How to Connect to Live Snowflake Data from crewAI Agents (via CData Connect AI)
crewAI is an open-source Python framework for building multi-agent systems. When combined with CData Connect AI Remote MCP, you can leverage crewAI to build intelligent agents that interact with your Snowflake data in real-time through natural language queries. This article outlines connecting to Snowflake using Connect AI Remote MCP and configuring a simple console-based chatbot agent that leverages the crewAI framework and OpenAI to interact with your Snowflake data.
CData Connect AI offers a dedicated cloud-to-cloud interface for connecting to Snowflake data. The CData Connect AI Remote MCP Server enables secure communication between crewAI agents and Snowflake. This allows your agents to read from and take actions on your live Snowflake data. With its inherent optimized data processing capabilities, CData Connect AI leverages server-side processing to swiftly deliver the requested Snowflake data.
About Snowflake Data Integration
CData simplifies access and integration of live Snowflake data. Our customers leverage CData connectivity to:
- Reads and write Snowflake data quickly and efficiently.
- Dynamically obtain metadata for the specified Warehouse, Database, and Schema.
- Authenticate in a variety of ways, including OAuth, OKTA, Azure AD, Azure Managed Service Identity, PingFederate, private key, and more.
Many CData users use CData solutions to access Snowflake from their preferred tools and applications, and replicate data from their disparate systems into Snowflake for comprehensive warehousing and analytics.
For more information on integrating Snowflake with CData solutions, refer to our blog: https://www.cdata.com/blog/snowflake-integrations.
Getting Started
Step 1: Configure Snowflake Connectivity for crewAI
Connectivity to Snowflake from crewAI agents is made possible through CData Connect AI Remote MCP. To interact with Snowflake data from your crewAI agent, we start by creating and configuring a Snowflake connection in CData Connect AI.
-
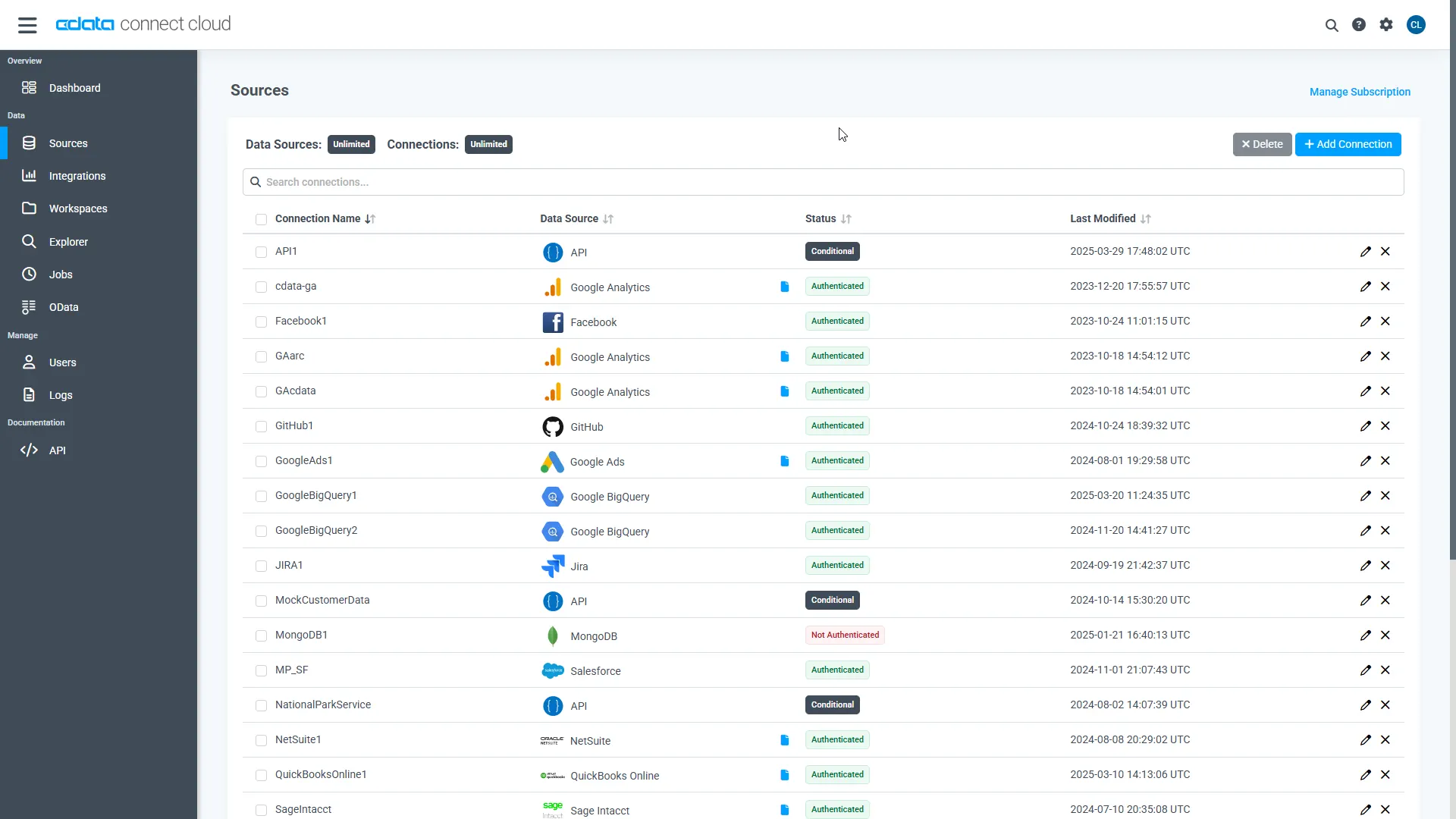
Log into Connect AI, click Connections and click Add Connection
-
Select "Snowflake" from the Add Connection panel

-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Snowflake.
To connect to Snowflake:
- Set User and Password to your Snowflake credentials and set the AuthScheme property to PASSWORD or OKTA.
- Set URL to the URL of the Snowflake instance (i.e.: https://myaccount.snowflakecomputing.com).
- Set Warehouse to the Snowflake warehouse.
- (Optional) Set Account to your Snowflake account if your URL does not conform to the format above.
- (Optional) Set Database and Schema to restrict the tables and views exposed.
See the Getting Started guide in the CData driver documentation for more information.
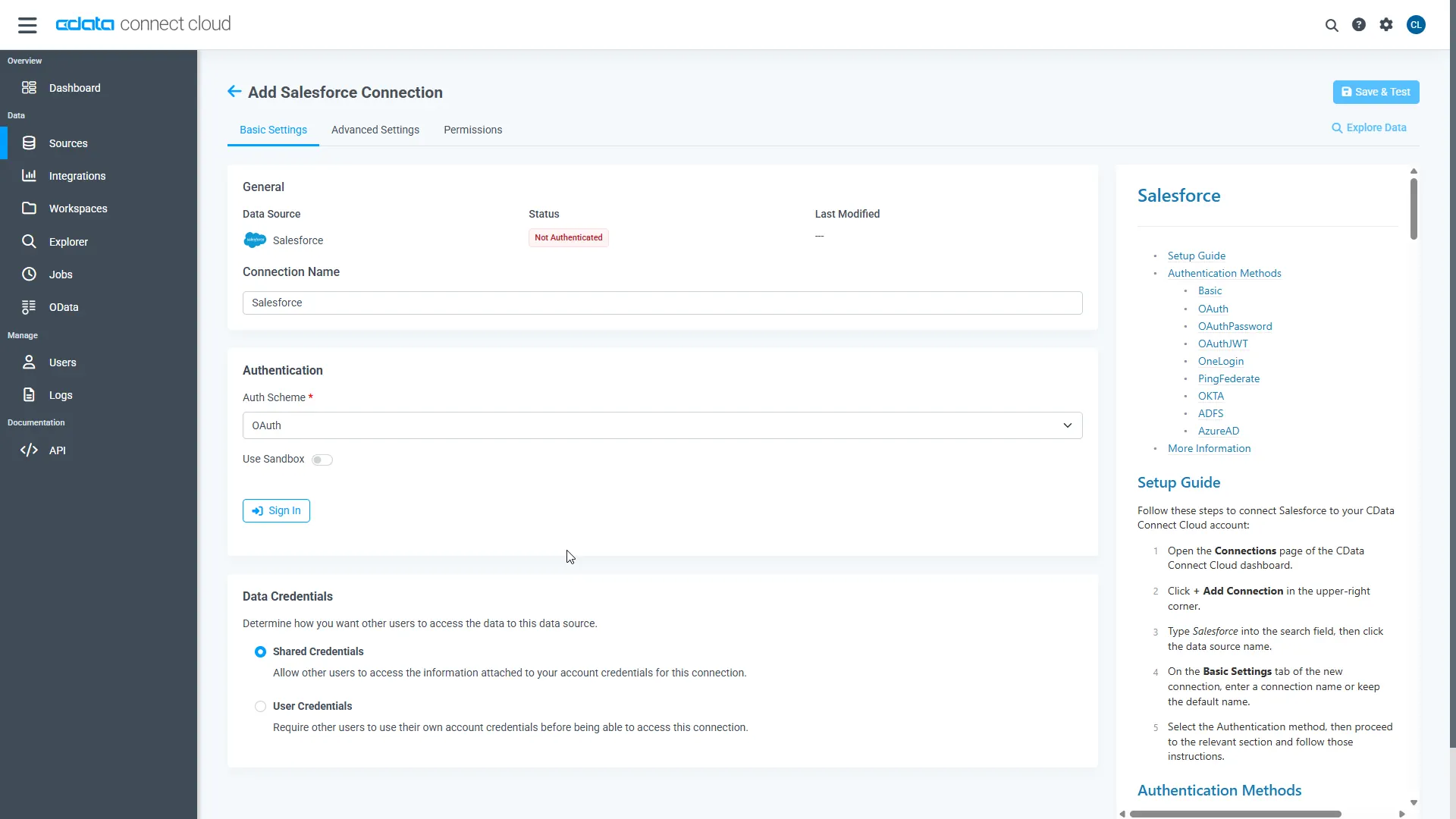 Click Save & Test
Click Save & Test
-
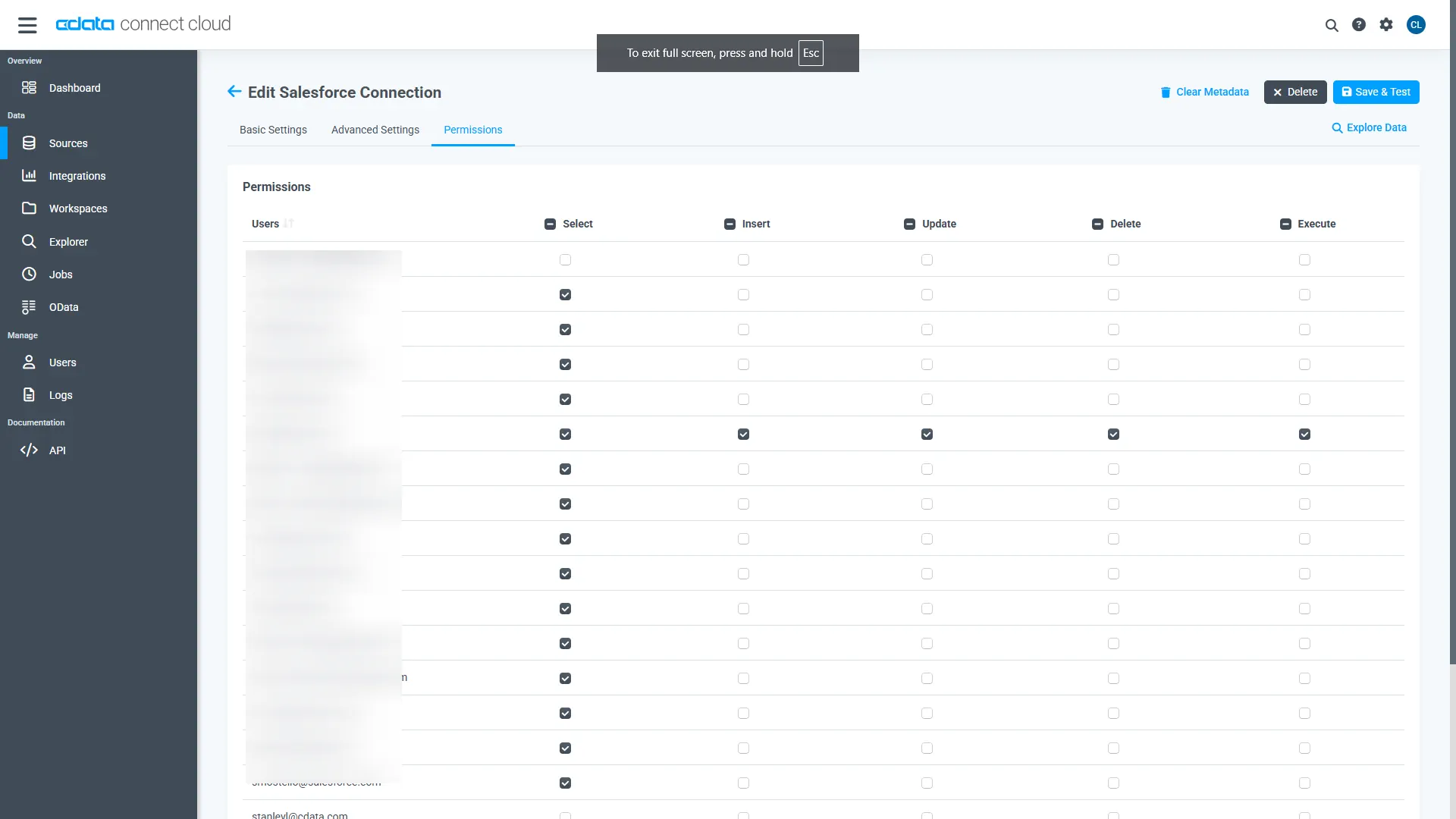
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add Snowflake Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
Add a Personal Access Token
A Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect AI from your crewAI agent. It is best practice to create a separate PAT for each service to maintain granularity of access.
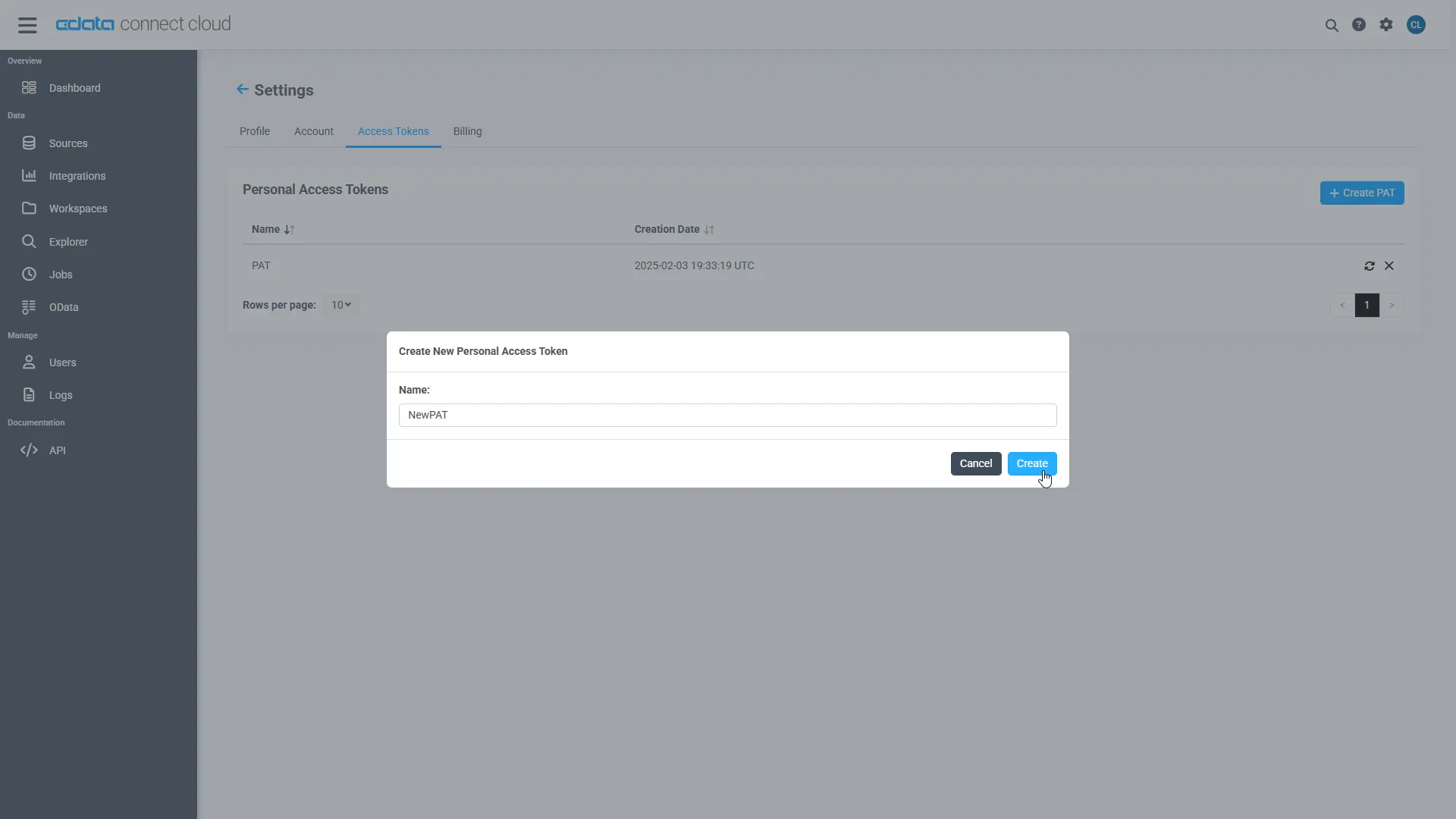
- Click on the Gear icon () at the top right of the Connect AI app to open the settings page.
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
-
Give the PAT a name and click Create.
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured and a PAT generated, we are ready to connect to Snowflake data from your crewAI agent.
Step 2: Set up your crewAI Environment
Before configuring your CrewAI agent, ensure you have the necessary dependencies installed and environment configured.
Configure the CData Connect AI MCP Server
- Create a folder named cdata-mcp-crew-agent.
- Create a file with the extension .env in the cdata-mcp-crew-agent folder.
-
Copy and paste the content below. Replace "CONNECT_AI_EMAIL" with your CData Connect AI username and replace "CONNECT_AI_PAT" with your PAT obtained in the prerequisites. Your OpenAI API key can be found at https://platform.openai.com/.
MCP_SERVER_URL=https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp MCP_USERNAME=YOUR_EMAIL MCP_PASSWORD=YOUR_PAT OPENAI_API_KEY=YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY
Install the crewAI Libraries
Run pip install crewai crewai-tools python-dotenv requests in your terminal.
Create and run the crewAI agent
- Create a file called crew-agent.py. This is the crewAI agent.
-
Configure your crew-agent.py file to use the CData Connect AI MCP Server.
Core Functionality
This Python script creates an intelligent crewAI agent that connects to CData Connect AI's MCP (Model Context Protocol) Server. The agent provides a natural language interface for interacting with your connected data sources, allowing you to query databases, explore schemas, and execute stored procedures without writing SQL directly.
Tool Classes
The script implements 8 specialized tools that handle different aspects of data interaction:
- GetCatalogsTool: Lists all available data sources and databases
- GetSchemasTool: Retrieves database schemas within a specific catalog
- GetTablesTool: Discovers tables with optional catalog/schema filtering
- GetColumnsTool: Fetches column metadata and structure information
- GetProceduresTool: Lists available stored procedures
- GetProcedureParametersTool: Details procedure parameter requirements
- ExecuteProcedureTool: Runs stored procedures with parameters
- QueryDataTool: Executes SQL queries against your data sources
Main Components
The implementation consists of three key components:
- BaseCDataTool: A base class that manages MCP server communication, handles authentication using your Connect AI credentials, and parses Server-Sent Events (SSE) responses
- CDataConnectAgent: The main agent class that uses OpenAI's GPT-4 model to process natural language queries and intelligently select the appropriate tools to fulfill user requests
- Interactive Console: A command-line interface that provides a conversational chatbot experience for exploring and querying your data
Here's the complete implementation:
import os import warnings from typing import Dict, Any, Optional from dotenv import load_dotenv from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew from crewai.tools import BaseTool import requests import json import base64 # Suppress warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Load environment variables load_dotenv() class BaseCDataTool(BaseTool): """Base class for CData Connect AI MCP tools""" def __init__(self, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self._server_url = os.getenv('MCP_SERVER_URL', '').rstrip('/') self._username = os.getenv('MCP_USERNAME', '') self._password = os.getenv('MCP_PASSWORD', '') if not all([self._server_url, self._username, self._password]): raise ValueError("MCP_SERVER_URL, MCP_USERNAME, and MCP_PASSWORD must be set in environment variables") # Create basic auth header credentials = base64.b64encode(f"{self._username}:{self._password}".encode()).decode() self._headers = { 'Authorization': f'Basic {credentials}', 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Accept': 'application/json, text/event-stream' } def _parse_sse_response(self, response_text: str) -> Dict[str, Any]: """Parse Server-Sent Events response format""" lines = response_text.strip().split(' ') data_line = None for line in lines: if line.startswith('data: '): data_line = line[6:] # Remove 'data: ' prefix break if data_line: try: return json.loads(data_line) except json.JSONDecodeError as e: return {"error": f"Invalid JSON in SSE data: {e}"} return {"error": "No data found in SSE response"} def _make_mcp_request(self, tool_name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]: """Make an MCP request to the Connect AI server""" payload = { "jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 1, "method": "tools/call", "params": { "name": tool_name, "arguments": arguments } } try: response = requests.post(self._server_url, json=payload, headers=self._headers) # Check response content before trying to parse if not response.text.strip(): return {"error": "Empty response from server"} response.raise_for_status() # Parse Server-Sent Events format result = self._parse_sse_response(response.text) if "error" in result: if "error" in result and isinstance(result["error"], dict): return {"error": result["error"]["message"]} return result return result.get("result", {}) except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e: return {"error": f"Request failed: {str(e)}"} class GetCatalogsTool(BaseCDataTool): """Tool to get available data catalogs/databases""" name: str = "Get Data Catalogs" description: str = "Get list of available data sources, databases, or catalogs in CData Connect AI" def _run(self, query: str = "") -> str: result = self._make_mcp_request("getCatalogs", {}) if "error" in result: return f"Error getting catalogs: {result['error']}" return json.dumps(result, indent=2) class GetSchemasTool(BaseCDataTool): """Tool to get schemas within a catalog""" name: str = "Get Schemas" description: str = "Get database schemas within a specific catalog. Requires catalog name." def _run(self, catalog_name: str) -> str: if not catalog_name: return "Error: catalog_name is required" result = self._make_mcp_request("getSchemas", {"catalogName": catalog_name}) if "error" in result: return f"Error getting schemas: {result['error']}" return json.dumps(result, indent=2) class GetTablesTool(BaseCDataTool): """Tool to get tables within catalogs/schemas""" name: str = "Get Tables" description: str = "Get tables within databases. Can optionally filter by catalog and/or schema." def _run(self, catalog_name: str = "", schema_name: str = "") -> str: params = {} if catalog_name: params["catalogName"] = catalog_name if schema_name: params["schemaName"] = schema_name result = self._make_mcp_request("getTables", params) if "error" in result: return f"Error getting tables: {result['error']}" return json.dumps(result, indent=2) class GetColumnsTool(BaseCDataTool): """Tool to get column information""" name: str = "Get Columns" description: str = "Get column information for tables. Can filter by catalog, schema, and/or table name." def _run(self, catalog_name: str = "", schema_name: str = "", table_name: str = "") -> str: params = {} if catalog_name: params["catalogName"] = catalog_name if schema_name: params["schemaName"] = schema_name if table_name: params["tableName"] = table_name result = self._make_mcp_request("getColumns", params) if "error" in result: return f"Error getting columns: {result['error']}" return json.dumps(result, indent=2) class GetProceduresTool(BaseCDataTool): """Tool to get stored procedures""" name: str = "Get Stored Procedures" description: str = "Get stored procedures within a specific catalog and schema. Requires both catalog and schema names." def _run(self, catalog_name: str, schema_name: str) -> str: if not catalog_name or not schema_name: return "Error: Both catalog_name and schema_name are required" params = { "catalogName": catalog_name, "schemaName": schema_name } result = self._make_mcp_request("getProcedures", params) if "error" in result: return f"Error getting procedures: {result['error']}" return json.dumps(result, indent=2) class GetProcedureParametersTool(BaseCDataTool): """Tool to get stored procedure parameters""" name: str = "Get Procedure Parameters" description: str = "Get parameter information for a specific stored procedure. Requires catalog, schema, and procedure names." def _run(self, catalog_name: str, schema_name: str, procedure_name: str) -> str: if not all([catalog_name, schema_name, procedure_name]): return "Error: catalog_name, schema_name, and procedure_name are all required" params = { "catalogName": catalog_name, "schemaName": schema_name, "procedureName": procedure_name } result = self._make_mcp_request("getProcedureParameters", params) if "error" in result: return f"Error getting procedure parameters: {result['error']}" return json.dumps(result, indent=2) class ExecuteProcedureTool(BaseCDataTool): """Tool to execute stored procedures""" name: str = "Execute Stored Procedure" description: str = "Execute a stored procedure. Requires catalog, schema, and procedure names. Optionally accepts parameters as key-value pairs." def _run(self, catalog_name: str, schema_name: str, procedure_name: str, parameters: str = "") -> str: if not all([catalog_name, schema_name, procedure_name]): return "Error: catalog_name, schema_name, and procedure_name are all required" params = { "catalogName": catalog_name, "schemaName": schema_name, "procedureName": procedure_name } if parameters: # Parse parameters string into dict try: param_dict = json.loads(parameters) params["parameters"] = param_dict except json.JSONDecodeError: return f"Error: parameters must be valid JSON. Got: {parameters}" result = self._make_mcp_request("executeProcedure", params) if "error" in result: return f"Error executing procedure: {result['error']}" return json.dumps(result, indent=2) class QueryDataTool(BaseCDataTool): """Tool to execute SQL queries""" name: str = "Execute SQL Query" description: str = "Execute SQL queries against data sources. Provide the SQL query as input. Optionally accepts parameters and default schema." def _run(self, query: str, parameters: str = "", default_schema: str = "") -> str: if not query: return "Error: SQL query is required" params = {"query": query} if parameters: try: param_dict = json.loads(parameters) params["parameters"] = param_dict except json.JSONDecodeError: return f"Error: parameters must be valid JSON. Got: {parameters}" if default_schema: params["defaultSchema"] = default_schema result = self._make_mcp_request("queryData", params) if "error" in result: return f"Error executing query: {result['error']}" return json.dumps(result, indent=2) class CDataConnectAgent: """Main agent class for CData Connect AI integration""" def __init__(self): # Configure OpenAI self.openai_api_key = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY') if not self.openai_api_key: raise ValueError("OPENAI_API_KEY must be set in environment variables") os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = self.openai_api_key os.environ["OPENAI_MODEL_NAME"] = "gpt-4" # Initialize all CData Connect tools self.tools = [ GetCatalogsTool(), GetSchemasTool(), GetTablesTool(), GetColumnsTool(), GetProceduresTool(), GetProcedureParametersTool(), ExecuteProcedureTool(), QueryDataTool() ] # Create the agent self.agent = Agent( role="Data Analyst and Query Specialist", goal="Help users query and analyze their data from CData Connect AI using natural language", backstory=( "You are an expert data analyst specializing in CData Connect AI. " "You help users explore their data sources, understand table structures, " "execute queries, and work with stored procedures to get the information they need. " "You can translate natural language requests into appropriate actions using the available tools. " "You have access to various data connectors like Salesforce, SharePoint, QuickBooks, and many others through CData Connect AI. " "When users ask about their data, you intelligently choose the right tools to help them. " "Always explain what you're doing and provide helpful context about the results." ), verbose=True, allow_delegation=False, tools=self.tools ) def process_query(self, user_query: str) -> str: """Process a user query and return the response""" # Create a task for the user's query task = Task( description=f""" Process this user query about data in CData Connect AI: "{user_query}" You have access to these tools to help answer the query: 1. Get Data Catalogs - to see available data sources 2. Get Schemas - to see schemas within a catalog 3. Get Tables - to see tables within catalogs/schemas 4. Get Columns - to see column structures 5. Get Stored Procedures - to see available procedures 6. Get Procedure Parameters - to understand procedure requirements 7. Execute Stored Procedure - to run procedures 8. Execute SQL Query - to run SQL queries Choose the appropriate tool(s) based on what the user is asking for. If they want to see available data sources, use Get Data Catalogs. If they want to query data, use Execute SQL Query. If they ask about table structures, use Get Tables or Get Columns. If they mention stored procedures, use the procedure-related tools. Always explain what you're doing and provide helpful, formatted responses. """, expected_output="A helpful and informative response to the user's query about their data", agent=self.agent ) # Create a crew with just this one agent and task crew = Crew( agents=[self.agent], tasks=[task], verbose=False ) # Execute the task result = crew.kickoff() return str(result) def main(): """Main function to run the console chatbot""" print("CData Connect AI AI Assistant") print("=" * 50) print("I can help you query and explore your data in CData Connect AI!") print("You can ask me about:") print("- Available data sources and catalogs") print("- Schemas and tables in your databases") print("- Column structures and table information") print("- Stored procedures and their parameters") print("- Execute SQL queries and stored procedures") print("- Analyze your data") print(" Type 'quit', 'exit', or 'bye' to stop.") print("=" * 50) try: # Initialize the agent agent = CDataConnectAgent() while True: # Get user input user_input = input(" Ask me about your data: ").strip() # Check for exit conditions if user_input.lower() in ['quit', 'exit', 'bye', 'q']: print(" Goodbye! Happy data exploring!") break if not user_input: print("Please enter a query or question.") continue try: print(" Processing your query...") # Process the query response = agent.process_query(user_input) print(f" Response: {response}") except Exception as e: print(f" Error processing query: {str(e)}") print("Please try rephrasing your question or check your connection.") except Exception as e: print(f" Failed to initialize agent: {str(e)}") print("Please check your environment variables and connection settings.") if __name__ == "__main__": main() -
Run python crew-agent.py in the terminal. The output displays the results of the task:


- Start interacting with your Snowflake data through natural language queries. Your agent now has access to your Snowflake data through the CData Connect AI MCP Server.
Step 3: Build Intelligent Agents with Live Snowflake Data Access
With your crewAI agent configured and connected to CData Connect AI, you can now build sophisticated agents & even multi-agent systems that interact with your Snowflake data using natural language. The MCP integration provides your agents with powerful data access capabilities.
Available MCP Tools for Your Agent
Your crewAI agent has access to the following CData Connect AI MCP tools:
- queryData: Execute SQL queries against connected data sources and retrieve results
- getCatalogs: Retrieve a list of available connections from CData Connect AI
- getSchemas: Retrieve database schemas for a specific catalog
- getTables: Retrieve database tables for a specific catalog and schema
- getColumns: Retrieve column metadata for a specific table
- getProcedures: Retrieve stored procedures for a specific catalog and schema
- getProcedureParameters: Retrieve parameter metadata for stored procedures
- executeProcedure: Execute stored procedures with parameters
Example Use Cases
Here are some examples of what your crewAI agents can do with live Snowflake data access:
- Data Analysis Agent: Build an agent that analyzes trends, patterns, and anomalies in your Snowflake data
- Report Generation Agent: Create agents that generate custom reports based on natural language requests
- Data Quality Agent: Develop agents that monitor and validate data quality in real-time
- Business Intelligence Agent: Build agents that answer complex business questions by querying multiple data sources
- Automated Workflow Agent: Create agents that trigger actions based on data conditions in Snowflake
Your crewAI agent will automatically translate these natural language queries and execute them against your Snowflake data through the CData Connect AI MCP Server, providing real-time insights without requiring users to write complex SQL or understand the underlying data structure.
Get CData Connect AI
To get live data access to 300+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your crewAI agents and cloud applications, try CData Connect AI today!






