How to Connect to Live SQL Server Data from Google ADK Agents (via CData Connect AI)
Google ADK (Agent Development Kit) is a powerful, model-agnostic framework for building AI agents that can interact with various data sources and services. When combined with CData Connect AI Remote MCP, you can leverage Google ADK to build intelligent agents that interact with your SQL Server data in real-time through natural language queries. This article outlines the process of connecting to SQL Server using Connect AI Remote MCP and configuring a Google ADK agent to interact with your SQL Server data through ADK Web.
CData Connect AI offers a dedicated cloud-to-cloud interface for connecting to SQL Server data. The CData Connect AI Remote MCP Server enables secure communication between Google ADK agents and SQL Server. This allows your agents to read from and take actions on your SQL Server data, all without the need for data replication to a natively supported database. With its inherent optimized data processing capabilities, CData Connect AI efficiently channels all supported SQL operations, including filters and JOINs, directly to SQL Server. This leverages server-side processing to swiftly deliver the requested SQL Server data.
In this article, we show how to configure a Google ADK agent to conversationally explore (or Vibe Query) your data using natural language. With Connect AI you can build agents with access to live SQL Server data, plus hundreds of other sources.
Step 1: Configure SQL Server Connectivity for Google ADK
Connectivity to SQL Server from Google ADK agents is made possible through CData Connect AI Remote MCP. To interact with SQL Server data from your ADK agent, we start by creating and configuring a SQL Server connection in CData Connect AI.
- Log into Connect AI, click Sources, and then click Add Connection
- Select "SQL Server" from the Add Connection panel
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to SQL Server.
Connecting to Microsoft SQL Server
Connect to Microsoft SQL Server using the following properties:
- Server: The name of the server running SQL Server.
- User: The username provided for authentication with SQL Server.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the SQL Server database.
Connecting to Azure SQL Server and Azure Data Warehouse
You can authenticate to Azure SQL Server or Azure Data Warehouse by setting the following connection properties:
- Server: The server running Azure. You can find this by logging into the Azure portal and navigating to "SQL databases" (or "SQL data warehouses") -> "Select your database" -> "Overview" -> "Server name."
- User: The name of the user authenticating to Azure.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the database, as seen in the Azure portal on the SQL databases (or SQL warehouses) page.
SSH Connectivity for SQL Server
You can use SSH (Secure Shell) to authenticate with SQL Server, whether the instance is hosted on-premises or in supported cloud environments. SSH authentication ensures that access is encrypted (as compared to direct network connections).
SSH Connections to SQL Server in Password Auth Mode
To connect to SQL Server via SSH in Password Auth mode, set the following connection properties:
- User: SQL Server User name
- Password: SQL Server Password
- Database: SQL Server database name
- Server: SQL Server Server name
- Port: SQL Server port number like 3306
- UserSSH: "true"
- SSHAuthMode: "Password"
- SSHPort: SSH Port number
- SSHServer: SSH Server name
- SSHUser: SSH User name
- SSHPassword: SSH Password
SSH Connections to SQL Server in Public Key Auth Mode
To connect to SQL Server via SSH in Password Auth mode, set the following connection properties:
- User: SQL Server User name
- Password: SQL Server Password
- Database: SQL Server database name
- Server: SQL Server Server name
- Port: SQL Server port number like 3306
- UserSSH: "true"
- SSHAuthMode: "Public_Key"
- SSHPort: SSH Port number
- SSHServer: SSH Server name
- SSHUser: SSH User name
- SSHClientCret: the path for the public key certificate file
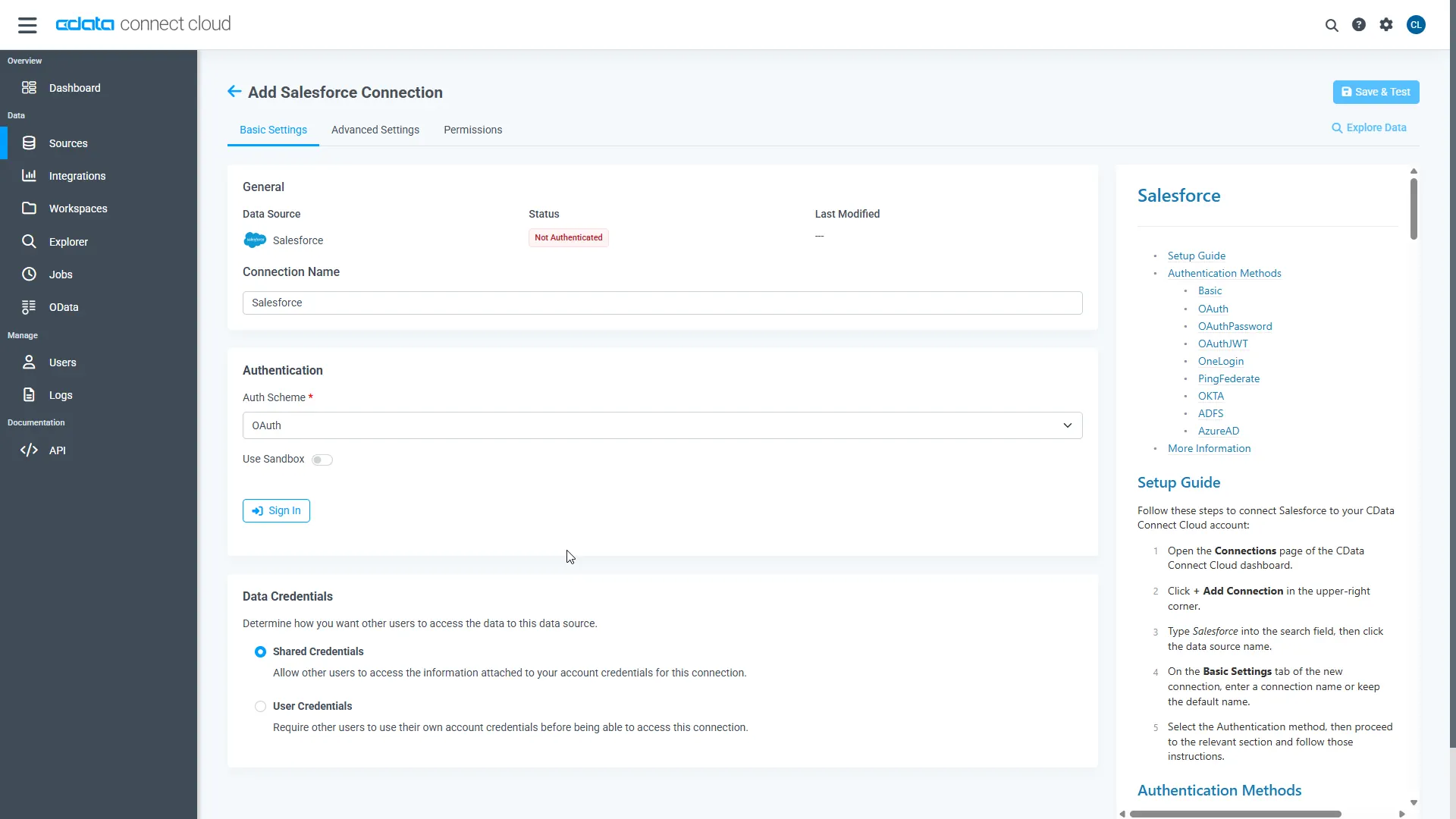
- Click Save & Test
-
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add SQL Server Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
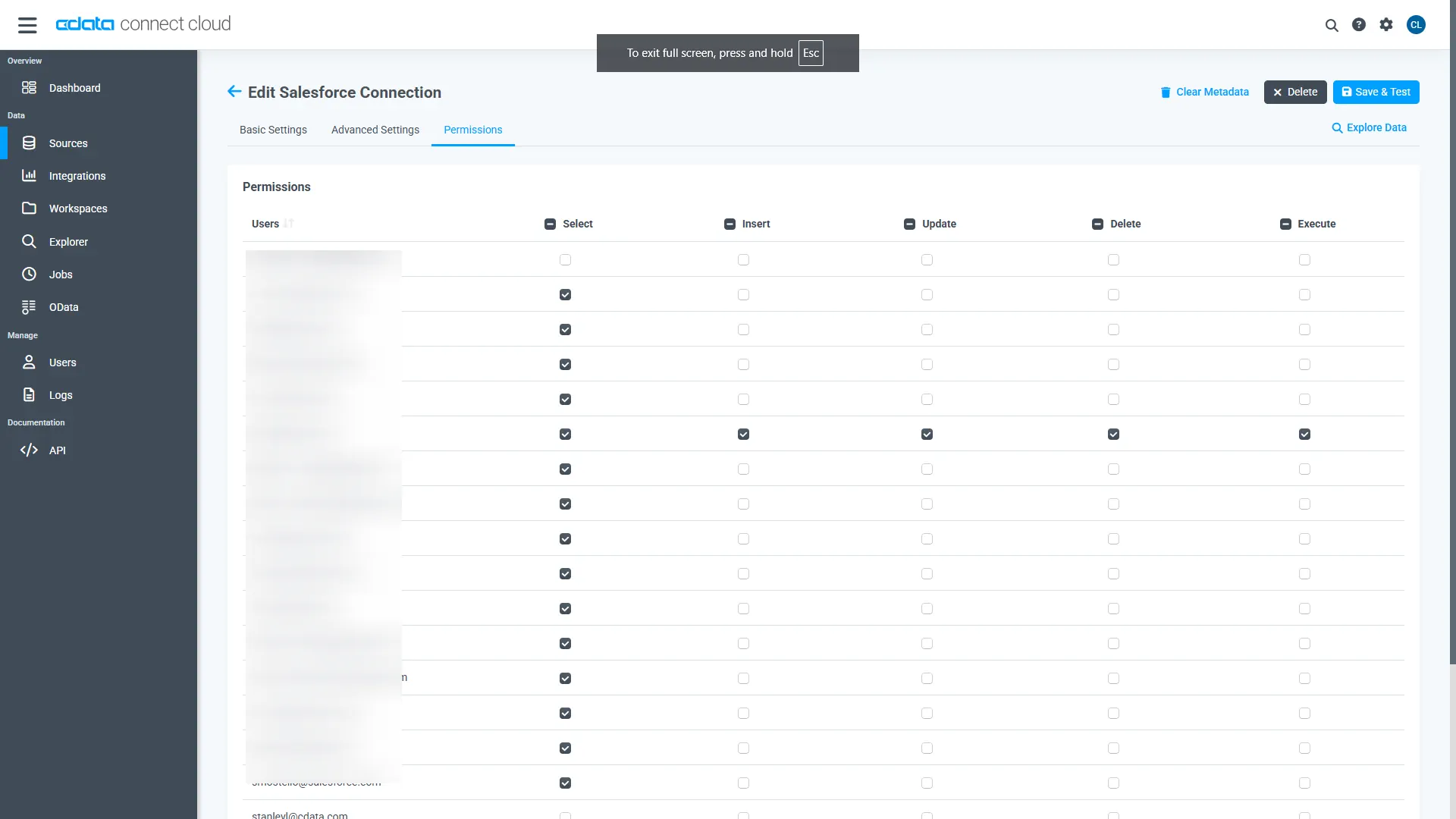

Add a Personal Access Token
A Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect AI from your Google ADK agent. It is best practice to create a separate PAT for each service to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on the Gear icon () at the top right of the Connect AI app to open the settings page.
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
-
Give the PAT a name and click Create.
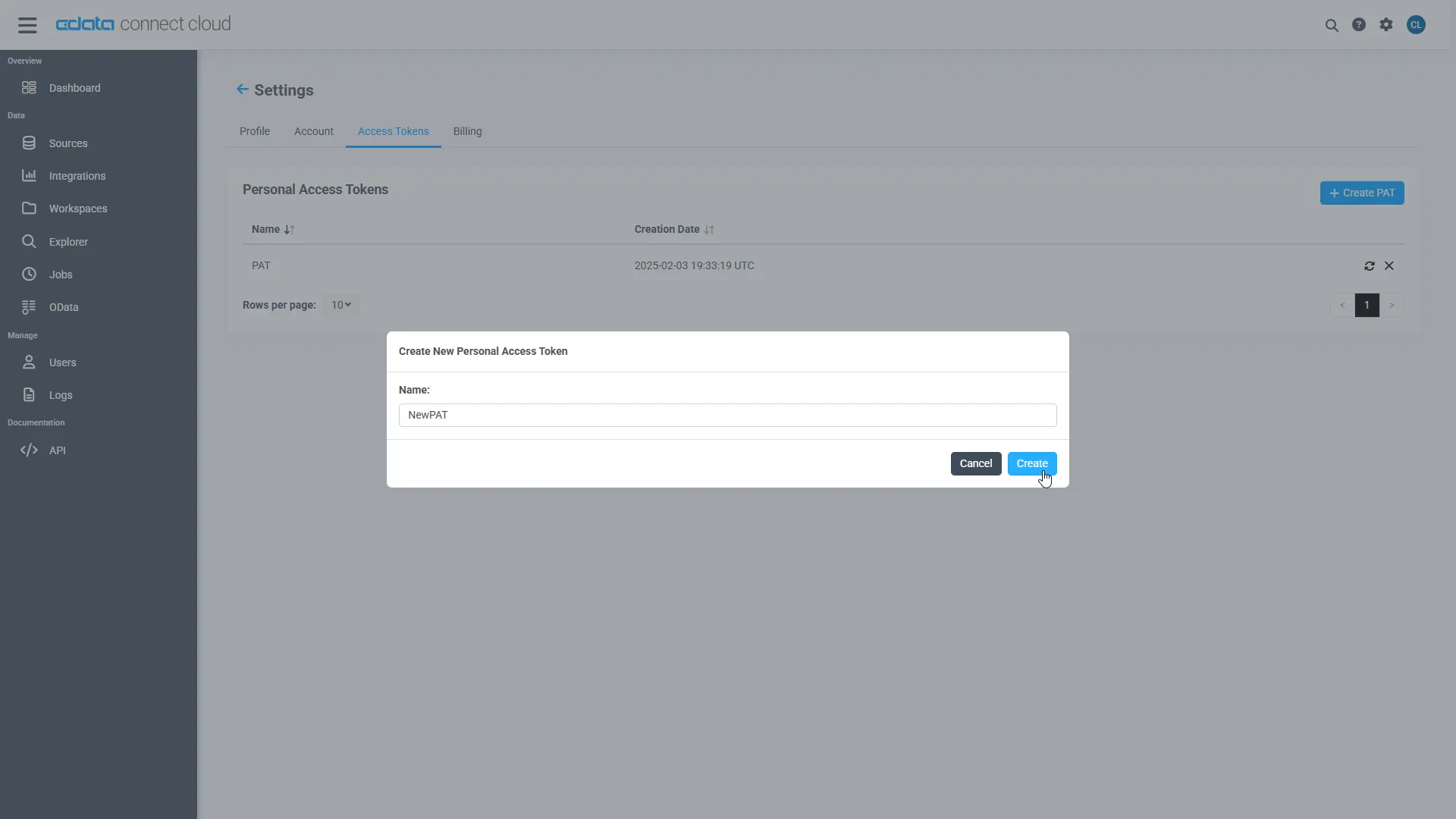
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured and a PAT generated, we are ready to connect to SQL Server data from your Google ADK agent.
Step 2: Configure Your Google ADK Agent for CData Connect AI
Follow these steps to configure your Google ADK agent to connect to CData Connect AI. You can use our pre-built agent as a starting point, available at https://github.com/CDataSoftware/adk-mcp-client, or follow the instructions below to create your own.
-
Ensure you have the Google ADK Python SDK installed. If not, install it using pip:
pip install google-genkit google-adk
- Create or update your agent's configuration file (typically agent.py) to include the CData Connect AI MCP connection. You'll need to configure the MCP toolset with your Connect AI credentials.
-
Set up your environment variables or configuration for the MCP server connection. Create a .env file in your project root with the following variables:
MCP_SERVER_URL=https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp MCP_USERNAME=YOUR_EMAIL MCP_PASSWORD=YOUR_PATReplace YOUR_EMAIL with your Connect AI email address and YOUR_PAT with the Personal Access Token created in Step 1. -
Configure your agent.py file to use the CData Connect AI MCP Server. Here's an example configuration:
import os import base64 from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent from google.adk.tools.mcp_tool.mcp_toolset import MCPToolset from google.adk.tools.mcp_tool.mcp_session_manager import StreamableHTTPConnectionParams from dotenv import load_dotenv # Load environment variables load_dotenv() # Get configuration from environment MCP_SERVER_URL = os.getenv('MCP_SERVER_URL', 'https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp') MCP_USERNAME = os.getenv('MCP_USERNAME', '') MCP_PASSWORD = os.getenv('MCP_PASSWORD', '') # Create auth header for MCP server auth_header = {} if MCP_USERNAME and MCP_PASSWORD: credentials = f"{MCP_USERNAME}:{MCP_PASSWORD}" auth_header = {"Authorization": f"Basic {base64.b64encode(credentials.encode()).decode()}"} # Define your agent with CData MCP tools root_agent = LlmAgent( model='gemini-2.0-flash-exp', # You can use any supported model name='data_query_assistant', instruction="""You are a data query assistant with access to SQL Server data through CData Connect AI. You can help users explore and query their SQL Server data in real-time. Use the available MCP tools to: - List available databases and schemas - Explore table structures - Execute SQL queries - Provide insights about the data Always explain what you're doing and format results clearly.""", tools=[ MCPToolset( connection_params=StreamableHTTPConnectionParams( url=MCP_SERVER_URL, headers=auth_header ) ) ], ) -
Run your agent with ADK Web. From your project directory, execute:
adk web --port 5000 .
Note: If you installed ADK with pip install --user, the adk command may not be in your PATH. You can either:
- Use the full path: ~/Library/Python/3.x/bin/adk (on macOS)
- Add to PATH: export PATH="$HOME/Library/Python/3.x/bin:$PATH"
- Use a virtual environment where the PATH is automatically configured
- Open the ADK Web interface in your browser (typically http://localhost:5000).
- Select your agent from the dropdown menu (it will be named based on the name parameter in your agent configuration).
- Start interacting with your SQL Server data through natural language queries. Your agent now has access to your SQL Server data through the CData Connect AI MCP Server.
Step 3: Build Intelligent Agents with Live SQL Server Data Access
With your Google ADK agent configured and connected to CData Connect AI, you can now build sophisticated agents that interact with your SQL Server data using natural language. The MCP integration provides your agents with powerful data access capabilities.
Available MCP Tools for Your Agent
Your Google ADK agent has access to the following CData Connect AI MCP tools:
- queryData: Execute SQL queries against connected data sources and retrieve results
- getCatalogs: Retrieve a list of available connections from CData Connect AI
- getSchemas: Retrieve database schemas for a specific catalog
- getTables: Retrieve database tables for a specific catalog and schema
- getColumns: Retrieve column metadata for a specific table
- getProcedures: Retrieve stored procedures for a specific catalog and schema
- getProcedureParameters: Retrieve parameter metadata for stored procedures
- executeProcedure: Execute stored procedures with parameters
Example Use Cases
Here are some examples of what your Google ADK agents can do with live SQL Server data access:
- Data Analysis Agent: Build an agent that analyzes trends, patterns, and anomalies in your SQL Server data
- Report Generation Agent: Create agents that generate custom reports based on natural language requests
- Data Quality Agent: Develop agents that monitor and validate data quality in real-time
- Business Intelligence Agent: Build agents that answer complex business questions by querying multiple data sources
- Automated Workflow Agent: Create agents that trigger actions based on data conditions in SQL Server
Testing Your Agent
Once deployed to ADK Web, you can interact with your agent through natural language queries. For example:
- "Show me all customers from the last 30 days"
- "What are the top performing products this quarter?"
- "Analyze sales trends and identify anomalies"
- "Generate a summary report of active projects"
- "Find all records that match specific criteria"
Your Google ADK agent will automatically translate these natural language queries into appropriate SQL queries and execute them against your SQL Server data through the CData Connect AI MCP Server, providing real-time insights without requiring users to write complex SQL or understand the underlying data structure.
Get CData Connect AI
To get live data access to 300+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your Google ADK agents and cloud applications, try CData Connect AI today!






