Connecting Agentforce with Amazon Athena Data via CData Connect AI MCP Server
Agentforce is built for enterprise teams. Its declarative tooling and API-first architecture make it straightforward to compose assistants and automate CRM-centric workflows. But when agents need to work with data beyond Amazon Athena data, many implementations fall back on periodic syncs or bespoke middleware to replicate external systems into local stores. That adds complexity, creates governance and maintenance overhead, introduces sync delays, and limits the real-time potential of your agents.
CData Connect AI fills this gap with direct, live connectivity to 300+ enterprise apps, databases, ERPs, and finance platforms. Using CData's remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server, Agentforce agents can securely read, write, and act on fresh, contextual data at runtime; no replication required. The result is grounded responses, real-time decisions, and cross-system automations with fewer moving parts and stronger control.
This article outlines the steps required to configure Amazon Athena connectivity in Connect AI, register the MCP server in Agentforce, and build a workflow that queries Amazon Athena data data.
About Amazon Athena Data Integration
CData provides the easiest way to access and integrate live data from Amazon Athena. Customers use CData connectivity to:
- Authenticate securely using a variety of methods, including IAM credentials, access keys, and Instance Profiles, catering to diverse security needs and simplifying the authentication process.
- Streamline their setup and quickly resolve issue with detailed error messaging.
- Enhance performance and minimize strain on client resources with server-side query execution.
Users frequently integrate Athena with analytics tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Excel for in-depth analytics from their preferred tools.
To learn more about unique Amazon Athena use cases with CData, check out our blog post: https://www.cdata.com/blog/amazon-athena-use-cases.
Getting Started
Prerequisites:
- CData Connect AI account
- Install Python 3.9+
- Amazon Athena data org with Agentforce enabled and permission to create/manage Connected Apps
Credentials Checklist:
Before you begin, you'll need a few credentials mentioned below:
CData Connect AI MCP:
- USERNAME: Your CData email login
- PAT: Connect AI, go to Settings and click on Access Tokens (copy once)
- MCP_BASE_URL: https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp
- MCP_AUTH: Base64 encoded (EMAIL:PAT), where EMAIL is your Connect AI email address and PAT is your Connect AI personal access token (see below).
Note: You can create the base64 encoded version of MCP_AUTH using any Base64 encoding tool.
Agentforce:
- SFDC_DOMAIN: My Domain URL (https://your_domain.my.salesforce.com)
- SFDC_CLIENT_ID & SFDC_CLIENT_SECRET: from your Connected App
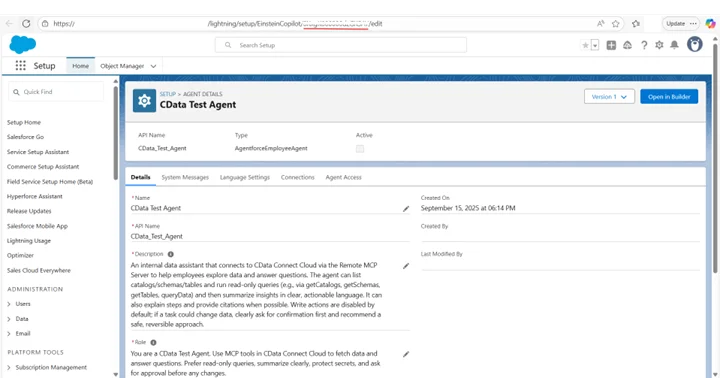
- AGENT_ID: open your agent in Agentforce Agents and copy the 18-char ID at the end of the URL
Step 1: Configure Amazon Athena Connectivity for Agentforce
Connectivity to Amazon Athena from Agentforce is made possible through CData Connect AI Remote MCP. To interact with Amazon Athena data from Agentforce, we start by creating and configuring a Amazon Athena connection in CData Connect AI.
- Log into Connect AI, click Sources, and then click Add Connection
- Select "Amazon Athena" from the Add Connection panel
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Amazon Athena.
Authenticating to Amazon Athena
To authorize Amazon Athena requests, provide the credentials for an administrator account or for an IAM user with custom permissions: Set AccessKey to the access key Id. Set SecretKey to the secret access key.
Note: Though you can connect as the AWS account administrator, it is recommended to use IAM user credentials to access AWS services.
Obtaining the Access Key
To obtain the credentials for an IAM user, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the IAM console.
- In the navigation pane, select Users.
- To create or manage the access keys for a user, select the user and then select the Security Credentials tab.
To obtain the credentials for your AWS root account, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the AWS Management console with the credentials for your root account.
- Select your account name or number and select My Security Credentials in the menu that is displayed.
- Click Continue to Security Credentials and expand the Access Keys section to manage or create root account access keys.
Authenticating from an EC2 Instance
If you are using the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 from an EC2 Instance and have an IAM Role assigned to the instance, you can use the IAM Role to authenticate. To do so, set UseEC2Roles to true and leave AccessKey and SecretKey empty. The CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 will automatically obtain your IAM Role credentials and authenticate with them.
Authenticating as an AWS Role
In many situations it may be preferable to use an IAM role for authentication instead of the direct security credentials of an AWS root user. An AWS role may be used instead by specifying the RoleARN. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to attempt to retrieve credentials for the specified role. If you are connecting to AWS (instead of already being connected such as on an EC2 instance), you must additionally specify the AccessKey and SecretKey of an IAM user to assume the role for. Roles may not be used when specifying the AccessKey and SecretKey of an AWS root user.
Authenticating with MFA
For users and roles that require Multi-factor Authentication, specify the MFASerialNumber and MFAToken connection properties. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to submit the MFA credentials in a request to retrieve temporary authentication credentials. Note that the duration of the temporary credentials may be controlled via the TemporaryTokenDuration (default 3600 seconds).
Connecting to Amazon Athena
In addition to the AccessKey and SecretKey properties, specify Database, S3StagingDirectory and Region. Set Region to the region where your Amazon Athena data is hosted. Set S3StagingDirectory to a folder in S3 where you would like to store the results of queries.
If Database is not set in the connection, the data provider connects to the default database set in Amazon Athena.
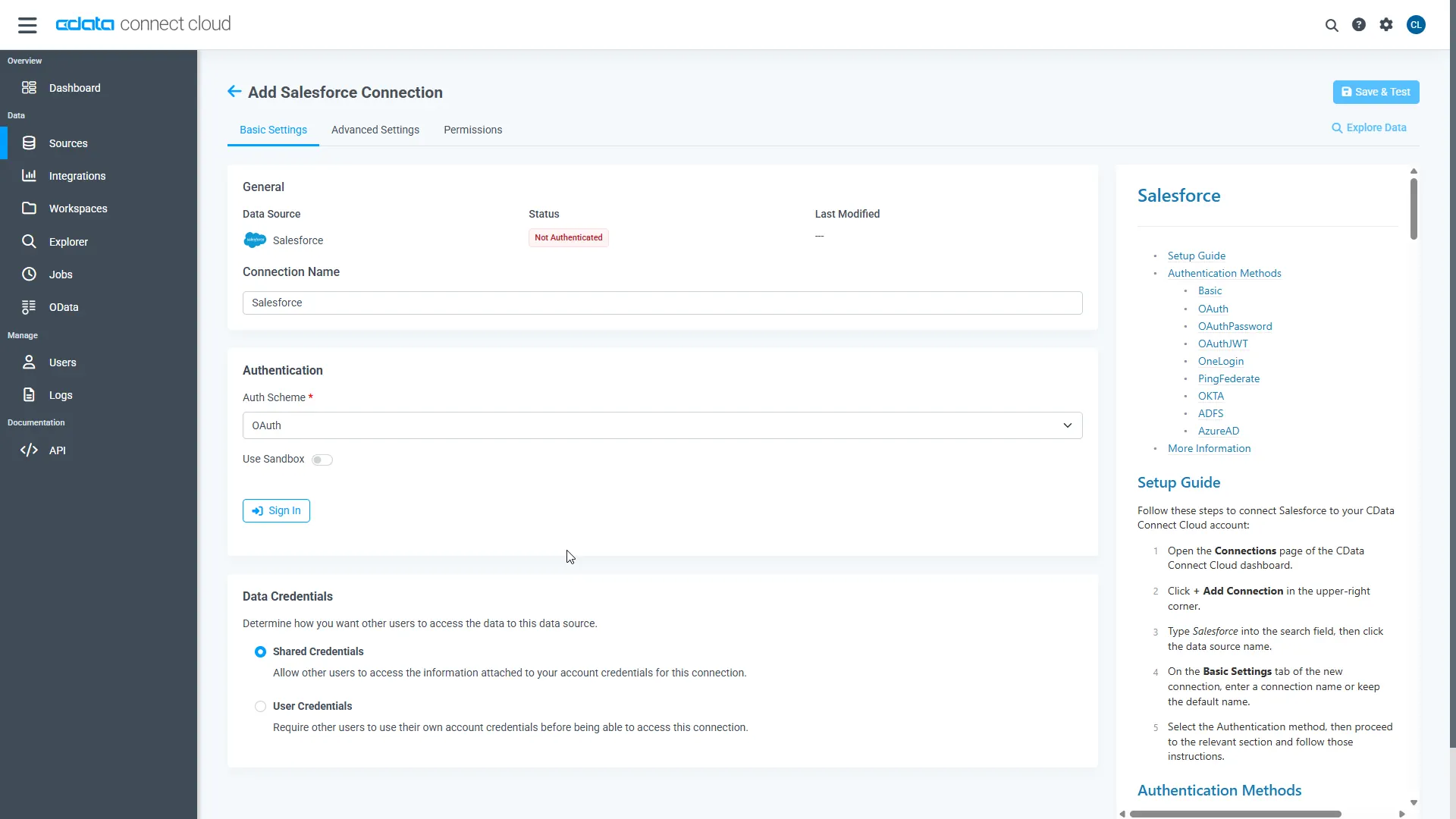
- Click Save & Test
-
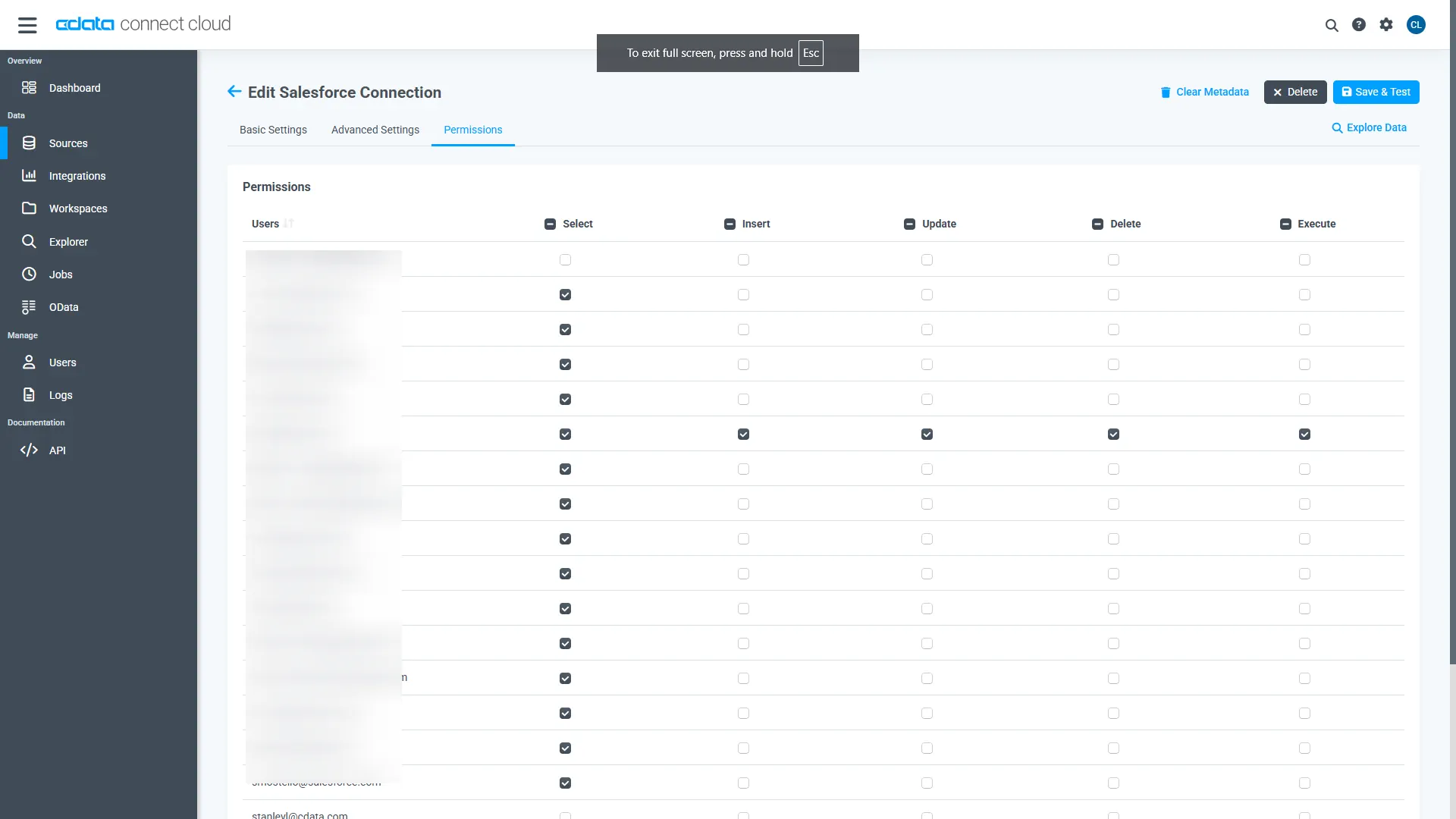
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add Amazon Athena Connection page and update the User-based permissions.

Add a Personal Access Token
A Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect AI from Agentforce. It is best practice to create a separate PAT for each service to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on the Gear icon () at the top right of the Connect AI app to open the settings page.
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
-
Give the PAT a name and click Create.
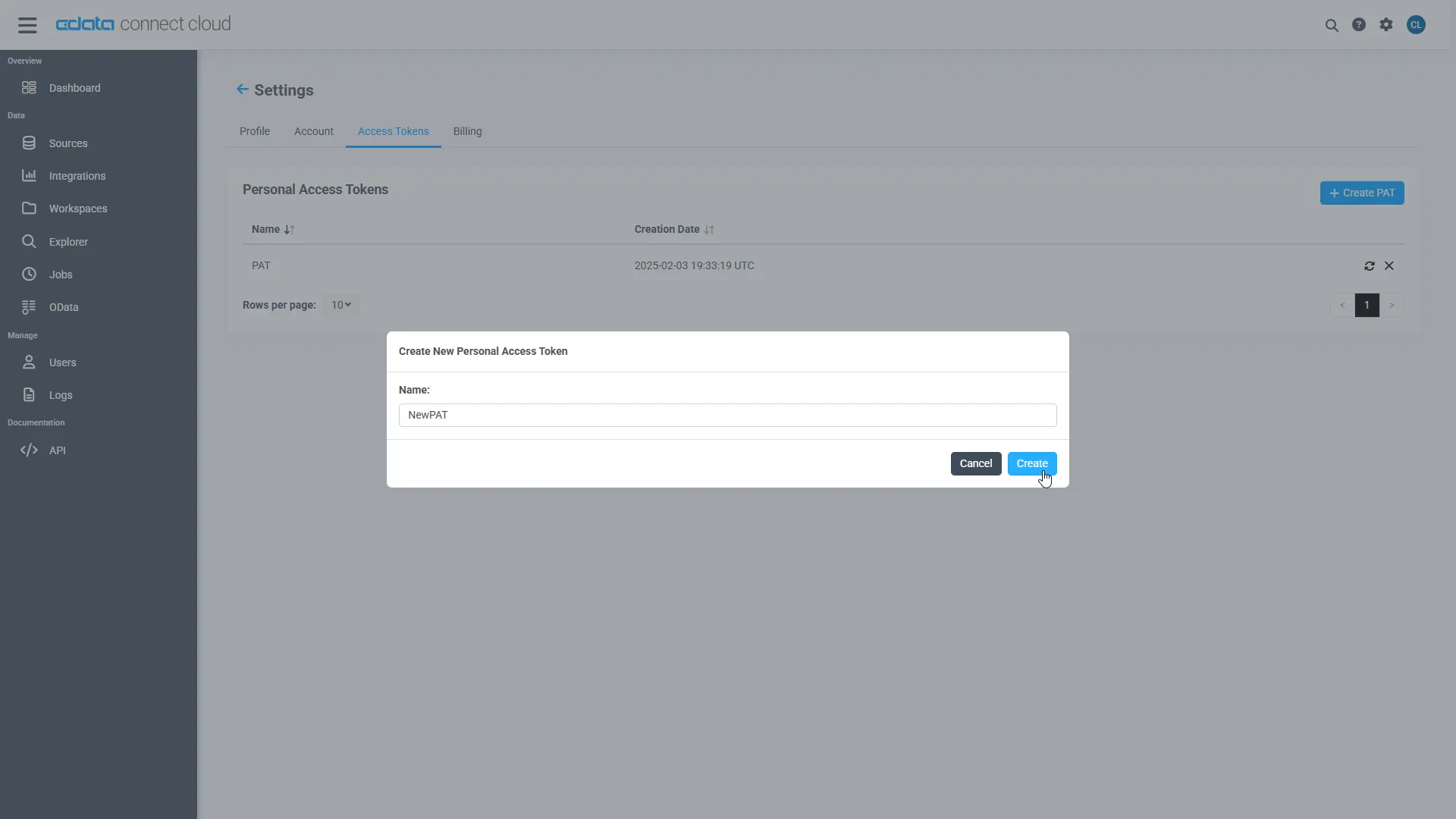
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured and a PAT generated, we are ready to connect to Amazon Athena data from Agentforce.
Step 2: Enable Agentforce and publish the Experience Cloud site
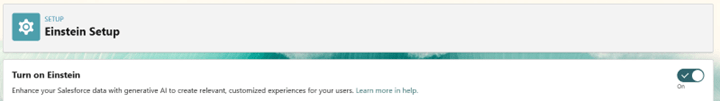
- In Salesforce Setup, go to Einstein Setup, toggle Turn on Einstein
- Go to Agentforce Agents, toggle Agentforce on
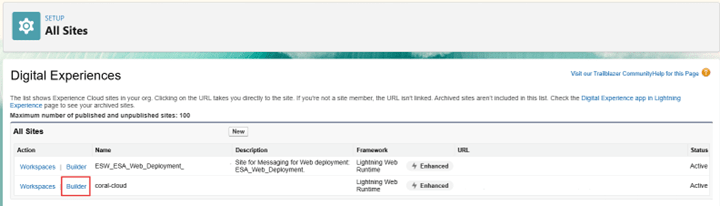
- Publish the Experience Cloud Site that hosts Coral Cloud: Setup, search for All Sites then select Builder (for coral-cloud) click Publish and Confirm
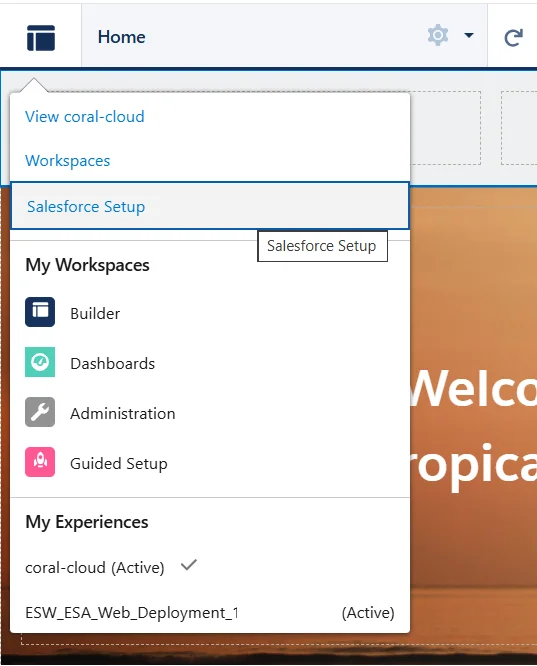
- Click the Experience Builder menu
- Click Salesforce Setup
- Refresh your browser to reload Setup. Feel free to close the Experience Site browser tab.

Step 3: Set up the EinsteinServiceAgent user and profile
- In the Setup Quick Find, search for and select Users
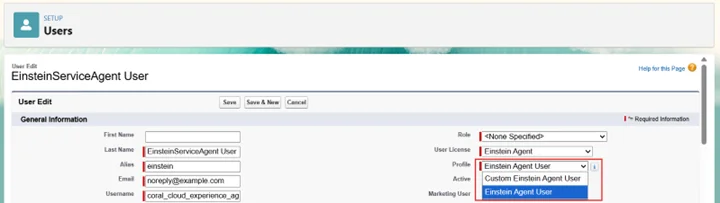
- Click Edit next to the EinsteinServiceAgent User
- Update the Profile to Einstein Agent User
- Keep everything else as-is
- Click Save
Step 4: Create the Agent and attach an external connection
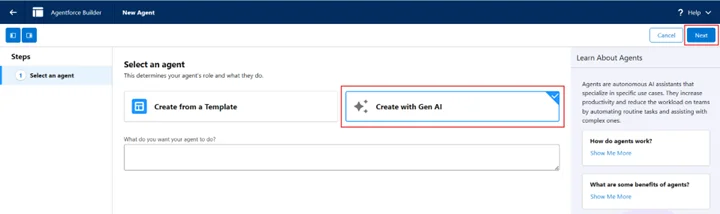
- Setup search for Agentforce Agents click New Agent
- Click Create with Gen AI
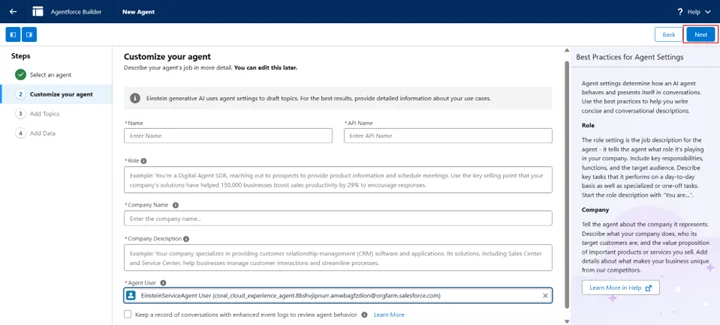
- Provide a summary, name, role, company info; set Agent User = EinsteinServiceAgent User
- Check Keep a record of conversations with enhanced event logs, and click Save
- Click Create
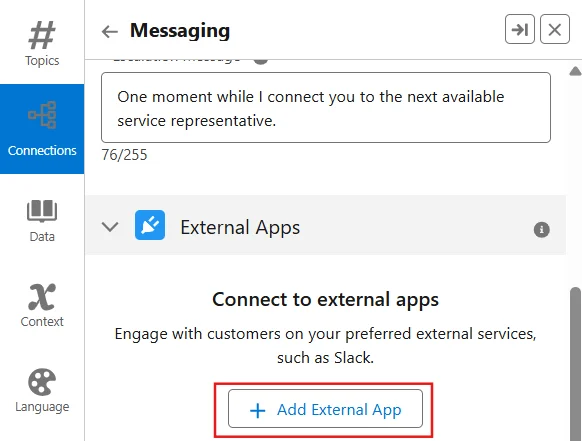
- Add Connections select Needs Setup click on Add External App
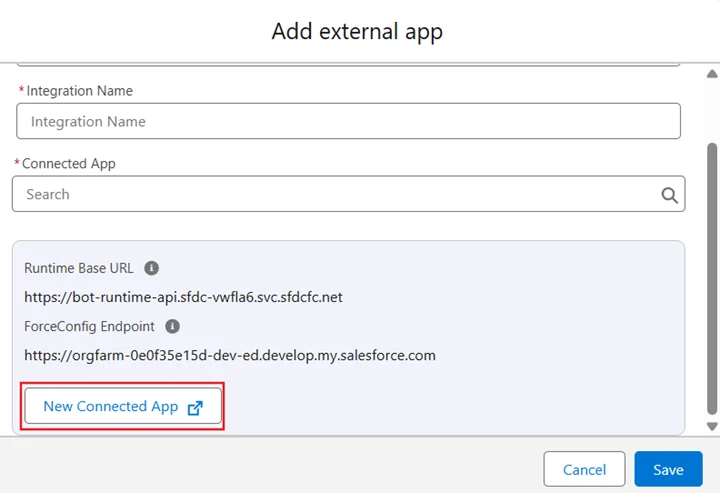
- Set Connection Type = API, and provide an Integration Name
- Click New Connected App (you'll configure it in the next step)
Step 5: Create and configure the Salesforce Connected App (Client Credentials)
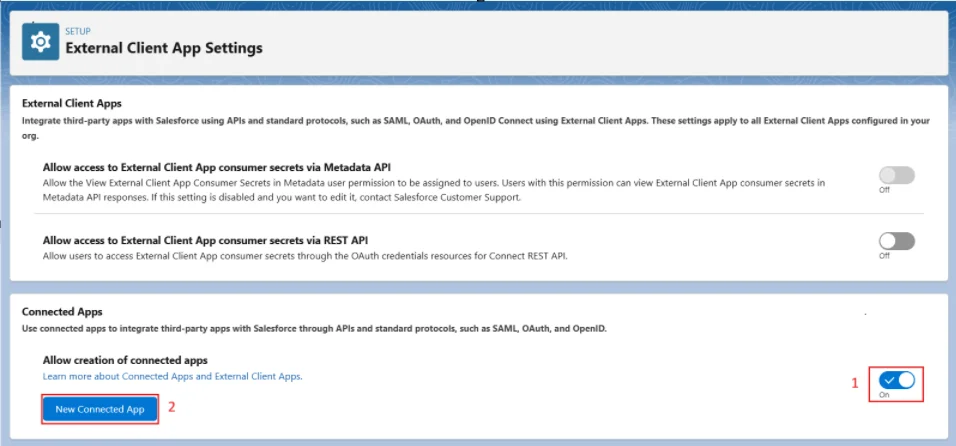
- Allow creation of Connected Apps
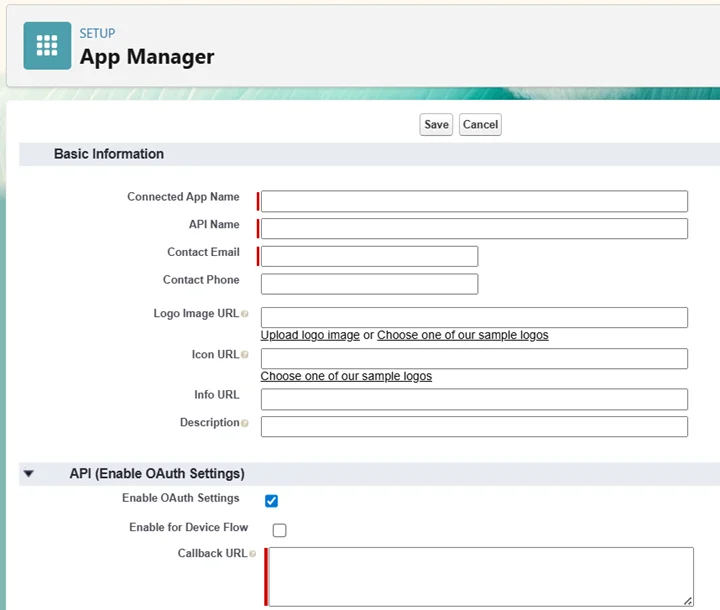
- Click on New Connected App and provide Name and Admin Email
- Enable OAuth Settings with Callback URL: https://login.salesforce.com
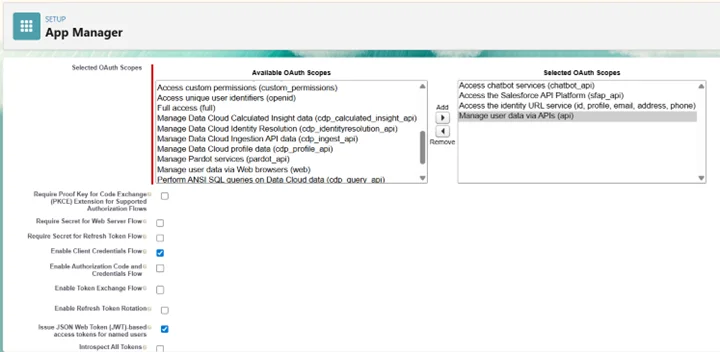
- OAuth Scopes (add all):
- Access chatbot services (chatbot_api)
- Access the Salesforce API Platform (sfap_api)
- Manage user data via APIs (api)
- Perform requests at any time (refresh_token, offline_access)
- Deselect:
- PKCE
- Require Secret for Web Server Flow
- Require Secret for Refresh Token Flow
- Select:
- Enable Client Credentials Flow
- Issue JWT-based access tokens for named users.
- Enable the Save option
- On the app's Manage page click on Edit Policies
- Permitted Users: Select the appropriate option for your org
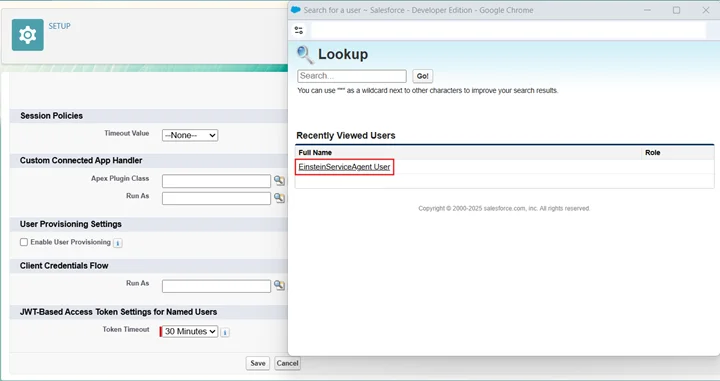
- In Client Credentials Flow set Run As: choose a user with at least API Only access.
- Enable JWT-based Access Tokens; Token Timeout: 30 minutes, and click Save
- Finally, return to your Agent Connection and select this Connected App, and click Save
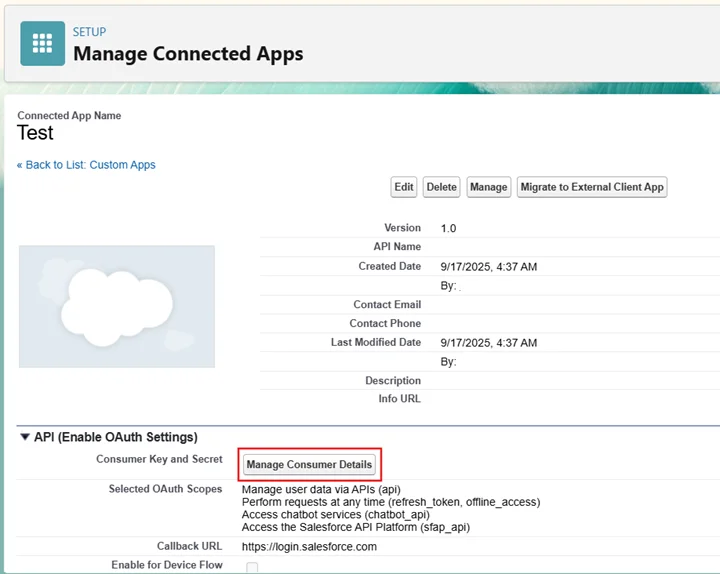
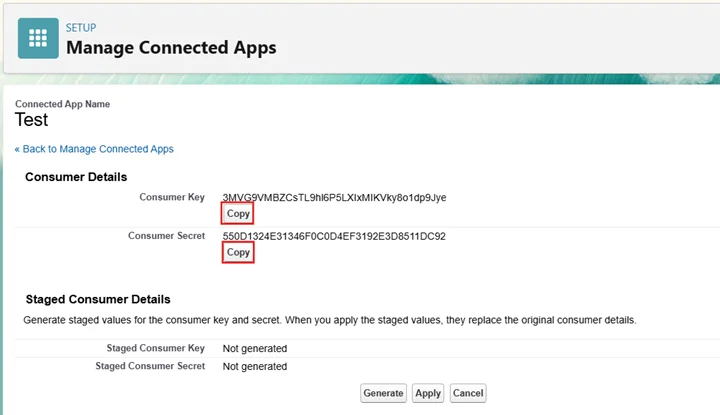
- Retrieve Consumer Key and Consumer Secret from App Manager
- Find your Connected App and View the Manage Consumer Details
- Copy Consumer Key and Consumer Secret

Step 6: Collect remaining IDs
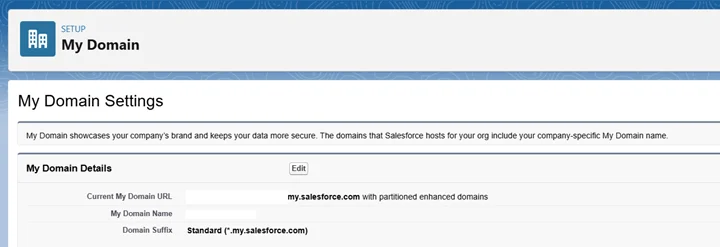
- My Domain: Setup go to My Domain and copy your ...my.salesforce.com URL for token requests
- AGENT_ID: Open the agent in Agentforce Agents and copy the 18-char ID from the URL tail
- MCP: USERNAME, PAT, MCP_BASE_URL, and compute MCP_AUTH = base64(username:pat)
- Salesforce: SFDC_DOMAIN, SFDC_CLIENT_ID, SFDC_CLIENT_SECRET, AGENT_ID
- Salesforce / Einstein Agent Functions
- get_salesforce_token() - obtains OAuth2 token
- start_agent_session() - starts an agent session
- post_message_to_agent() - sends messages to the agent
- MCP Functions
- query_mcp() - retrieves catalogs and runs a sample query from MCP tools
- Main Execution
- Calls MCP functions
- Gets Salesforce token and starts Agent Session
- Sends MCP results to the agent for reasoning
- Prints Agent Response
Step 7: Set up Python project
Install packages:
pip install requests asyncio langchain-mcp-adapters
Create config.py (replace placeholders with your actual values). It should define:
import base64 # --- MCP (CData Connect AI) --- EMAIL = "[email protected]" PAT = "your_PAT" MCP_BASE_URL = "https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp" MCP_AUTH = base64.b64encode(f"{EMAIL}:{PAT}".encode()).decode() # --- Salesforce Agentforce --- SFDC_DOMAIN = "https://your_domain.my.salesforce.com" SFDC_CLIENT_ID = "your_SFDC_CLIENT_ID" SFDC_CLIENT_SECRET = "your_SFDC_CLIENT_SECRET" AGENT_ID = "your_AGENT_ID"
The complete Python script (flow and key functions)
The Python script has three main sections:
Open a terminal in the project directory where the script is and run:
python agentforce_script.py
agentforce_script.py
import asyncio
import requests
import time
import uuid
from langchain_mcp_adapters.client import MultiServerMCPClient
from config import SFDC_DOMAIN, SFDC_CLIENT_ID, SFDC_CLIENT_SECRET, AGENT_ID, MCP_BASE_URL, MCP_AUTH
# ---------------- Salesforce / Einstein Agent ---------------- #
def get_salesforce_token():
"""Fetch a fresh Salesforce OAuth token using client credentials."""
print(" Requesting fresh Salesforce token...")
token_url = f"{SFDC_DOMAIN}/services/oauth2/token"
data = {
"grant_type": "client_credentials",
"client_id": SFDC_CLIENT_ID,
"client_secret": SFDC_CLIENT_SECRET,
}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"}
resp = requests.post(token_url, data=data, headers=headers)
resp.raise_for_status()
token_data = resp.json()
print(" Got access token.")
return token_data["access_token"], token_data["instance_url"]
def start_agent_session(access_token):
"""Start a session with Salesforce Einstein Agent."""
session_url = f"https://api.salesforce.com/einstein/ai-agent/v1/agents/{AGENT_ID}/sessions"
payload = {
"externalSessionKey": str(uuid.uuid4()),
"instanceConfig": {"endpoint": SFDC_DOMAIN},
"streamingCapabilities": {"chunkTypes": ["Text"]},
"bypassUser": True,
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}",
}
resp = requests.post(session_url, json=payload, headers=headers)
resp.raise_for_status()
session_data = resp.json()
print(f" Agent session started: {session_data['sessionId']}")
return session_data["sessionId"]
def post_message_to_agent(access_token, session_id, message_text):
"""Send a message to the Salesforce Einstein Agent session."""
messages_url = f"https://api.salesforce.com/einstein/ai-agent/v1/sessions/{session_id}/messages"
payload = {
"message": {
"sequenceId": int(time.time() * 1000),
"type": "Text",
"text": message_text,
},
"variables": [],
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}",
}
resp = requests.post(messages_url, json=payload, headers=headers)
resp.raise_for_status()
return resp.json()
# ---------------- MCP part ---------------- #
async def query_mcp():
"""Query MCP server for catalogs and a sample query."""
mcp_client = MultiServerMCPClient(
connections={
"default": {
"transport": "streamable_http",
"url": MCP_BASE_URL,
"headers": {"Authorization": f"Basic {MCP_AUTH}"},
}
}
)
tools = await mcp_client.get_tools()
print("Discovered MCP tools:", [t.name for t in tools])
# List catalogs
get_catalogs_tool = next(t for t in tools if t.name == "getCatalogs")
catalogs = await get_catalogs_tool.ainvoke({})
print("Catalogs:", catalogs)
# Run a sample query
query_tool = next(t for t in tools if t.name == "queryData")
query_result = await query_tool.ainvoke({
"query": "SELECT * FROM [AmazonAthena].[PUBLIC].[EMPLOYEES] LIMIT 5"
})
print("Query result:", query_result)
return catalogs, query_result
# ---------------- Main ---------------- #
async def main():
# Step 1: MCP
catalogs, query_result = await query_mcp()
# Step 2: Salesforce token and agent
access_token, _ = get_salesforce_token()
session_id = start_agent_session(access_token)
# Step 3: Post MCP results to agent with instructions
context_message = (
f"You are a helpful assistant.\n"
f"The following MCP data was retrieved:\n\n"
f"Catalogs: {catalogs}\n"
f"Query result: {query_result}\n\n"
f"Please answer the user's question based on this data: "
f"List all available catalogs and summarize the query results."
)
response = post_message_to_agent(access_token, session_id, context_message)
print("\n Agent response:")
print(response)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
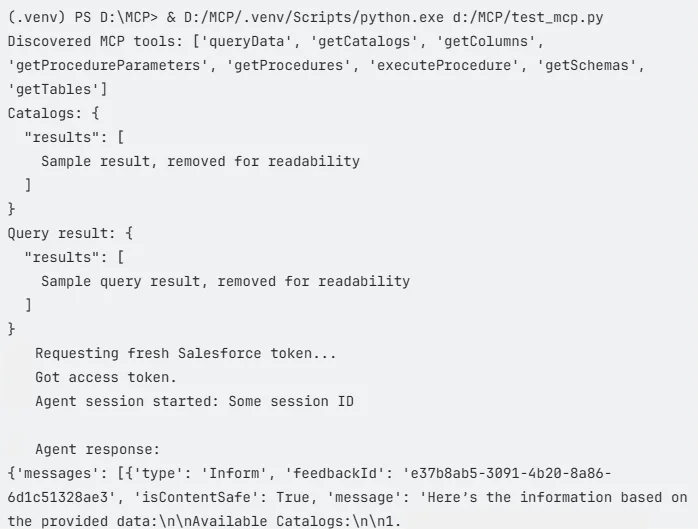
Sample Output
Build data-powered agents in Salesforce Agentforce
Agentforce lets you orchestrate AI agents and automate CRM workflows. With live connectivity through CData Connect AI and the remote MCP Server, your agents can operate on real-time, contextual data across your stack CRMs, ERPs, databases, finance platforms, and more.
Start your free trial today to see how CData can empower Agentforce with live, secure access to 300+ external systems.






