file resides.
- Navigate to the project root directory in file explorer or terminal.
- Create the .cursor directory if it does not exist yet in the project root.
- Create a new file named mcp.json inside the .cursor directory.
- Click the Copy JSON button in the Code Assist MCP interface and paste the complete contents into the mcp.json file.
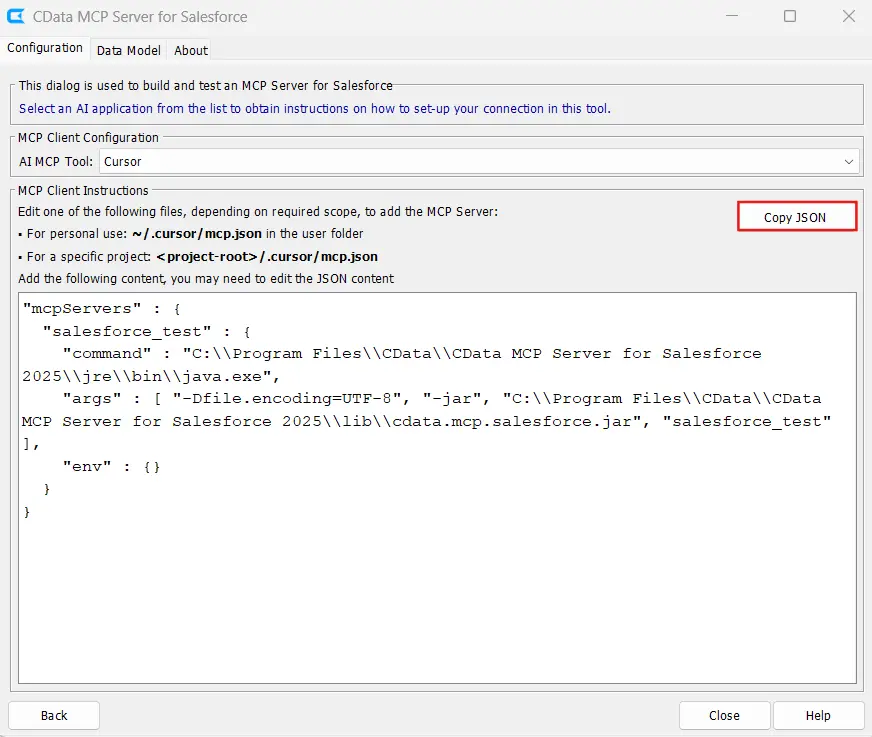
- Save the mcp.json file and close it.
- Restart Cursor IDE to load the new MCP configuration.
Verifying the MCP Connection in Cursor
After restarting Cursor, verify that the MCP connection has been properly established by following these steps:
- Open the Command Palette in Cursor by pressing Ctrl+Shift+P (or Cmd+Shift+P on macOS). This displays all available commands in the IDE.
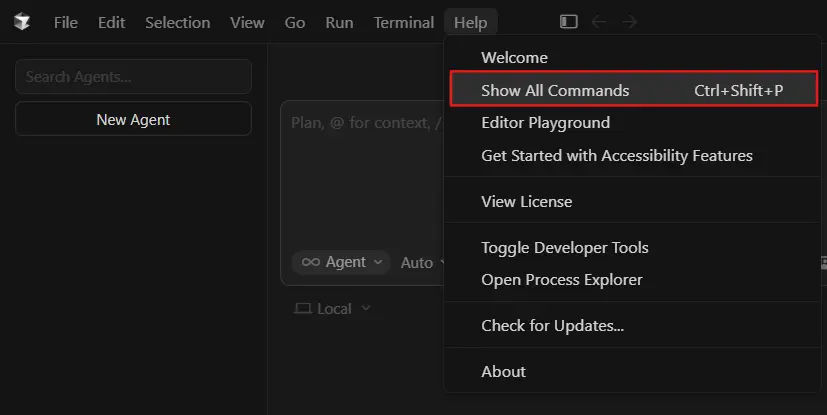
- Type View: Open MCP Settings in the command palette and select it. This opens the MCP configuration interface.
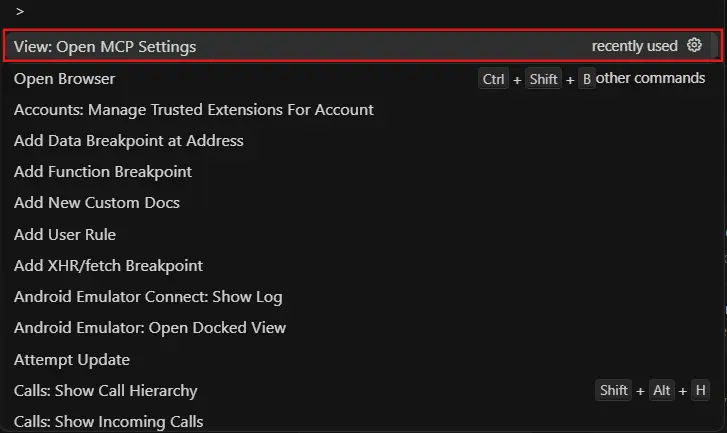
- Navigate to the Tools & MCP section in the Cursor Settings sidebar. This section displays all installed and configured MCP add-ons. Locate the Salesforce MCP connection in the Installed MCP Servers list.
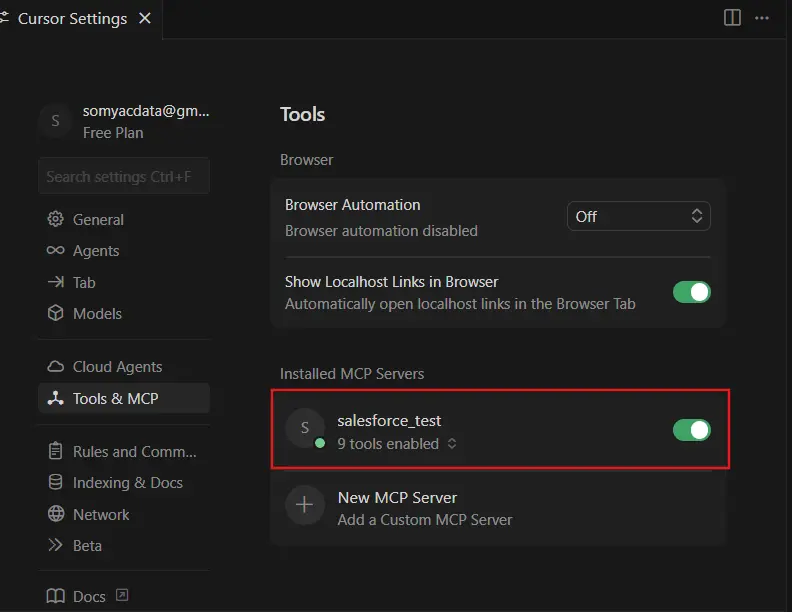
Once these steps are complete, the MCP connection appears verified in the IDE interface, indicating that Cursor can now access the Salesforce schema and connection details. The enabled tools allow Cursor to interact with Salesforce objects, retrieve schema information, and generate accurate code based on the actual data model.
Building with Cursor
With the MCP connection verified, Cursor can now generate accurate C# code leveraging the Salesforce schema information to interact with objects using proper field names, data types, and relationships.
- Open a new agent chat session in Cursor and begin by prompting the AI to review the instructions for the MCP connection. This step ensures Cursor has complete context about the Salesforce environment, including available objects, fields, and connection requirements.
"Review the instructions for my cdata-salesforce connection" (or enter the name of your connection)
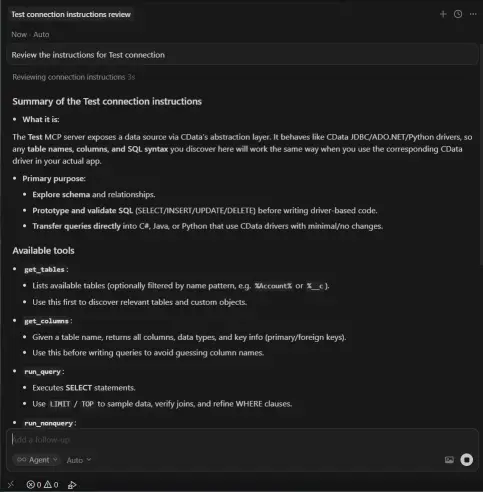
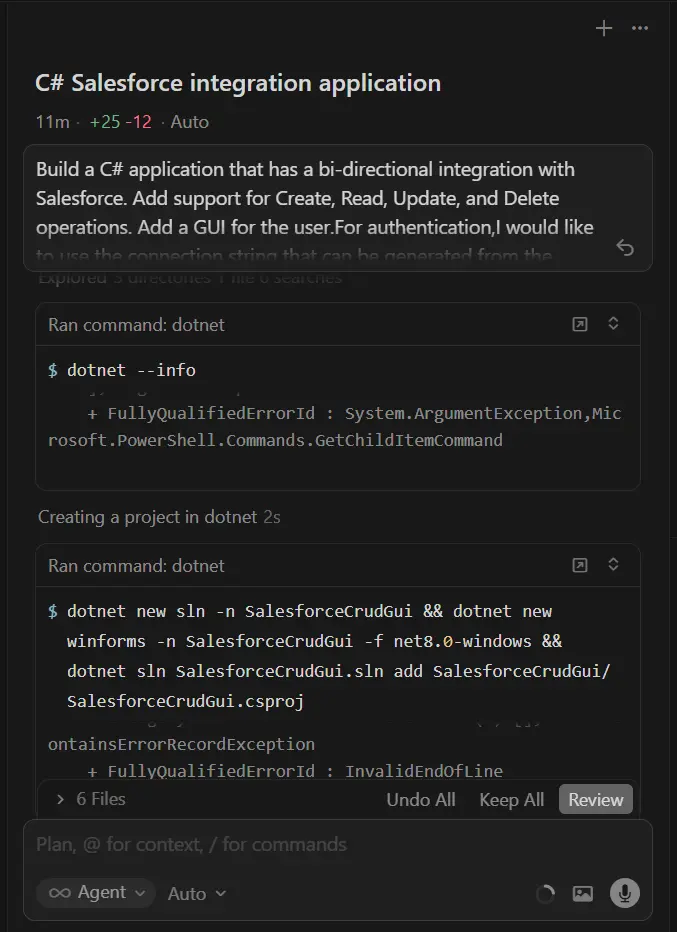
- After Cursor confirms it has reviewed the connection instructions, provide the following prompt:
"Build a C# application that has a bidirectional integration with Salesforce. Add support for Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations. Add a GUI for the user. For authentication, I would like to use the connection string that can be generated from the CData ADO.NET Driver for Salesforce. Review the cdata-salesforce connection instructions before getting started."
- For authentication configuration, specify using the connection string generated from the CData ADO.NET Driver for Salesforce. The CData Driver interface provides a connection string builder tool to obtain this connection string.
- Ensure both the Driver files and the License file are included in the project directory. The connection instructions provided to Cursor contain the correct file paths, ensuring smooth integration during runtime.
Testing the application
With the application built and configured, testing validates that all CRUD operations function correctly against the live Salesforce environment.
- After building the application and configuring the connection string, launch it through the terminal. The user interface displays connection status and provides controls for each CRUD operation.
- Enter the CData Salesforce Driver connection string in the configuration section. The application establishes a connection and validates credentials.
- Upon successful connection, the interface activates all CRUD operation controls.
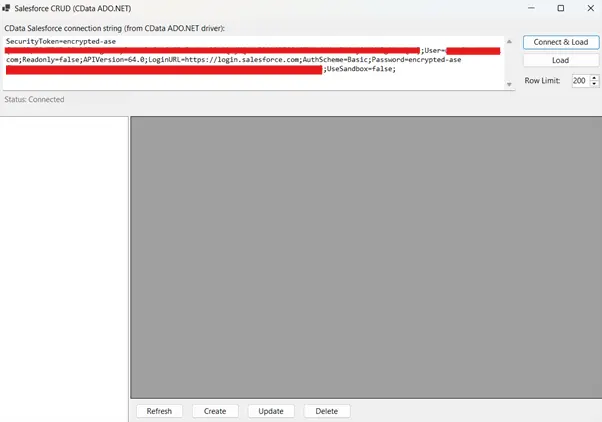
- Test each operation to verify functionality. Create a new Account record, read it back to confirm creation, update one of its fields, and finally delete it. Each operation should execute smoothly with appropriate success or error messages displayed in the interface.
Accelerate Salesforce integration with CData
CData Code Assist MCP and CData drivers enable rapid development of enterprise-grade applications, reducing development time from weeks to hours. Both share an identical data model, allowing developers to test using the same SQL queries that will be deployed. By leveraging Cursor with CData Code Assist MCP and the CData Salesforce ADO.NET Driver, developers create production-ready C# applications quickly with AI-generated code.
Start your 30-day free trial with CData Code Assist MCP and CData ADO.NET Driver to build integrations faster with AI-powered development. Need assistance? Contact our support team.





