Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to Import AlloyDB Data into SQL Server using SSIS
Easily back up AlloyDB data to SQL Server using the SSIS components for AlloyDB.
Using SQL Server as a backup for critical business data provides an essential safety net against loss. Backing up data to SQL Server enables business users to more easily connect that data with features like reporting, analytics, and more.
This example demonstrates how to use the CData SSIS Tasks for AlloyDB inside of a SQL Server SSIS workflow to transfer AlloyDB data into a Microsoft SQL Server database.
Add the Components
To get started, add a new AlloyDB source and SQL Server ADO.NET destination to a new data flow task.
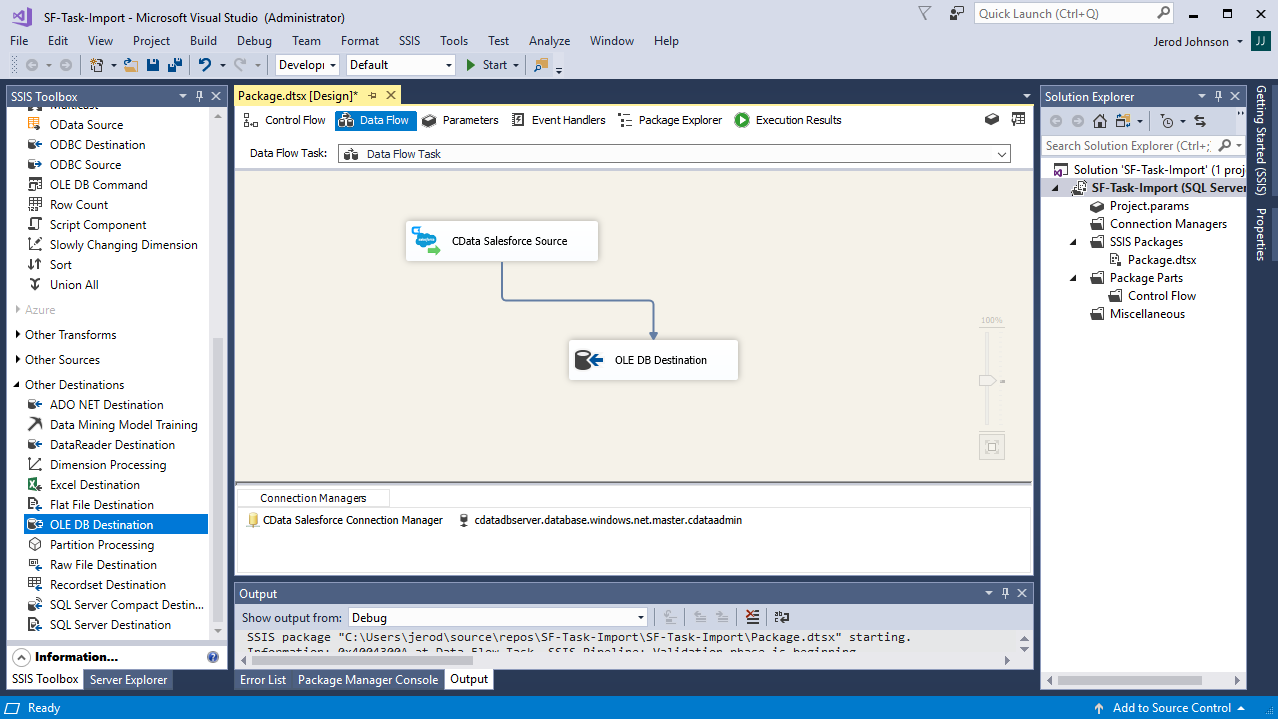
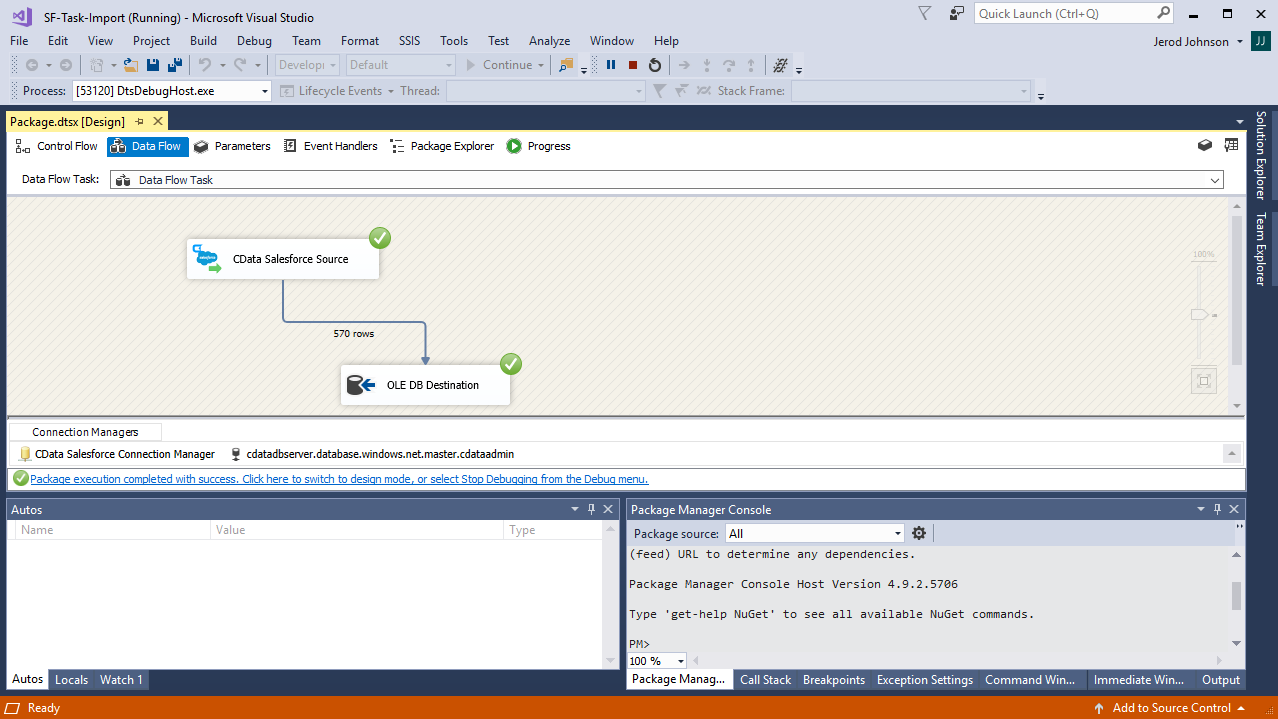
Create a New Connection Manager
Follow the steps below to save AlloyDB connection properties in a connection manager.
- In the Connection Manager window, right-click and then click New Connection. The Add SSIS Connection Manager dialog is displayed.
- In the Connection Manager type menu, select AlloyDB. The CData AlloyDB Connection Manager is displayed.
- Configure connection properties.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown).]()
Configure the AlloyDB Source
Follow the steps below to specify the query to be used to extract AlloyDB data.
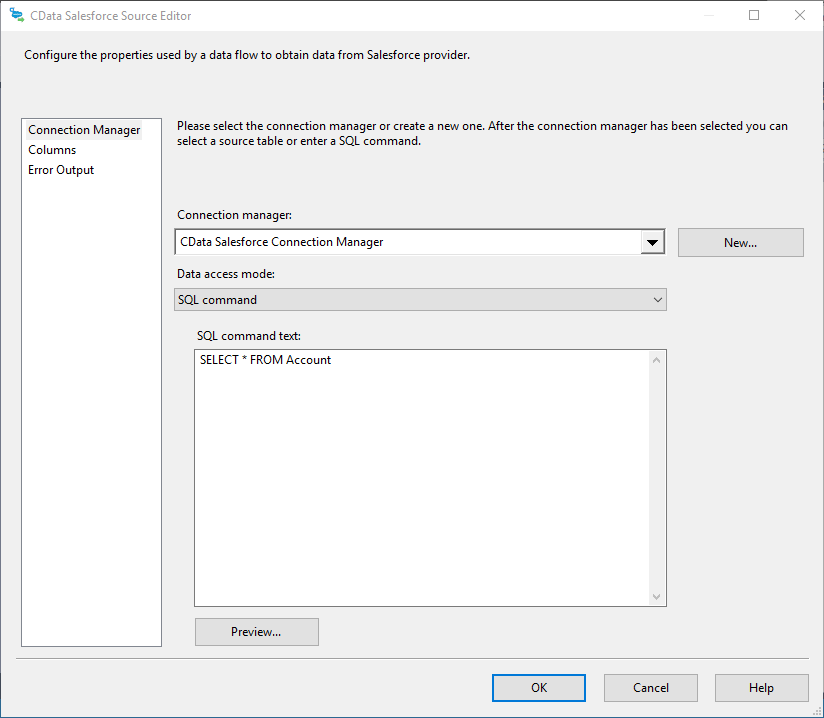
- Double-click the AlloyDB source to open the source component editor.
- In the Connection Manager menu, select the connection manager previously created.
- Specify the query to use for the data extraction. For example:
SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM Orders WHERE ShipCountry = 'USA'![The SQL query to retrieve records. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Close the AlloyDB Source control and connect it to the ADO.NET Destination.
Configure the SQL Server Destination
Follow the steps below to specify the SQL server table to load the AlloyDB data into.
- Open the ADO.NET Destination and add a New Connection. Enter your server and database information here.
- In the Data access mode menu, select "table or view".
- In the Table Or View menu, select the table or view to populate.
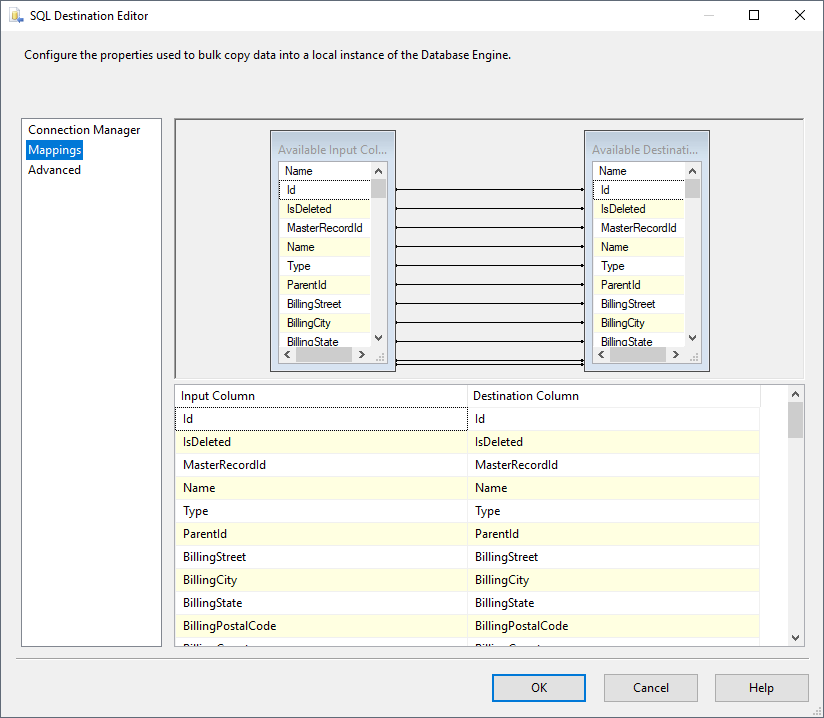
- Configure any properties you wish to on the Mappings screen.
![The mappings from the SSIS source component to SQL Server. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Run the Project
You can now run the project. After the SSIS Task has finished executing, your database will be populated with AlloyDB data.