Connecting Mastra with Jira Data via CData Connect AI MCP Server
Mastra is designed for developers and enterprise teams building intelligent, composable AI agents. Its modular framework and declarative architecture make it simple to orchestrate agents, integrate LLMs, and automate data-driven workflows. But when agents need to work with data beyond their local memory or predefined APIs, many implementations rely on custom middleware or scheduled syncs to copy data from external systems into local stores. This approach adds complexity, increases maintenance overhead, introduces latency, and limits the real-time potential of your agents.
CData Connect AI bridges this gap with live, direct connectivity to more than 300 enterprise applications, databases, ERPs, and analytics platforms. Through CData's remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server, Mastra agents can securely query, read, and act on real-time data without replication. The result is grounded responses, faster reasoning, and automated decision-making across systems all with stronger governance and fewer moving parts.
This article outlines the steps required to configure CData Connect AI MCP connectivity, register the MCP server in Mastra Studio, and build an agent that queries live Jira data in real time.
About Jira Data Integration
CData simplifies access and integration of live Jira data. Our customers leverage CData connectivity to:
- Gain bi-directional access to their Jira objects like issues, projects, and workflows.
- Use SQL stored procedures to perform functional actions like changing issues status, creating custom fields, download or uploading an attachment, modifying or retrieving time tracking settings, and more.
- Authenticate securely using a variety of methods, including username and password, OAuth, personal access token, API token, Crowd or OKTA SSO, LDAP, and more.
Most users leverage CData solutions to integrate Jira data with their database or data warehouse, whether that's using CData Sync directly or relying on CData's compatibility with platforms like SSIS or Azure Data Factory. Others are looking to get analytics and reporting on live Jira data from preferred analytics tools like Tableau and Power BI.
Learn more about how customers are seamlessly connecting to their Jira data to solve business problems from our blog: Drivers in Focus: Collaboration Tools.
Getting Started
Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure you have:
- A CData Connect AI account
- Node.js 18+ and npm installed
- A working Mastra project (created via npm create mastra@latest)
- Access to Jira
Credentials checklist
Ensure you have these credentials ready for the connection:
- USERNAME: Your CData email login
- PAT: Connect AI, go to Settings and click on Access Tokens (copy once)
- MCP_BASE_URL: https://mcp.cloud.cdata.com/mcp
Step 1: Configure Jira connectivity for Mastra
Connectivity to Jira from Mastra is made possible through CData Connect AI Remote MCP. To interact with Jira data from Mastra, we start by creating and configuring a Jira connection in CData Connect AI.
- Log into Connect AI, click Sources, and then click Add Connection
- Select "Jira" from the Add Connection panel
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Jira.
To connect to JIRA, provide the User and Password. Additionally, provide the Url; for example, https://yoursitename.atlassian.net.
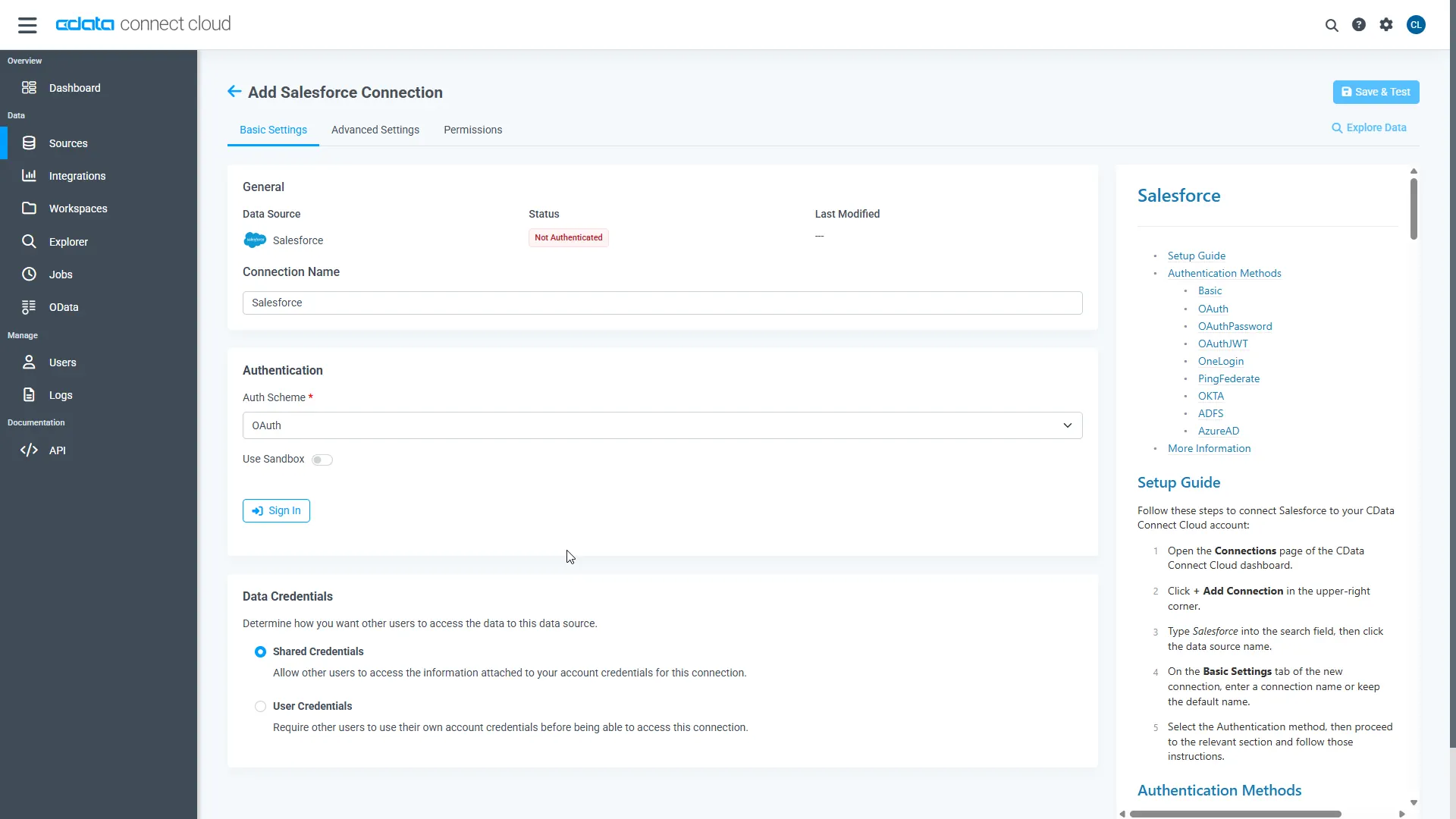
- Click Save & Test
-
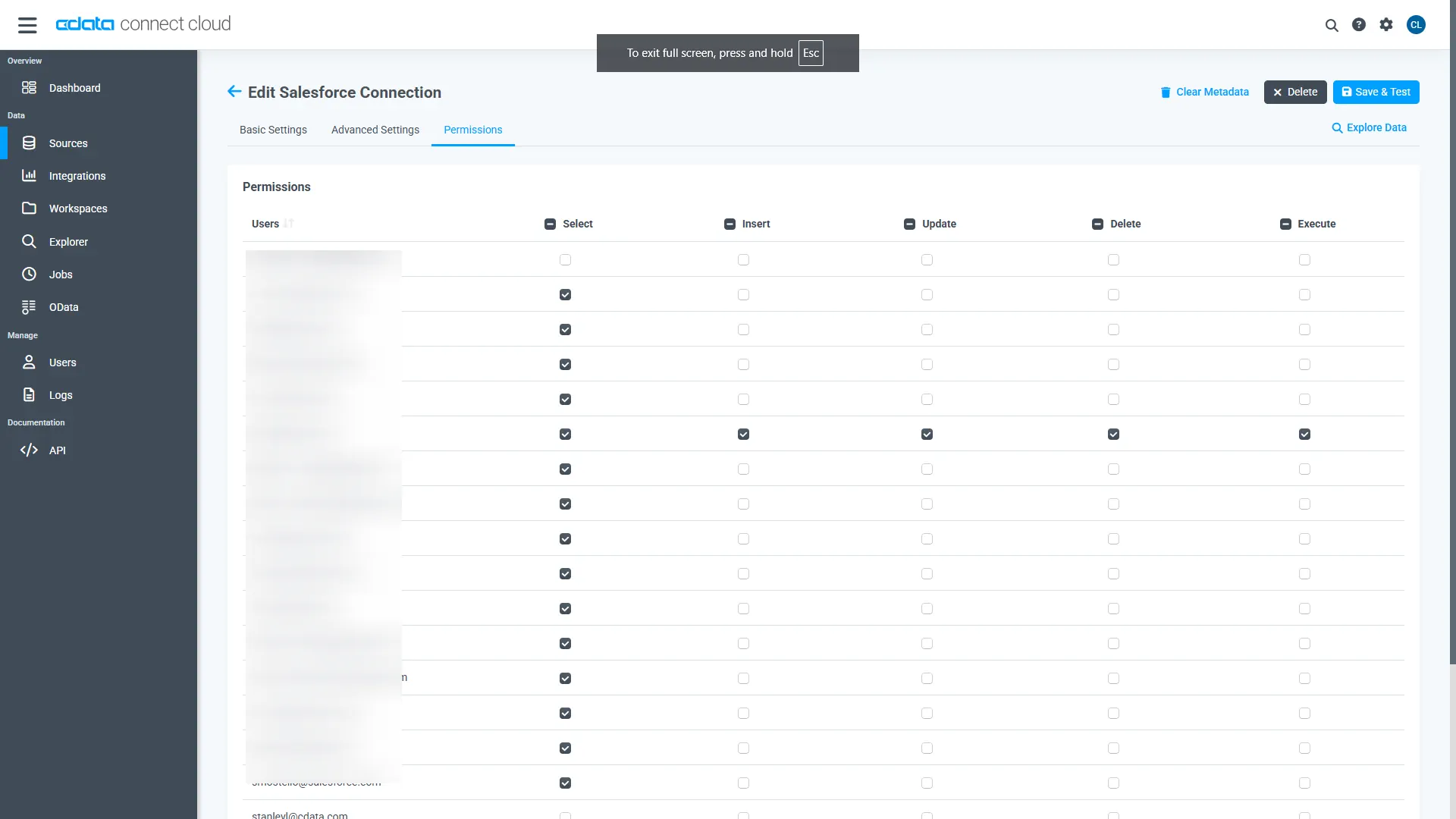
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add Jira Connection page and update the User-based permissions.

Add a Personal Access Token
A Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect AI from Mastra. It is best practice to create a separate PAT for each service to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on the Gear icon () at the top right of the Connect AI app to open the settings page.
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
-
Give the PAT a name and click Create.
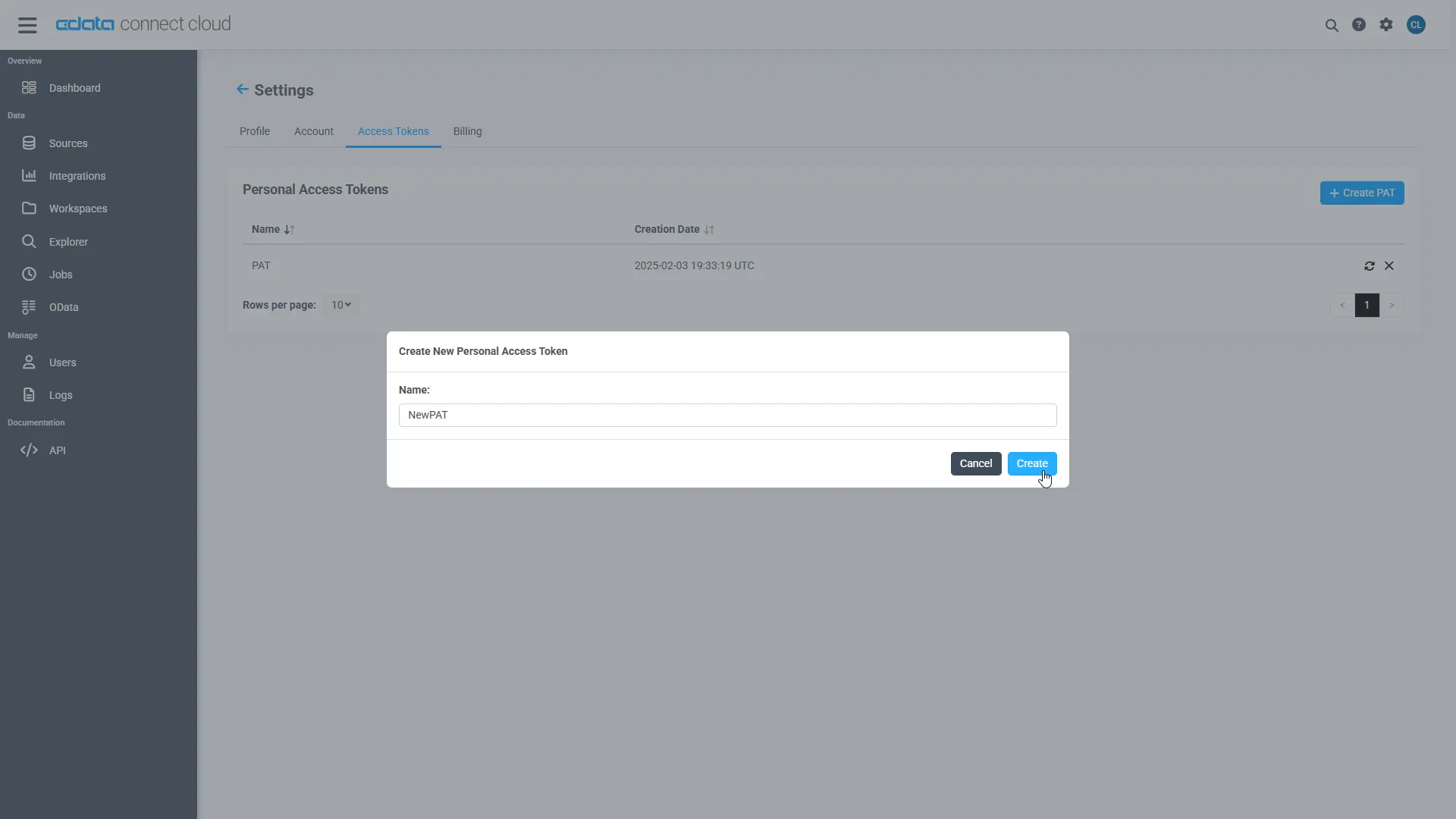
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured and a PAT generated, we are ready to connect to Jira data from Mastra.
Step 2: Set up the Mastra project
- Open a terminal and navigate to your desired folder
- Create a new project:
npm create mastra@latest
- Open the folder in VS Code
- Install the required Mastra dependencies:
npm install @mastra/core @mastra/libsql @mastra/memory
- Then install the MCP integration package separately:
npm install @mastra/mcp

Step 3: Configure environment variables
Create a .env file at the project root with the following keys:
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-... [email protected] CDATA_CONNECT_AI_PASSWORD=your_PAT
Restart your dev server after saving changes:
npm run dev
Step 4: Add the CData Connect AI agent
Create a file src/mastra/agents/connect-ai-agent.ts with the following code:
import { Agent } from "@mastra/core/agent";
import { Memory } from "@mastra/memory";
import { LibSQLStore } from "@mastra/libsql";
import { MCPClient } from "@mastra/mcp";
const mcpClient = new MCPClient({
servers: {
cdataConnectAI: {
url: new URL("https://connect.cdata.com/mcp/"),
requestInit: {
headers: {
Authorization: `Basic ${Buffer.from(
`${process.env.CDATA_CONNECT_AI_USER}:${process.env.CDATA_CONNECT_AI_PASSWORD}`
).toString("base64")}`,
},
},
},
},
});
export const connectAIAgent = new Agent({
name: "Connect AI Agent",
instructions: "You are a data exploration and analysis assistant with access to CData Connect AI.",
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
tools: await mcpClient.getTools(),
memory: new Memory({
storage: new LibSQLStore({ url: "file:../mastra.db" }),
}),
});
Step 5: Update index.ts to register the agent
Replace the contents of src/mastra/index.ts with:
import { Mastra } from "@mastra/core/mastra";
import { PinoLogger } from "@mastra/loggers";
import { LibSQLStore } from "@mastra/libsql";
import { connectAIAgent } from "./agents/connect-ai-agent.js";
export const mastra = new Mastra({
agents: { connectAIAgent },
storage: new LibSQLStore({ url: "file:../mastra.db" }),
logger: new PinoLogger({ name: "Mastra", level: "info" }),
observability: { default: { enabled: true } },
});
Step 6: Run and verify the connection
Start your Mastra server:
npm run dev

Step 7: Run a live query in Mastra Studio
In Mastra Studio, open the chat interface and enter one of the following sample prompts:
List available catalogs from my connected data sources.

Build real-time, data-aware agents with Mastra and CData
Mastra and CData Connect AI together enable powerful AI-driven workflows where agents have live access to enterprise data and act intelligently without sync pipelines or manual integration logic.
Start your free trial today to see how CData can empower Mastra with live, secure access to 300+ external systems.






