Integrate Cursor with Live SQL Server Data via CData Connect AI
Cursor is an AI-powered code editor that embeds conversational and agent-style assistance alongside your development workflow. By extending Cursor with MCP (Model Context Protocol) tools, you can give its AI agents secure access to external systems such as APIs and databases.
Integrating Cursor with CData Connect AI via the built-in CData MCP Server allows the editor's AI to query, analyze, and act on live SQL Server data without copying data into the IDE. The result is a development experience where you can chat with your governed enterprise data directly from Cursor.
This article outlines how to configure SQL Server connectivity in Connect AI, generate the required access token, register the CData MCP Server in Cursor, and then use the AI chat pane to explore live SQL Server data.
Step 1: Configure SQL Server connectivity for Cursor
Connectivity to SQL Server from Cursor is made possible through CData Connect AI's Remote MCP Server. To interact with SQL Server data from Cursor, start by creating and configuring a SQL Server connection in CData Connect AI.
- Log into Connect AI, click Sources, and then click Add Connection
- Select SQL Server from the Add Connection panel
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to SQL Server.
Connecting to Microsoft SQL Server
Connect to Microsoft SQL Server using the following properties:
- Server: The name of the server running SQL Server.
- User: The username provided for authentication with SQL Server.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the SQL Server database.
Connecting to Azure SQL Server and Azure Data Warehouse
You can authenticate to Azure SQL Server or Azure Data Warehouse by setting the following connection properties:
- Server: The server running Azure. You can find this by logging into the Azure portal and navigating to "SQL databases" (or "SQL data warehouses") -> "Select your database" -> "Overview" -> "Server name."
- User: The name of the user authenticating to Azure.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the database, as seen in the Azure portal on the SQL databases (or SQL warehouses) page.
SSH Connectivity for SQL Server
You can use SSH (Secure Shell) to authenticate with SQL Server, whether the instance is hosted on-premises or in supported cloud environments. SSH authentication ensures that access is encrypted (as compared to direct network connections).
SSH Connections to SQL Server in Password Auth Mode
To connect to SQL Server via SSH in Password Auth mode, set the following connection properties:
- User: SQL Server User name
- Password: SQL Server Password
- Database: SQL Server database name
- Server: SQL Server Server name
- Port: SQL Server port number like 3306
- UserSSH: "true"
- SSHAuthMode: "Password"
- SSHPort: SSH Port number
- SSHServer: SSH Server name
- SSHUser: SSH User name
- SSHPassword: SSH Password
SSH Connections to SQL Server in Public Key Auth Mode
To connect to SQL Server via SSH in Password Auth mode, set the following connection properties:
- User: SQL Server User name
- Password: SQL Server Password
- Database: SQL Server database name
- Server: SQL Server Server name
- Port: SQL Server port number like 3306
- UserSSH: "true"
- SSHAuthMode: "Public_Key"
- SSHPort: SSH Port number
- SSHServer: SSH Server name
- SSHUser: SSH User name
- SSHClientCret: the path for the public key certificate file
- Click Save & Test
- Navigate to the Permissions tab and update user-based permissions

Add a Personal Access Token
A Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect AI from Cursor. It is best practice to create a separate PAT for each integration to maintain granular access control.
- Click the gear icon () at the top right of the Connect AI app to open Settings
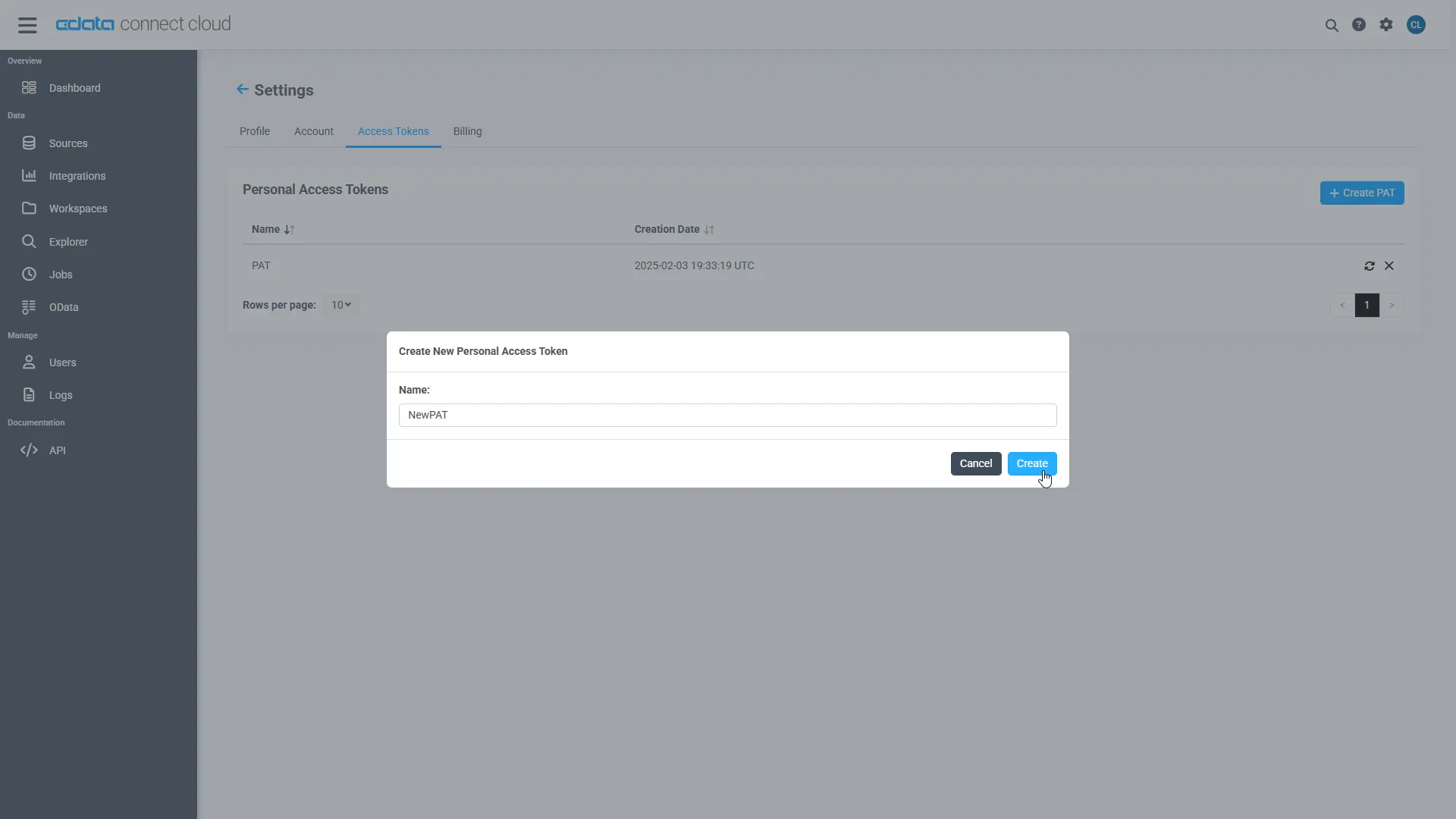
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT
- Give the PAT a descriptive name and click Create
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use
With the SQL Server connection configured and a PAT generated, Cursor can now connect to SQL Server data through the CData MCP Server.
Step 2: Configure the CData MCP Server in Cursor
Next, configure Cursor to use the CData MCP Server. Cursor reads MCP configuration from an mcp.json file in the user configuration directory and exposes the registered servers under the Tools & MCP settings. Once configured, Cursor's AI chat can call the tools exposed by CData Connect AI.
- Download the Cursor desktop application and complete the sign-up flow for your account
-
From the top menu, click Settings to open the settings panel
-
In the left navigation, open the Tools & MCP tab and click Add Custom MCP
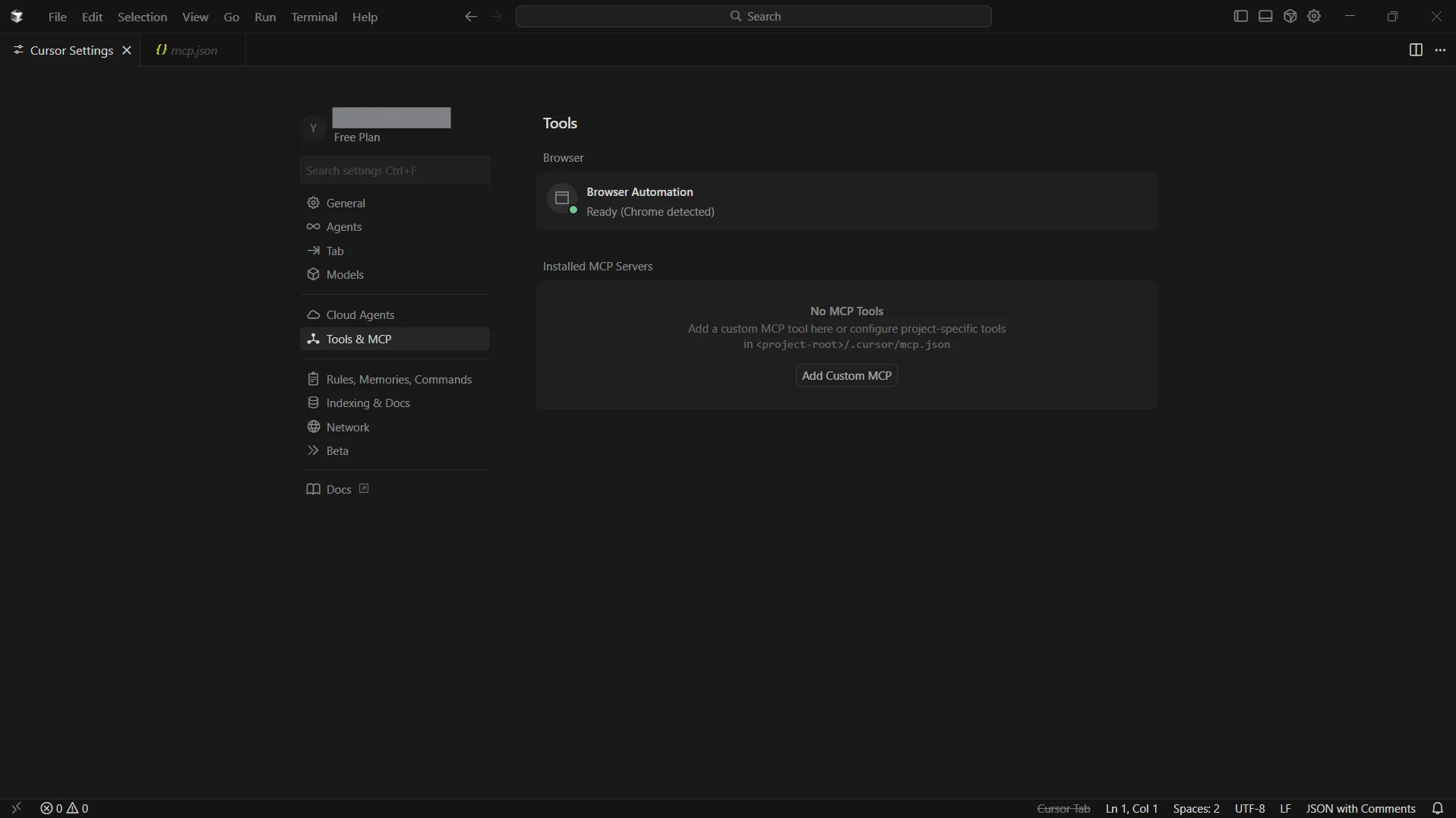
- Cursor opens an mcp.json file in the editor
-
Add the following configuration. Make sure to base64-encode your email:PAT before inserting into the header:
{ "mcpServers": { "cdata-mcp": { "url": "https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp", "headers": { "Authorization": "Basic your_base64_encoded_email_PAT" } } } }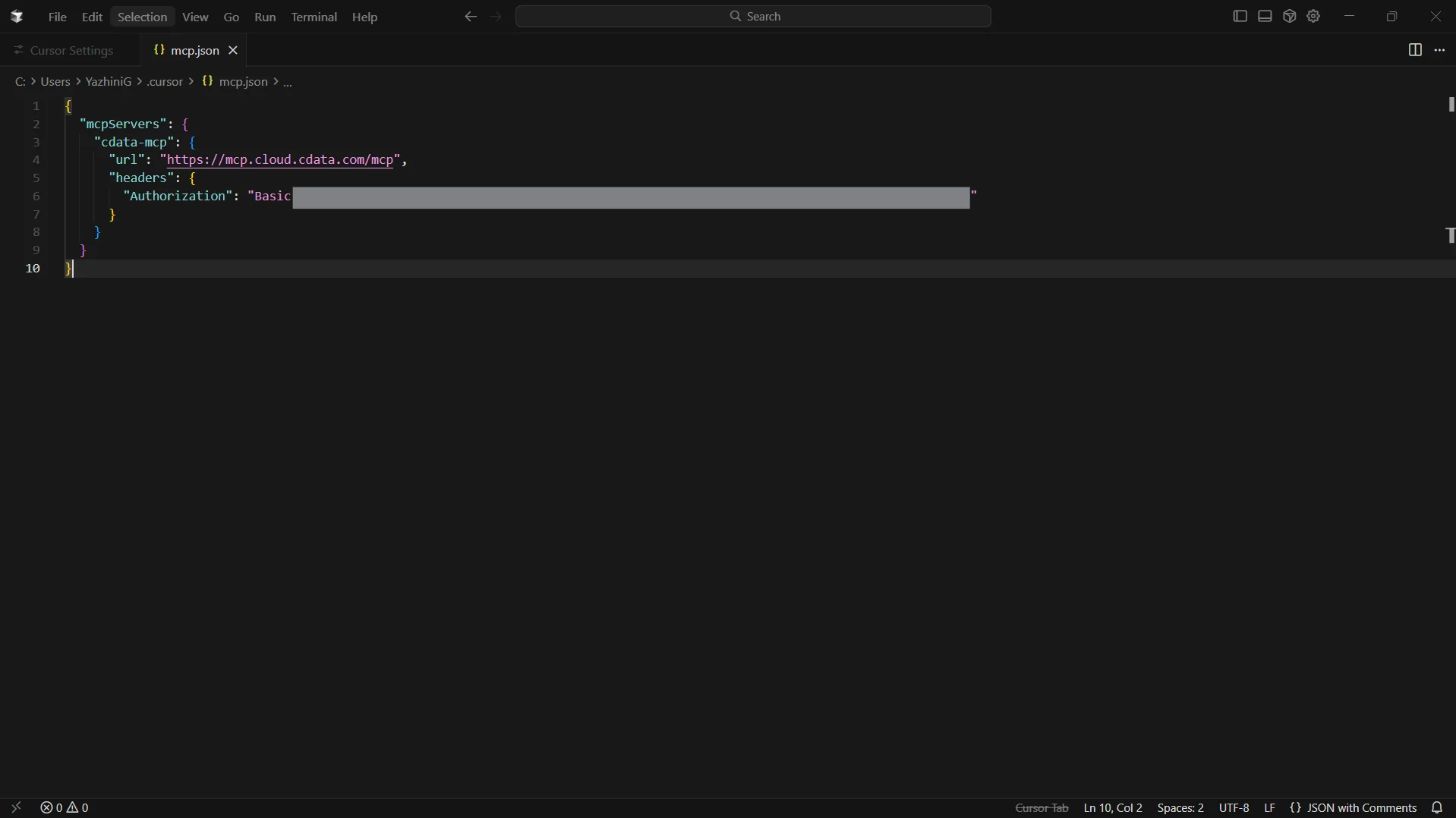
- Save the file
-
Return to Settings and then select Tools & MCP. You can now see cdata-mcp enabled with an active indicator
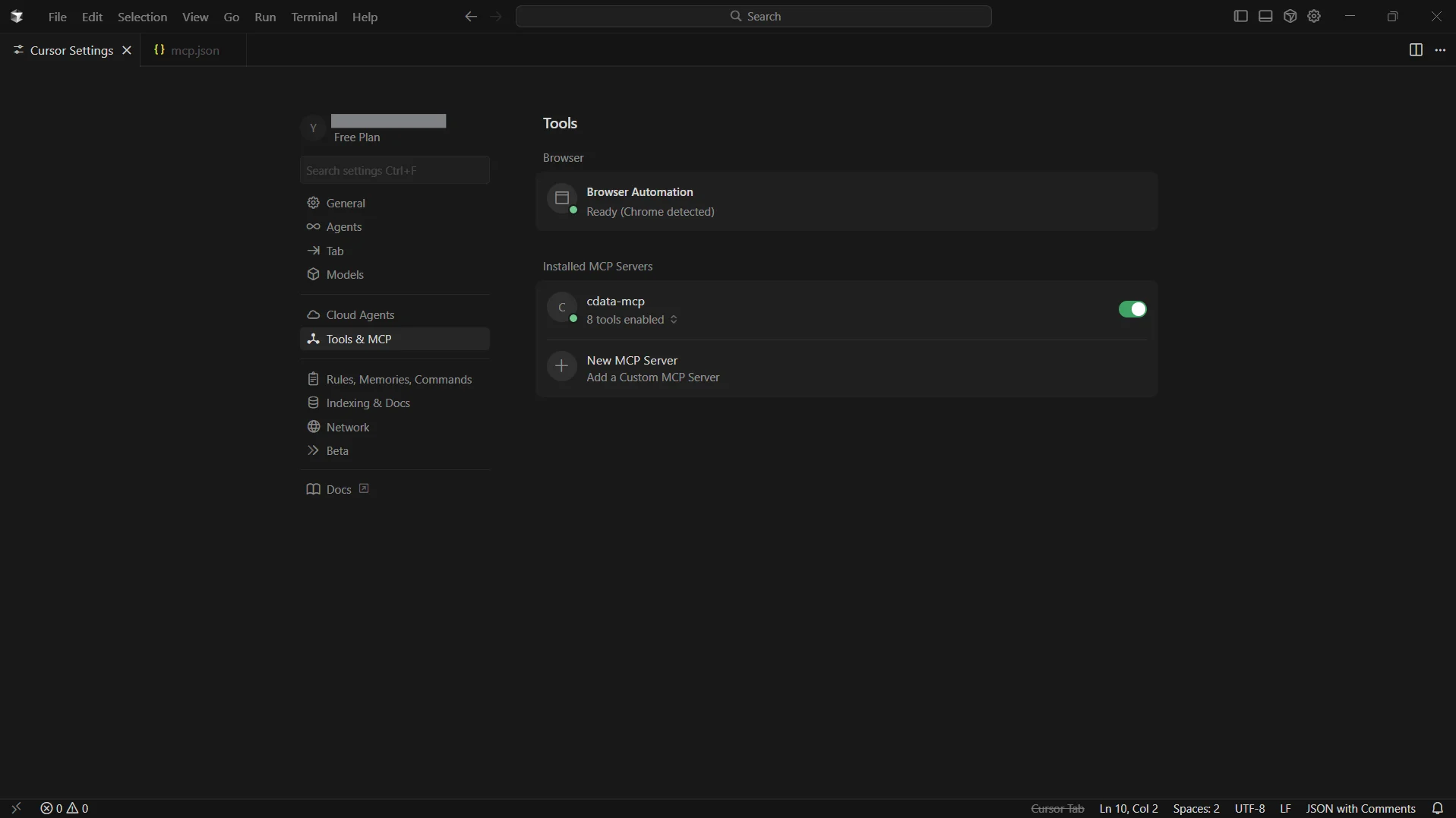
Step 3: Chat with CData Connect AI from Cursor
-
From the top bar, click Toggle AI Pane to open the chat window
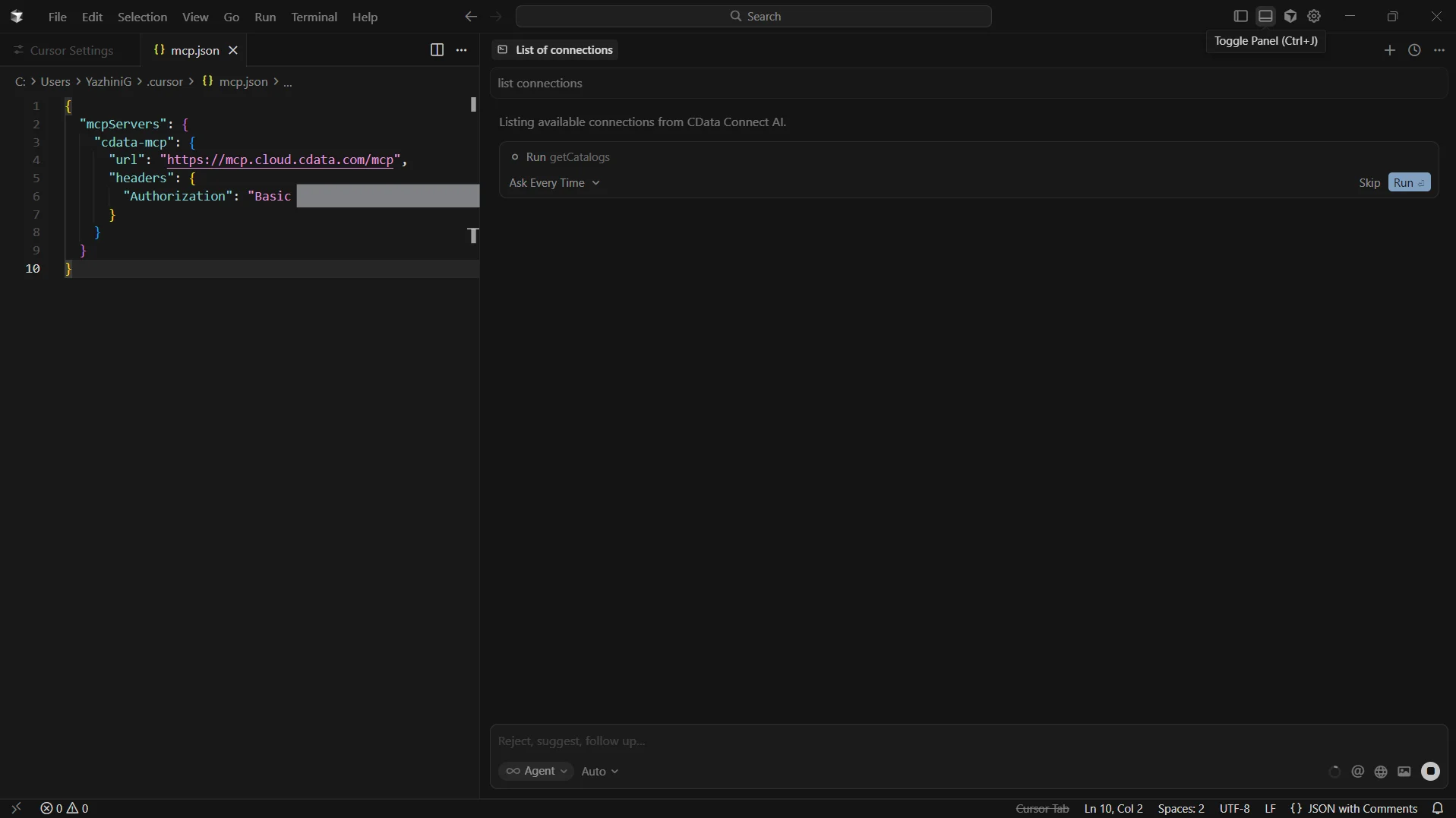
- Test the connection by entering "List connections"
-
You can also run queries like "Query SQL Server data and list the high priority accounts"
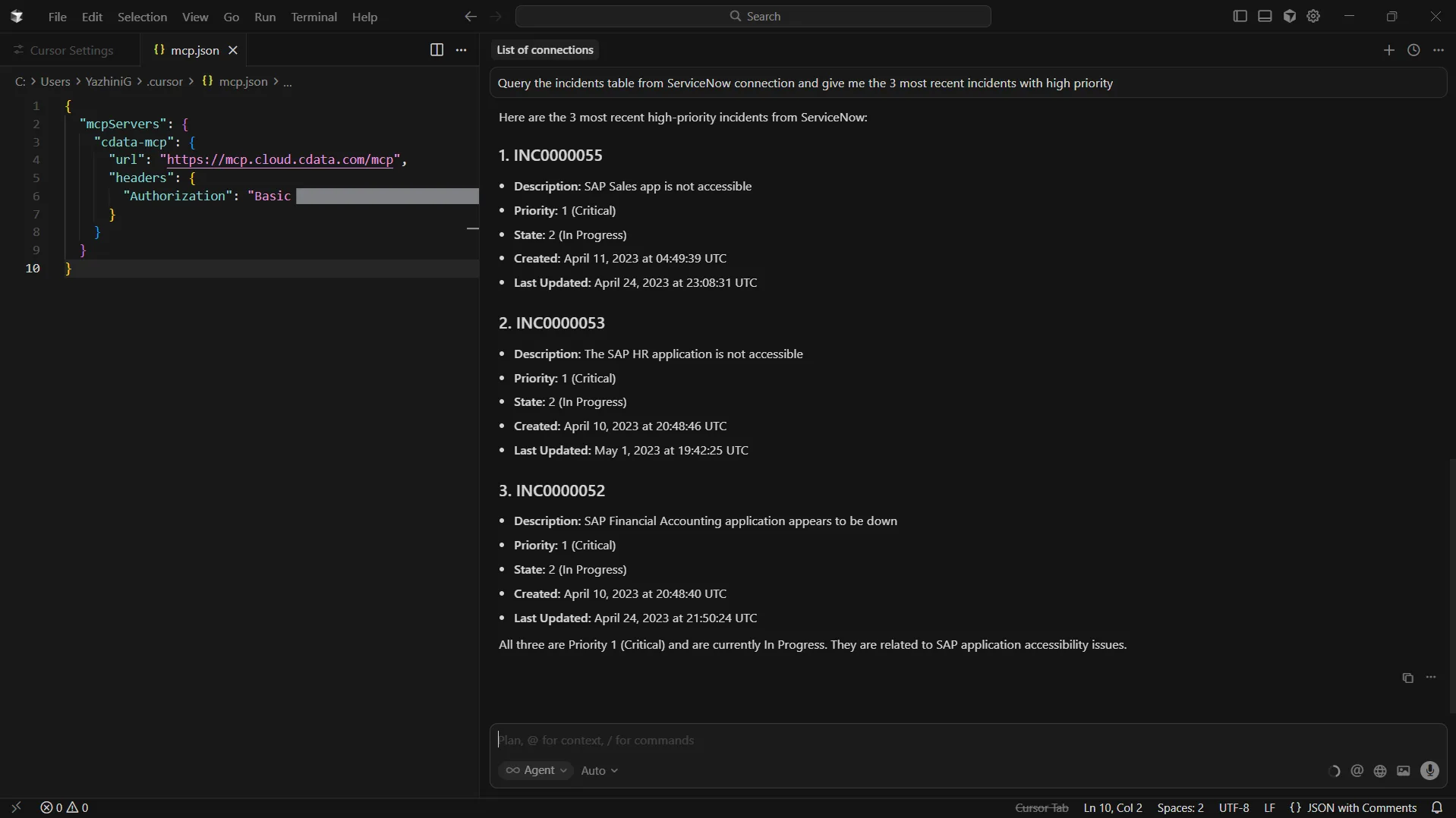
Cursor is now fully integrated with the CData Connect AI MCP Server and can act on live SQL Server data directly from the editor.
Get CData Connect AI
To access 300+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your development tools, try CData Connect AI today!






