How to Connect to Live AlloyDB Data from Gemini CLI (via CData Connect AI)
Gemini CLI is a command-line interface tool that provides direct access to Google's Gemini AI models for code generation, text analysis, and conversational AI capabilities. When combined with CData Connect AI Remote MCP, you can leverage Gemini CLI to interact with your AlloyDB data in real-time through natural language queries. This article outlines the process of connecting to AlloyDB using Connect AI Remote MCP and configuring Gemini CLI to interact with your AlloyDB data.
CData Connect AI offers a dedicated cloud-to-cloud interface for connecting to AlloyDB data. The CData Connect AI Remote MCP Server enables secure communication between Gemini CLI and AlloyDB. This allows you to ask questions and take actions on your AlloyDB data using natural language through Gemini CLI, all without the need for data replication to a natively supported database. With its inherent optimized data processing capabilities, CData Connect AI efficiently channels all supported SQL operations, including filters and JOINs, directly to AlloyDB. This leverages server-side processing to swiftly deliver the requested AlloyDB data.
In this article, we show how to configure Gemini CLI to conversationally explore (or Vibe Query) your data using natural language. With Connect AI you can query and interact with live AlloyDB data, plus hundreds of other sources.
Step 1: Configure AlloyDB Connectivity for Gemini CLI
Connectivity to AlloyDB from Gemini CLI is made possible through CData Connect AI Remote MCP. To interact with AlloyDB data from Gemini CLI, we start by creating and configuring a AlloyDB connection in CData Connect AI.
- Log into Connect AI, click Sources, and then click Add Connection
- Select "AlloyDB" from the Add Connection panel
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to AlloyDB.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
- Click Save & Test
-
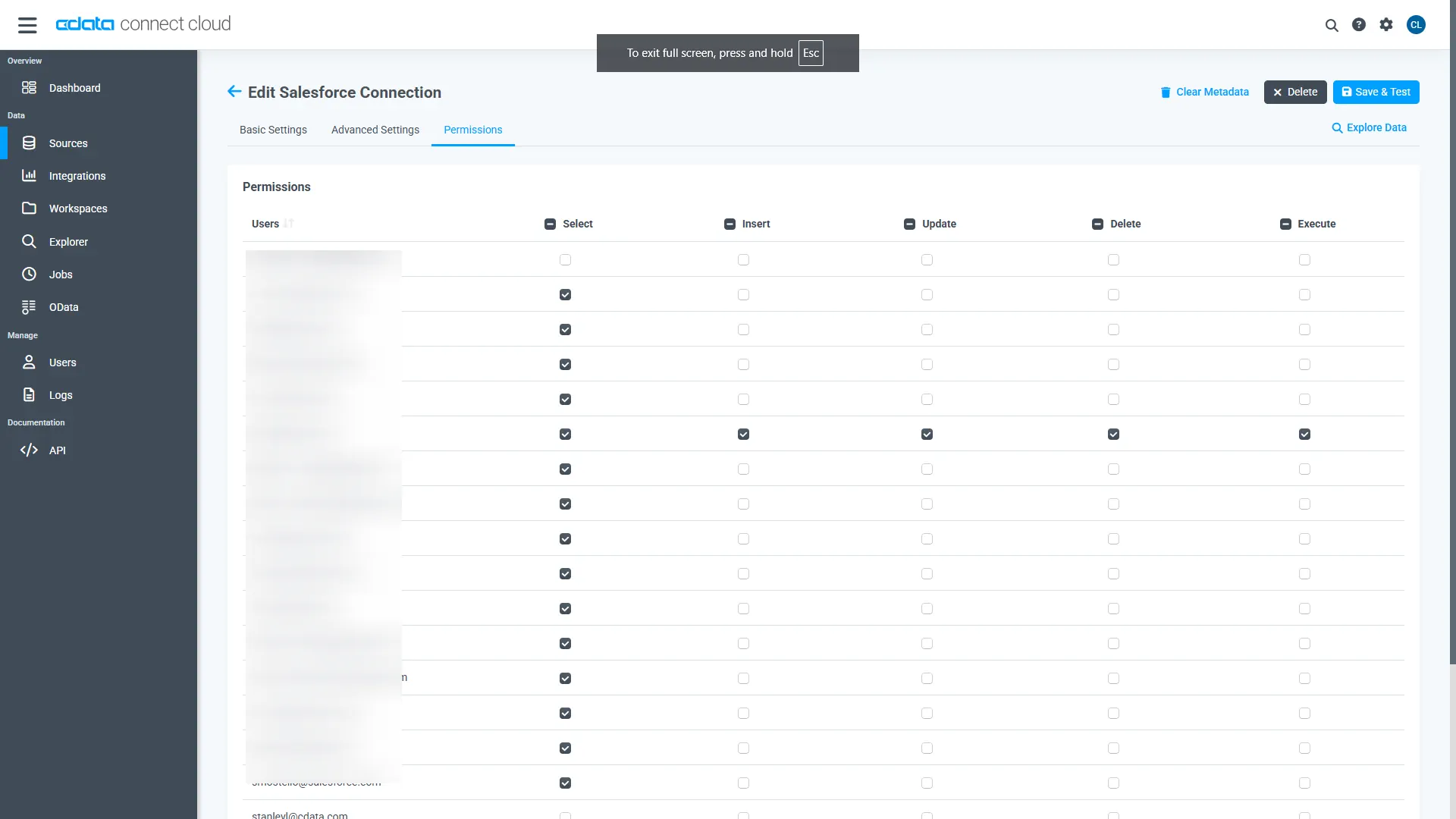
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add AlloyDB Connection page and update the User-based permissions.

Add a Personal Access Token
A Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect AI from Gemini CLI. It is best practice to create a separate PAT for each service to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on the Gear icon () at the top right of the Connect AI app to open the settings page.
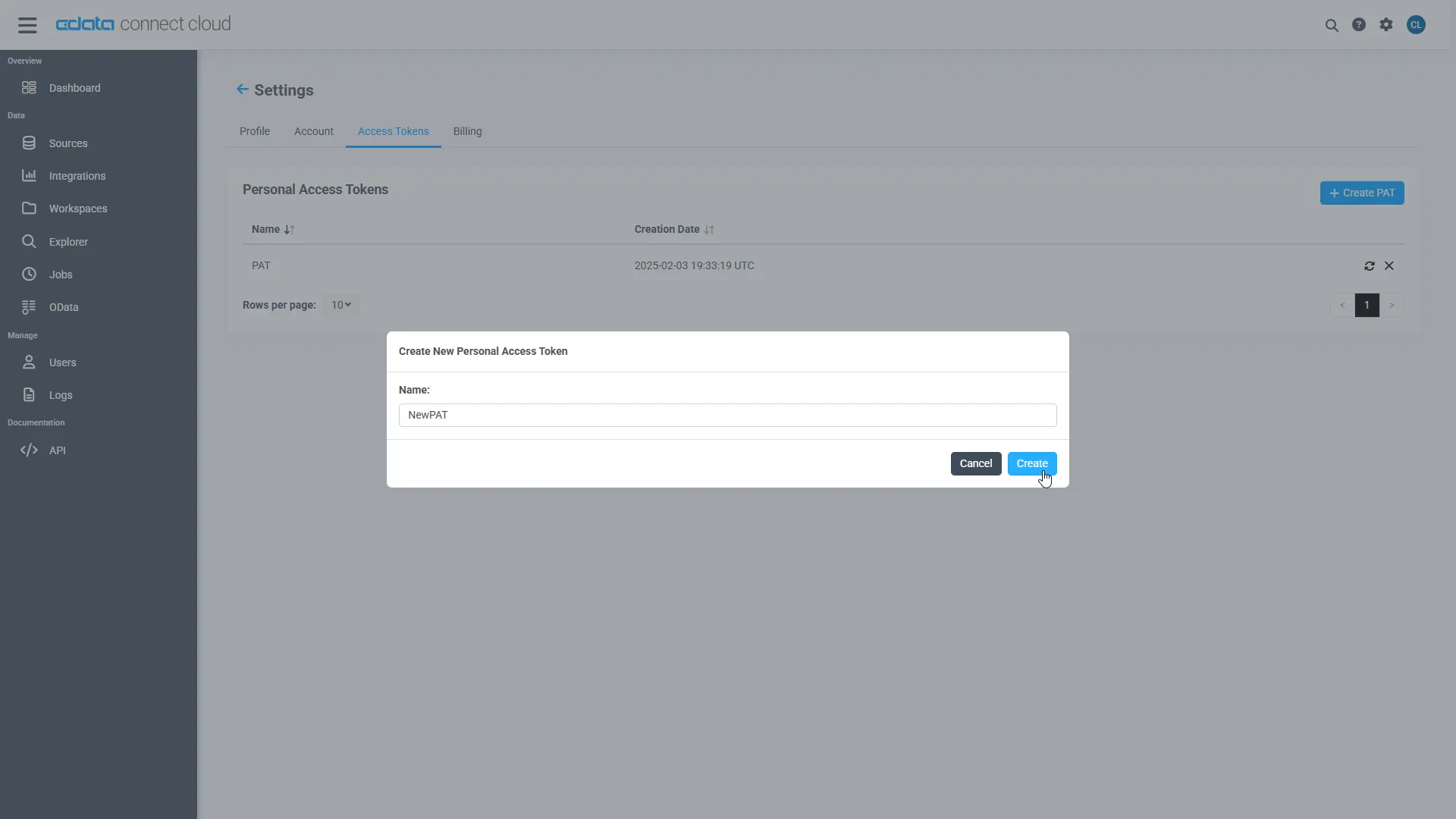
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
-
Give the PAT a name and click Create.
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured and a PAT generated, we are ready to connect to AlloyDB data from Gemini CLI.
Step 2: Configure Gemini CLI for CData Connect AI
Follow these steps to configure Gemini CLI to connect to CData Connect AI:
-
Ensure Gemini CLI is installed on your system. If not, install it using npm:
npm install -g @google-gemini/cli
-
Locate your Gemini CLI settings file. If the file doesn't exist, create it:
- Linux/Unix/Mac: ~/.gemini/settings.json
- Windows: %USERPROFILE%\.gemini\settings.json
-
Add the CData Connect AI Remote MCP Server to the mcpServers object in your settings file. Replace YOUR_EMAIL and YOUR_PAT with your Connect AI email address and the PAT created previously:
{ "mcpServers": { "cdata-connect-cloud": { "httpUrl": "https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp", "headers": { "Authorization": "Basic YOUR_EMAIL:YOUR_PAT" } } } }For example, if your email is [email protected] and your PAT is Uu90pt5vEO..., the Authorization header would be:"Authorization": "Basic [email protected]:Uu90pt5vEO..."
- Save the settings file. Gemini CLI will now use the CData Connect AI MCP Server for data operations.
Step 3: Query Live AlloyDB Data with Natural Language
With Gemini CLI configured and connected to CData Connect AI, you can now interact with your AlloyDB data using natural language queries. The MCP integration allows you to ask questions and receive responses from the AlloyDB data source in real-time.
Start using Gemini CLI to explore your data:
-
Open your terminal and start a Gemini CLI session:
gemini
-
You can now use natural language to query your AlloyDB data. For example:
- "Show me all customers from the last 30 days"
- "What are my top performing products?"
- "Analyze sales trends for Q4"
- "List all active projects with their current status"
- Gemini CLI will automatically translate your natural language queries into appropriate SQL queries and execute them against your AlloyDB data through the CData Connect AI MCP Server.
The combination of Gemini CLI's natural language processing capabilities and CData Connect AI's robust data connectivity enables you to explore and analyze your AlloyDB data without writing complex SQL queries or needing deep technical knowledge of the underlying data structure.
Get CData Connect AI
To get live data access to 300+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your cloud applications, try CData Connect AI today!






