Using Claude Projects to Work Effectively with Dynamic Data Models with CData Connect AI
Claude’s Projects feature helps you keep important context in one place, so you do not need to repeat information in every new chat. When you work with data sources that have custom or constantly changing structures, this feature becomes extremely valuable. By combining Claude Projects with CData Connect AI's managed MCP platform, you give Claude the context it needs to generate cleaner, more consistent, and more efficient results.
In this article, we explore:
- What Claude Projects are and how they work
- Why they produce better results when you use them with dynamic or custom data models
- How CData Connect AI MCP connectors benefit from project-level context
- How you can create and maintain your own schema instructions
- A complete example that includes project files and prompts you can use to test your setup
We use Google Sheets as the reference data source throughout the article as an example, but the same method works for any connector available in CData Connect AI.
What are Claude Projects?
Claude Projects creates a dedicated workspace where all information for a specific system or task stays organized. A Project keeps instructions, settings, and documentation in one place, so you do not need to repeat context every time you start a new conversation. You can add markdown files, notes, schema descriptions, and any reference material that Claude should use. Claude Projects also supports tools such as CData Connect AI MCP connectors, which are available in every session.
A new chat inside a Project automatically loads everything you have stored:
- All Project instructions
- Any markdown files you uploaded
- All MCP tools exposed by CData Connect AI
- Any prior context you defined for your environment
Projects act as long-term workspaces that keep Claude grounded in your data model. This is especially helpful for structured systems such as spreadsheets, databases, SaaS APIs, and BI sources, because Claude can use your context to understand tables, columns, relationships, and usage rules before generating output.
Why Claude Projects Improve the Experience with CData Connect AI
CData Connect AI exposes hundreds of data sources through the Model Context Protocol. These include Google Sheets, Salesforce, Snowflake, MySQL, SQL Server, and many more. Claude interacts with these sources through Connect AI’s managed MCP connectors. This creates a flexible and powerful workflow, but Claude still needs help understanding each user’s structure.
Claude does not automatically know:
- Which sheets or tables exist
- How columns relate
- What naming conventions you follow
- Which operations are efficient or inefficient
- Which fields hold identifiers, dates, amounts, or categorical values
Because Connect AI must support many different data structures, the MCP driver does not embed static instructions. Instead, Claude Projects allow you to describe your actual data model.
Without this context, Claude may produce:
- Incorrect or missing column names
- SELECT queries that do not match your sheet layout
- Incorrect JOIN or filtering logic
- Unnecessary scans or unbounded reads
- SQL or logic that does not match the connector’s capabilities
Claude Projects solves this by letting you store your schema information directly inside a Project so that Claude uses it every time.
You can add:
- Sheet descriptions
- Column definitions
- Relationships between sheets
- Expected aggregation patterns
- Allowed operations
- Performance guidelines
This gives Claude a stable foundation for generating accurate and efficient output via CData Connect AI. Your Project-level context becomes the “schema layer” Claude reads before interacting with the live data source.
How this setup helps Claude understand your data
This approach gives you a simple and reliable way to teach Claude how your Google Sheets data is organized. Instead of relying on static driver-level documentation, you define the structure inside your Project. Claude reads that structure before generating any queries or transformations.
To set this up, create a Claude Project and connect your CData Connect AI environment. Then add files that describe your spreadsheet structure and write instructions that outline:
- Sheets
- Columns
- Relationships
- Indexing patterns (if applicable)
- Allowed query patterns
- Performance guidelines
Claude uses this information whenever you start a new conversation inside the Project. This leads to:
- More accurate query generation
- Fewer mistakes
- Better use of the Connect AI MCP connector
- Cleaner, optimized requests against your Google Sheets data
Example Setup: Using Claude Projects with Google Sheets via CData Connect AI
The following example shows how Claude Projects work together with CData Connect AI when your data source is Google Sheets. The same setup applies to any data source you connect through Connect AI.
The goal of this workflow is to give Claude a structured understanding of your sheet layout so that it can read, filter, transform, and aggregate data accurately.
Prerequisites
To start with, make sure you have the following:
- A Google Sheets document containing your data
- An account in CData Connect AI
- A Google Sheets connection configured in Connect AI
- An account in Claude.ai
After you prepare these items, continue with the steps below.
Step 1: Create the data structure in Google Sheets
For this example, we set up a simple e-commerce dataset across Google Sheets. Claude uses this structure to understand your layout before generating SQL-like queries or structured transformations.
Create a sheet with the following tabs:
- Customers
- Products
- Orders
- OrderItems
- Inventory
Each tab contains relevant columns, including ID, name, price, orderdate, and stockcount.
You can adapt this layout to your own Sheets environment as long as you match it in your Project instructions.
Step 2: Connect Google Sheets to CData Connect AI
Connect AI manages your MCP connectors, so you do not need to install or run anything locally. Simply configure your Google Sheets connection in the Connect AI interface.
Follow these steps:
- Open CData Connect AI.
- Go to Connections.
- Add a new connection for Google Sheets.
- Authenticate with your Google account.
- Choose the spreadsheet you want Claude to use.
- Save the configuration.
Connect AI automatically exposes this Google Sheets connection to Claude as an MCP server tool. Once the connection is active, Claude can read your worksheet metadata and run structured queries.
Step 3: Create a new Claude Project
Create a Project in Claude to organize your instructions and files.
Follow the given steps:
- Open Claude.ai
- Go to Projects
- Select New Project
- Enter a descriptive name, such as “Google Sheets MCP Workspace”
The Project becomes the long-term environment where Claude learns your data structure and applies your context consistently.
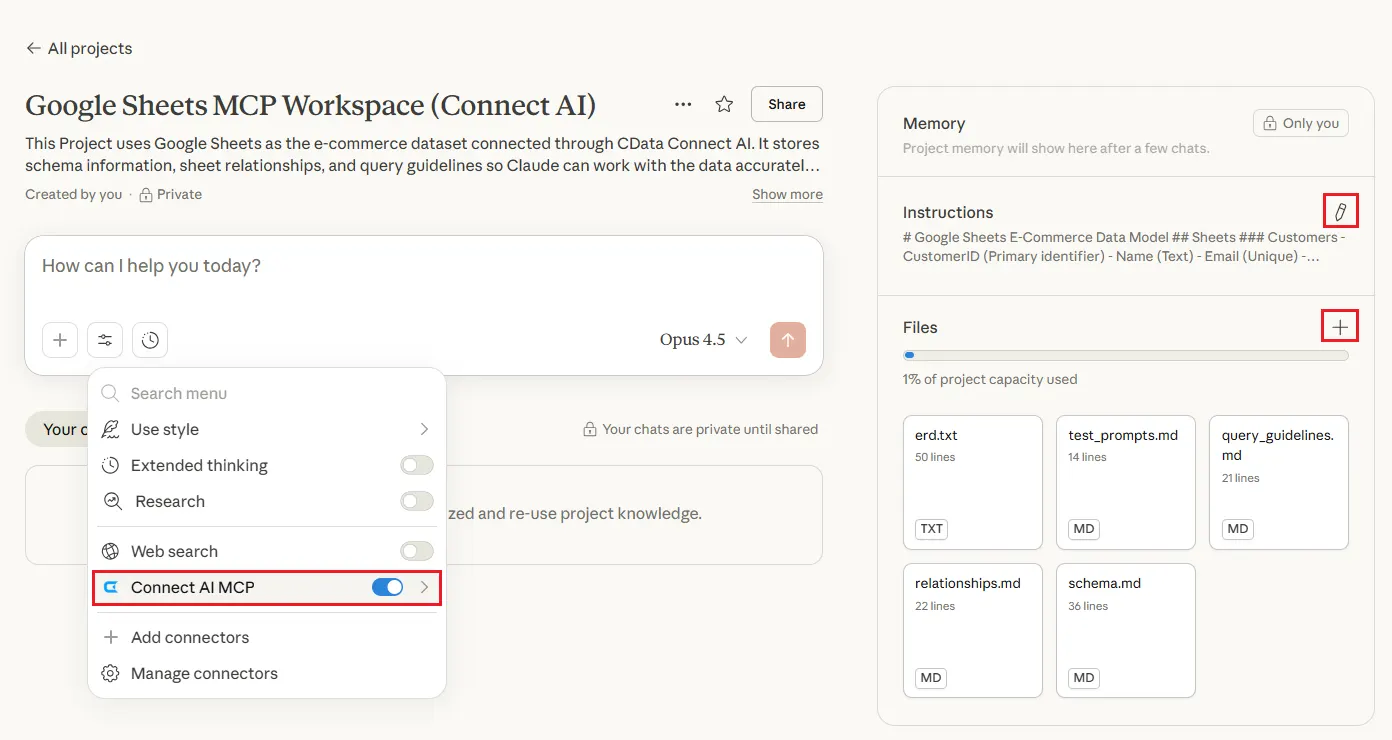
Note: Check if the CData Connect AI is already added as a tool in the Claude Project. If not, log in to it and enable it as an MCP tool.
Step 4: Add Project instructions and schema files
Claude works best when you give it clear information about your tables, relationships, and performance expectations. In this setup, we add context in two places:
- The Project’s Instructions panel
- Markdown files stored under the Files section
Together, these elements give Claude a comprehensive view of your Google Sheets data.
a. Project instructions
Add content to the Instructions panel in your Claude Project based on your data. In this example, we’ve included instructions based on the data model in our Google Sheets:
# Google Sheets E-Commerce Data Model ## Sheets ### Customers - CustomerID (Primary identifier) - Name (Text) - Email (Unique) - CreatedAt (DateTime) ### Products - ProductID (Primary identifier) - Name (Text) - Price (Numeric) ### Orders - OrderID (Primary identifier) - CustomerID (Reference to Customers.CustomerID) - OrderDate (DateTime) - Status: pending | shipped | delivered ### OrderItems - ItemID (Primary identifier) - OrderID (Reference to Orders.OrderID) - ProductID (Reference to Products.ProductID) - Quantity (Number) ### Inventory - ProductID (Reference to Products.ProductID) - Stock (Number) ## Relationships - Customers (1) → Orders (N) - Orders (1) → OrderItems (N) - Products (1) → OrderItems (N) - Products (1) → Inventory (1) ## Query Guidelines - Use sheet names exactly as defined - Reference IDs using the relationships above - Apply filters instead of reading full sheets whenever possible - Use OrderDate for time filtering - Avoid operations that require full scans of large sheets unless necessary
This instruction block describes your data model in a compact and easy-to-read format.
b. Add files to the project
Upload the following files or add them as text content into the Files section of the Project. Claude reads these files automatically in every new session. Some relevant markdown files that you can create and add are listed below:
- schema.md: Contains detailed descriptions of each sheet and column.
- relationships.md: Lists the relationships between sheets and cross-sheet references. Guides Claude to choose the correct JOIN paths.
- query_guidelines.md: Explains SQL expectations such as:
- Preferred filtering patterns
- Calculation logic
- Avoiding full-sheet scans
- Using IDs for joins
- test_prompts.md: Contains prompts you can use to verify that the Project works correctly. These prompts help confirm that Claude reads your schema and interacts with the Google Sheets via Connect AI MCP accurately.
- erd.txt: Contains an ASCII diagram of your sheet structure or database. Claude uses the diagram when explaining or reasoning about the schema.
Example input:
# Google Sheets E-Commerce Schema Overview This document describes the structure of the Google Sheets dataset used in this Project. It provides Claude with a detailed understanding of each sheet and the purpose of every column. ## Customers Stores customer information. - CustomerID: unique identifier - Name: full customer name - Email: unique email address - CreatedAt: date when the customer was added ## Products Stores product catalog details. - ProductID: unique identifier - Name: product name - Price: product price in USD ## Orders Represents customer orders. - OrderID: unique identifier - CustomerID: reference to Customers sheet - OrderDate: date the order was placed - Status: pending, shipped, or delivered ## OrderItems Represents individual line items within orders. - ItemID: unique identifier - OrderID: reference to Orders sheet - ProductID: reference to Products sheet - Quantity: number of items purchased ## Inventory Tracks product stock levels. - ProductID: reference to Products sheet - Stock: inventory count for the product
Example input:
# Sheet Relationships These relationships help Claude understand how sheets connect to each other so it can generate correct joins. ## Relationships ### Customers → Orders - One customer can have many orders - Link: Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID ### Orders → OrderItems - One order can contain many order items - Link: Orders.OrderID = OrderItems.OrderID ### Products → OrderItems - One product can appear in many order items - Link: Products.ProductID = OrderItems.ProductID ### Products → Inventory - One product has one inventory record - Link: Products.ProductID = Inventory.ProductID
Claude reads this guidance before generating SQL.
Example input:
# Query Guidelines for Google Sheets via Connect AI These guidelines help Claude produce accurate and efficient queries when interacting with Google Sheets through CData Connect AI. ## Best Practices - Use exact sheet names when referencing data. - Avoid selecting entire sheets unless required by the task. - Filter using OrderDate or other indexed-like columns to reduce data volume. - Use relationships to join sheets correctly. - Summaries and aggregations should always specify clear fields. - Limit the number of columns when returning large results. - Use CustomerID, ProductID, OrderID, and ItemID as anchor fields for linking data. - Apply grouping only when needed and specify numeric fields for aggregations. ## Efficiency Principles - Apply WHERE conditions before JOIN-like operations. - Avoid heavy operations on large sheets without filters. - Pull only the columns needed for the user’s question.
Example input:
# Test Prompts for Validating the Project Setup Use these prompts to confirm that Claude understands your sheet structure and uses Connect AI correctly. 1. From Google Sheets, list all sheets in the dataset. 2. Show orders with the customer name included. 3. Explain the ERD for this project. 4. Show revenue per product. 5. Show all orders placed in the last 24 hours. 6. Show customers who have never placed an order. 7. Show total quantity purchased per product. 8. Show inventory items with stock below 20. 9. Show top 5 customers by total purchase value. 10. Show all order items grouped by product name.
Example input:
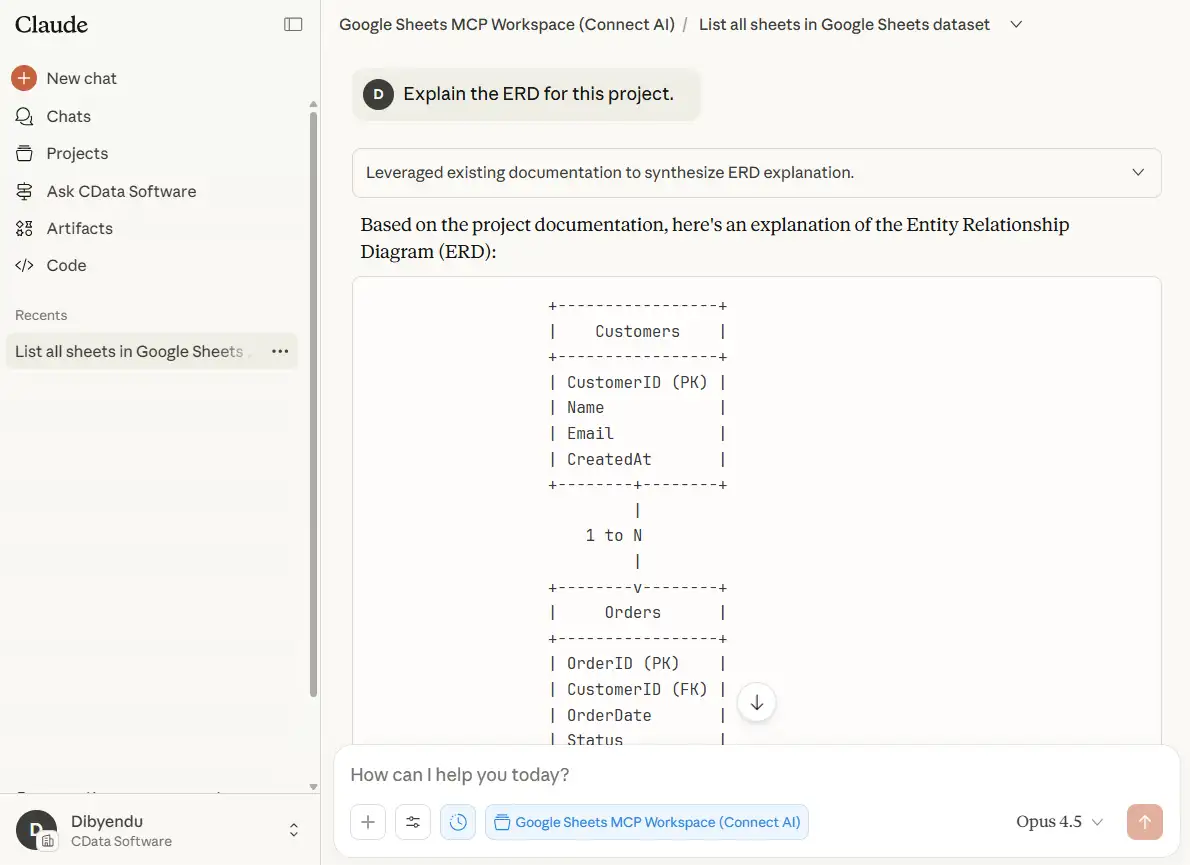
+-----------------+
| Customers |
+-----------------+
| CustomerID (PK) |
| Name |
| Email |
| CreatedAt |
+--------+--------+
|
1 to N
|
+--------v--------+
| Orders |
+-----------------+
| OrderID (PK) |
| CustomerID (FK) |
| OrderDate |
| Status |
+--------+--------+
|
1 to N
|
+--------v-----------+
| OrderItems |
+--------------------+
| ItemID (PK) |
| OrderID (FK) |
| ProductID (FK) |
| Quantity |
+--------+-----------+
|
N to 1
|
+--------v--------+
| Products |
+-----------------+
| ProductID (PK) |
| Name |
| Price |
+--------+--------+
|
1 to 1
|
+--------v--------+
| Inventory |
+-----------------+
| ProductID (PK) |
| Stock |
+-----------------+
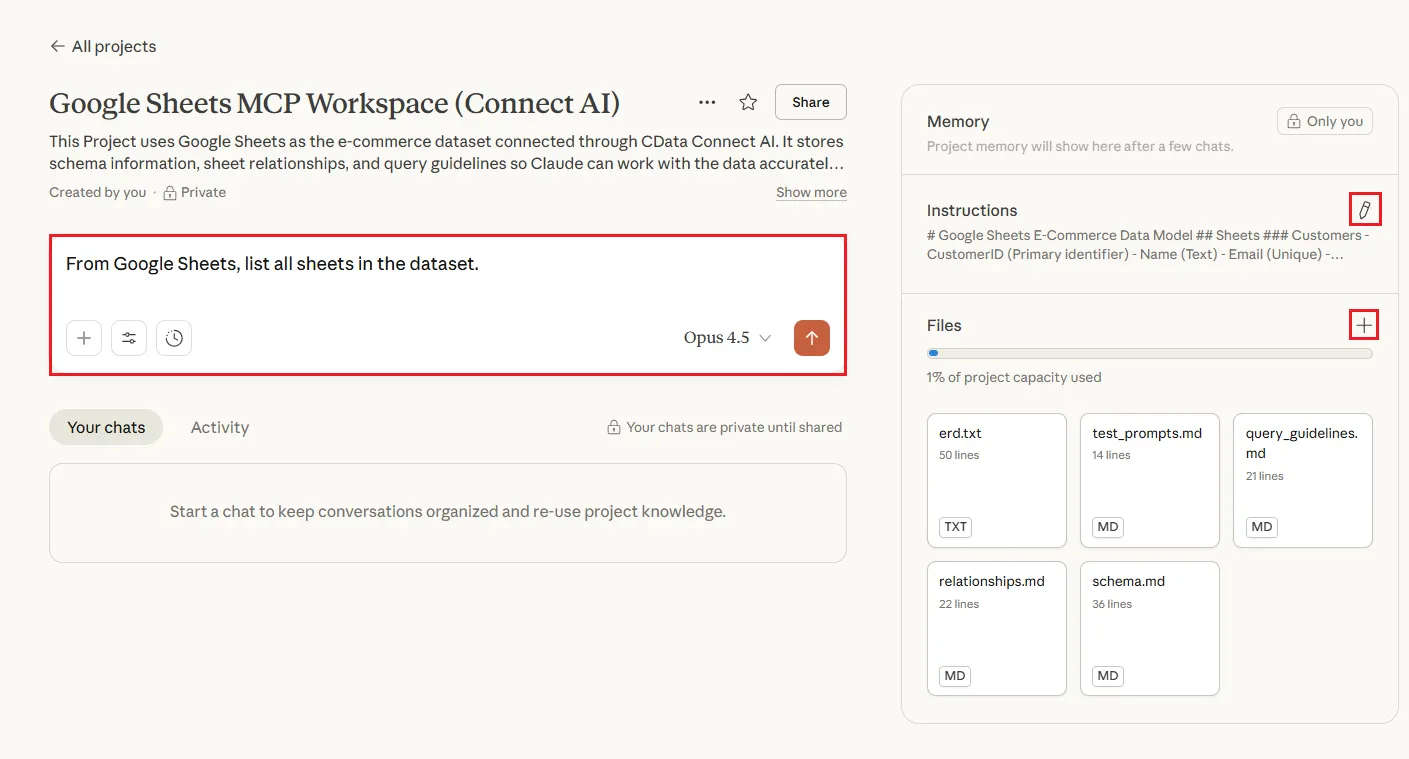
Together, these files create a complete knowledge layer for Claude.
What Claude can do after you add context
Once Claude has your Project instructions, files, and CData Connect AI connection, it can:
- Join your sheets correctly without guessing
- Use accurate column names
- Avoid inefficient full-sheet reads
- Apply your filtering and performance guidelines
- Interpret your sheet structure
- Explain your schema using the ERD
- Generate structured queries that reflect Connect AI’s capabilities
Claude uses your Project context before interacting with Google Sheets, which leads to more reliable and precise results.
Step 5: Test the Project
Run the following prompts inside your Project to confirm everything is working as intended:
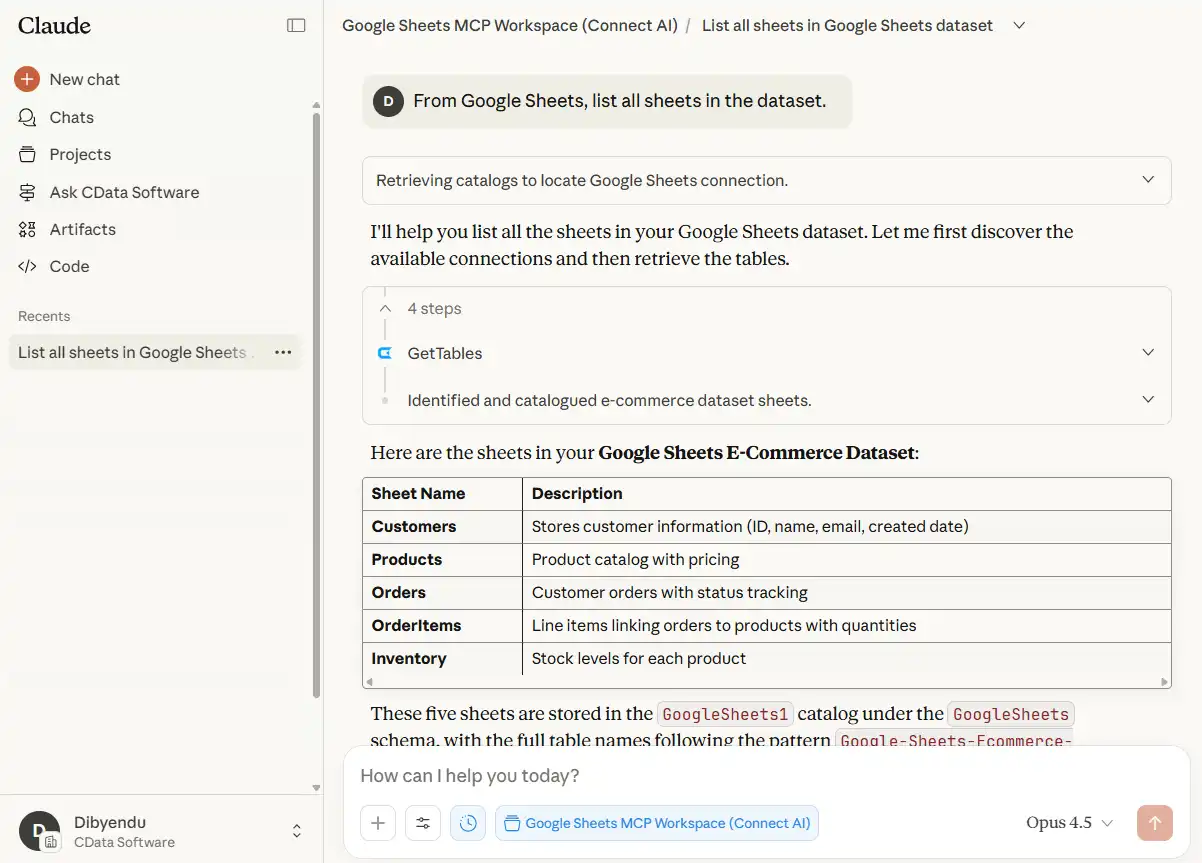
- "From Google Sheets, list all sheets in the dataset."
Claude should return all of your tabs and describe them accurately.
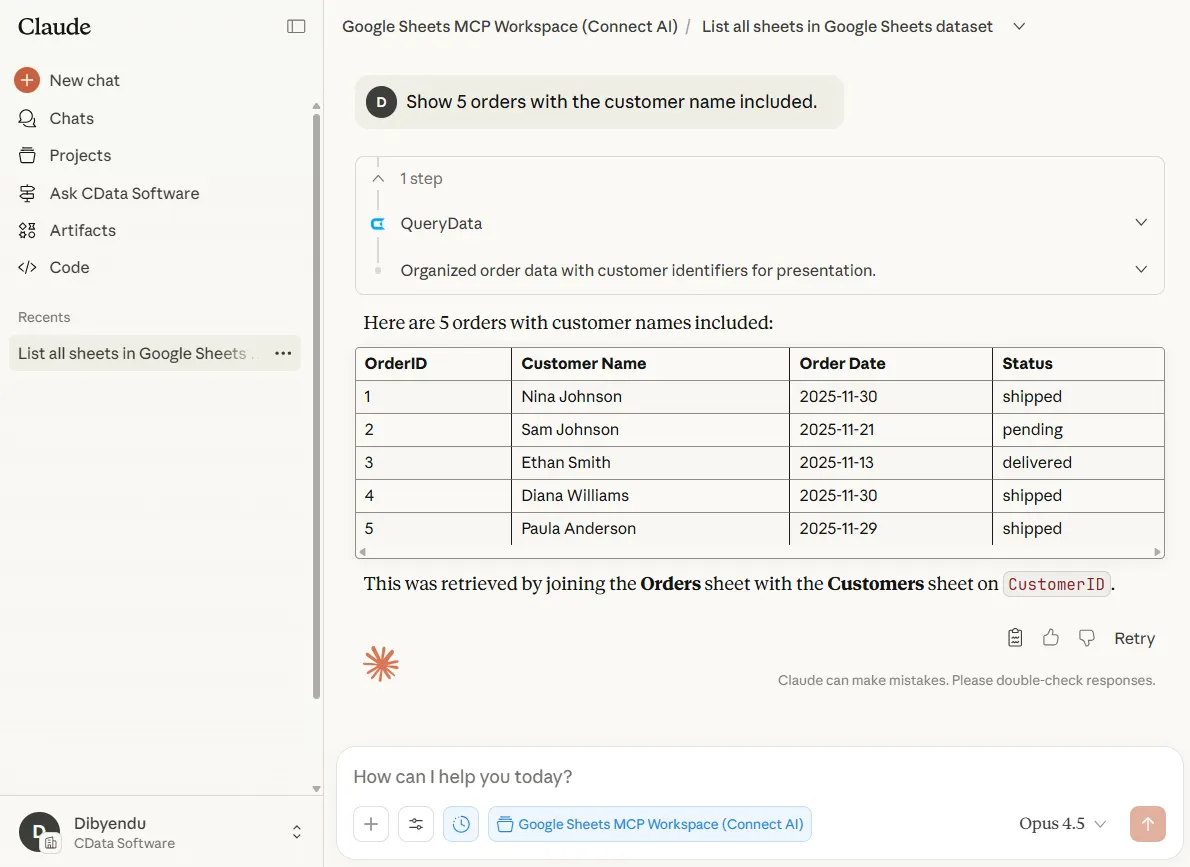
- "Show orders with the customer name included."
Claude should reference the correct sheet names and relationships.
- "Explain the ERD for this project."
Claude should refer to the ASCII diagram in erd.txt.
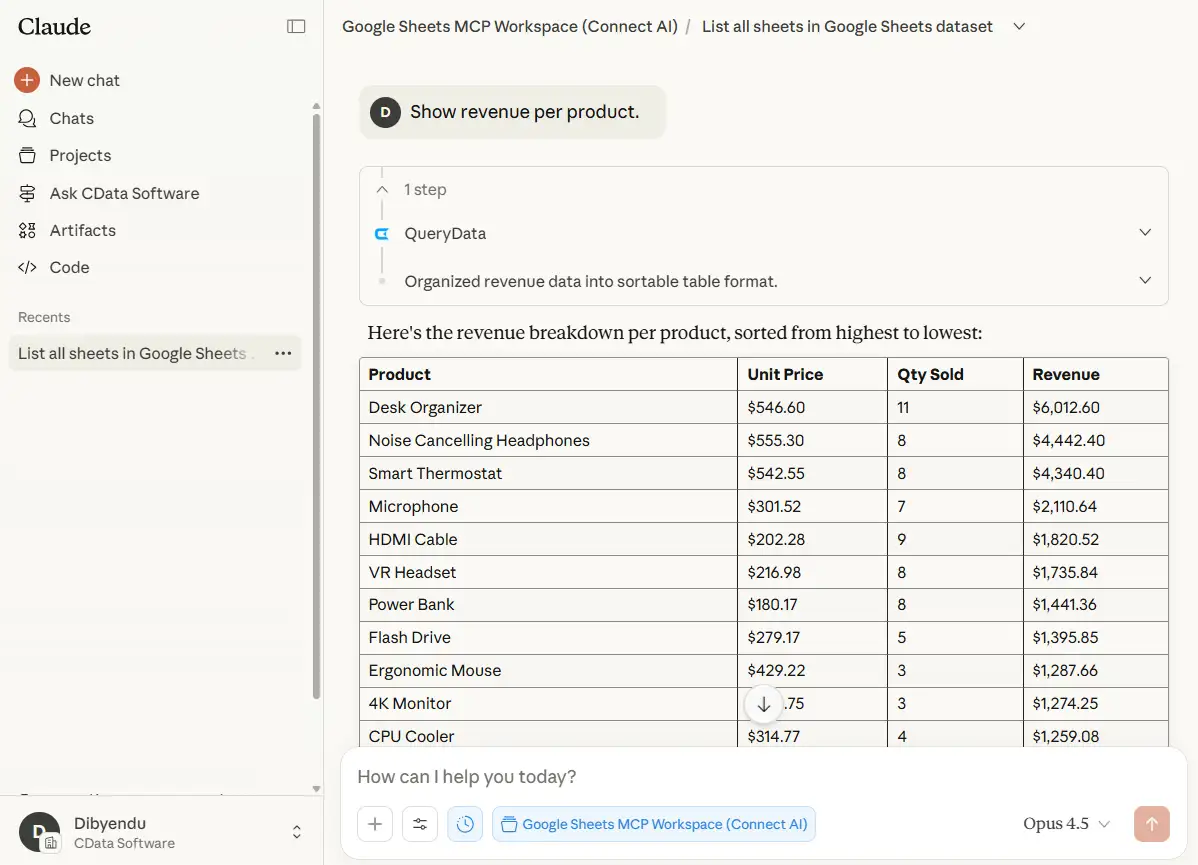
- "Show revenue per product."
Claude should use correct references, including Prices and OrderItems.
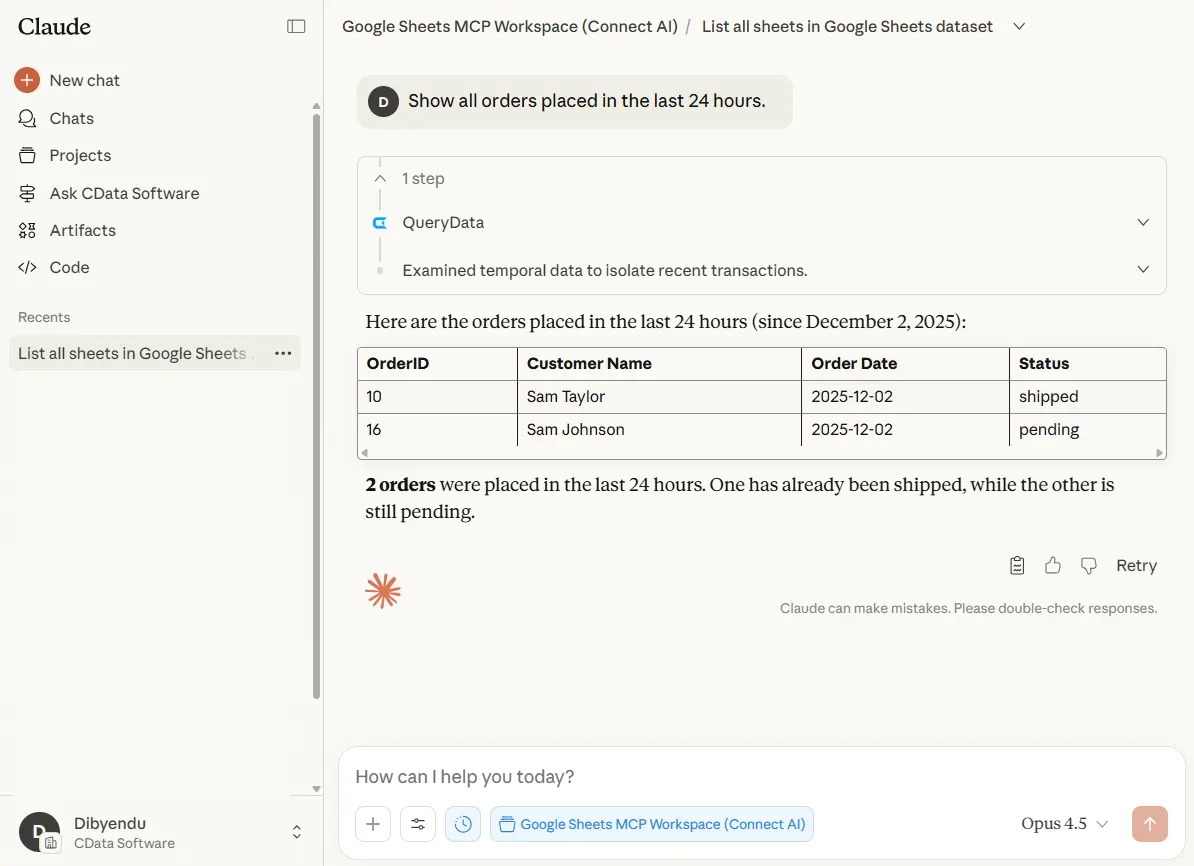
- "Show all orders placed in the last 24 hours."
Claude should filter on OrderDate using a time range and avoid reading the entire sheet.
Optimize your query accuracy with Claude Projects and CData Connect AI
Claude Projects works with CData Connect AI to provide a flexible, effective way to interact with data sources, even when their structures change. By storing your schema information inside a Project and using Connect AI to access your live data, you create a reliable environment where Claude understands your structure from the start.
To get live data access to 300+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your cloud applications, try CData Connect AI today!





