Lakebase Reporting in OBIEE with the Lakebase JDBC Driver
The CData JDBC Driver for Lakebase is a standard database driver that can integrate real-time access to Lakebase data into your Java-based reporting server. This article shows how to deploy the driver to Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition (OBIEE) and create reports on Lakebase data that reflect any changes.
Deploy the JDBC Driver
Follow the steps below to add the JDBC driver to WebLogic's classpath.
For WebLogic 12.2.1, simply place the driver JAR and .lic file into DOMAIN_HOME\lib; for example, ORACLE_HOME\user_projects\domains\MY_DOMAIN\lib. These files will be added to the server classpath at startup.
You can also manually add the driver to the classpath: This is required for earlier versions. Prepend the following to PRE_CLASSPATH in setDomainEnv.cmd (Windows) or setDomainEnv.sh (Unix). This script is located in the bin subfolder of the folder for that domain. For example: ORACLE_HOME\user_projects\domains\MY_DOMAIN\bin.
set PRE_CLASSPATH=your-installation-directory\lib\cdata.jdbc.lakebase.jar;%PRE_CLASSPATH%
Restart all servers; for example, run the stop and start commands in DOMAIN_HOME\bitools\bin.
Create a JDBC Data Source for Lakebase
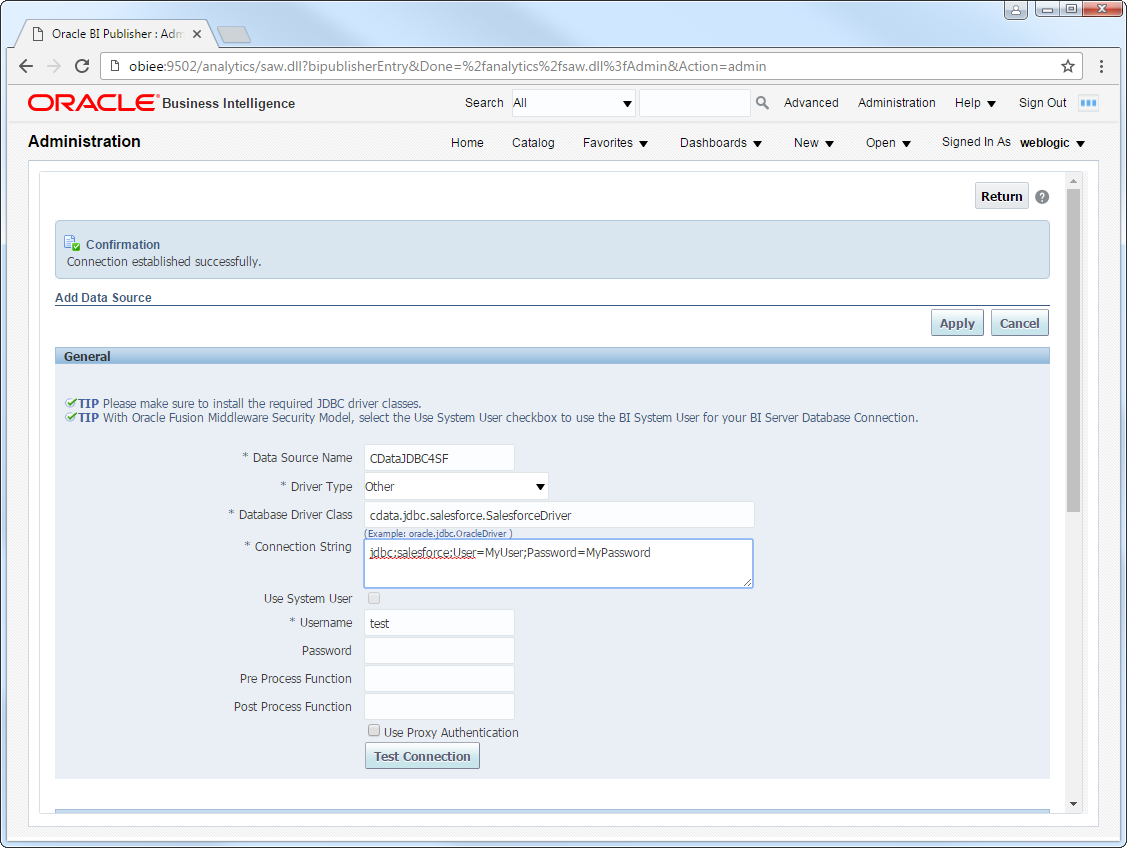
After deploying the JDBC driver, you can create a JDBC data source from BI Publisher.
- Log into BI Publisher, at the URL http://localhost:9502/analytics, for example, and click Administration -> Manage BI Publisher.
- Click JDBC Connection -> Add Data Source.
- Enter the following information:
- Data Source Name: Enter the name that users will create connections to in their reports.
- Driver Type: Select Other.
- Database DriverClass: Enter the driver class, cdata.jdbc.lakebase.LakebaseDriver.
- Connection String: Enter the JDBC URL.
To connect to Databricks Lakebase, start by setting the following properties:
- DatabricksInstance: The Databricks instance or server hostname, provided in the format instance-abcdef12-3456-7890-abcd-abcdef123456.database.cloud.databricks.com.
- Server: The host name or IP address of the server hosting the Lakebase database.
- Port (optional): The port of the server hosting the Lakebase database, set to 5432 by default.
- Database (optional): The database to connect to after authenticating to the Lakebase Server, set to the authenticating user's default database by default.
OAuth Client Authentication
To authenicate using OAuth client credentials, you need to configure an OAuth client in your service principal. In short, you need to do the following:
- Create and configure a new service principal
- Assign permissions to the service principal
- Create an OAuth secret for the service principal
For more information, refer to the Setting Up OAuthClient Authentication section in the Help documentation.
OAuth PKCE Authentication
To authenticate using the OAuth code type with PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange), set the following properties:
- AuthScheme: OAuthPKCE.
- User: The authenticating user's user ID.
For more information, refer to the Help documentation.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Lakebase JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.lakebase.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.

When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
A typical JDBC URL is below:
jdbc:lakebase:DatabricksInstance=lakebase;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432;Database=my_database;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH;
- Username: Enter the username.
- Password: Enter the password.
- In the Security section, select the allowed user roles.
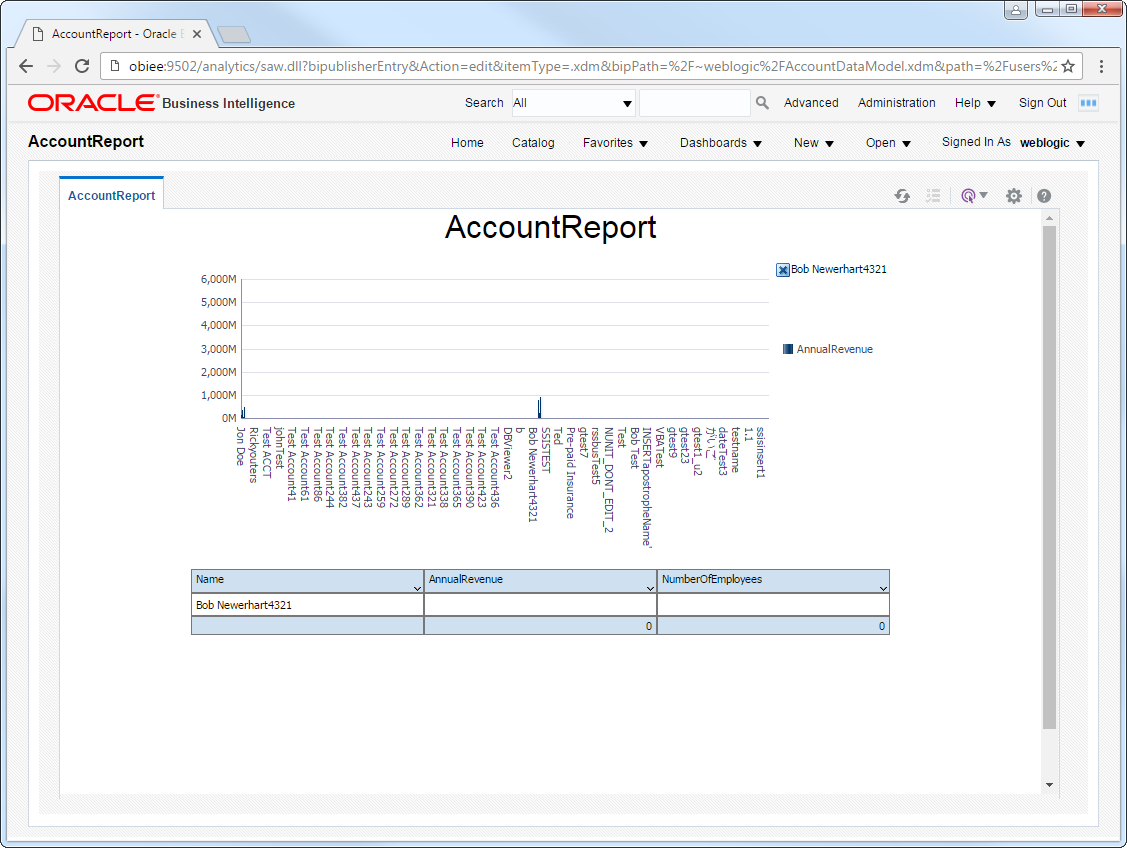
Create Real-Time Lakebase Reports
You can now create reports and analyses based on real-time Lakebase data. Follow the steps below to use the standard report wizard to create an interactive report that reflects any changes to Lakebase data.
- On the global header, click New -> Data Model.
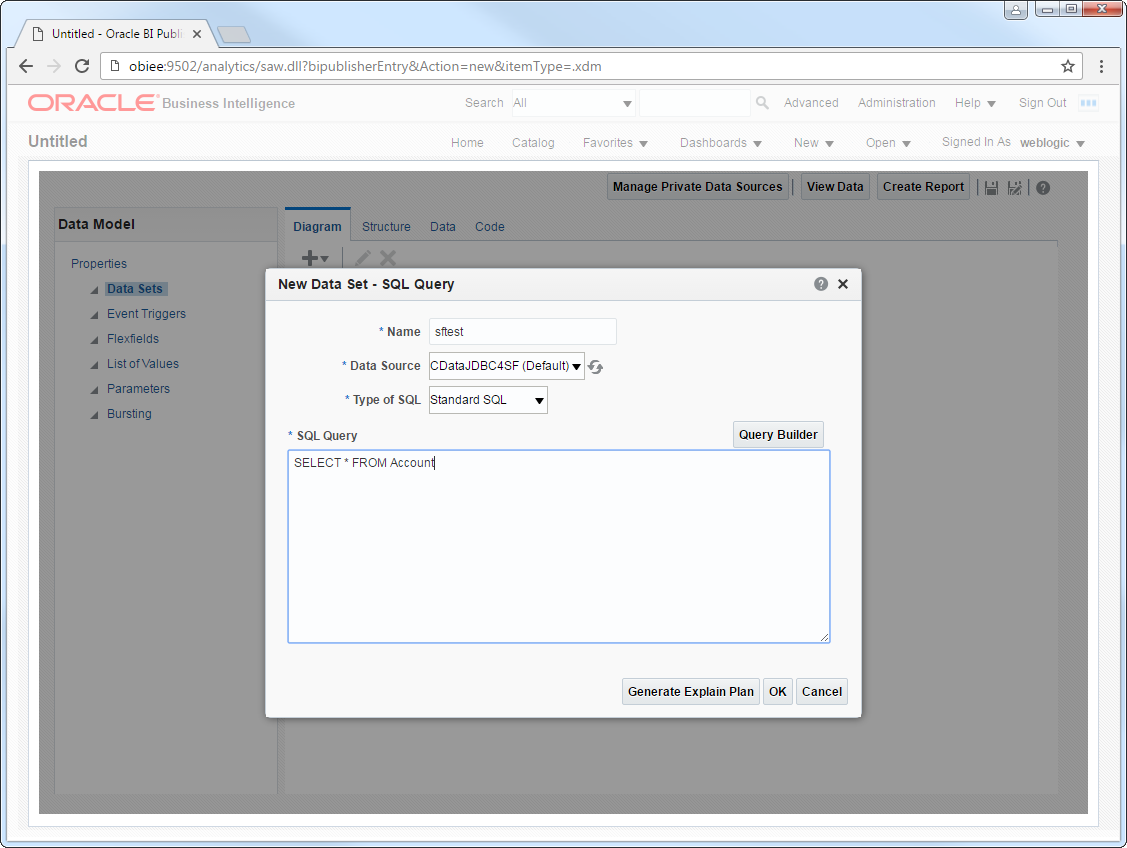
- On the Diagram tab, select SQL query in the menu.
- Enter a name for the query and in the Data Source menu select the Lakebase JDBC data source you created.
- Select standard SQL and enter a query like the following:
SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM Orders WHERE ShipCountry = 'USA'
- Click View Data to generate the sample data to be used as you build your report.
- Select the number of rows to include in the sample data, click View, and then click Save As Sample Data.
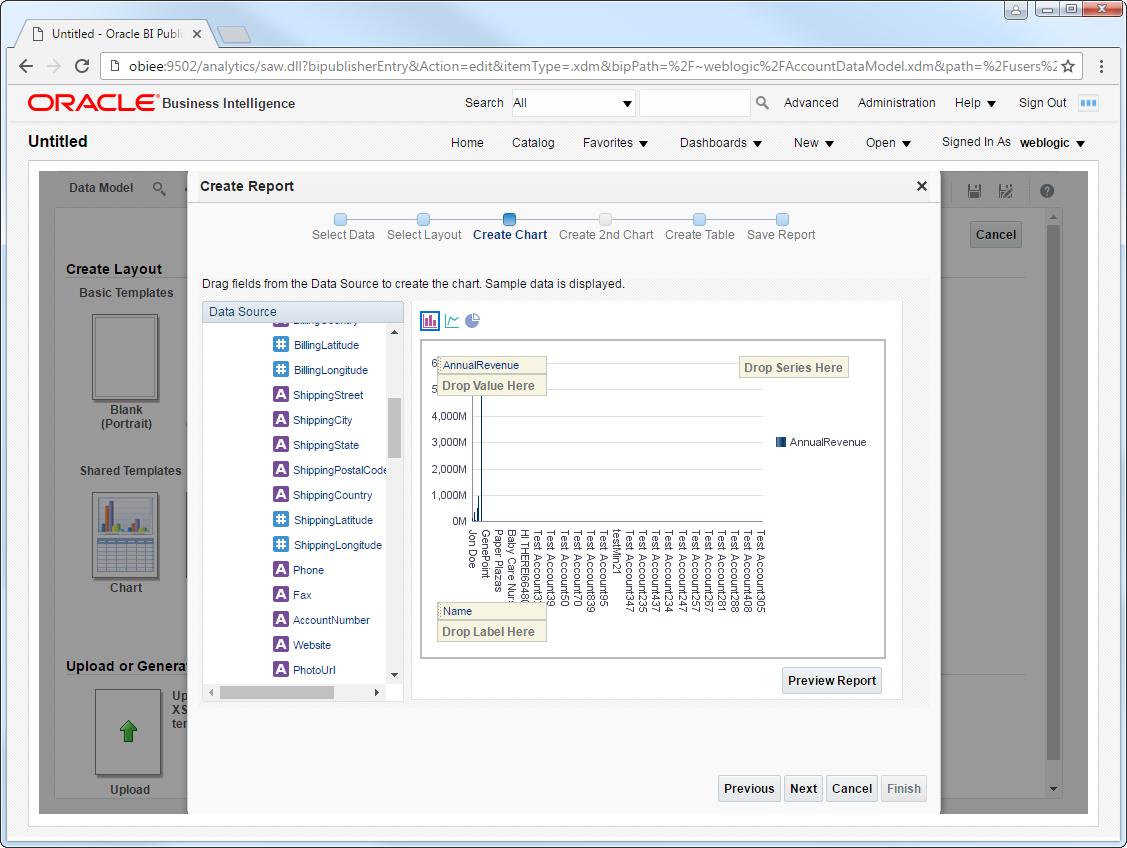
- Click Create Report -> Use Data Model.
- Select Guide Me and on the Select Layout page select the report objects you want to include. In this example we select Chart and Table.
- Drop a numeric column like ShipCity onto the Drop Value Here box on the y-axis. Drop a dimension column like ShipName onto the Drop Label Here box on the x-axis.
- Click Refresh to pick up any changes to the Lakebase data.