Connecting Moonlit Workflow with Google Spanner Data via CData Connect AI MCP Server
Moonlit enables teams to design automated workflows and AI-driven processes through flexible orchestration blocks. But when workflows must rely on live enterprise data like CRM, ERP, finance, analytics, or cloud applications, developers often resort to custom backend logic or scheduled syncs. This increases maintenance overhead and restricts workflows to stale data snapshots.
CData Connect AI solves this problem by exposing real-time access to 300+ enterprise systems through its secure Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server. Moonlit workflows can interact with live data using a lightweight Claude-based agent service that forwards workflow questions to CData Connect AI.
This guide outlines the steps required to configure the Claude MCP agent, deploy a FastAPI endpoint for live tool access, expose the agent to Moonlit, and build workflows that operate on real-time data through CData Connect AI.
Prerequisites:
- CData Connect AI account
- Install Python 3.9+
- Anthropic API Key (Claude)
- Google Spanner data org with Moonlit enabled and permission to create/manage Connected Apps
Credentials checklist:
Before you begin, you'll need a few credentials mentioned below:
CData Connect AI MCP:
- USERNAME: Your CData email login
- PAT: Connect AI, go to Settings and click on Access Tokens (copy once)
- MCP_BASE_URL: https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp
Moonlit:
- Moonlit account with Workflow Builder access
- ngrok installed and authenticated
Step 1: Configure Google Spanner connectivity for Moonlit
Connectivity to Google Spanner from Moonlit is made possible through CData Connect AI Remote MCP. To interact with Google Spanner data from Moonlit, we start by creating and configuring a Google Spanner connection in CData Connect AI.
- Log into Connect AI, click Sources, and then click Add Connection
- Select "Google Spanner" from the Add Connection panel
-
Google Spanner uses OAuth to authenticate. Click "Sign in" to authenticate with Google Spanner.
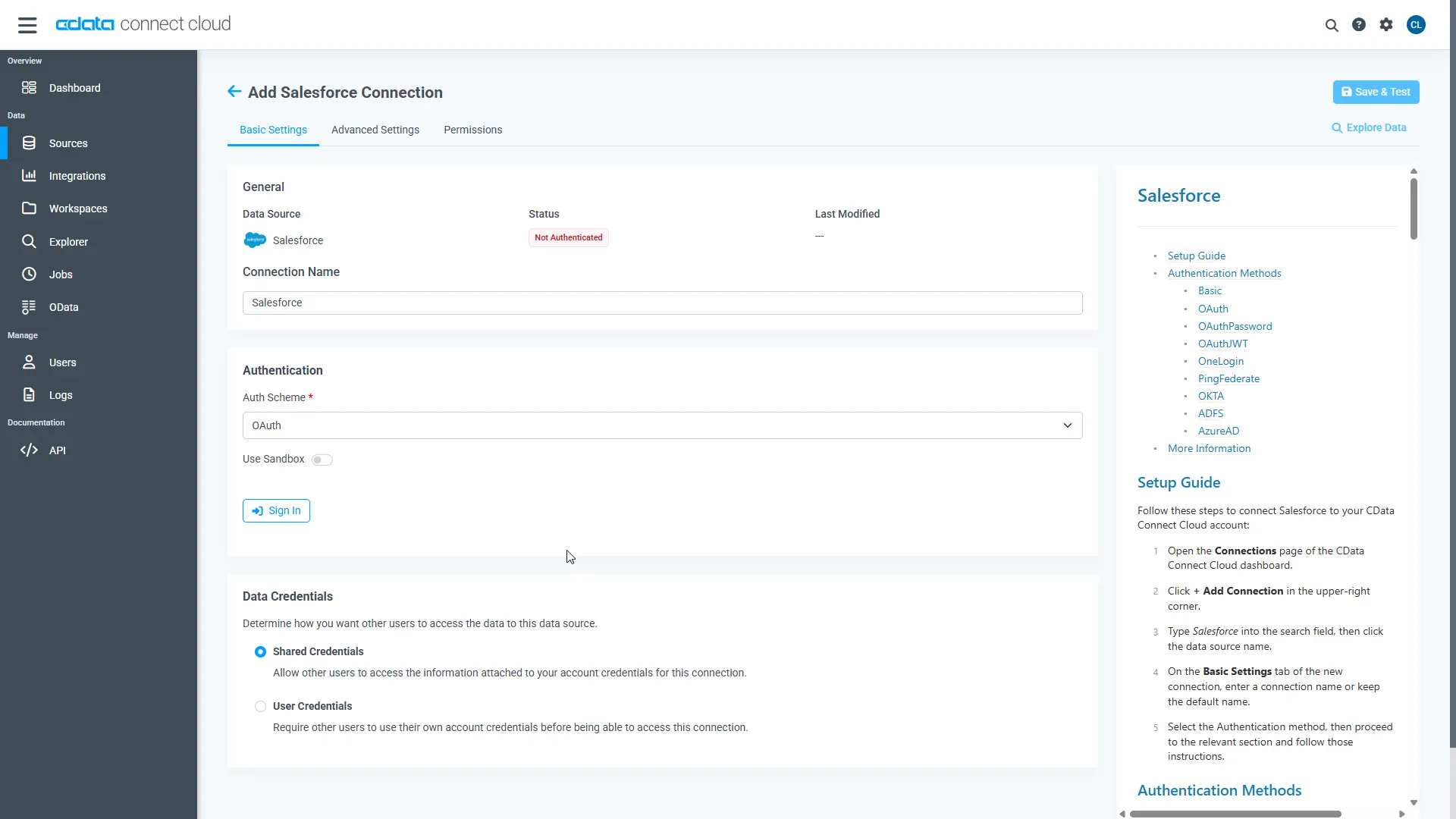
-
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add Google Spanner Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
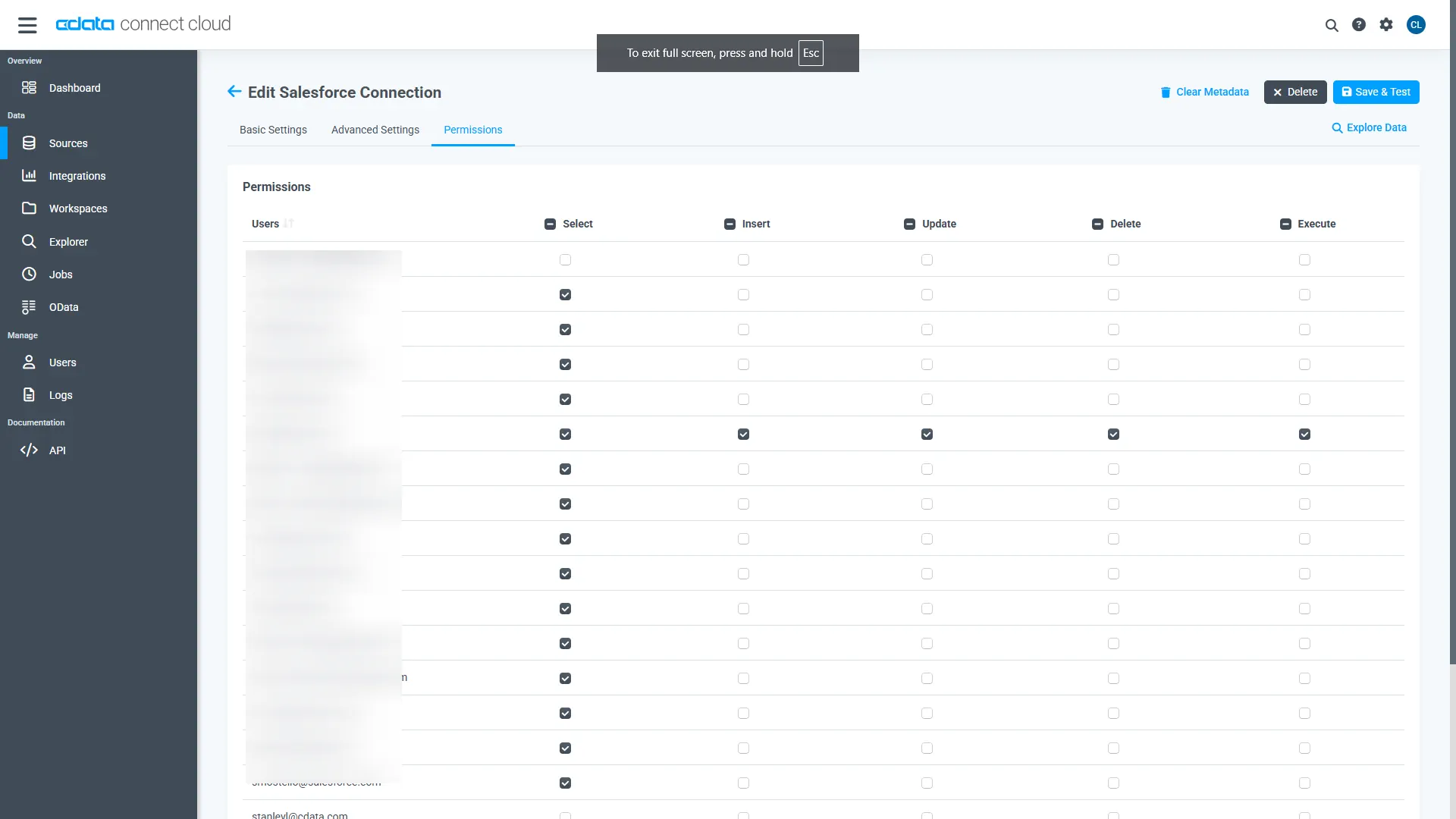

Add a Personal Access Token
A Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect AI from Moonlit. It is best practice to create a separate PAT for each service to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on the Gear icon () at the top right of the Connect AI app to open the settings page.
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
-
Give the PAT a name and click Create.
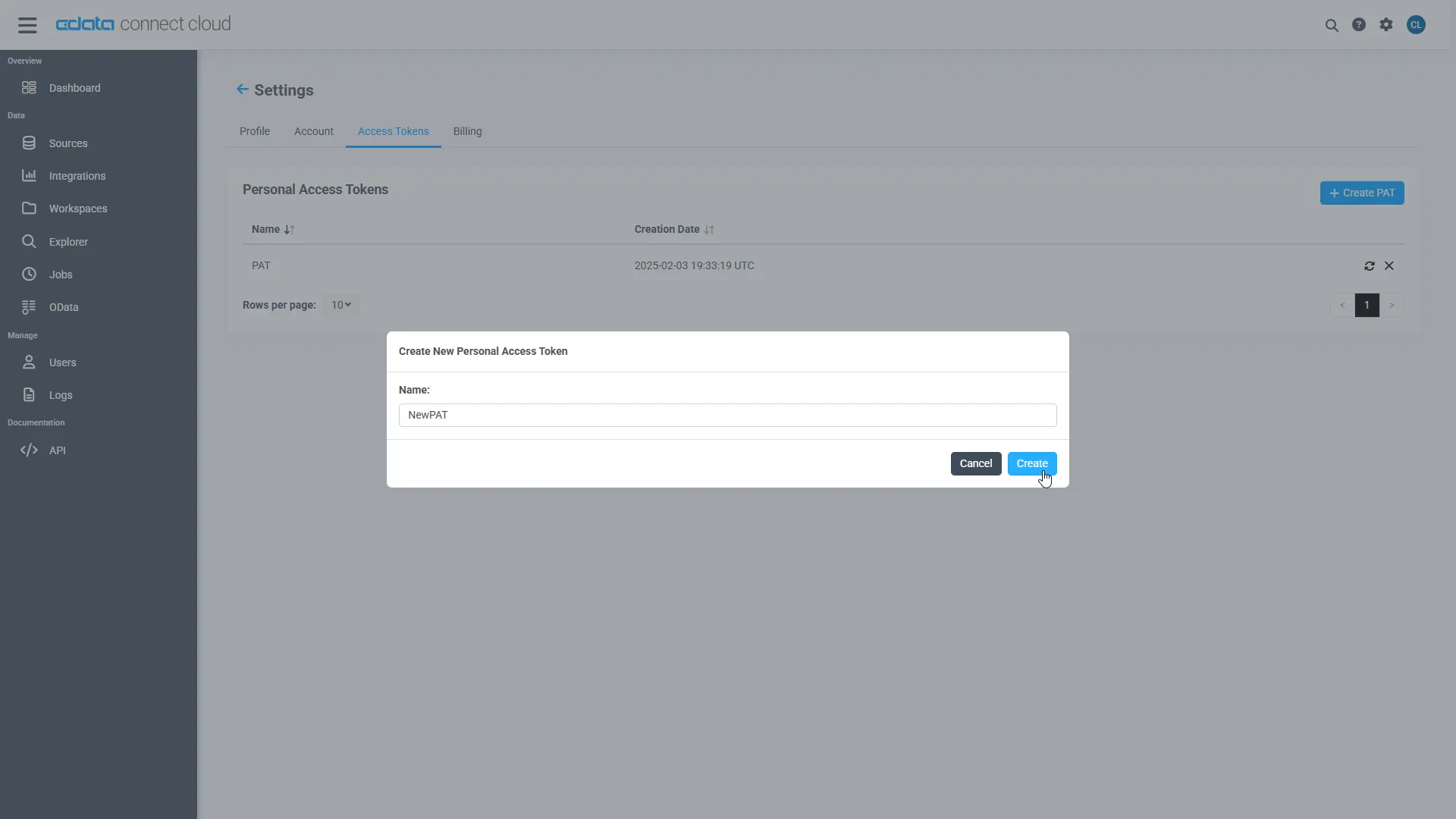
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
Step 2: Clone the agent repository & install dependencies
Begin by cloning the official CData MCP agent repository and setting up the required Python environment to prepare your project for integration.
git clone https://github.com/CDataSoftware/connect-ai-claude-agent.git cd connect-ai-claude-agent
(Optional but recommended):
python -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate # macOS/Linux .venv\Scripts\activate # Windows
Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt pip install fastapi uvicorn python-dotenv pydantic
Step 3: Configure the environment variables
Copy and configure the .env file:
cp .env.example .env
Update values:
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your_anthropic_key_here CDATA_EMAIL=your_email CDATA_ACCESS_TOKEN=your_cdata_pat MCP_SERVER_URL=https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp/
Step 4: Add the CData Connect AI Claude agent
Replace your agent_chatbot.py with the full version below :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
import json
import base64
import asyncio
from typing import Optional, Dict, Any, List
import requests
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from anthropic import Anthropic
# Load environment variables from .env file
load_dotenv()
class MCPClient:
"""Client for interacting with CData Connect AI MCP server over HTTP."""
def __init__(self, server_url: str, email: Optional[str] = None, access_token: Optional[str] = None):
self.server_url = server_url.rstrip("/")
self.session = requests.Session()
# Default headers for MCP JSON-RPC over SSE
self.session.headers.update(
{
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Accept": "application/json, text/event-stream",
}
)
if email and access_token:
# Basic authentication: email:personal_access_token
credentials = f"{email}:{access_token}"
encoded_credentials = base64.b64encode(credentials.encode()).decode()
self.session.headers.update(
{
"Authorization": f"Basic {encoded_credentials}",
}
)
def _parse_sse_response(self, response_text: str) -> dict:
"""Parse Server-Sent Events (SSE) response."""
# SSE format: event: message\n data: {...}\n\n
for line in response_text.split("\n"):
if line.startswith("data: "):
data_json = line[6:] # Remove 'data: ' prefix
return json.loads(data_json)
raise ValueError("No data found in SSE response")
def list_tools(self) -> list:
"""Get available tools from the MCP server."""
response = self.session.post(
self.server_url,
json={
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "tools/list",
"params": {},
"id": 1,
},
)
response.raise_for_status()
result = self._parse_sse_response(response.text)
return result.get("result", {}).get("tools", [])
def call_tool(self, tool_name: str, arguments: dict) -> dict:
"""Call a tool on the MCP server."""
response = self.session.post(
self.server_url,
json={
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {"name": tool_name, "arguments": arguments},
"id": 2,
},
)
response.raise_for_status()
result = self._parse_sse_response(response.text)
return result.get("result", {})
class MCPAgentChatbot:
"""
AI agent chatbot for CData Connect AI using Anthropic's HTTP API.
- Loads tools from the CData MCP server
- Maps them to Anthropic 'tools' spec
- Orchestrates tool_use / tool_result loop without Claude Code CLI
"""
def __init__(self, mcp_server_url: str, email: Optional[str] = None, access_token: Optional[str] = None):
# Anthropic client (HTTP only, no CLI)
api_key = os.environ.get("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY")
if not api_key:
raise RuntimeError("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY is not set in the environment/.env")
self.client = Anthropic(api_key=api_key)
# Hard-coded model: do NOT use ANTHROPIC_MODEL from env
self.model = "claude-3-haiku-20240307"
print(f"Using Anthropic model: {self.model} (hard-coded, env ANTHROPIC_MODEL ignored)")
# MCP client
self.mcp_client = MCPClient(mcp_server_url, email, access_token)
print("Connecting to CData Connect AI MCP server...")
self.mcp_tools_list = self.mcp_client.list_tools()
print(f"Loaded {len(self.mcp_tools_list)} tools from MCP server")
if self.mcp_tools_list:
print(" Available tools:")
for tool_info in self.mcp_tools_list[:5]:
print(f" - {tool_info.get('name', 'unknown')}")
if len(self.mcp_tools_list) > 5:
print(f" ... and {len(self.mcp_tools_list) - 5} more")
# Convert MCP tools to Anthropic tools spec
self.tools_for_claude = self._create_tools_for_claude()
# Stronger instructions for tool use and final answers
self.system_prompt = (
"You are a helpful assistant with access to CData Connect AI tools over MCP. "
"Use these tools to answer questions about data sources, connections, tables, and queries. "
"When tools fail or return errors, always explain clearly what went wrong instead of "
"continuing to call tools. After at most 3 tool calls, you MUST respond with the best "
"possible final answer using whatever data or error messages you have."
)
def _create_tools_for_claude(self) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""Convert MCP tool definitions into Anthropic 'tools' format."""
tools = []
for t in self.mcp_tools_list:
name = t.get("name")
if not name:
continue
tools.append(
{
"name": name,
"description": t.get("description", ""),
"input_schema": t.get("inputSchema", {"type": "object", "properties": {}}),
}
)
return tools
def _run_agent_sync(self, user_message: str) -> str:
"""
Synchronous agent loop using Anthropic tools API.
We run this in a thread from async contexts.
"""
messages: List[Dict[str, Any]] = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": user_message,
}
]
# Safety: avoid infinite loops
max_tool_rounds = 6
# Keep track of the last tool result so we can surface real errors
last_tool_result_text: Optional[str] = None
for _ in range(max_tool_rounds):
try:
response = self.client.messages.create(
model=self.model,
max_tokens=1024,
system=self.system_prompt,
tools=self.tools_for_claude,
messages=messages,
)
except Exception as e:
# Surface Anthropic errors (e.g., bad model) as a normal answer
return (
f"Error when calling Anthropic model '{self.model}': {e}. "
"Check that the model name is valid for your API key."
)
# Extract tool_use contents, if any
tool_uses = [
block
for block in response.content
if getattr(block, "type", None) == "tool_use"
]
# If no tools requested, return the assistant's text reply
if not tool_uses:
texts = [
getattr(block, "text", "")
for block in response.content
if getattr(block, "type", None) == "text"
]
texts = [t for t in texts if t]
if texts:
# Include model tag to make debugging easier
return f"[model={self.model}] " + "\n\n".join(texts)
# No tools and no text – dump raw response for debugging
return f"[model={self.model}] Raw response:\n" + json.dumps(
response.model_dump(), indent=2
)
# Add the tool_use content as an assistant message
messages.append(
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": response.content,
}
)
# For each requested tool, call the MCP server and send tool_result back
tool_result_messages: List[Dict[str, Any]] = []
for tu in tool_uses:
tool_name = getattr(tu, "name", None)
tool_use_id = getattr(tu, "id", None)
tool_input = getattr(tu, "input", {}) or {}
try:
result = self.mcp_client.call_tool(tool_name, tool_input)
result_text = json.dumps(result, indent=2)
except Exception as e:
result_text = f"Error calling tool {tool_name}: {e}"
# Remember the last tool result for better error messages later
last_tool_result_text = result_text
tool_result_messages.append(
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "tool_result",
"tool_use_id": tool_use_id,
"content": result_text,
}
],
}
)
messages.extend(tool_result_messages)
# Fallback if we exit loop without a final answer – but show last tool result
if last_tool_result_text:
return (
f"[model={self.model}] I was unable to produce a final natural-language answer "
f"after using tools. Here is the last tool result I received:\n\n"
f"{last_tool_result_text}"
)
else:
return f"[model={self.model}] I was unable to produce a final answer after using tools."
async def chat_once(self, user_message: str) -> str:
"""Async wrapper around the synchronous agent loop."""
return await asyncio.to_thread(self._run_agent_sync, user_message)
async def interactive_mode(chatbot: MCPAgentChatbot):
"""Run the chatbot in interactive CLI mode (uses same HTTP-only agent)."""
print("\nChatbot ready! Type 'quit' to exit.\n")
while True:
try:
user_input = input("You: ").strip()
if not user_input:
continue
if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit", "q"]:
print("Goodbye!")
break
response = await chatbot.chat_once(user_input)
print(f"\nAssistant: {response}\n")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\nGoodbye!")
break
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}\n")
async def main():
"""Run the chatbot in interactive mode (for local testing)."""
MCP_SERVER_URL = os.getenv("MCP_SERVER_URL", "https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp/")
CDATA_EMAIL = os.environ.get("CDATA_EMAIL")
CDATA_ACCESS_TOKEN = os.environ.get("CDATA_ACCESS_TOKEN")
print("=== CData Connect AI Agent Chatbot ===")
print(f"MCP Server: {MCP_SERVER_URL}\n")
if not CDATA_EMAIL or not CDATA_ACCESS_TOKEN:
print("CData credentials not found.")
print("\nThis app requires your CData email and personal access token.")
print("\nTo configure:")
print(" set [email protected]")
print(" set CDATA_ACCESS_TOKEN=your_personal_access_token\n")
return
try:
chatbot = MCPAgentChatbot(MCP_SERVER_URL, CDATA_EMAIL, CDATA_ACCESS_TOKEN)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error connecting to MCP server or Anthropic: {e}")
return
await interactive_mode(chatbot)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
This implementation:
- Uses Claude 3 Haiku
- Connects to the CData Connect AI MCP Server
- Converts MCP tools into Claude tool schema
- Handles the tool-use loop without relying on CLI wrappers
Step 5: Add the FastAPI integration layer
Below is the full api_server.py, which exposes the agent over a POST /ask endpoint :
import os
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
from agent_chatbot import MCPAgentChatbot
app = FastAPI()
# Environment variables (also loaded in agent_chatbot via load_dotenv)
CDATA_EMAIL = os.getenv("CDATA_EMAIL")
CDATA_ACCESS_TOKEN = os.getenv("CDATA_ACCESS_TOKEN")
MCP_SERVER_URL = os.getenv("MCP_SERVER_URL", "https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp/")
# Instantiate chatbot at startup
try:
chatbot = MCPAgentChatbot(
mcp_server_url=MCP_SERVER_URL,
email=CDATA_EMAIL,
access_token=CDATA_ACCESS_TOKEN,
)
except Exception as e:
# Fail fast if configuration is broken
raise RuntimeError(f"Failed to initialize MCPAgentChatbot: {e}")
class AskRequest(BaseModel):
question: str
class AskResponse(BaseModel):
answer: str
@app.post("/ask", response_model=AskResponse)
async def ask(req: AskRequest):
try:
answer = await chatbot.chat_once(req.question)
return AskResponse(answer=answer)
except Exception as e:
# Convert unexpected backend errors into a 500 with a readable message
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=f"Agent error: {e}")
Run the server:
uvicorn api_server:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
Test the API through:
http://localhost:8000/docs
Step 6: Expose the agent with ngrok
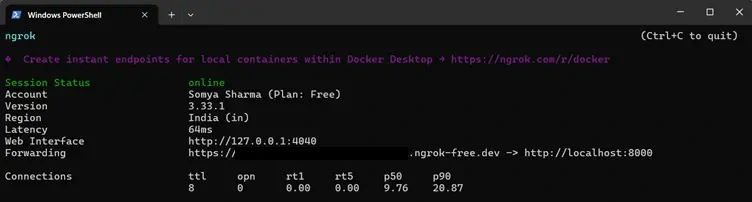
To allow Moonlit or any external application to communicate with your FastAPI agent, you need to make your local server accessible over the internet. ngrok creates a secure public URL that tunnels directly to your running FastAPI service.
- Ensure your FastAPI server is running on port 8000:
- In a separate terminal, start an ngrok tunnel to expose this port:
- ngrok will generate a publicly accessible HTTPS URL (for example: https://your-ngrok-id.ngrok-free.dev). Use this URL-specifically the /ask endpoint-inside Moonlit when configuring your Custom API Request step.
uvicorn api_server:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
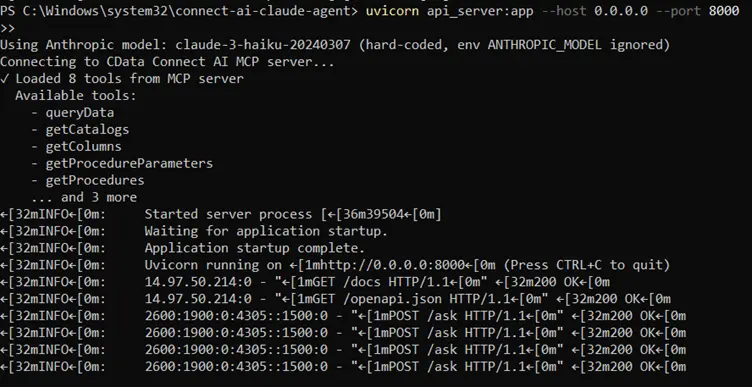
ngrok http 8000
This ensures your Moonlit workflow can reach your agent service reliably during development.
Step 7: Connect the agent to Moonlit
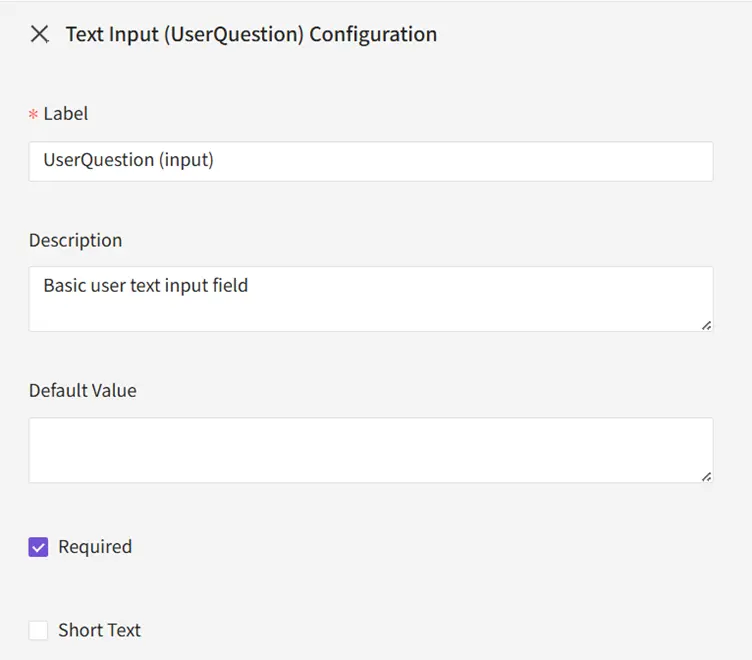
7.1 Input
Add a Text Input: UserQuestion
7.2 Function
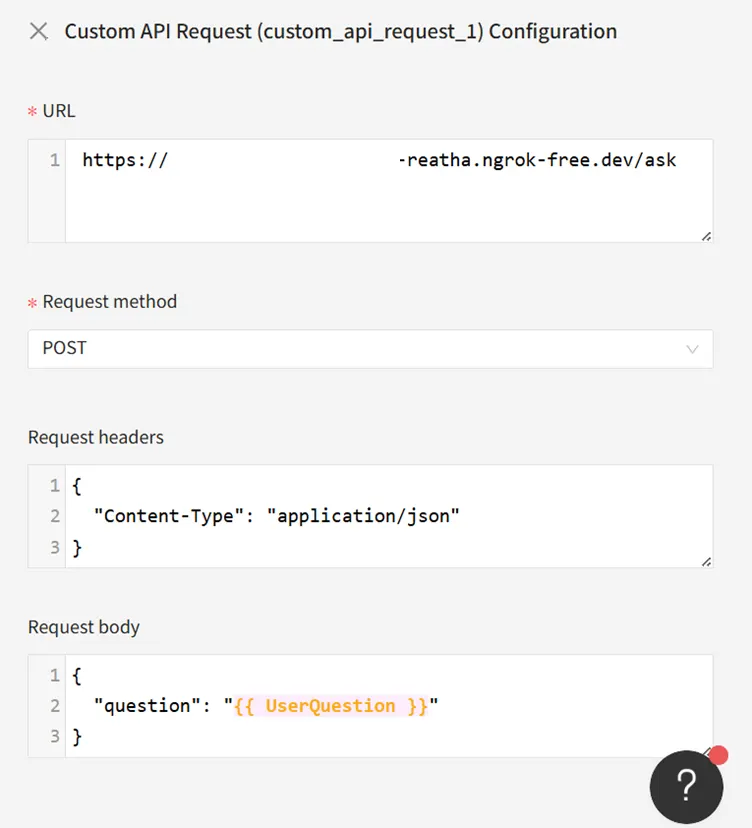
Configure:
- URL: https://your-ngrok-id.ngrok-free.dev/ask
- Method: POST
- Headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" }
- Body: { "question": "{{ UserQuestion }}" }
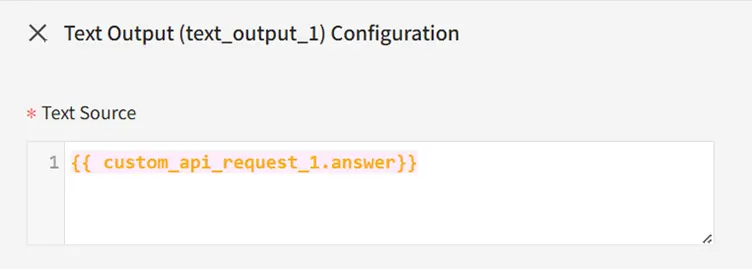
7.3 Output
Add Text Output: {{ custom_api_request_1.answer }}
Step 8: Test the complete workflow
In Moonlit's Test panel, run:
" What are the tools available in CData Connect AI MCP Server."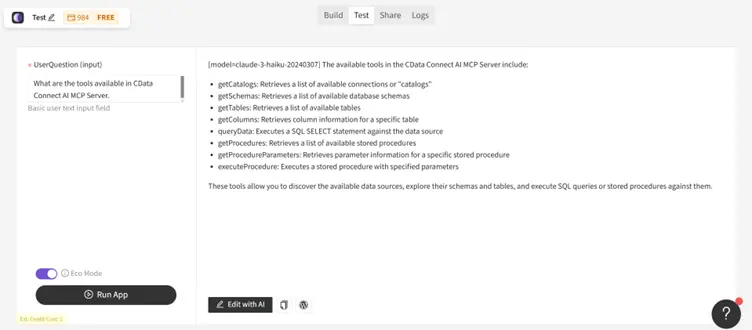
The workflow will:
- Send the input to your FastAPI service
- Forward it to Claude
- Claude will call CData MCP tools as needed
- The grounded real-time answer returns to Moonlit
Build real-time, data-aware agents with Moonlit and CData
Moonlit and CData Connect AI together enable powerful AI-driven workflows where agents have live access to enterprise data and act intelligently without sync pipelines or manual integration logic.
Start your free trial today to see how CData can empower Moonlit with live, secure access to 300+ external systems.






