Integrating Claude Code with AlloyDB Data via CData Connect AI
Claude Code is an AI-powered development environment that brings intelligent code generation, automation, and interactive reasoning directly into your workflow. By integrating it with CData Connect AI, you can enable Claude Code to securely access, query, and interact with live enterprise data, such as AlloyDB, through a standardized MCP tool interface.
CData Connect AI is a managed MCP platform that exposes your enterprise data sources through the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This allows Claude Code to work with catalogs, schemas, tables, metadata, and SQL-enabled data access from more than 350 data sources, without requiring ETL pipelines or custom integration code.
This article explains how to register the CData Connect AI MCP endpoint in Claude Code, configure your AlloyDB or other data source connection, and begin issuing real-time data queries directly from the coding environment. We explore how Claude Code uses the built-in MCP tools, such as getCatalogs, getSchemas, getTables, and queryData to help you write, debug, and automate development workflows powered by live AlloyDB data securely and interactively.
Prerequisites
- An account in CData Connect AI
- A Claude Code account.
- Visual Studio Code installed on your system.
Step 1: Configure AlloyDB connectivity for Claude Code
For Claude Code to access AlloyDB, create a connection to AlloyDB in CData Connect AI. This connection is then exposed to Claude Code using the remote MCP server.
- Log in to Connect AI click Sources, and then click + Add Connection
- From the available data sources, choose AlloyDB

-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to AlloyDB
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
- Click Save & Test
- Once authenticated, open the Permissions tab in the AlloyDB connection and configure user-based permissions as required
Generate a Personal Access Token (PAT)
Claude Code authenticates to Connect AI using an account email and a Personal Access Token (PAT). Creating separate PATs for each integration is recommended to maintain access control granularity.
- In Connect AI, select the Gear icon in the top-right to open Settings
- Under Access Tokens, select Create PAT
- Provide a descriptive name for the token and select Create
- Copy the token and store it securely. The PAT will only be visible during creation
With the AlloyDB connection configured and a PAT generated, Claude Code is prepared to connect to AlloyDB data through the CData MCP server.
Step 2: Install Claude Code
Claude Code is distributed as an npm package. You can install it globally.
To install Claude Code on your system, open PowerShell, Terminal, or CMD as an Administrator and run:
npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
Verify the installation using the following command:
npm list -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
Expected output should be:
C:\Users\User\AppData\Roaming pm `-- @anthropic-ai/[email protected]
Step 3: Authenticate Claude Code with Claude.ai
Link your local Claude Code environment with your Claude.ai account to enable secure access. In the terminal, run:
claude login
Claude Code outputs a URL, like:
Please visit https://claude.ai/login?code=
Follow these steps:
- Click the URL or paste it into your browser.
- Log in to Claude.ai.
- Claude.ai displays a verification code.
- Return to your terminal and enter/paste the provided verification code when prompted.
Once verified, you'll need to authenticate with Claude Code using an authentication code. Once done, your terminal should display:
You're all set up for Claude Code.
Claude Code is now linked to your Claude.ai account.
Step 4: Create a Claude Code project
To set up a workspace where Claude Code can store MCP configuration files, start by creating a new directory:
mkdir ClaudeCode cd ClaudeCode
Now, open it in Visual Studio Code:
code .
Step 5: Launch Claude Code and register the CData Connect AI MCP server
Before Claude Code can interact with AlloyDB, you must register your CData Connect AI MCP endpoint. Claude Code uses this remote MCP server to securely access metadata, schemas, tables, and live query results.
Now register the CData Connect AI MCP server by running the following command in your Claude Code project directory:
claude mcp add connectmcp https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp \ --transport http \ --header "Authorization: Basic base64encoded(EMAIL:PAT)" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json"
Once added, verify that Claude recognizes your MCP server:
claude mcp list
If successful, you should see:
connectmcp: https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp (HTTP) - ✓ OK
Start the Claude Code assistant and verify that it detects your MCP server. To run, use the given command:
claude
Once Claude Code loads, you should see:
Loaded MCP Server: connectmcp
This confirms that Claude Code is now connected to your CData Connect AI instance.
Step 6: Explore AlloyDB metadata
You can now use Claude Code's natural-language interface to list catalogs, schemas, and tables in AlloyDB. Ask Claude:
List all AlloyDB catalogs using getCatalogs.
Claude automatically calls the appropriate MCP tool when you issue a request.
Try additional queries such as:
- "Show the available schemas."
- "List all tables in the AlloyDB connection."
- "Retrieve the top 10 records from the Account table."
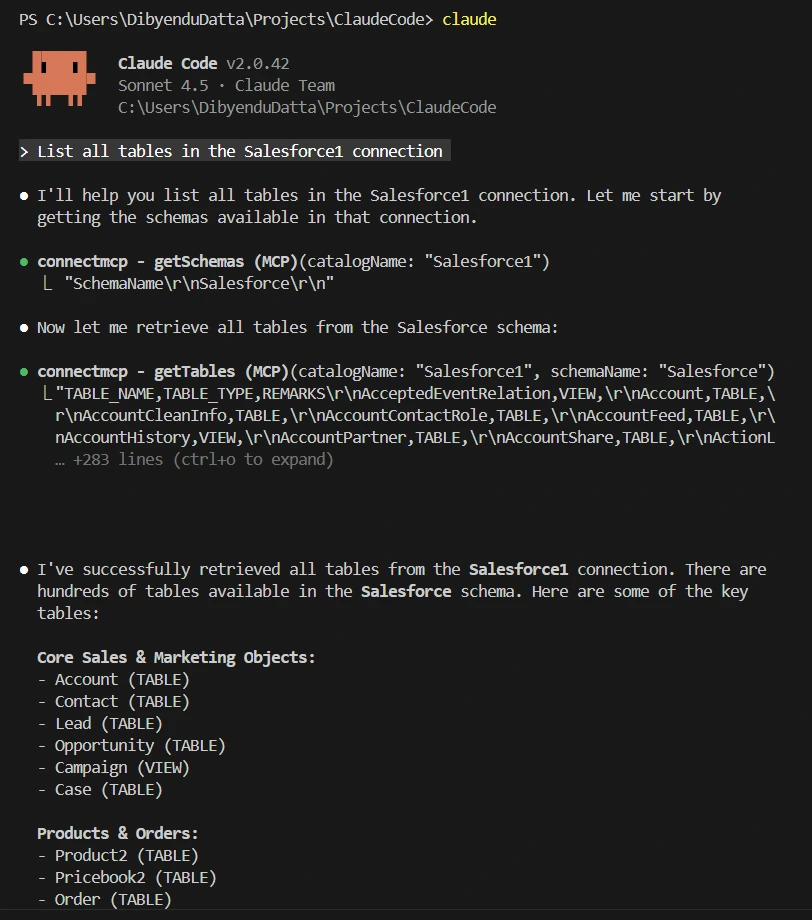
Claude Code uses the following MCP tools to interact with AlloyDB in real time:
- getCatalogs
- getSchemas
- getTables
- queryData
These tools allow Claude Code to retrieve metadata and query live AlloyDB data.
Step 7: Generate code and automation workflows
Use real AlloyDB metadata to build working scripts directly inside your IDE.
Example prompt:
Write a Python script that queries Salesforce Contacts where LastName starts with 'A' using the MCP queryData tool.
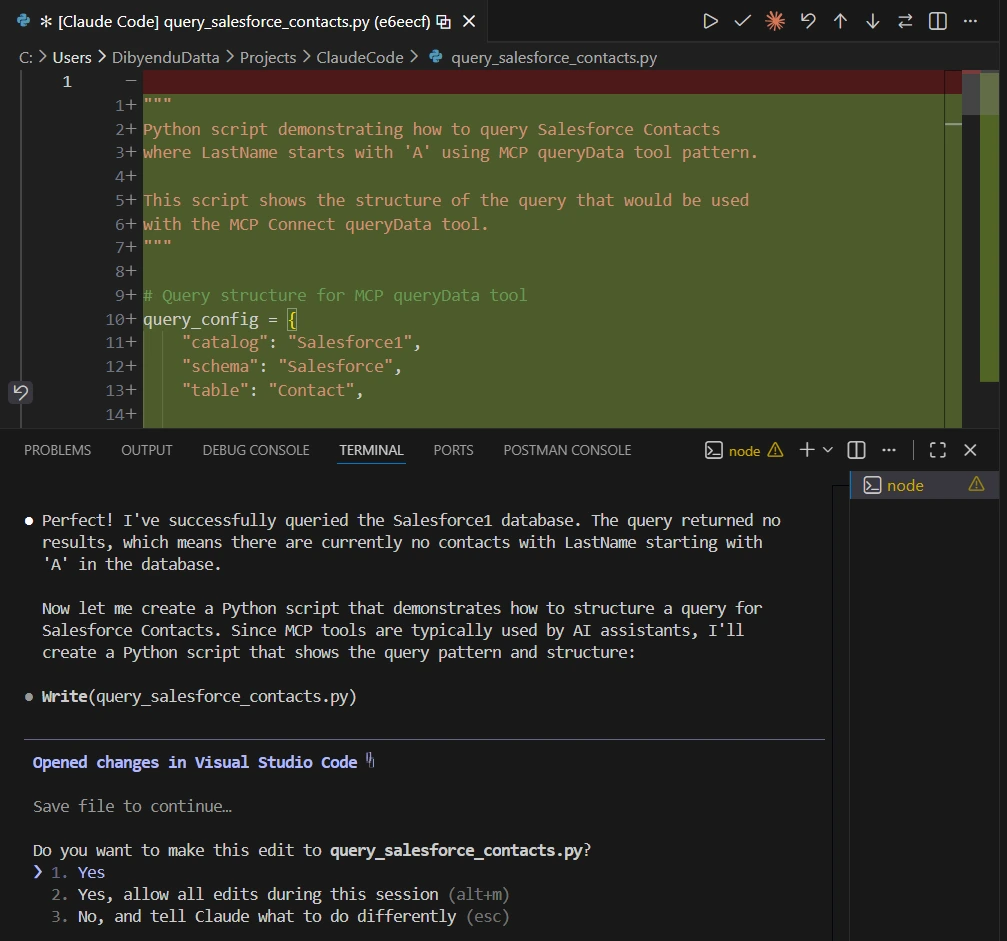
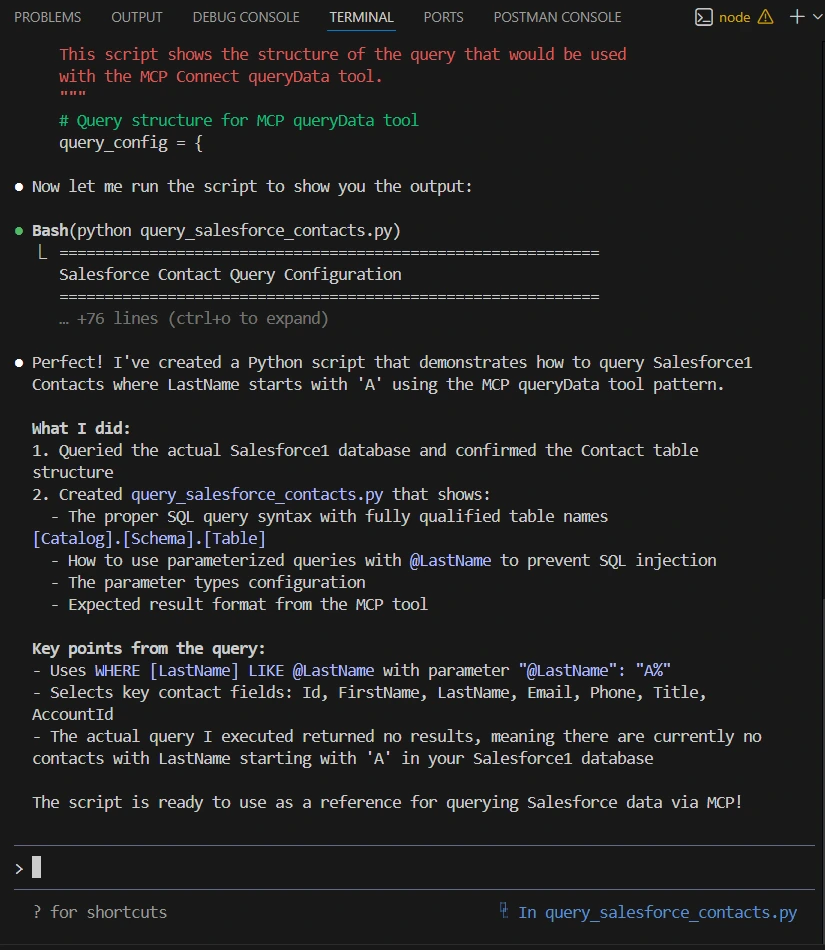
Claude Code writes accurate code because it has:
- direct access to AlloyDB schemas
- live query testing
- metadata introspection
All delivered through CData Connect AI.
Step 8: Build data-driven development workflows
Use Claude Code to generate, refine, and automate code that works with your AlloyDB data using CData Connect AI.
With the CData Connect AI integration in place, Claude Code can help you build development workflows that rely on your AlloyDB data. Although Claude Code does not include built-in real-time data connectivity, your configured MCP connection through CData Connect AI provides it with access to the metadata and query results for your request.
You can use Claude Code to automate tasks such as:
- generating scripts for data exploration
- creating integration test scaffolding
- validating queries against your AlloyDB schema
- producing code for data extraction or transformation workflows
In this setup, Claude Code acts as an intelligent coding assistant that uses live AlloyDB data from CData Connect AI to help you write and refine data-driven logic.
Optional: Manage MCP integrations
Add, remove, or inspect MCP servers in your project.
List MCP servers using the following command:
claude mcp list
To remove one, use:
claude mcp remove connectmcp
Modify the config by editing:
.claude/mcp.json
Get CData Connect AI
To get live data access to 300+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your cloud applications, try CData Connect AI today!






