Integrating Dataiku with SingleStore Data via CData Connect AI
Dataiku is a collaborative data science and AI platform that enables teams to design, deploy, and manage machine learning and generative AI projects within a governed environment. It's Agent and GenAI framework allows users to build intelligent agents that can analyze, generate, and act on data through custom workflows and model orchestration.
By integrating Dataiku with CData Connect AI through the built-in MCP (Model Context Protocol) Server, these agents gain secure, real-time access to live SingleStore data. The integration bridges Dataiku's agent execution environment with CData's governed enterprise connectivity layer, allowing every query or instruction to run safely against authorized data sources without manual exports or staging.
This article demonstrates how to configure SingleStore connectivity in Connect AI, prepare a Python code environment in Dataiku with MCP support, and create an agent that queries and interacts with live SingleStore data directly from within Dataiku.
Step 1: Configure SingleStore Connectivity for Dataiku
Connectivity to SingleStore from Dataiku is made possible through CData Connect AI's Remote MCP Server. To interact with SingleStore data from Dataiku, you start by creating and configuring a SingleStore connection in CData Connect AI.
- Log into Connect AI, click Sources, then click Add Connection
- Select "SingleStore" from the Add Connection panel
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to SingleStore.
The following connection properties are required in order to connect to data.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Database (Optional): The default database to connect to when connecting to the SingleStore Server. If this is not set, tables from all databases will be returned.
Connect Using Standard Authentication
To authenticate using standard authentication, set the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
Connect Using Integrated Security
As an alternative to providing the standard username and password, you can set IntegratedSecurity to True to authenticate trusted users to the server via Windows Authentication.
Connect Using SSL Authentication
You can leverage SSL authentication to connect to SingleStore data via a secure session. Configure the following connection properties to connect to data:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate. Used in the case of 2-way SSL, where truststore and keystore are kept on both the client and server machines.
- SSLClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSLClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSLClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSLServerCert: The certificate to be accepted from the server.
Connect Using SSH Authentication
Using SSH, you can securely login to a remote machine. To access SingleStore data via SSH, configure the following connection properties:
- SSHClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate.
- SSHClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSHClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSHClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSHPassword: The password that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
- SSHPort: The port used for SSH operations.
- SSHServer: The SSH authentication server you are trying to authenticate against.
- SSHServerFingerPrint: The SSH Server fingerprint used for verification of the host you are connecting to.
- SSHUser: Set this to the username that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
- Click Save & Test
- Open the Permissions tab and set user-based permissions

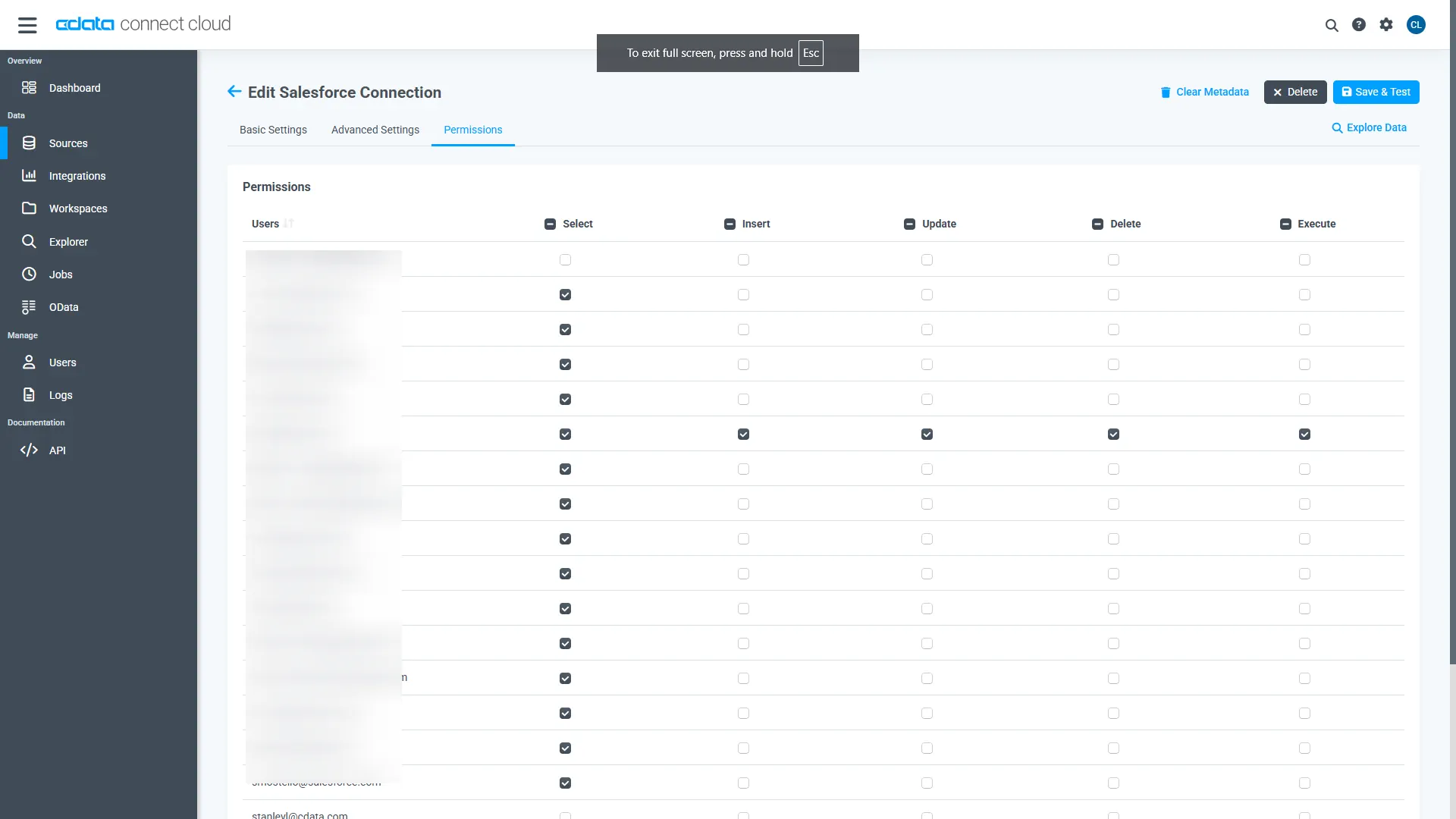
Add a Personal Access Token
A Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect AI from Dataiku. It is best practice to create a separate PAT for each integration to maintain granular access control
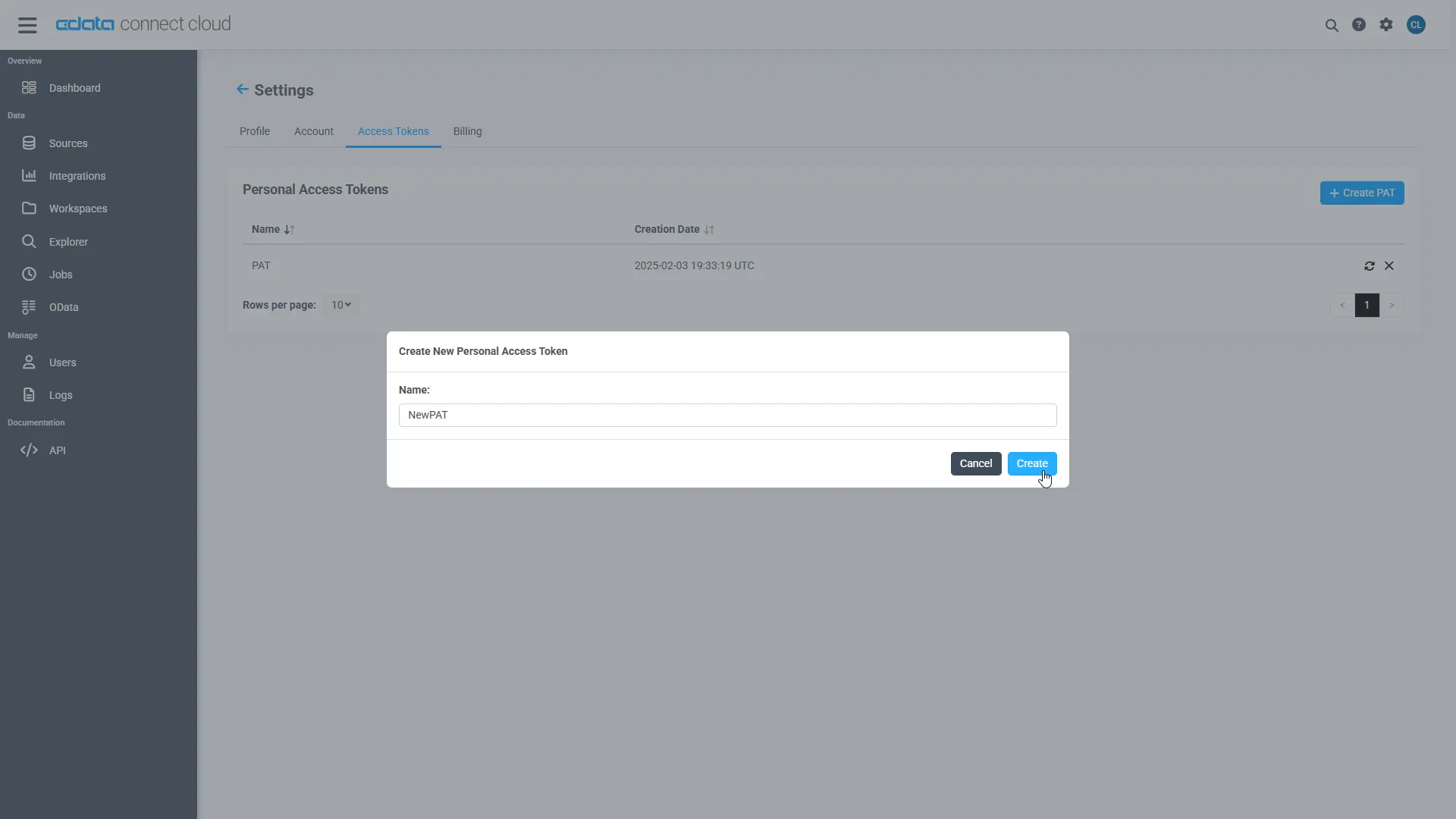
- Click the gear icon () at the top right of the Connect AI app to open Settings
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT
- Give the PAT a descriptive name and click Create
- Copy the token when displayed and store it securely. It will not be shown again
With the SingleStore connection configured and a PAT generated, Dataiku can now connect to SingleStore data through the CData MCP Server.
Step 2: Prepare Dataiku and the Code Environment
A dedicated python code environment in Dataiku provides the runtime support needed for MCP-based communication. To enable Dataiku Agents to connect to CData Connect AI, create a Python environment and install the MCP client dependencies required for agent-to-server interaction.
- In Dataiku Cloud, open Code Envs
- Click Add a code env to open the DSS settings window
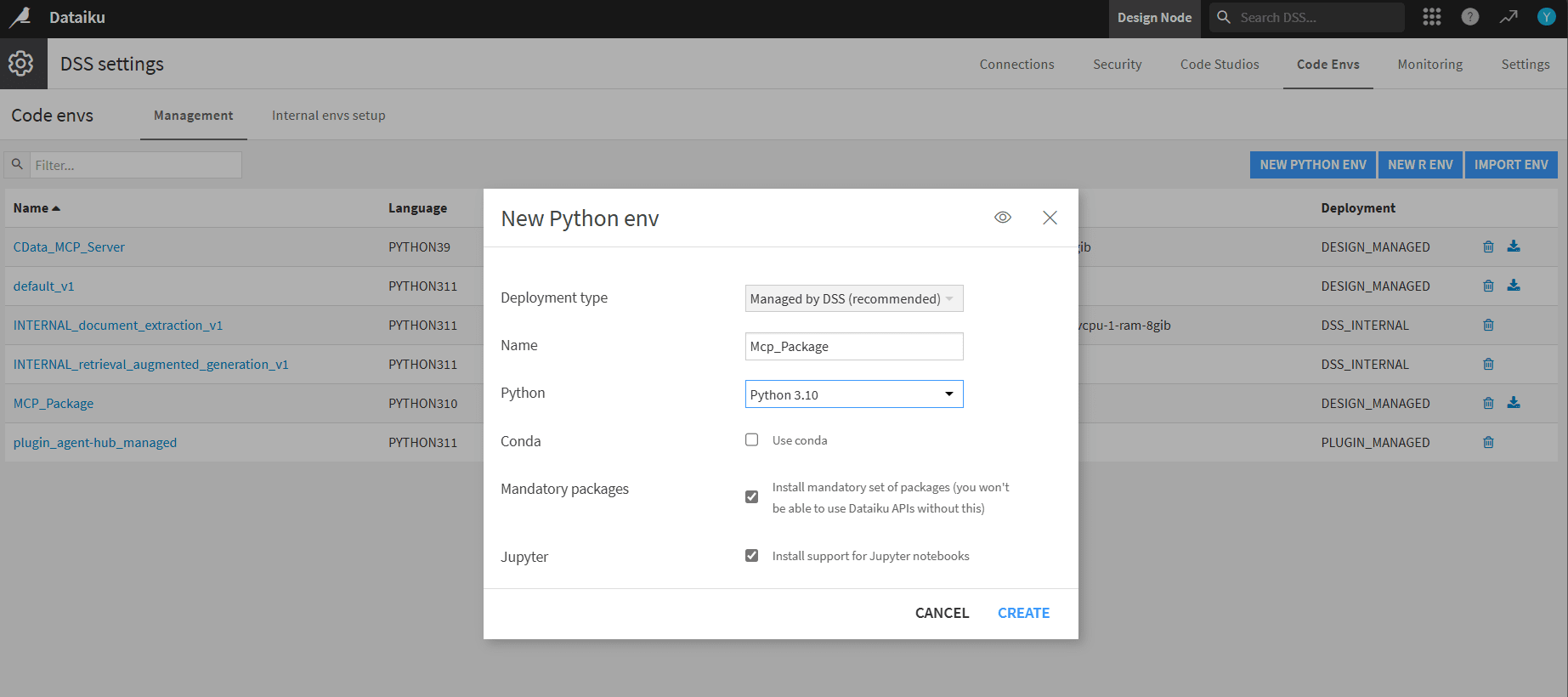
- In DSS, click New Python env. Name it (for example, MCP_Package) and choose Python 3.10 (3.10 to 3.13 supported)
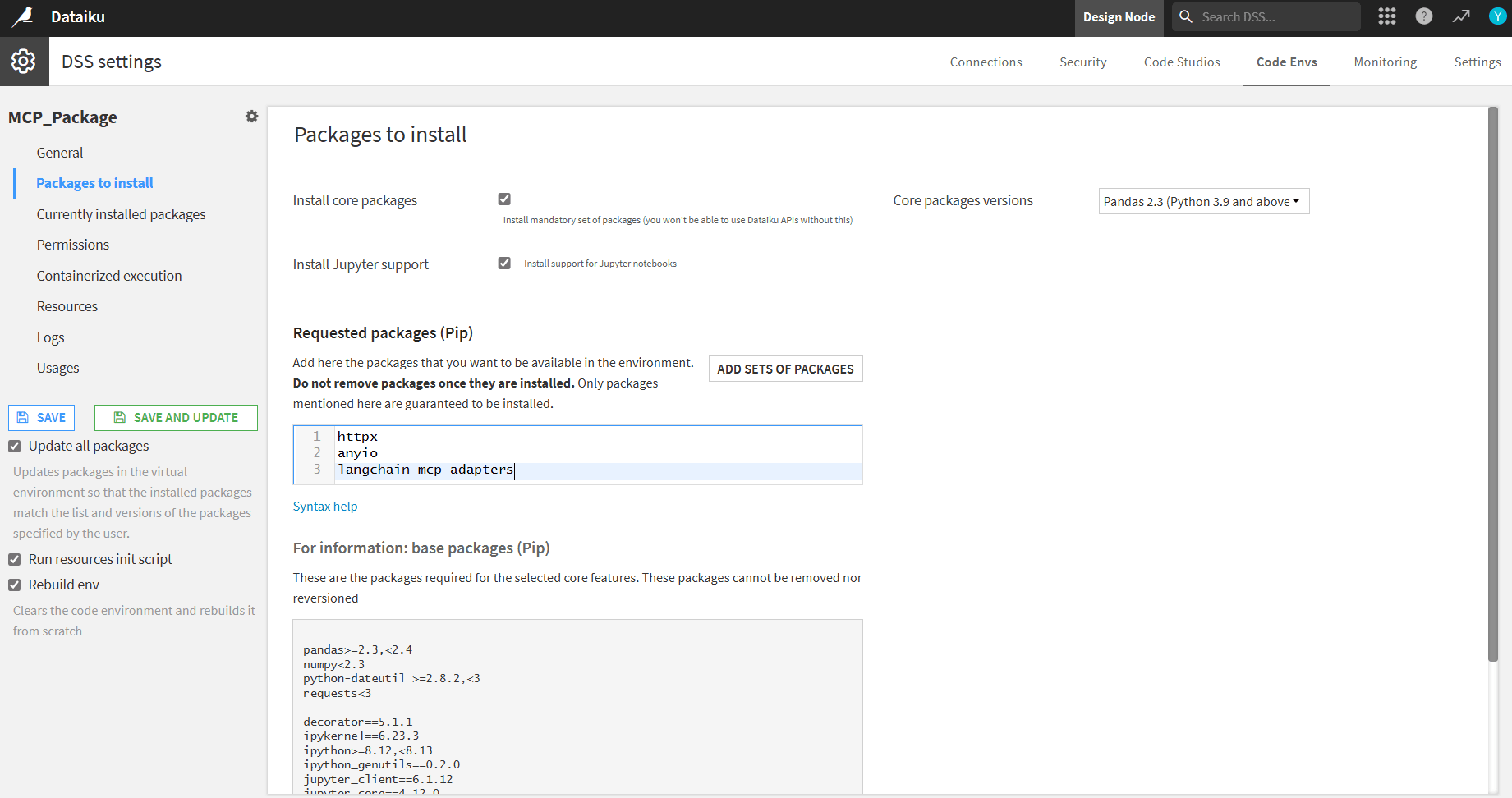
- Open Packages to install and add the following pip packages:
- httpx
- anyio
- langchain-mcp-adapters
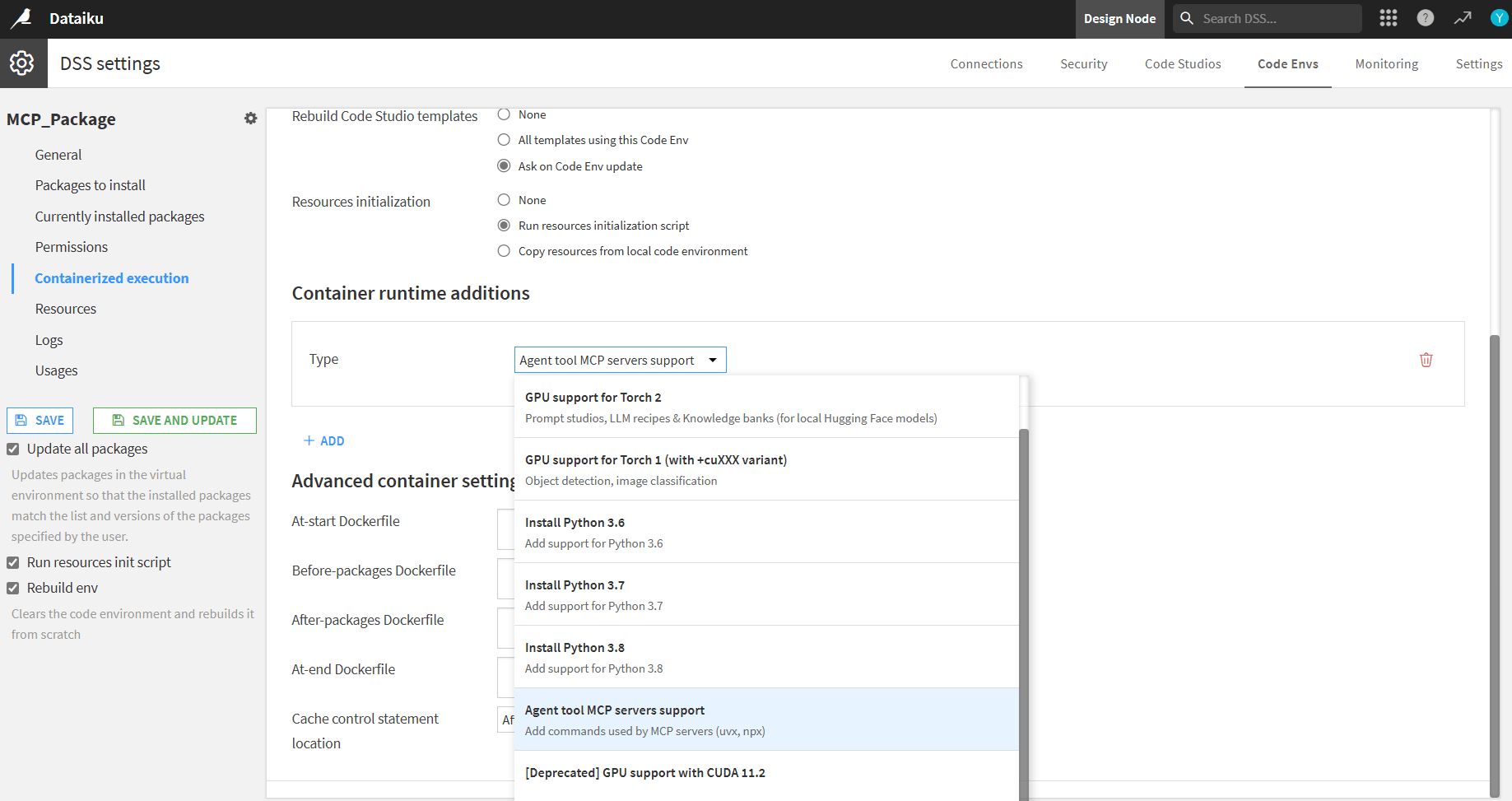
- Open Containerized execution and under Container runtime additions select Agent tool MCP servers support
- Check Rebuild env and click Save and update to install packages
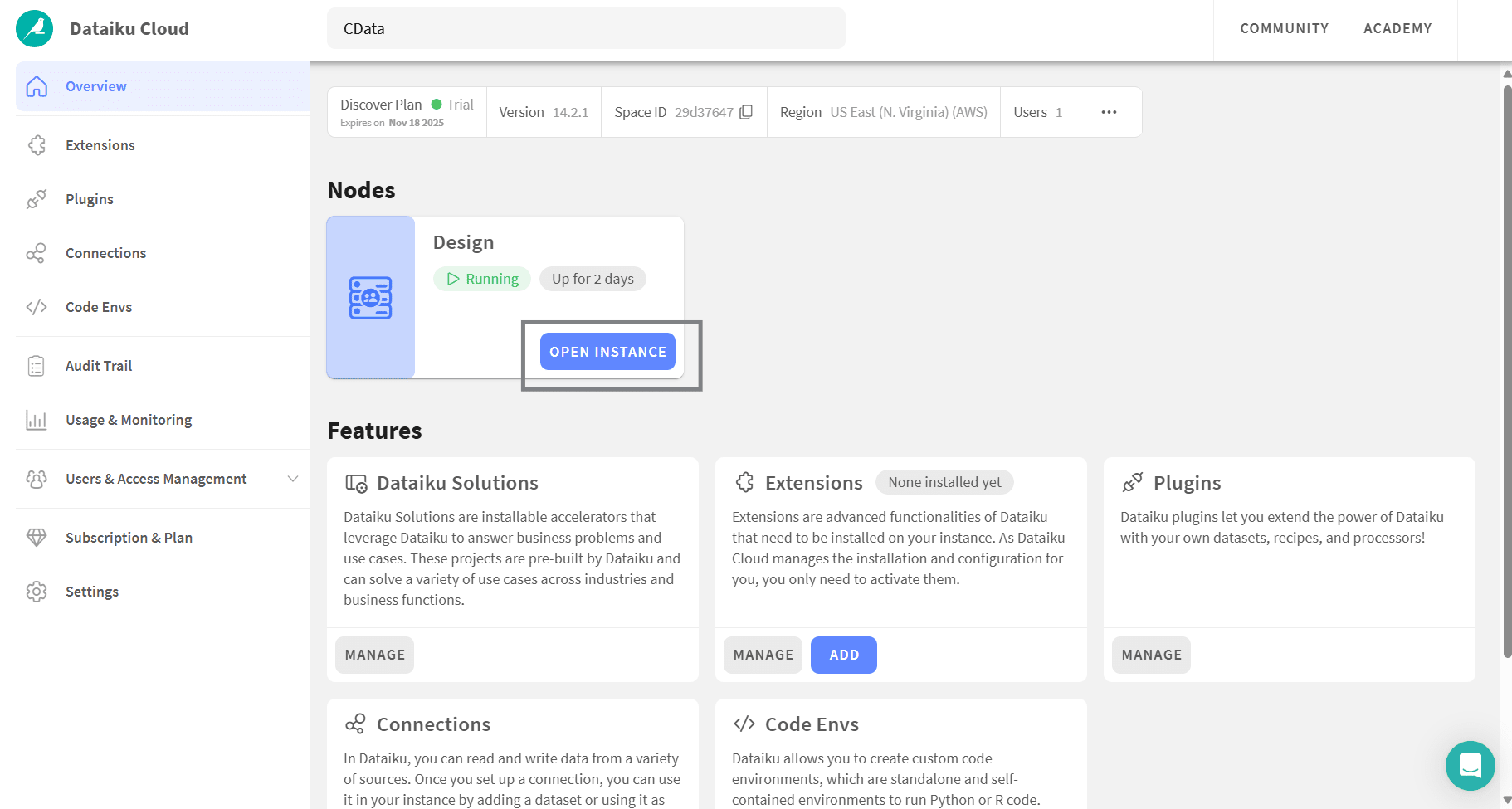
- Back in Dataiku Cloud, open Overview and click Open instance
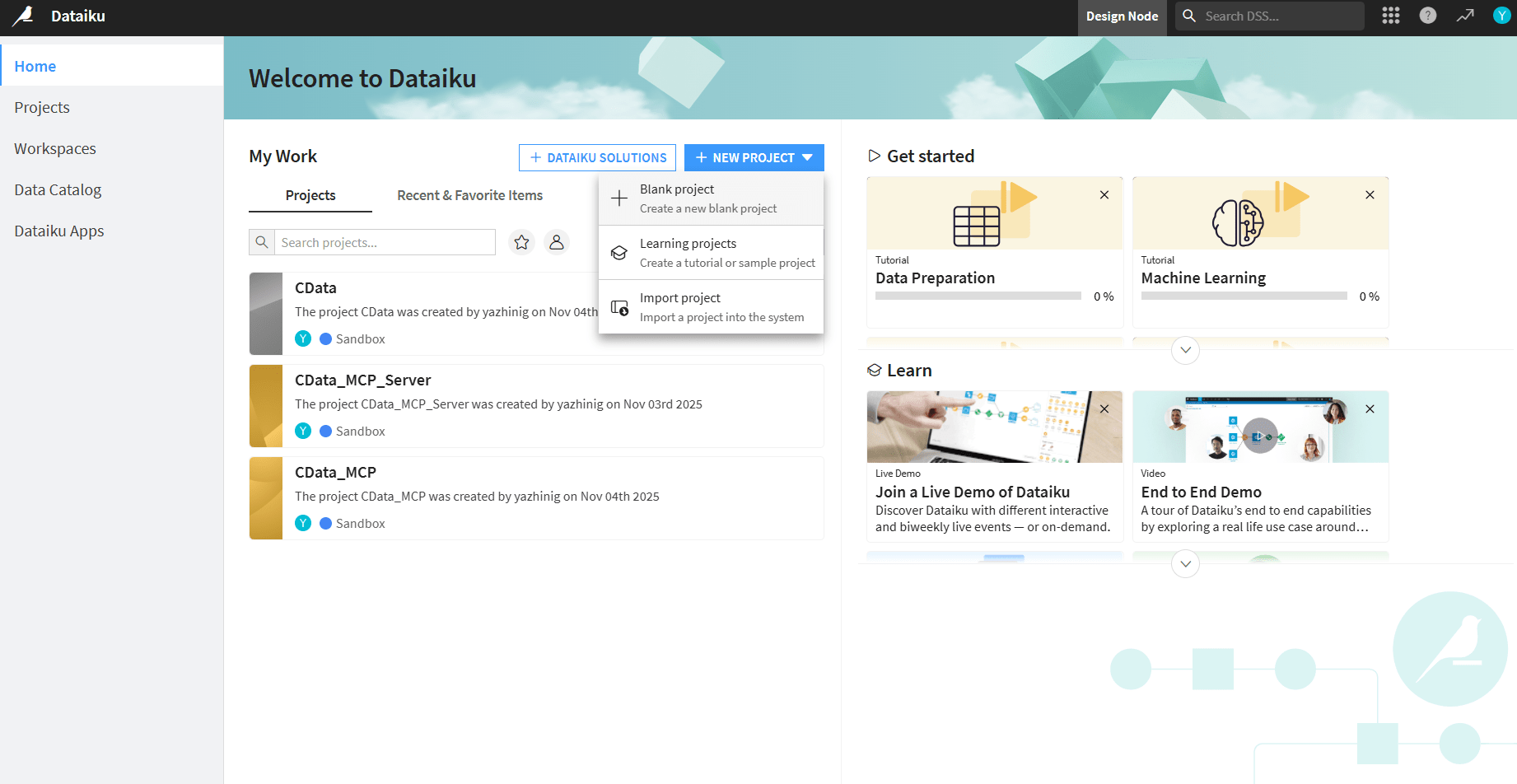
- Click + New project and select Blank project. Name the project
Step 3: Create a Dataiku Agent and connect to the MCP server
The Dataiku Agent serves as the bridge between the Dataiku workspace and the CData MCP Server. To enable this connection, create a custom code-based agent, assign it the configured Python environment, and embed your Connect AI credentials to allow the agent to query and interact with live SingleStore data.
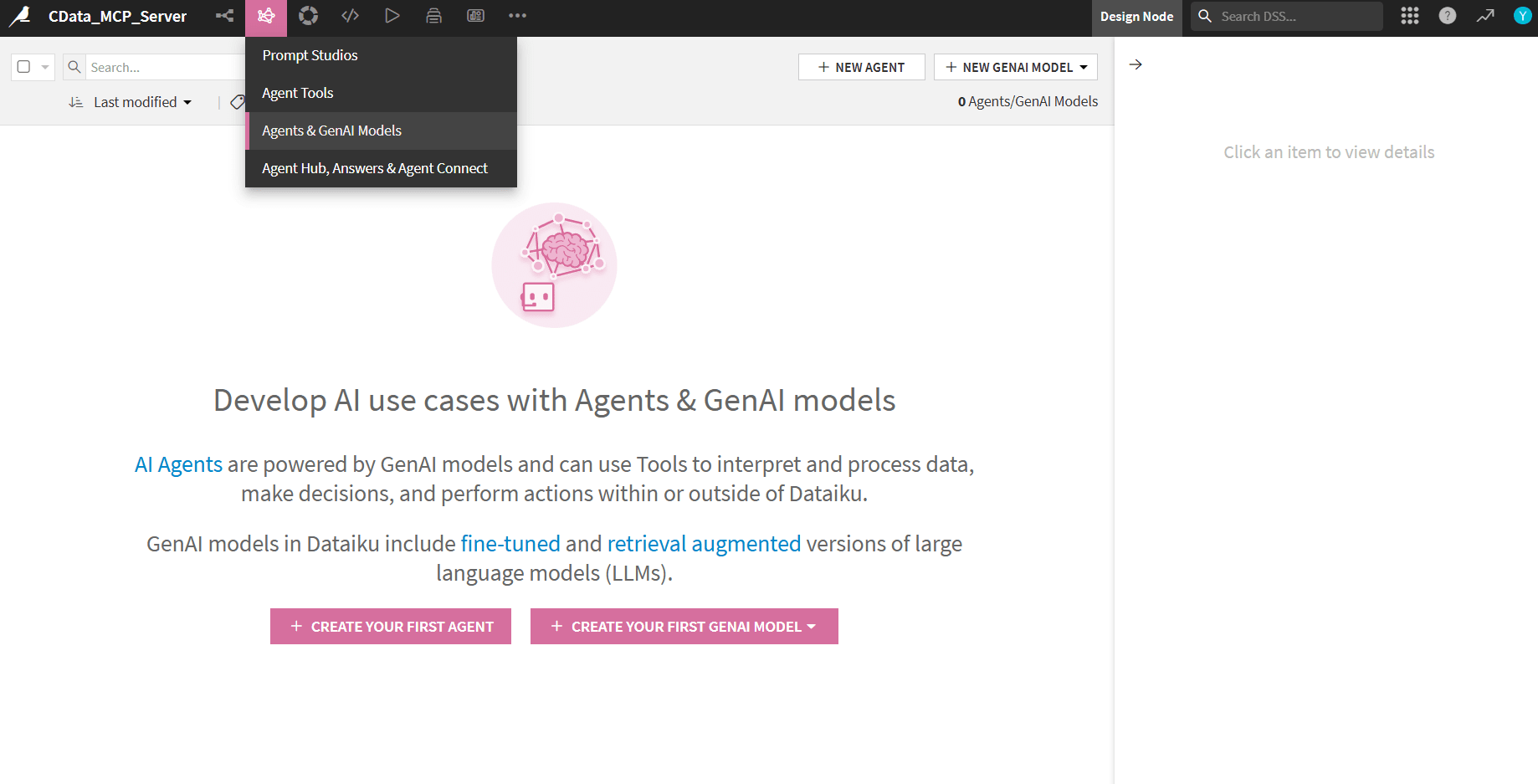
- Go to Agents & GenAI Models and click Create your first agent
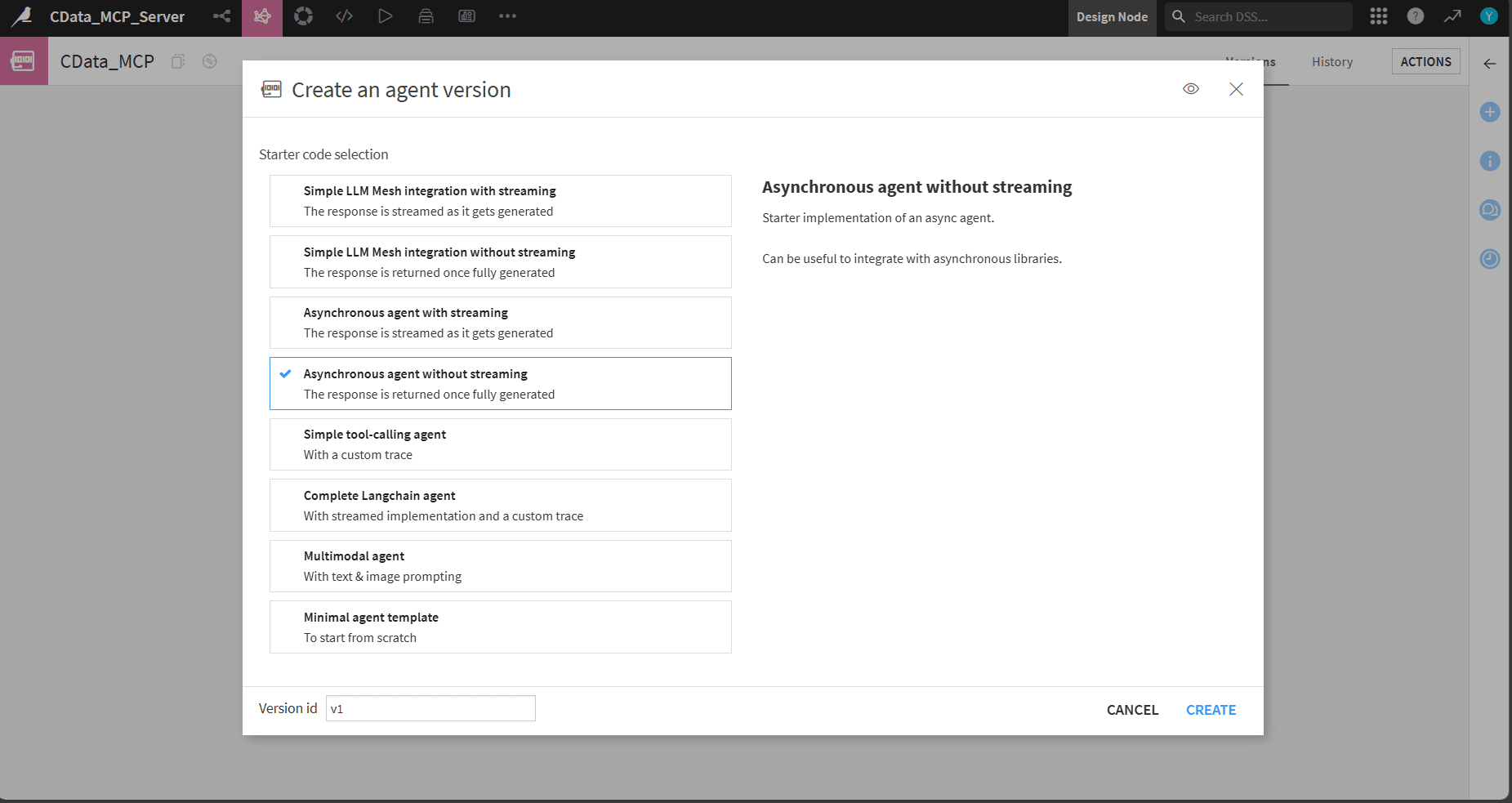
- Choose Code agent, name it, and for Agent version select Asynchronous agent without streaming
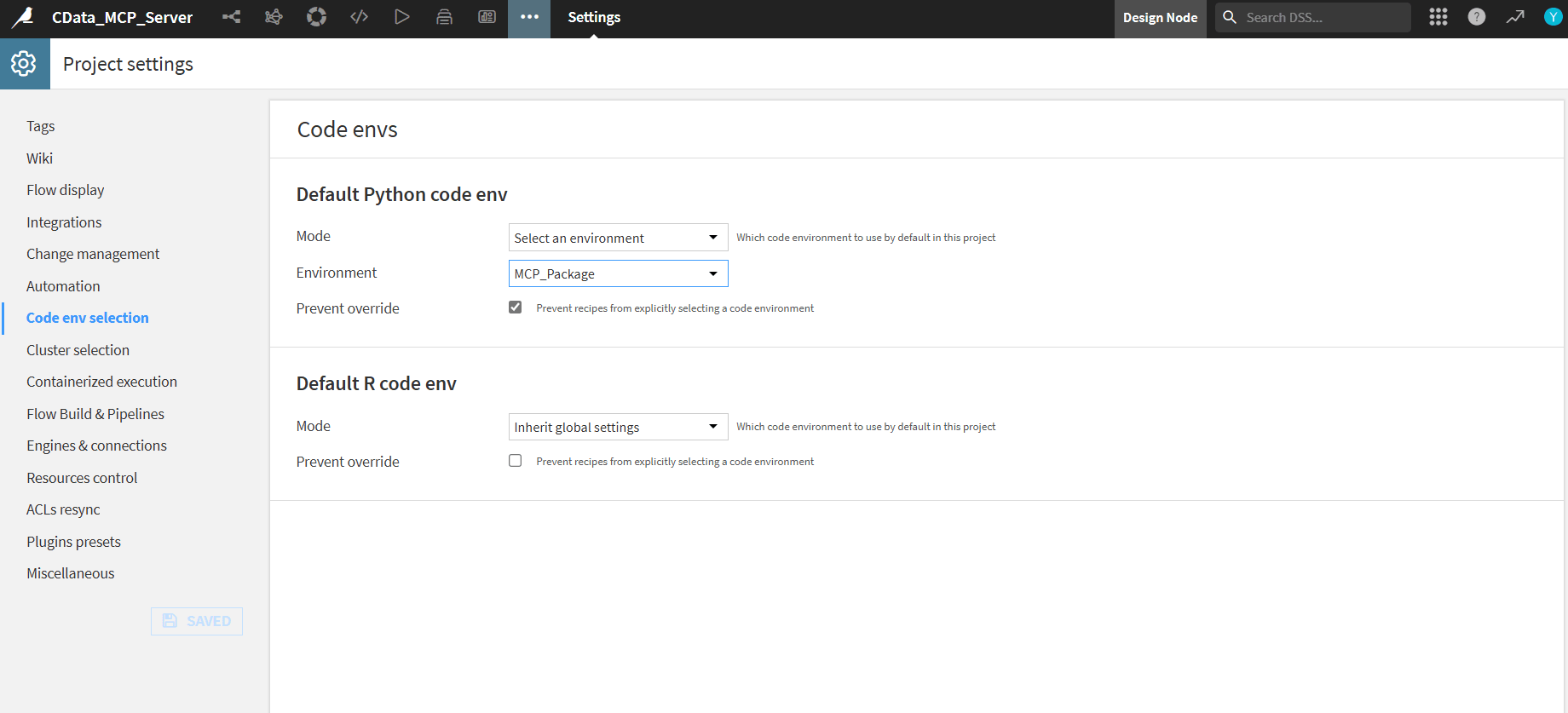
- From the tab above select Settings. In Code env selection set Default Python code env to the environment you created (for example, MCP_Package)
- Return to the Agent Design tab and paste the following code. Replace EMAIL, and PAT with your values
- Open Quick Test on the right side panel
- Paste the JSON code and click Run test
import os
import base64
from typing import Dict, Any, List
from dataiku.llm.python import BaseLLM
from langchain_mcp_adapters.client import MultiServerMCPClient
# ---------- Persistent MCP client (cached between calls) ----------
_MCP_CLIENT = None
def _get_mcp_client() -> MultiServerMCPClient:
"""Create (or reuse) a MultiServerMCPClient to CData Cloud MCP."""
global _MCP_CLIENT
if _MCP_CLIENT is not None:
return _MCP_CLIENT
# Set creds via env/project variables ideally
EMAIL = os.getenv("CDATA_EMAIL", "YOUR_EMAIL")
PAT = os.getenv("CDATA_PAT", "YOUR_PAT")
BASE_URL = "https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp"
if not EMAIL or PAT == "YOUR_PAT":
raise ValueError("Set CDATA_EMAIL and CDATA_PAT as env variables or inline in the code.")
token = base64.b64encode(f"{EMAIL}:{PAT}".encode()).decode()
headers = {"Authorization": f"Basic {token}"}
_MCP_CLIENT = MultiServerMCPClient(
connections={
"cdata": {
"transport": "streamable_http",
"url": BASE_URL,
"headers": headers,
}
}
)
return _MCP_CLIENT
def _pick_tool(tools, names: List[str]):
L = [n.lower() for n in names]
return next((t for t in tools if t.name.lower() in L), None)
async def _route(prompt: str) -> str:
"""
Simple intent router:
- 'list connections' / 'list catalogs' -> getCatalogs
- 'sql: ...' or 'query: ...' -> queryData
- otherwise -> help text
"""
client = _get_mcp_client()
tools = await client.get_tools()
p = prompt.strip()
low = p.lower()
# 1) List connections (catalogs)
if "list connections" in low or "list catalogs" in low:
t = _pick_tool(tools, ["getCatalogs", "listCatalogs"])
if not t:
return "No 'getCatalogs' tool found on the MCP server."
res = await t.ainvoke({})
return str(res)[:4000]
# 2) Run SQL
if low.startswith("sql:") or low.startswith("query:"):
sql = p.split(":", 1)[1].strip()
t = _pick_tool(tools, ["queryData", "sqlQuery", "runQuery", "query"])
if not t:
return "No query-capable tool (queryData/sqlQuery) found on the MCP server."
try:
res = await t.ainvoke({"query": sql})
return str(res)[:4000]
except Exception as e:
return f"Query failed: {e}"
# 3) Help
return (
"Connected to CData MCP
"
"Say **'list connections'** to view available sources, or run a SQL like:
"
" sql: SELECT * FROM [Salesforce1].[SYS].[Connections] LIMIT 5
"
"Remember to use bracket quoting for catalog/schema/table names."
)
class MyLLM(BaseLLM):
async def aprocess(self, query: Dict[str, Any], settings: Dict[str, Any], trace: Any):
# Extract last user message from the Quick Test payload
prompt = ""
try:
prompt = (query.get("messages") or [])[-1].get("content", "")
except Exception:
prompt = ""
try:
reply = await _route(prompt)
except Exception as e:
reply = f"Error: {e}"
# The template expects a dict with a 'text' key
return {"text": reply}
Run a Quick Test
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "list connections"
}
],
"context": {}
}
Chat with your Agent
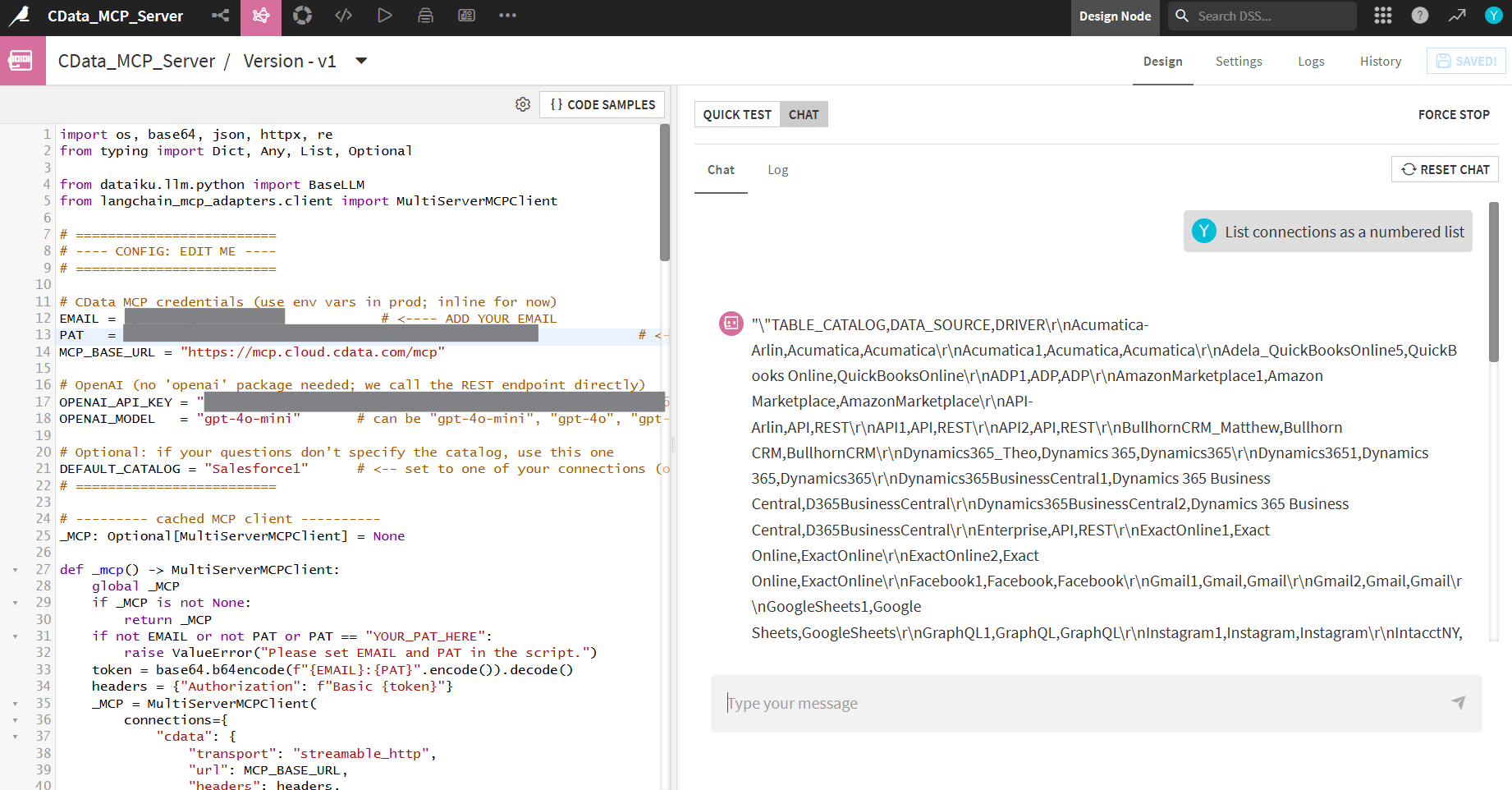
Switch to the Chat tab and try prompting like, "List all connections". The chat output will show a list of connection catalogs.
Get CData Connect AI
To access 300+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources from your AI agents, try CData Connect AI today.






