Configure a Receive Location for the CData BizTalk Adapter for PingOne
You can follow the procedure in this article to connect to PingOne data, configure a static one-way receive location, and use it to perform a simple test: retrieving PingOne data and writing it to an XML file.
A receive location can execute SQL commands and create BizTalk messages that contain the results. If you want to execute updategram commands, use a send port.
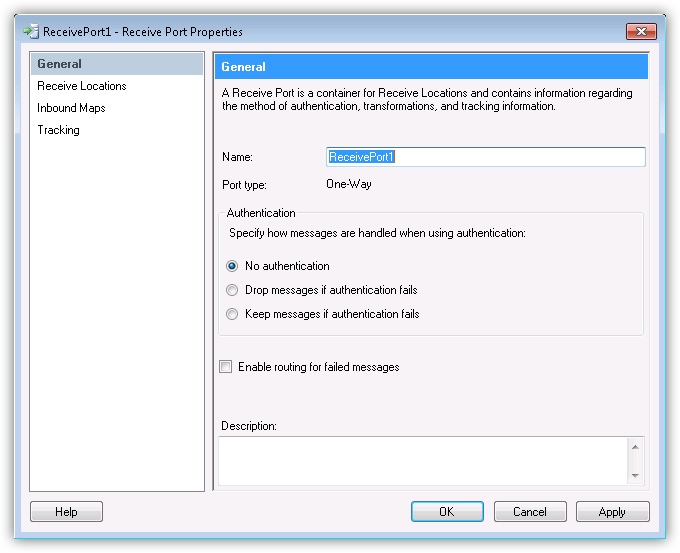
Create the Receive Port
To add a receive location to your application, you first need to add a receive port. Receive ports can receive data from multiple receive locations.
- If you have not already done so, open your application in the BizTalk Administration Console.
- In your application, right-click Receive Ports and click New -> Static One-Way Receive Port. The Receive Port Properties dialog is displayed.
- In the Name menu, enter a name for the receive port.
Create the Receive Location
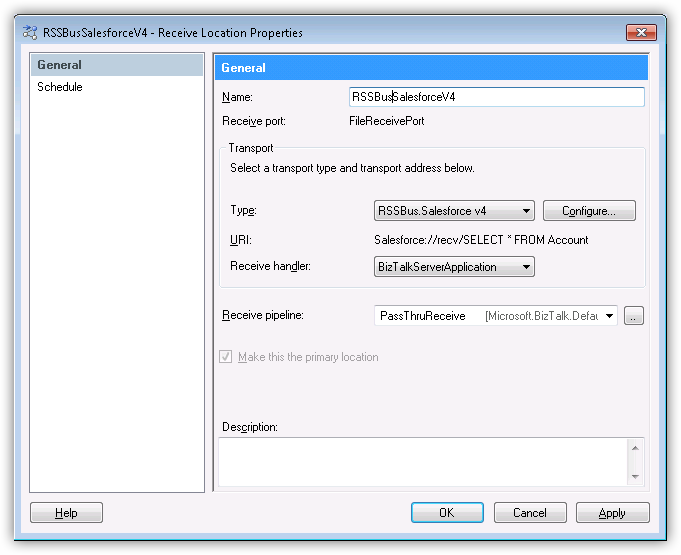
After you create the receive port, create the receive location and configure it to use the PingOne adapter as its transport type.
- Right-click Receive Locations and click New -> One-Way Receive Location.
- Select the appropriate receive port of which the new receive location will be a member. The Receive Location Properties dialog is displayed.
- In the Name menu, enter a name for the receive location.
- In the Receive Location properties, select CData.PingOne in the Transport Type menu.
- In the Receive pipeline menu, select the default option, PassThruReceive.
Configure the Adapter
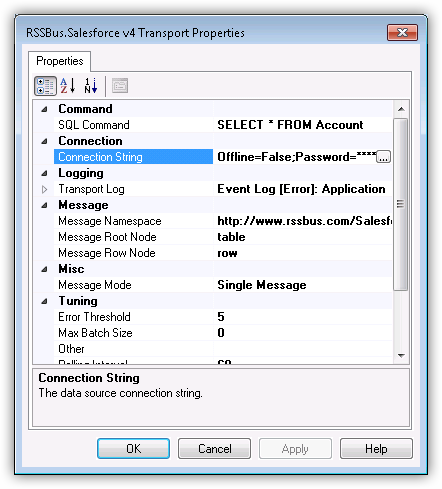
In the Transport Properties dialog, specify the command that the adapter will execute.
- In the receive location properties, click Configure. The Transport Properties dialog for the adapter is displayed.
- In the SQL Command property, enter the command. This example uses
SELECT Id, Username FROM [CData].[Administrators].Users WHERE EmployeeType = 'Contractor'
Configure the Connection String
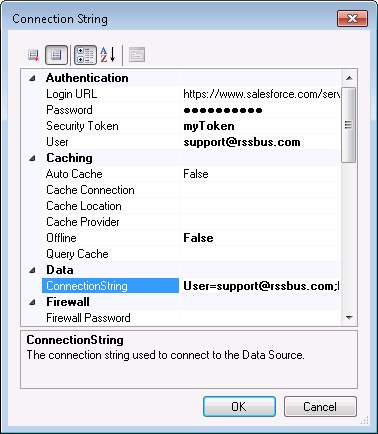
Set credentials and other connection properties in the Connection String Options dialog.
- In the receive location properties, click Configure. The adapter properties dialog is displayed.
- Click the button in the Connection String property.
- Click the box in the Connection String property. The Connection String Options dialog is displayed.
- Enter connection properties. Below is a typical connection string:
AuthScheme=OAuth;WorkerAppEnvironmentId=eebc33a8-xxxx-4f3a-yyyy-d3e5262fd49e;Region=NA;OAuthClientId=client_id;OAuthClientSecret=client_secret;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH;
To connect to PingOne, configure these properties:
- Region: The region where the data for your PingOne organization is being hosted.
- AuthScheme: The type of authentication to use when connecting to PingOne.
- Either WorkerAppEnvironmentId (required when using the default PingOne domain) or AuthorizationServerURL, configured as described below.
Configuring WorkerAppEnvironmentId
WorkerAppEnvironmentId is the ID of the PingOne environment in which your Worker application resides. This parameter is used only when the environment is using the default PingOne domain (auth.pingone). It is configured after you have created the custom OAuth application you will use to authenticate to PingOne, as described in Creating a Custom OAuth Application in the Help documentation.
First, find the value for this property:
- From the home page of your PingOne organization, move to the navigation sidebar and click Environments.
- Find the environment in which you have created your custom OAuth/Worker application (usually Administrators), and click Manage Environment. The environment's home page displays.
- In the environment's home page navigation sidebar, click Applications.
- Find your OAuth or Worker application details in the list.
-
Copy the value in the Environment ID field.
It should look similar to:
WorkerAppEnvironmentId='11e96fc7-aa4d-4a60-8196-9acf91424eca'
Now set WorkerAppEnvironmentId to the value of the Environment ID field.
Configuring AuthorizationServerURL
AuthorizationServerURL is the base URL of the PingOne authorization server for the environment where your application is located. This property is only used when you have set up a custom domain for the environment, as described in the PingOne platform API documentation. See Custom Domains.
Authenticating to PingOne with OAuth
PingOne supports both OAuth and OAuthClient authentication. In addition to performing the configuration steps described above, there are two more steps to complete to support OAuth or OAuthCliet authentication:
- Create and configure a custom OAuth application, as described in Creating a Custom OAuth Application in the Help documentation.
- To ensure that the driver can access the entities in Data Model, confirm that you have configured the correct roles for the admin user/worker application you will be using, as described in Administrator Roles in the Help documentation.
- Set the appropriate properties for the authscheme and authflow of your choice, as described in the following subsections.
OAuth (Authorization Code grant)
Set AuthScheme to OAuth.
Desktop Applications
Get and Refresh the OAuth Access Token
After setting the following, you are ready to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: GETANDREFRESH. To avoid the need to repeat the OAuth exchange and manually setting the OAuthAccessToken each time you connect, use InitiateOAuth.
- OAuthClientId: The Client ID you obtained when you created your custom OAuth application.
- OAuthClientSecret: The Client Secret you obtained when you created your custom OAuth application.
- CallbackURL: The redirect URI you defined when you registered your custom OAuth application. For example: https://localhost:3333
When you connect, the driver opens PingOne's OAuth endpoint in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions to the application. The driver then completes the OAuth process:
- The driver obtains an access token from PingOne and uses it to request data.
- The OAuth values are saved in the location specified in OAuthSettingsLocation, to be persisted across connections.
The driver refreshes the access token automatically when it expires.
For other OAuth methods, including Web Applications, Headless Machines, or Client Credentials Grant, refer to the Help documentation.
- Click Test Connection to verify the connection values and test connectivity.
Refer to the help documentation for a description of the various properties and their functions.
Use a Send Port to Write Data to an XML File
The Static One-Way Receive Location is now ready for use with a send port: A send port must be associated with the BizTalk message that is created by the receive location. To write data to a file, create a file send port.
- In the BizTalk Administration console, right-click Send Ports -> New -> Static One-Way Send Port.
Enter a name for the send port at the top of the configuration window and select FILE from the Type menu.
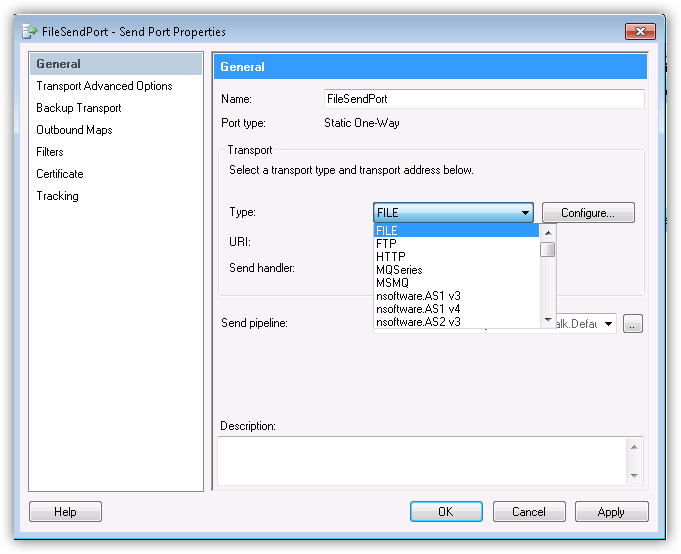
- Configure a destination folder; this will be the location where the files are created on disk.
For the file name, a macro can be used to easily identify what day the file was created. By default, %MessageId%.xml is used. However, this is not a very user-friendly name, as it is a randomly generated BizTalk Id. To produce a file in the format [CData].[Administrators].Users_yyyy-MM-dd.xml, enter [CData].[Administrators].Users_%Date%.xml.
Note: For additional information regarding macros, visit the BizTalk Configuration section in the help documentation.
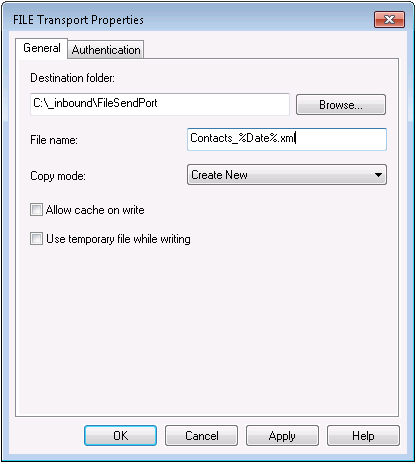
- Click OK. The URI field should now contain a value.
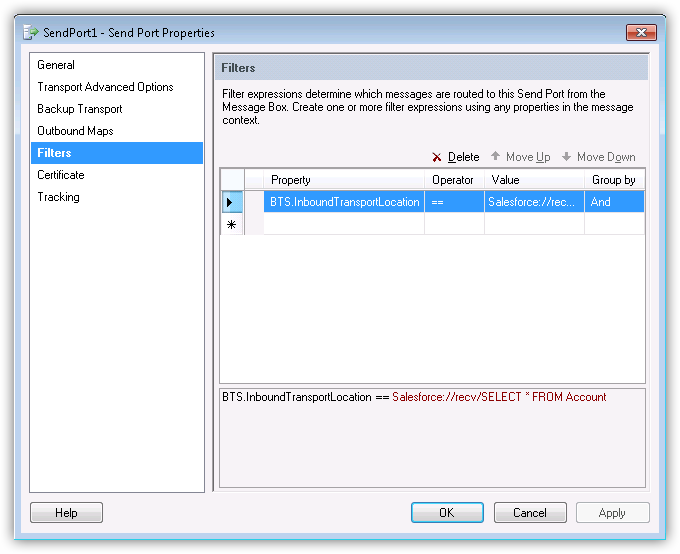
- Click Filters in the left-hand side of the configuration screen for the send port.
- Set the following properties:
- Property: Select "BTS.InboundTransportLocation" from the menu.
- Operator: Select "==" from the menu.
- Value: Enter the URI of the receive location. The URI is shown in the receive location properties.
- Operator: Select "==" from the menu.
- Property: Select "BTS.InboundTransportLocation" from the menu.
You can now use the send port to write files that have been sent from the receive location.
Enlist and Enable the Locations and Ports
The final step is to enlist the send port and enable the receive location: Right-click the send port and click Enlist. Then right-click the receive location and click Enable.
Note: Enable the receive location last: This makes sure the file gets picked up for writing by the send port.
Troubleshooting
To check if errors are occurring, expand "Event Viewer (Local)" in the navigation tree in the Administration Console. Expand Windows Logs and click Applications.
The log will include error messages for all applications on the system, so it is important to check that the source of the error message is "CData BizTalk PingOne Receive Adapter". Details of the error message should provide insight into why the error is occurring. For guidance on resolving the error, contact [email protected].





