How to Work with Oracle Eloqua Reporting Data in ETL Validator JDBC
ETL Validator provides data movement and transformation capabilities for integrating data platforms across your organization. CData's JDBC driver seamlessly integrates with ETL Validator and extends its native connectivity to include Oracle Eloqua Reporting data.
This tutorial walks through the process of building a simple ETL validator data flow to extract data from Oracle Eloqua Reporting data and load it into an example data storage solution: SQL Server.
Add a new ETL Validator data source via CData
CData extends ETL Validator's data connectivity capabilities by providing the ability to add data sources that connect via CData's JDBC drivers. Connecting to Oracle Eloqua Reporting data simply requires creating a new data source in ETL Validator through CData's connectiviy suite as described below.
Login to ETL Validator
Begin by logging into ETL Validator to view the application dashboard.
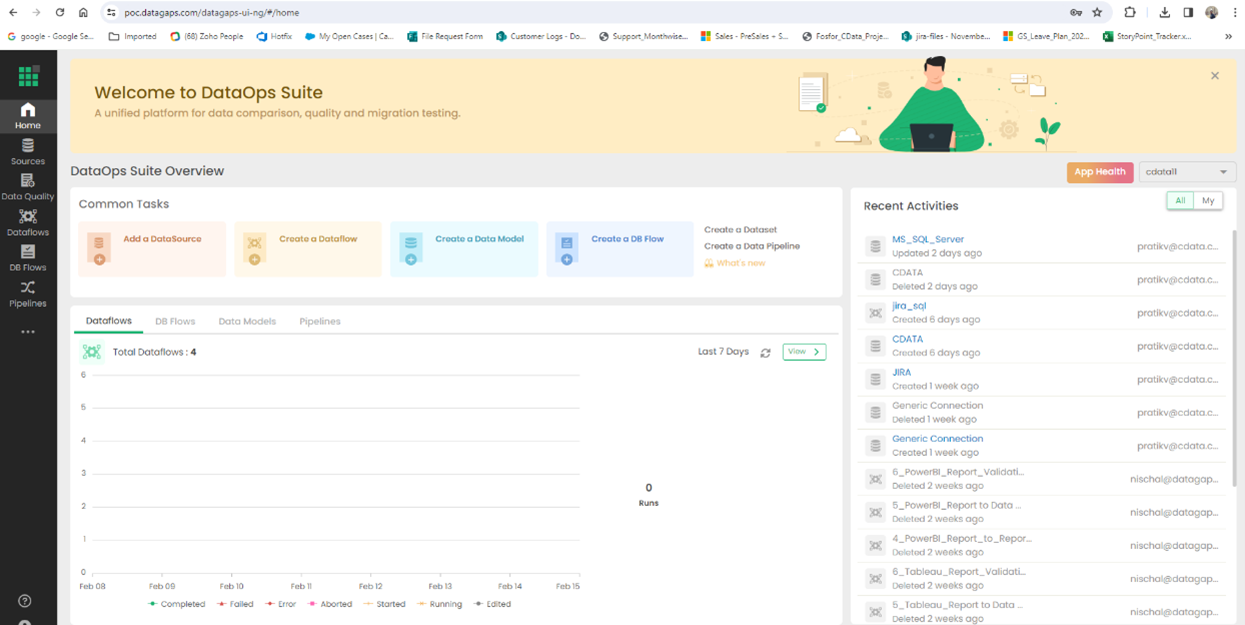
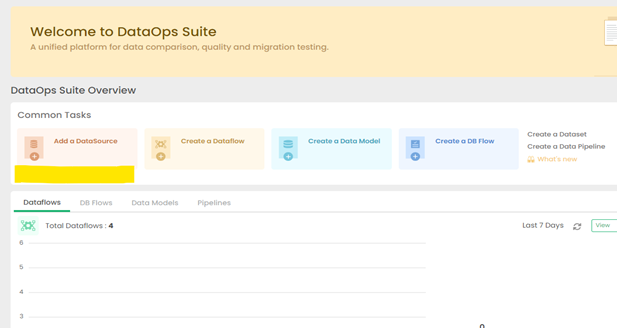
Click on Add a DataSource
CData extends the data source options within ETL Validator.
Click on CData
CData's connectivity is embedded within ETL Validator's data source options.

Configure the CData Driver Connection String
You will need a JDBC connection string to establish a connection to Oracle Eloqua Reporting in ETL Validator.
Oracle Eloqua Reporting supports the following authentication methods:
- Basic authentication (User and Password)
- OAuth 2.0 code grant flow
- OAuth 2.0 password grant flow
Basic Authentication (User and Password)
To perform authentication with a user and password, specify these properties:
- AuthScheme: Basic.
- Company: The company name associated with your Oracle Eloqua Reporting account.
- User: Your login account name.
- Password: Your login password.
OAuth Authentication (Code Grant Flow)
To authenticate with the OAuth code grant flow, you must set AuthScheme to OAuth and create a custom OAuth application. For information about how to create a custom OAuth application, see the Help documentation.
Then set the following properties:
- InitiateOAuth: GETANDREFRESH. Used to automatically get and refresh the OAuthAccessToken.
- OAuthClientId: The client Id assigned when you registered your application.
- OAuthClientSecret: The client secret that was assigned when you registered your application.
- CallbackURL: The redirect URI that was defined when you registered your application.
When you connect, the driver opens Oracle Eloqua Reporting's OAuth endpoint in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions to the application. When the access token expires, the driver refreshes it automatically.
OAuth Authentication (Password Grant Flow)
With the OAuth password grant flow, you can use your OAuth application's credentials alongside your user credentials to authenticate without the need to grant permission manually via a browser prompt. You must create an OAuth app (see the Help documentation) to use this authentication method.
Set the following properties:
- AuthScheme: OAuthPassword
- Company: The company's unique identifier.
- User: Your login account name.
- Password: Your login password.
- OAuthClientId: The client Id assigned when you registered your custom OAuth application.
- OAuthClientSecret: The client secret assigned when you registered your custom OAuth application.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Oracle Eloqua Reporting JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.oracleeloquareporting.jar

A typical connection string looks like this:
jdbc:oracleeloquareporting:AuthScheme=Basic;User=user;Password=password;Company=MyCompany;
Licensing the Driver
To ensure the JDBC driver is licensed appropriately, copy the license file to the appropriate location:
Copy the JDBC Driver for Oracle Eloqua Reporting and lic file from "C:\Program Files\CData[product_name]\lib" to "C:\Datagaps\ETLValidator\Server\apache-tomcat\bin".
cdata.jdbc.oracleeloquareporting.jar
cdata.jdbc.oracleeloquareporting.lic
Note: If you do not copy the .lic file with the jar, you will see a licensing error that indicates you do not have a valid license installed. This is true for both the trial and full versions.
Save the connection
Should you encounter any difficulties loading the CData JDBC driver class, please contact DataGap's team, and they will provide you instructions on how to load the jar file for the relevant driver.
Add SQL Server as a Target
This example will use SQL Server as a destination for Oracle Eloqua Reporting data data, but any preferred destination can be used instead.
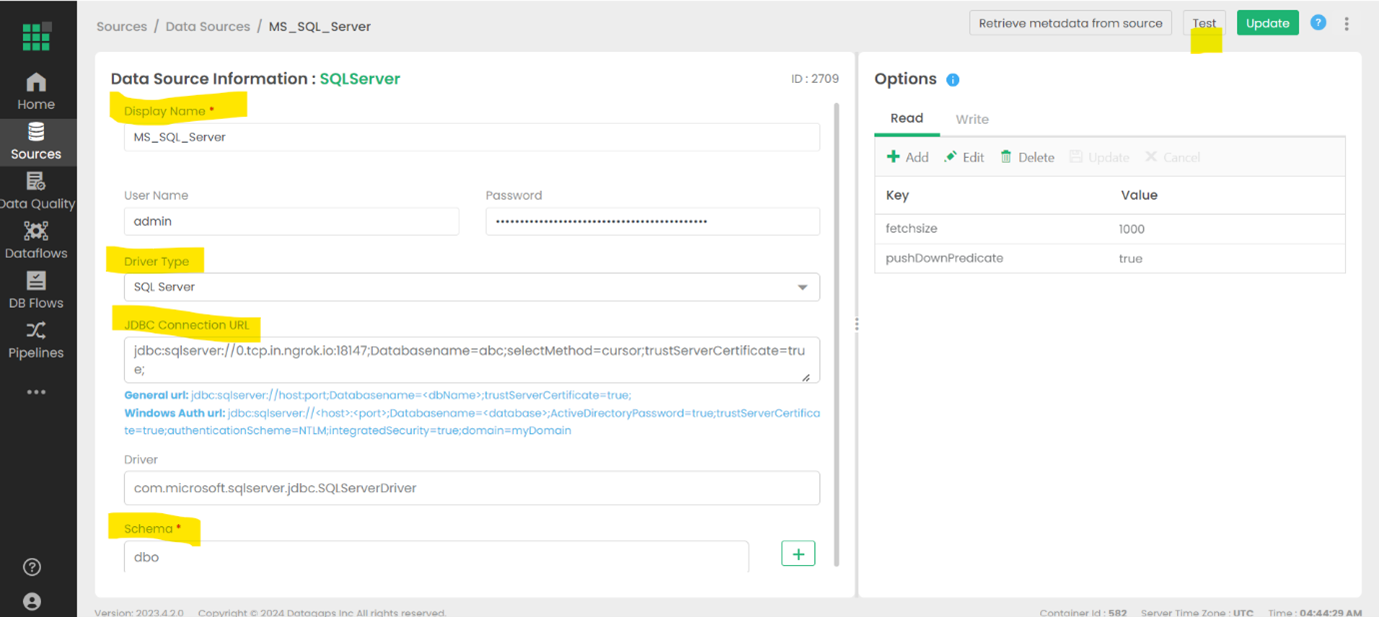
Go to DataSources and select MS_SQL_SERVER
This option is the default.
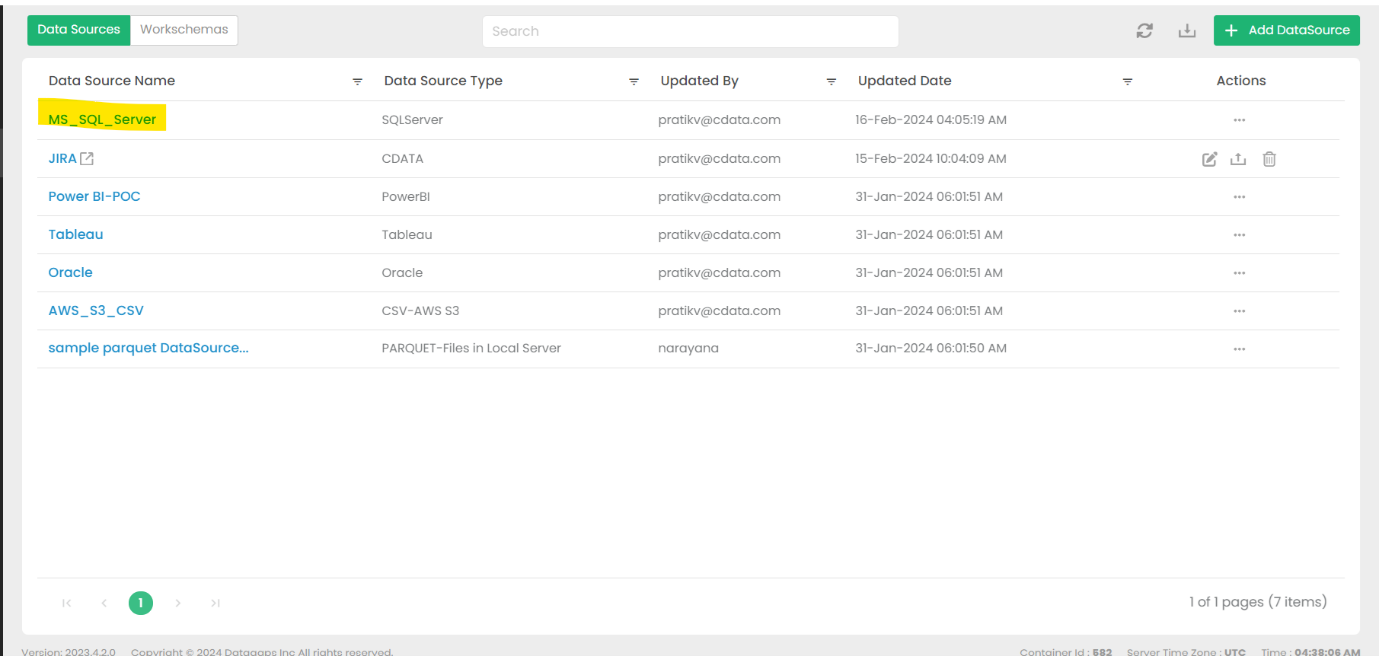
Fill in the necessary connection details and test the connection
The details will depend on the specific target, but these details may include a URL, authentiation credentials, etc.
Create a Dataflow in ETL Validator
Open the Dataflows tab
Configured data flows will appear in this window.
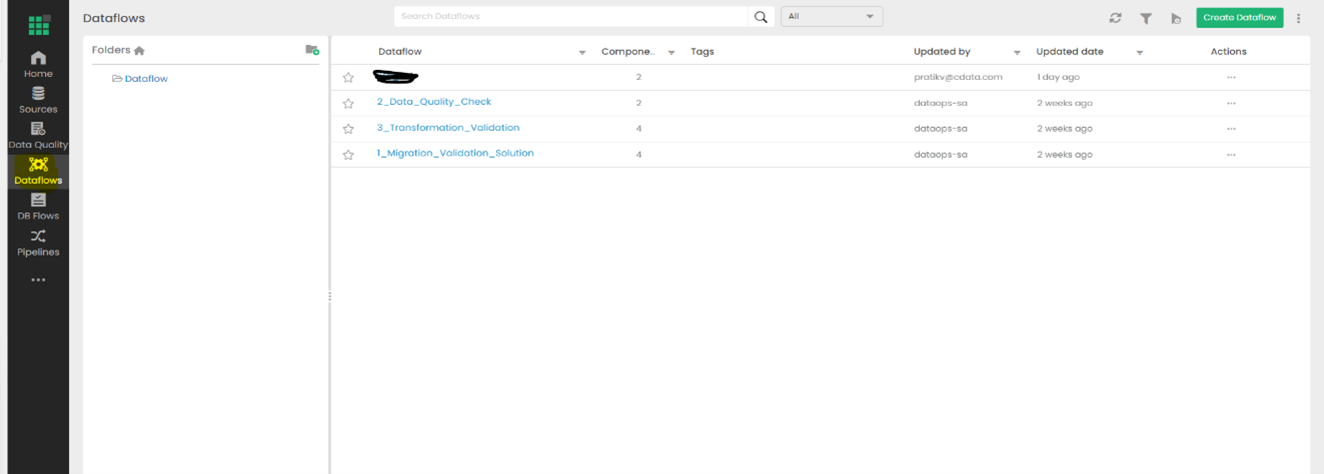
Select Create Dataflow
Name your new dataflow and save it.
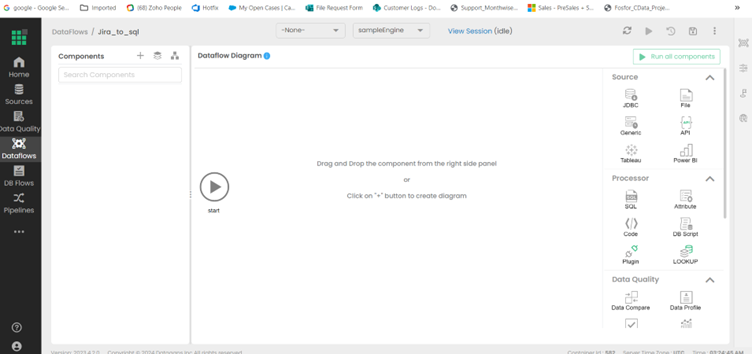
Open the Dataflow to view the Dataflow Diagram
The details of the data movement will be configured in this panel.
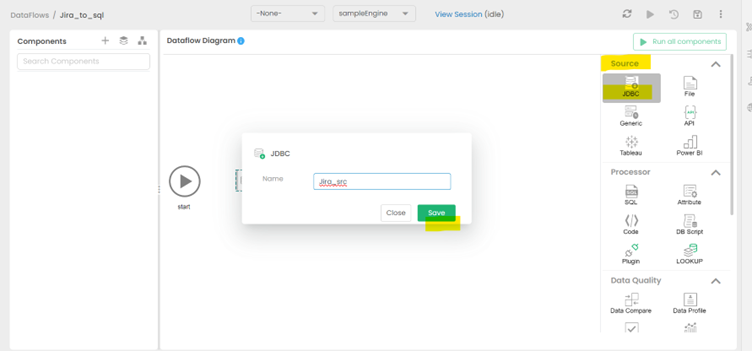
Drag & drop the JDBC as a source from the right side
Give the new source an appropriate name and save it.
Fill in the Query section of the new source
Select the Table from the Schema option that reflects which data should be pulled from Oracle Eloqua Reporting data.
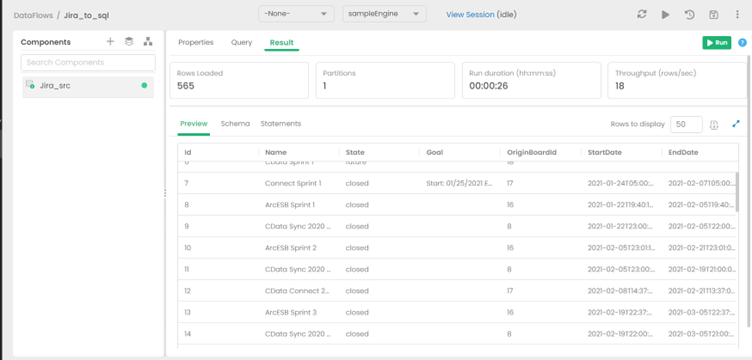
View the expected results of your query
The anticipated outcome of the configured query is displayed in the Result tab.
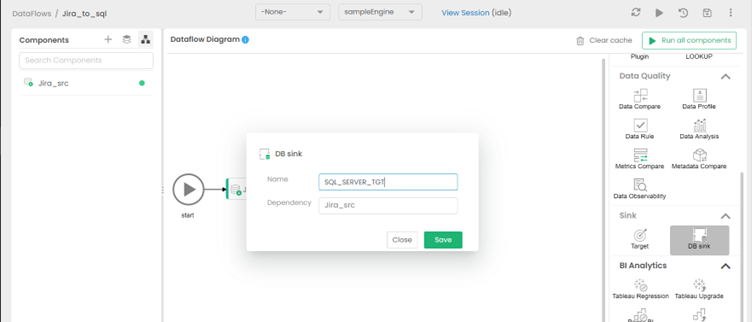
Add the destination to the Dataflow
Select Switch to Diagram, then drag & drop the DB Sink as a target from the right side (under Sink options). Give the sink an appropriate name and save it.
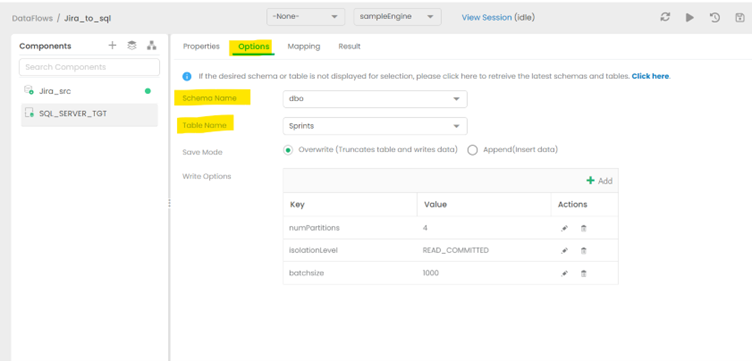
Set the appropriate Schema for the destination
Choose the Schema and table that matches the structure of the source table. For this example, the table on the target side was created to match the Source so that data flow seamlessly. More advanced schema transformation operations are beyond the scope of this article.
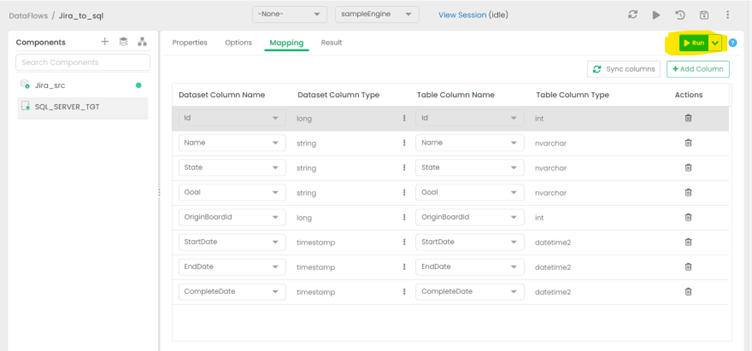
Hit the RUN option to begin replication
Running the job will take some time.
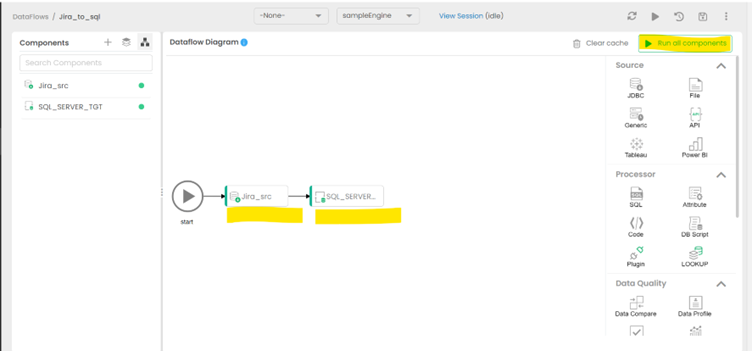
View the finished Dataflow
Return to the diagram to see the finished data replication job from Oracle Eloqua Reporting data to SQL Server.
Get Started Today
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Oracle Eloqua Reporting and start building Oracle Eloqua Reporting-connected applications with ETL Validator. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.






