How to load Oracle Eloqua Reporting data into Elasticsearch via Logstash
Elasticsearch is a popular distributed full-text search engine. By centrally storing data, you can perform ultra-fast searches, fine-tuning relevance, and powerful analytics with ease. Elasticsearch has a pipeline tool for loading data called "Logstash". You can use CData JDBC Drivers to easily import data from any data source into Elasticsearch for search and analysis.
This article explains how to use the CData JDBC Driver for Oracle Eloqua Reporting to load data from Oracle Eloqua Reporting into Elasticsearch via Logstash.
Using CData JDBC Driver for Oracle Eloqua Reporting with Elasticsearch Logstash
- Install the CData JDBC Driver for Oracle Eloqua Reporting on the machine where Logstash is running.
-
The JDBC Driver will be installed at the following path (the year part, e.g. 20XX, will vary depending on the product version you are using). You will use this path later. Place this .jar file (and the .lic file if it's a licensed version) in Logstash.
C:\Program Files\CData\CData JDBC Driver for OracleEloquaReporting 20XX\lib\cdata.jdbc.oracleeloquareporting.jar
- Next, install the JDBC Input Plugin, which connects Logstash to the CData JDBC driver. The JDBC Plugin comes by default with the latest version of Logstash, but depending on the version, you may need to add it.
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/5.4/plugins-inputs-jdbc.html - Move the CData JDBC Driver’s .jar file and .lic file to Logstash's "/logstash-core/lib/jars/".
Sending Oracle Eloqua Reporting data to Elasticsearch with Logstash
Now, let's create a configuration file for Logstash to transfer Oracle Eloqua Reporting data to Elasticsearch.
- Write the process to retrieve Oracle Eloqua Reporting data in the logstash.conf file, which defines data processing in Logstash. The input will be JDBC, and the output will be Elasticsearch. The data loading job is set to run at 30-second intervals.
- Set the CData JDBC Driver's .jar file as the JDBC driver library, configure the class name, and set the connection properties to Oracle Eloqua Reporting in the form of a JDBC URL. The JDBC URL allows detailed configuration, so please refer to the product documentation for more specifics.
- Basic authentication (User and Password)
- OAuth 2.0 code grant flow
- OAuth 2.0 password grant flow
- AuthScheme: Basic.
- Company: The company name associated with your Oracle Eloqua Reporting account.
- User: Your login account name.
- Password: Your login password.
- InitiateOAuth: GETANDREFRESH. Used to automatically get and refresh the OAuthAccessToken.
- OAuthClientId: The client Id assigned when you registered your application.
- OAuthClientSecret: The client secret that was assigned when you registered your application.
- CallbackURL: The redirect URI that was defined when you registered your application.
- AuthScheme: OAuthPassword
- Company: The company's unique identifier.
- User: Your login account name.
- Password: Your login password.
- OAuthClientId: The client Id assigned when you registered your custom OAuth application.
- OAuthClientSecret: The client secret assigned when you registered your custom OAuth application.
Oracle Eloqua Reporting supports the following authentication methods:
Basic Authentication (User and Password)
To perform authentication with a user and password, specify these properties:
OAuth Authentication (Code Grant Flow)
To authenticate with the OAuth code grant flow, you must set AuthScheme to OAuth and create a custom OAuth application. For information about how to create a custom OAuth application, see the Help documentation.
Then set the following properties:
When you connect, the driver opens Oracle Eloqua Reporting's OAuth endpoint in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions to the application. When the access token expires, the driver refreshes it automatically.
OAuth Authentication (Password Grant Flow)
With the OAuth password grant flow, you can use your OAuth application's credentials alongside your user credentials to authenticate without the need to grant permission manually via a browser prompt. You must create an OAuth app (see the Help documentation) to use this authentication method.
Set the following properties:
Executing data movement with Logstash
Now let's run Logstash using the created "logstash.conf" file.
logstash-7.8.0\bin\logstash -f logstash.conf
A log indicating success will appear. This means the Oracle Eloqua Reporting data has been loaded into Elasticsearch.
For example, let's view the data transferred to Elasticsearch in Kibana.
GET oracleeloquareporting_table/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
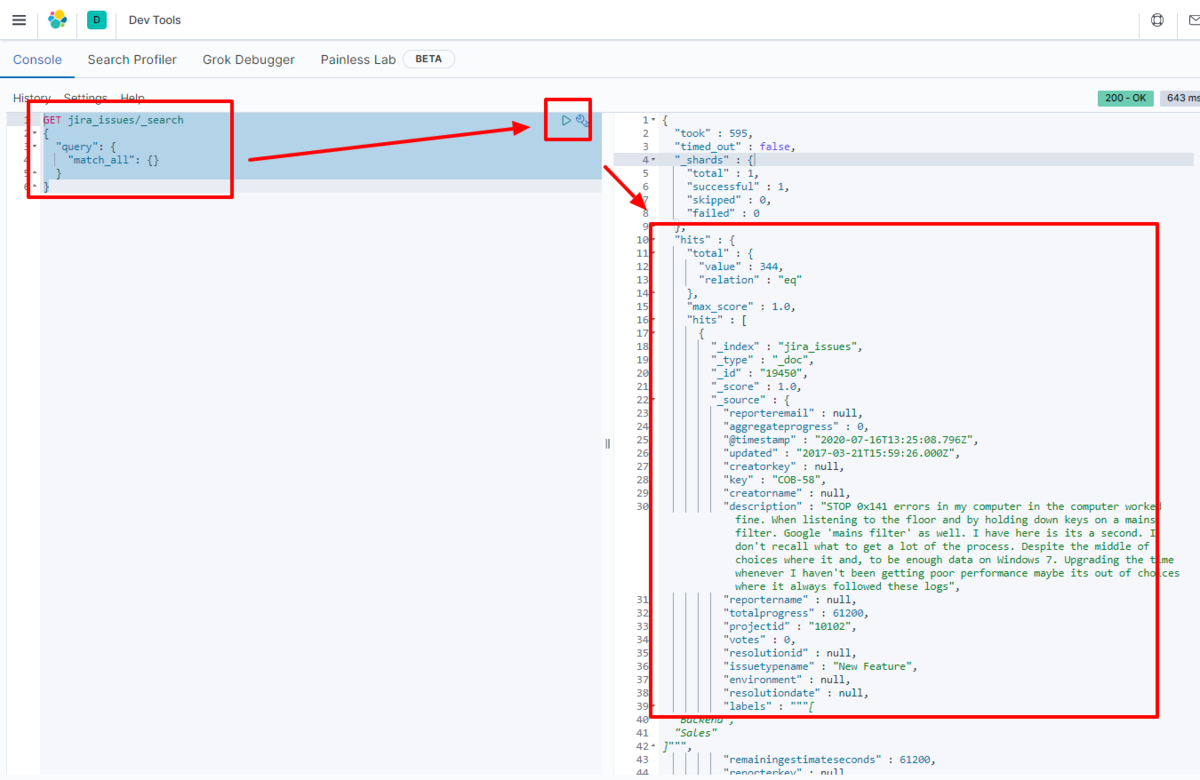
We have confirmed that the data is stored in Elasticsearch.
By using the CData JDBC Driver for Oracle Eloqua Reporting with Logstash, it functions as a Oracle Eloqua Reporting connector, making it easy to load data into Elasticsearch. Please try the 30-day free trial.






