Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →The Azure Data Lake Storage ADO.NET Data Provider enables user to easily connect to Azure Data Lake Storage from .NET applications. Rapidly create and deploy powerful .NET applications that integrate with Azure Data Lake Storage.
Features
- SQL access to Azure Data Lake operational data
- Compatible with Gen1 and Gen2 instances
- Connect to live Azure Data Lake Storage data, for real-time data access
- Full support for data aggregation and complex JOINs in SQL queries
- Secure connectivity through modern cryptography, including TLS 1.2, SHA-256, ECC, etc.
- Seamless integration with leading BI, reporting, and ETL tools and with custom applications
Specifications
- DataBind to Azure Data Lake Storage using standard Visual Studio wizards.
- Supports ADO.NET Entity Framework (EF 5 & 6), LINQ to Datasets, etc.
- Full Unicode support for data, parameter, & metadata.
- Support for 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems.
- Supports .NET Framework 4.0+ and .NET Standard 2.0 (.NET Core 2.1+, .NET 6.0).
ADO.NET Access to Azure Data Lake Storage
Full-featured and consistent SQL access to any supported data source through ADO.NET
-
Fully-managed .NET
100% fully managed ADO.NET libraries supporting .NET Standard, .NET Core 2.0, & Xamarin.
-
Developer Friendly
Seamless integration with all versions of Visual Studio.
-
Powerful ADO.NET Features
Including support for ADO.NET Entity Framework (EF 5 & 6), ADO.NET 2.0, LINQ to Datasets, etc.
-
Replication and Caching
Our replication and caching commands make it easy to copy data to local and cloud data stores such as Oracle, SQL Server, Google Cloud SQL, etc. The replication commands include many features that allow for intelligent incremental updates to cached data.
-
String, Date, Numeric SQL Functions
The driver includes a library of 50 plus functions that can manipulate column values into the desired result. Popular examples include Regex, JSON, and XML processing functions.
-
Collaborative Query Processing
Our drivers enhance the data source's capabilities by additional client side processing, when needed, to enable analytic summaries of data such as SUM, AVG, MAX, MIN, etc.
-
Easily Customizable and Configurable
The data model exposed by our ADO.NET Providers can easily be customized to add or remove tables/columns, change data types, etc. without requiring a new build. These customizations are supported at runtime using human-readable schema files that are easy to edit.
-
Secure Connectivity
Includes standard Enterprise-class security features such as TLS/ SSL data encryption for all client-server communications.
Standard ADO.NET Access to AzureDataLakeStorage
The Azure Data Lake Storage ADO.NET Provider offers the most natural way to access Azure Data Lake Storage data from any .NET application. Simply use Azure Data Lake Storage Data Provider objects to connect and access data just as you would access any traditional database. You will be able to use the Azure Data Lake Storage Data Provider through Visual Studio Server Explorer, in code through familiar classes, and in data controls like DataGridView, GridView, DataSet, etc.
The CData ADO.NET Provider for Azure Data Lake Storage hides the complexity of accessing data and provides additional powerful security features, smart caching, batching, socket management, and more.
Working with DataAdapters, DataSets, DataTables, etc.
The Azure Data Lake Storage Data Provider has the same ADO.NET architecture as the native .NET data providers for SQL Server and OLEDB, including: AzureDataLakeStorageConnection, AzureDataLakeStorageCommand, AzureDataLakeStorageDataAdapter, AzureDataLakeStorageDataReader, AzureDataLakeStorageDataSource, AzureDataLakeStorageParameter, etc. Because of this you can now access Azure Data Lake Storage data in an easy, familiar way.
For example:
using (AzureDataLakeStorageConnection conn = new AzureDataLakeStorageConnection("...")) {
string select = "SELECT * FROM ADLSData";
AzureDataLakeStorageCommand cmd = new AzureDataLakeStorageCommand(select, conn);
AzureDataLakeStorageDataAdapter adapter = new AzureDataLakeStorageDataAdapter(cmd);
using (adapter) {
DataTable table = new DataTable();
adapter.Fill(table);
...
}
}
ADO.NET Provider Performance
With traditional approaches to remote access, performance bottlenecks can spell disaster for applications. Regardless if an application is created for internal use, a commercial project, web, or mobile application, slow performance can rapidly lead to project failure. Accessing data from any remote source has the potential to create these problems. Common issues include:
- Network Connections - Slow network connections and latency issues are common in mobile applications.
- Service Delays - Delays due to service interruptions, resulting in server hardware or software updates.
- Large Data - Intentional or unintentional requests for large amounts of data.
- Disconnects - Complete loss of network connectivity.
The CData ADO.NET Provider for Azure Data Lake Storage solves many of these issues with support for replication queries that can be used to sync data to local databases, greatly improving the performance and dramatically reduce application bottlenecks.
More information about ADO.NET Provider performance capabilities are available in the included documentation.
Visual Studio Integration & Server Explorer
Working with the new Azure Data Lake Storage ADO.NET Provider is easy. As a fully-managed .NET Data Provider, the Azure Data Lake Storage Data Provider integrates seamlessly with the Visual Studio development environment as well as any .NET application.
As an ADO.NET Data Provider, Azure Data Lake Storage ADO.NET Provider can be used to access and explore Azure Data Lake Storage data directly from the Visual Studio Server Explorer.
It's easy. As a standard ADO.NET adapter, developers can connect the Server Explorer to Azure Data Lake Storage ADO.NET Provider just like connecting to any standard database.
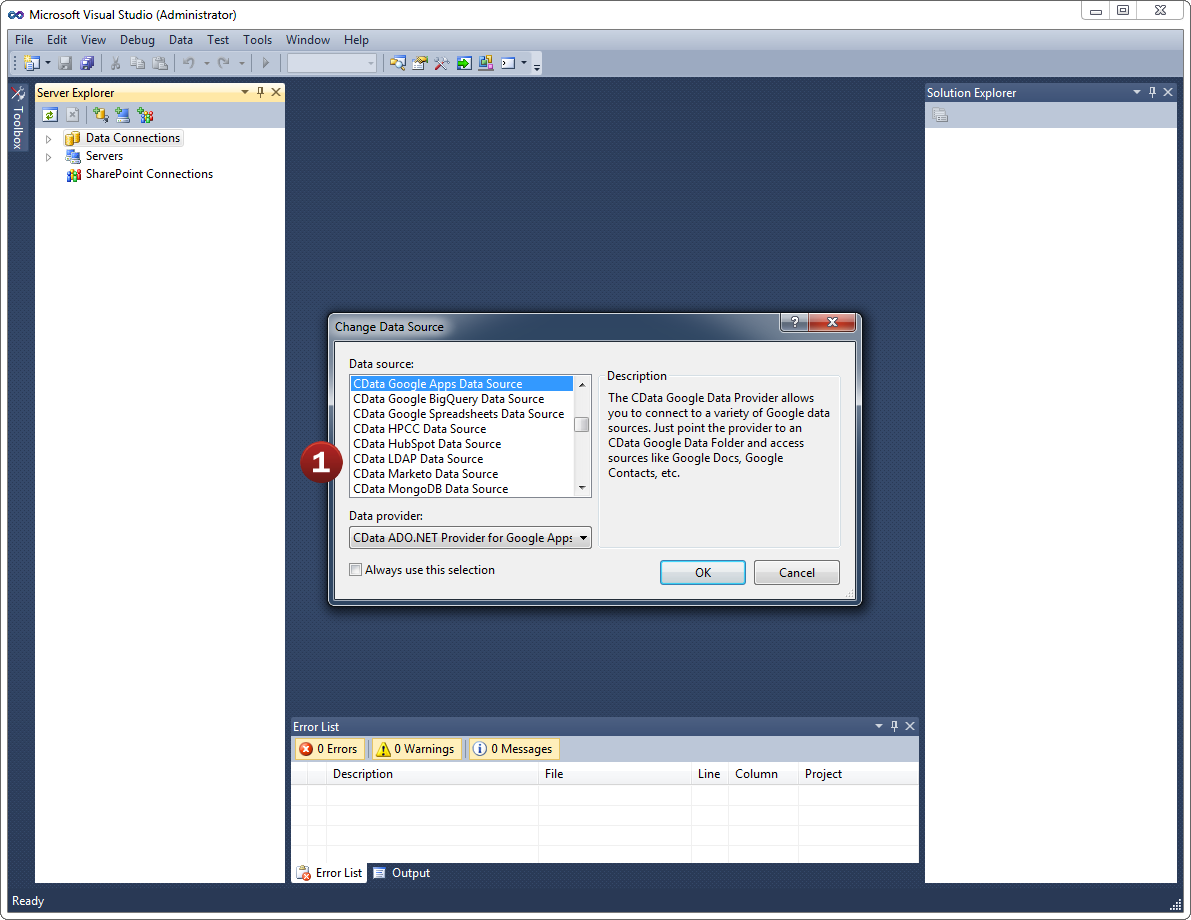
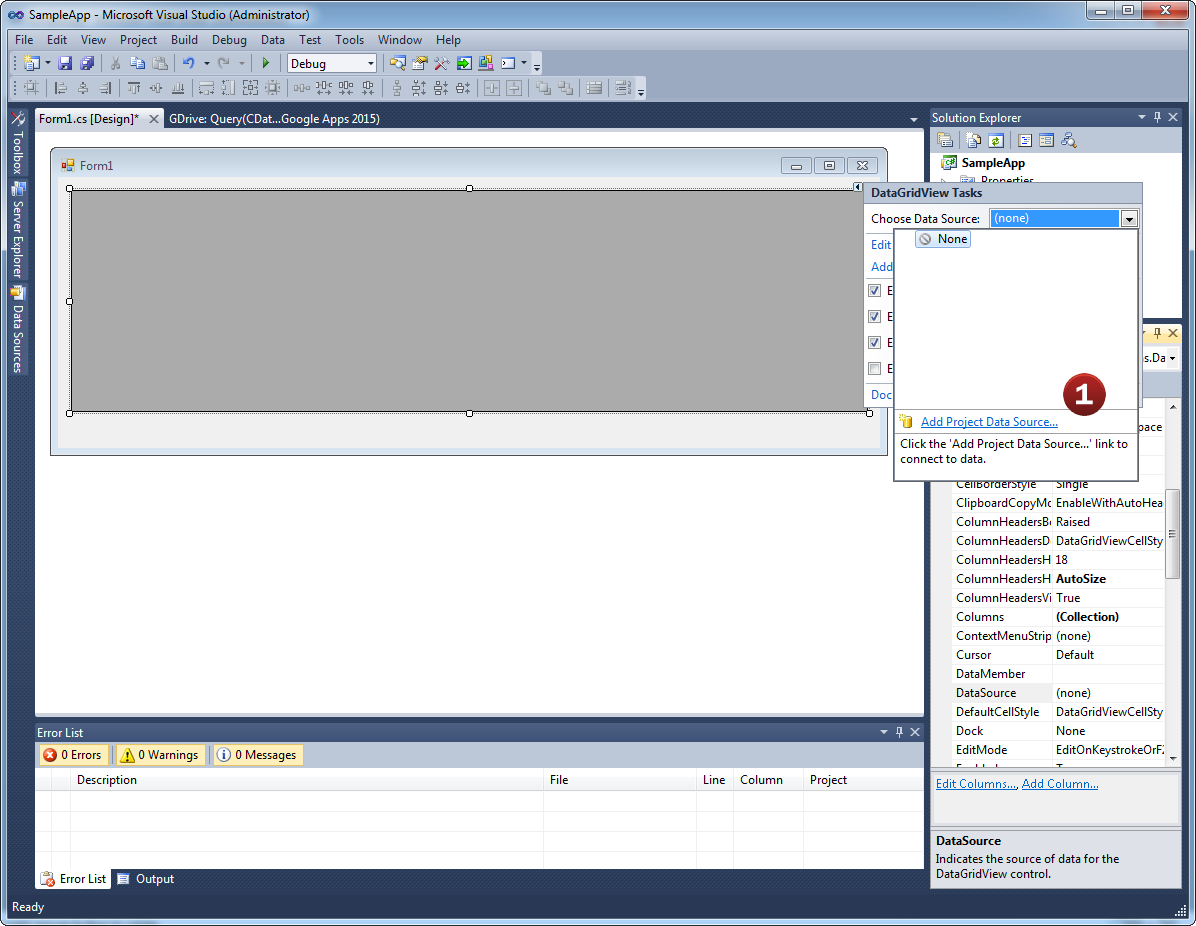
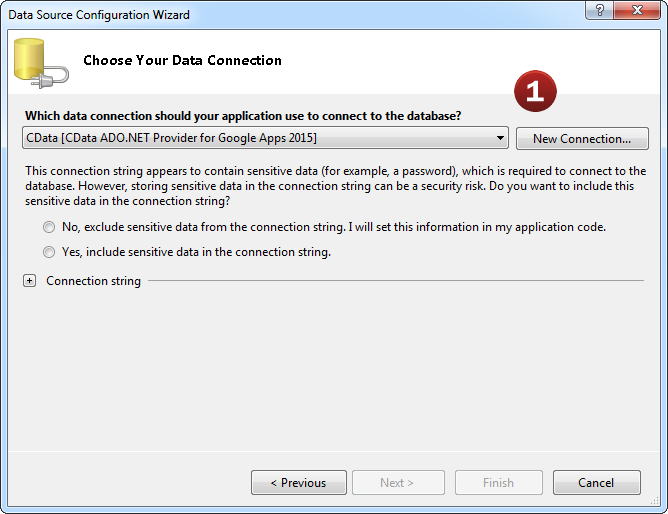
- Add a new Data Connection from the Server Explorer and select the Azure Data Lake Storage Data Source
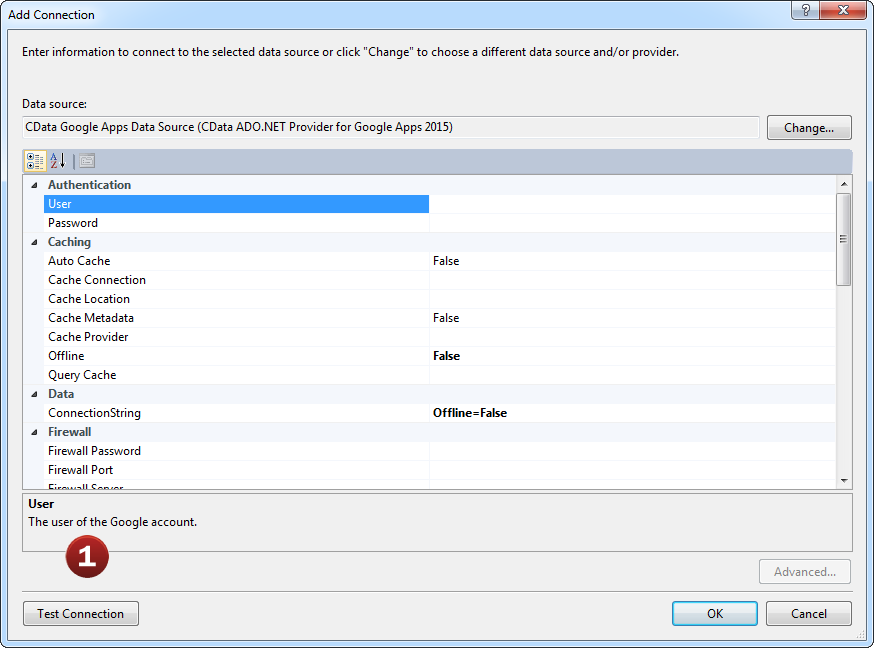
- Configure the basic connection properties to access your Azure Data Lake Storage account data.
Explore all of the data available! Azure Data Lake Storage ADO.NET Provider makes it easy to access live Azure Data Lake Storage data from Visual Studio.
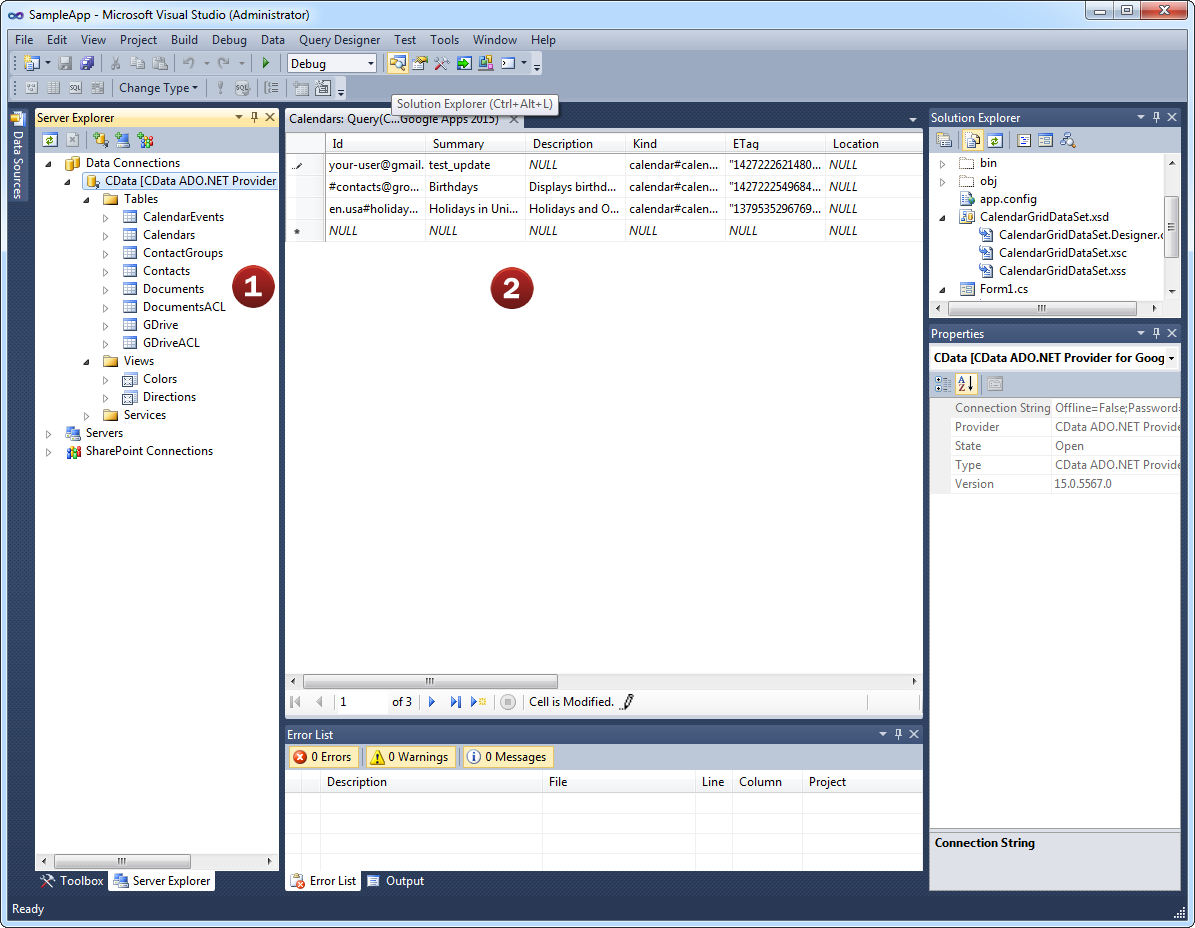
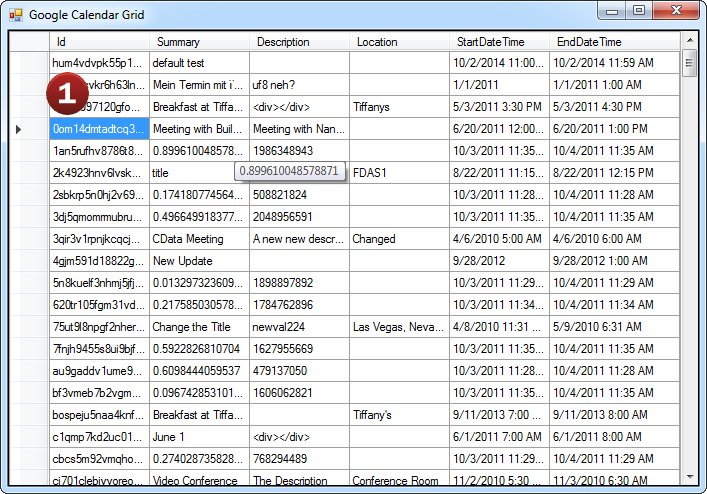
- After configuring the connection, explore the feeds, views, and services provided by the Azure Data Lake Storage Data Source.
- These constructs return live Azure Data Lake Storage data that developers can work with directly from within Visual Studio!
Developer Integration: Databind to Azure Data Lake Storage
Connecting Web, Desktop, and Mobile .NET applications with Azure Data Lake Storage is just like working with SQL Server. It is even possible to integrate Azure Data Lake Storage ADO.NET Provider into applications without writing code.
Developers are free to access the Azure Data Lake Storage ADO.NET Provider in whatever way they like best. Either visually through the Visual Studio Winforms or Webforms designers, or directly through code.
- Developers can connect the Azure Data Lake Storage Data Source directly to form components by configuring the object's smart tags.
- Add a new Data Connection from the Server Explorer and select the Azure Data Lake Storage Data Source. Then, select the feed, view, or services you would like to connect the object to.
Done! It's just like connecting to SQL Server.
- Once the object is bound to the data source, applications can easily interact with Azure Data Lake Storage data with full read/write (CRUD) support.
Popular ADO Videos: