Connect Salesforce to IBM WebSphere Using the CData JDBC Driver
IBM WebSphere is a powerful application server that runs many enterprise level Java applications and services. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce, IBM WebSphere applications can connect to Salesforce and work with data using standard SQL queries instead of complex APIs. This simplifies integration, reduces development effort, and provides secure, real-time access to critical business data.
About Salesforce Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from Salesforce has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access to custom entities and fields means Salesforce users get access to all of Salesforce.
- Create atomic and batch update operations.
- Read, write, update, and delete their Salesforce data.
- Leverage the latest Salesforce features and functionalities with support for SOAP API versions 30.0.
- See improved performance based on SOQL support to push complex queries down to Salesforce servers.
- Use SQL stored procedures to perform actions like creating, retrieving, aborting, and deleting jobs, uploading and downloading attachments and documents, and more.
Users frequently integrate Salesforce data with:
- other ERPs, marketing automation, HCMs, and more.
- preferred data tools like Power BI, Tableau, Looker, and more.
- databases and data warehouses.
For more information on how CData solutions work with Salesforce, check out our Salesforce integration page.
Getting Started
Prerequisites
- Access to a Salesforce account (with API permissions)
- IBM WebSphere Application Server (configured and running)
- CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce
- Java Servlet WAR application ready for deployment
Note: This article uses Salesforce as a demonstration data source, but the same steps can be followed to connect to any of the 250+ JDBC Drivers available in our portfolio.
Getting Started
Step 1: Download and install the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce
Download and install the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce, which provides a .jar file: cdata.jdbc.salesforce.jar
Step 2: Install and configure IBM Websphere
- Create an account in IBM WebSphere using the official IBM site.
- Install and configure the IBM Websphere Application server in the local system using the documentation: IBM Websphere Application Server
- Once the application server is installed, start the WebSphere Server using the Admin Console in your browser: https://your-server:9043/ibm/console
Step 3: Set up the JDBC provider and data source for Salesforce
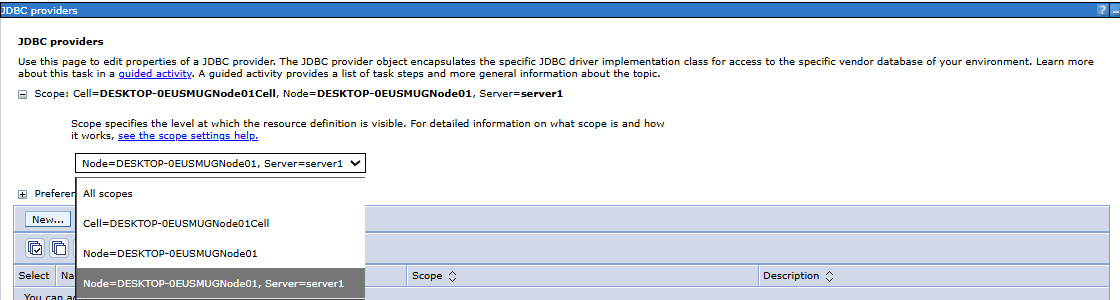
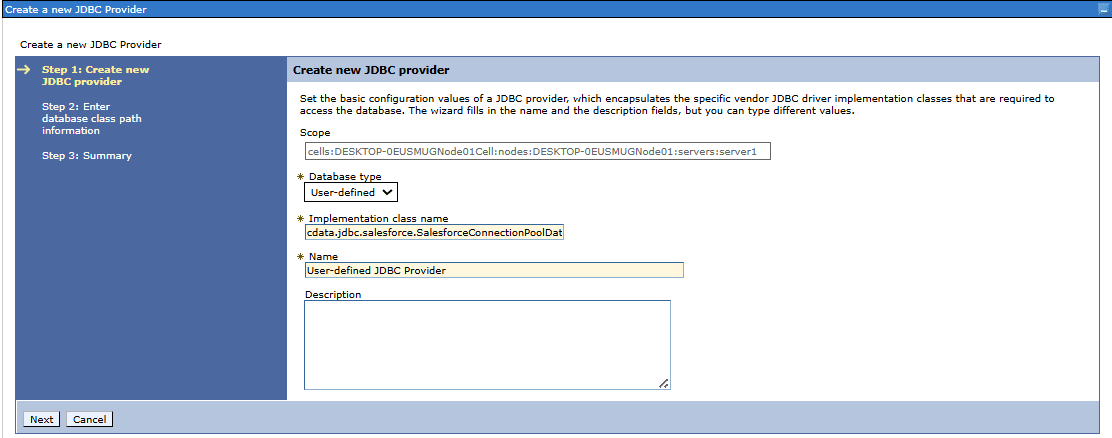
- Go to Resources, expand the JDBC section, and then select JDBC providers to create a new provider
- Select the appropriate scope from the drop down menu
- Click New to add a JDBC provider
- Choose User defined as the database type
- Enter cdata.jdbc.salesforce.SalesforceConnectionPoolDataSource as the implementation class name
- Type a name for the provider, for example User defined JDBC Provider
- Enter the full path of the JDBC driver JAR file in the classpath field
- Click Next, then Finish, and save the changes to the master configuration.
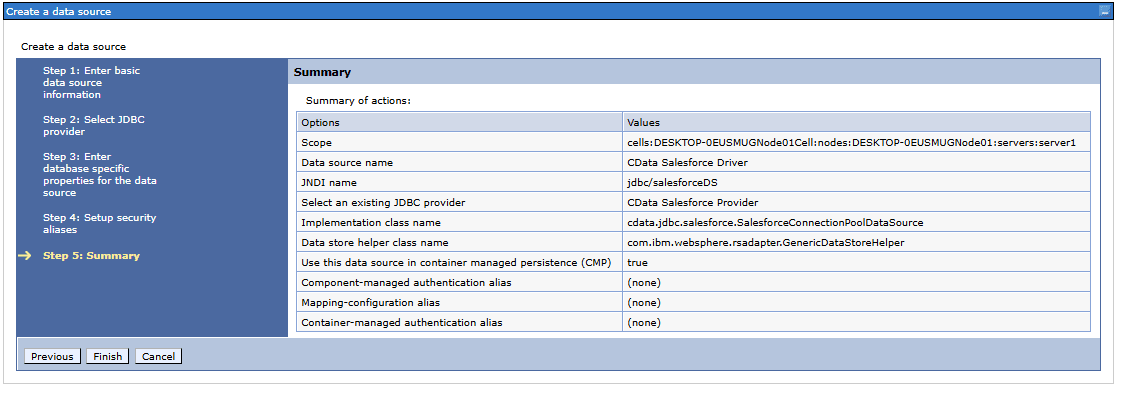
- Once the JDBC provider is created, add a JDBC data source.
- Enter the basic details such as Data Source Name and JNDI name
- Select the existing JDBC provider created earlier (e.g., CData Salesforce Provider)
- Provide the Implementation class name: cdata.jdbc.salesforce.SalesforceConnectionPoolDataSource
- Add the Data Store Helper Class Name: com.ibm.websphere.rsadapter.GenericDataStoreHelper
- Configure security by setting authentication aliases if required
- Review the Summary page to verify all details and click Finish to complete the data source creation
- Select the newly created data source from the list and open Custom properties
-
Add the JDBC connection string under the URL property and press OK. For example:
jdbc:salesforce:RTK=5246...;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH;
There are several authentication methods available for connecting to Salesforce: OAuth, Login (or basic), and SSO. The Login method requires you to have the username, password, and security token of the user.
OAuth Authentication (default)
The default authentication mechanism (and the one preferred by Salesforce) is OAuth. To use OAuth with CData's embedded OAuth application, leave the connection properties blank. If you have configured your own custom OAuth application with Salesforce (see the Help documentation for more information), set OAuthClientId, OAuthClientSecret, and CallbackURL to the properties for you application. Set InitiateOAuth to the desired OAuth flow ("GETANDREFRESH" will have the connector manage the entire OAuth flow).
Login (or Basic) Authentication
If you do not wish do not wish to use OAuth authentication, you can use Login (or basic) authentication. Set AuthScheme to Basic, and set the User, Password, and SecurityToken properties. You can configure your security token in Salesforce.
SSO (single sign-on) Authentication
SSO (single sign-on) can be used by setting the SSOProperties, SSOLoginUrl, and SSOExchangeURL connection properties, which allow you to authenticate to an identity provider. See the "Getting Started" chapter in the Help documentation for more information.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Salesforce JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.salesforce.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.

Note: If the URL property is not available, create it and then add the JDBC connection string.
Tip: Always test the connection string with the driver before entering it in the URL property.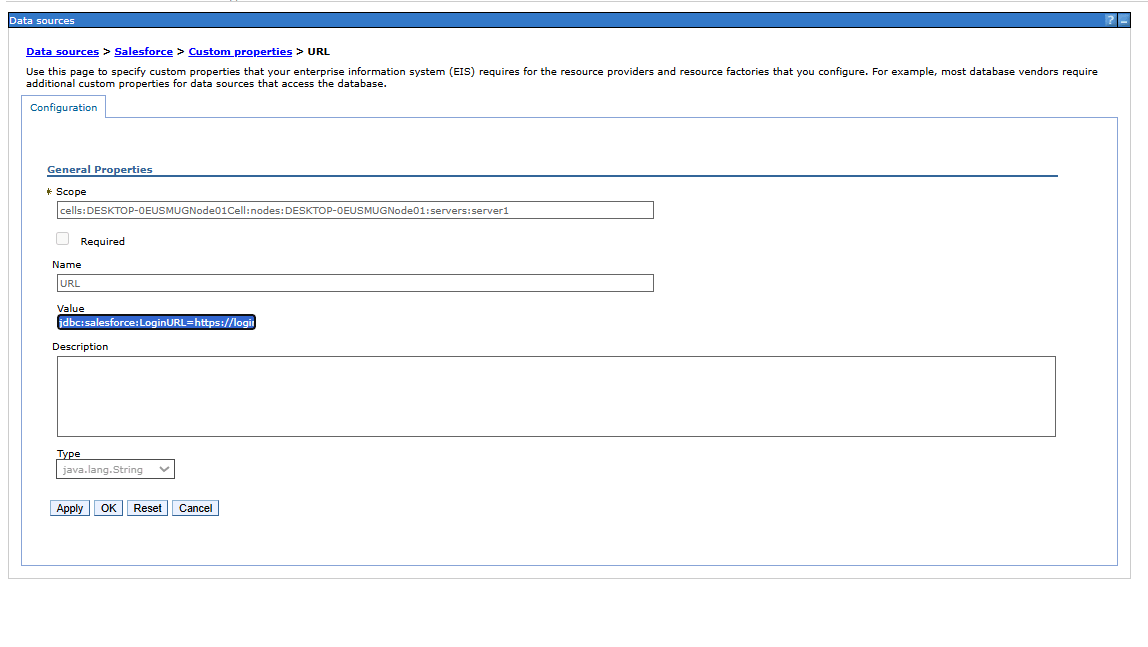
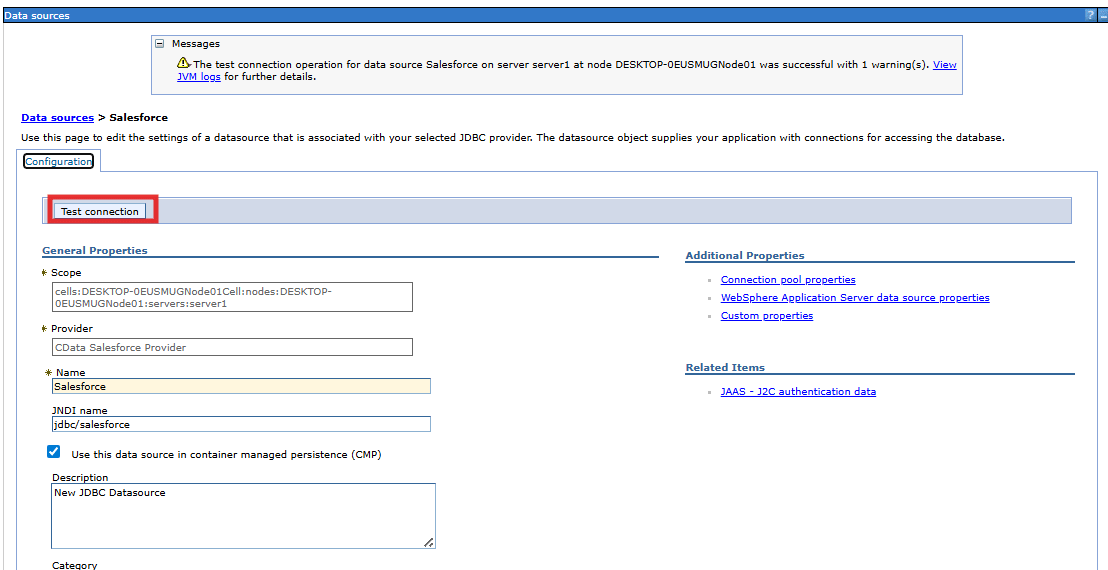
- Now open the data source and choose Test Connection
Step 4: Build the web application
- Build the web application using preferred Java framework (Servlet, JSP, or Spring). The resulting .war file will typically follow a structure like this:
- Define the data access logic using JDBC or JPA, referencing the data source through a JNDI name
- This article walks through JDBC connection setup and deploying a Java Servlet application
- Package the project as a WAR (Web Application Archive) or EAR (Enterprise Archive) file for deployment
- In a terminal compile the java file using the command:
cd webcontent jar cvf ..\SalesforceServletApp.war *
SalesforceServletApp.war |--webcontent | |--index.jsp -- JSP page (entry point) | | | |--WEB-INF/ --Hidden from direct browser access | |--web.xml -- Deployment descriptor | | | |--classes/ --Compiled .class files | |--com/example/Salesforce/ | |--SalesforceServlet.class | |--lib/ --Dependency JARs |--cdata.jdbc.salesforce.jar
Step 5: Deploy the Salesforce application in WebSphere
- In the WebSphere admin console, go to Applications and select Install New Application
- Browse and upload the WAR file, then continue with the installation wizard.
Step 6: Retrieve Salesforce data through WebSphere
- Access the application using its context root: http://hostname:port/context-root/page
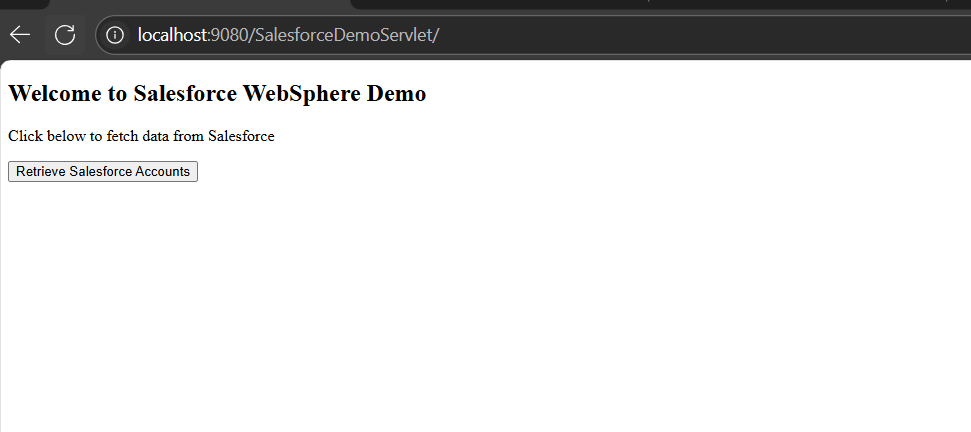 Note: Ensure the deployed application is started before opening it in the browser.
Note: Ensure the deployed application is started before opening it in the browser.
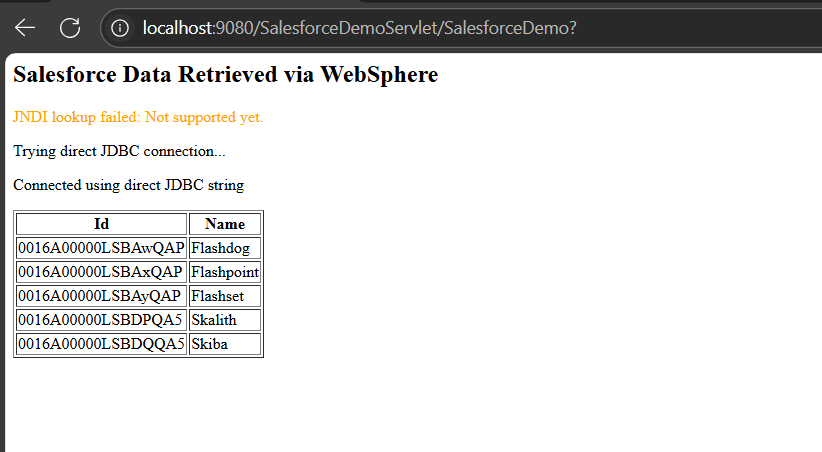
We can now view the retrieved data from the source. The data is accessible directly through IBM WebSphere. This setup demonstrates how a servlet can be deployed in WebSphere to retrieve Salesforce data using the JDBC driver, creating a strong foundation for building advanced Salesforce powered enterprise applications.
Get Started with Connecting Salesforce to IBM WebSphere
Start connecting Salesforce to IBM WebSphere with the CData JDBC Connector today. Download the free 30-day trial and explore how easy it is to enable secure, real-time data access for your applications. As always, our world-class Support Team is available to help with any questions you may have.






