Getting Started with the CData Excel Add-In for SQL Server
This guide explains everything you need to get started with the CData Excel Add-In for SQL Server. You will learn how to install the add-in, understand licensing behavior, configure your first connection, and import real-time SQL Server data directly into Excel for analysis, reporting, and automation.
Installation & Licensing
System Requirements
- Windows: Windows 10/11 or Windows Server 2016+
- Microsoft Excel: Excel 2016 or later, Excel for Microsoft 365
- .NET Framework: .NET Framework 4.0 or later
Installing the Excel Add-In
Download and install the Excel Add-In from the CData website by visiting the Excel Add-In download page. Fill in the appropriate contact information when prompted.
Note: If you are downloading a licensed installer, use your company email address and license key.
- Run the installer and follow the setup wizard
- Once installation is complete, open Excel and verify that the CData tab appears in the Excel ribbon
Licensing the Excel Add-In
The Excel Add-In handles licensing during installation. When running the installer, you can choose to:
- Use the trial license, or
- Install a licensed build provided by CData
If you require a subscription license, contact the CData Orders Team at [email protected] to obtain your license key. Once the add-in is installed, it is ready for use.
Common Licensing Questions
Can I install the add-in on multiple machines?
Your subscription tier determines how many activations are included. Contact [email protected] for details.
I lost my license key. How do I retrieve it?
Email [email protected] with your order number, and we'll resend your license key.
How do I transfer my license?
To transfer the license to a different machine, you will need to submit a License Transfer Request on our site linked below:
https://www.cdata.com/lic/transfer/
After the License Transfer Request is submitted and successfully processed, an activation will be added to your Product Key and you will be able to activate the full license on the other machine. Once this process is finished, the license on the previous machine will be invalid.
For additional licensing questions, contact [email protected]. Viewing and upgrading your license can now be done through our self-service portal at portal.cdata.com.
Connection Configuration
Once the add-in is installed, you can configure a secure connection to SQL Server directly from the Excel ribbon. The add-in stores connection settings inside the Excel environment and uses them to fetch live SQL Server data.
Creating a New Connection
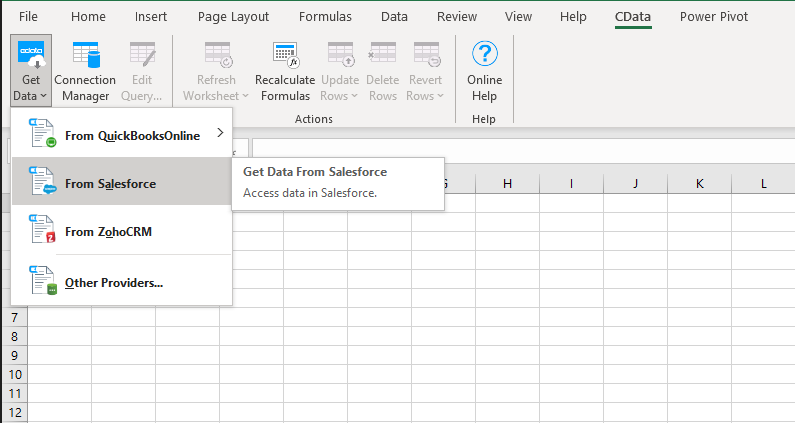
- Open Excel and navigate to the CData tab in the ribbon
- Click Get Data > From SQL Server. Then, click New SQL Connection to create a new connection
- Provide a name for your connection and enable Update, Insert, or Delete operations as required
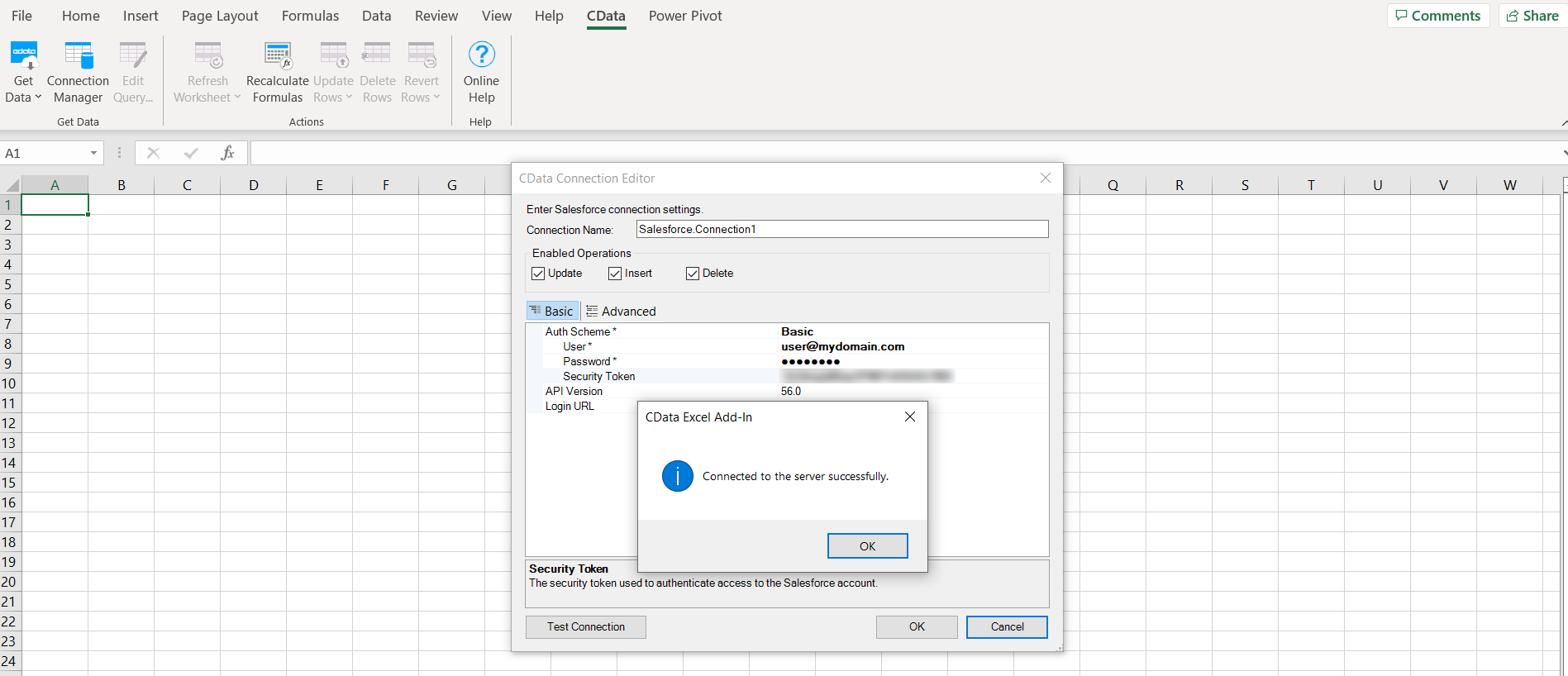
- The CData Connection dialog opens. Enter the authentication details required for SQL Server (OAuth, API token, credentials, etc.)
Configuring Connection Properties
Connecting to Microsoft SQL Server
Connect to Microsoft SQL Server using the following properties:
- Server: The name of the server running SQL Server.
- User: The username provided for authentication with SQL Server.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the SQL Server database.
Connecting to Azure SQL Server and Azure Data Warehouse
You can authenticate to Azure SQL Server or Azure Data Warehouse by setting the following connection properties:
- Server: The server running Azure. You can find this by logging into the Azure portal and navigating to "SQL databases" (or "SQL data warehouses") -> "Select your database" -> "Overview" -> "Server name."
- User: The name of the user authenticating to Azure.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the database, as seen in the Azure portal on the SQL databases (or SQL warehouses) page.
SSH Connectivity for SQL Server
You can use SSH (Secure Shell) to authenticate with SQL Server, whether the instance is hosted on-premises or in supported cloud environments. SSH authentication ensures that access is encrypted (as compared to direct network connections).
SSH Connections to SQL Server in Password Auth Mode
To connect to SQL Server via SSH in Password Auth mode, set the following connection properties:
- User: SQL Server User name
- Password: SQL Server Password
- Database: SQL Server database name
- Server: SQL Server Server name
- Port: SQL Server port number like 3306
- UserSSH: "true"
- SSHAuthMode: "Password"
- SSHPort: SSH Port number
- SSHServer: SSH Server name
- SSHUser: SSH User name
- SSHPassword: SSH Password
SSH Connections to SQL Server in Public Key Auth Mode
To connect to SQL Server via SSH in Password Auth mode, set the following connection properties:
- User: SQL Server User name
- Password: SQL Server Password
- Database: SQL Server database name
- Server: SQL Server Server name
- Port: SQL Server port number like 3306
- UserSSH: "true"
- SSHAuthMode: "Public_Key"
- SSHPort: SSH Port number
- SSHServer: SSH Server name
- SSHUser: SSH User name
- SSHClientCret: the path for the public key certificate file
Testing your Connection
- Click Test Connection to validate your input
- Click OK to save the connection
Importing Data into Excel
After creating a connection, you can import SQL Server data into Excel using the built-in query interface.
Selecting Tables and Views
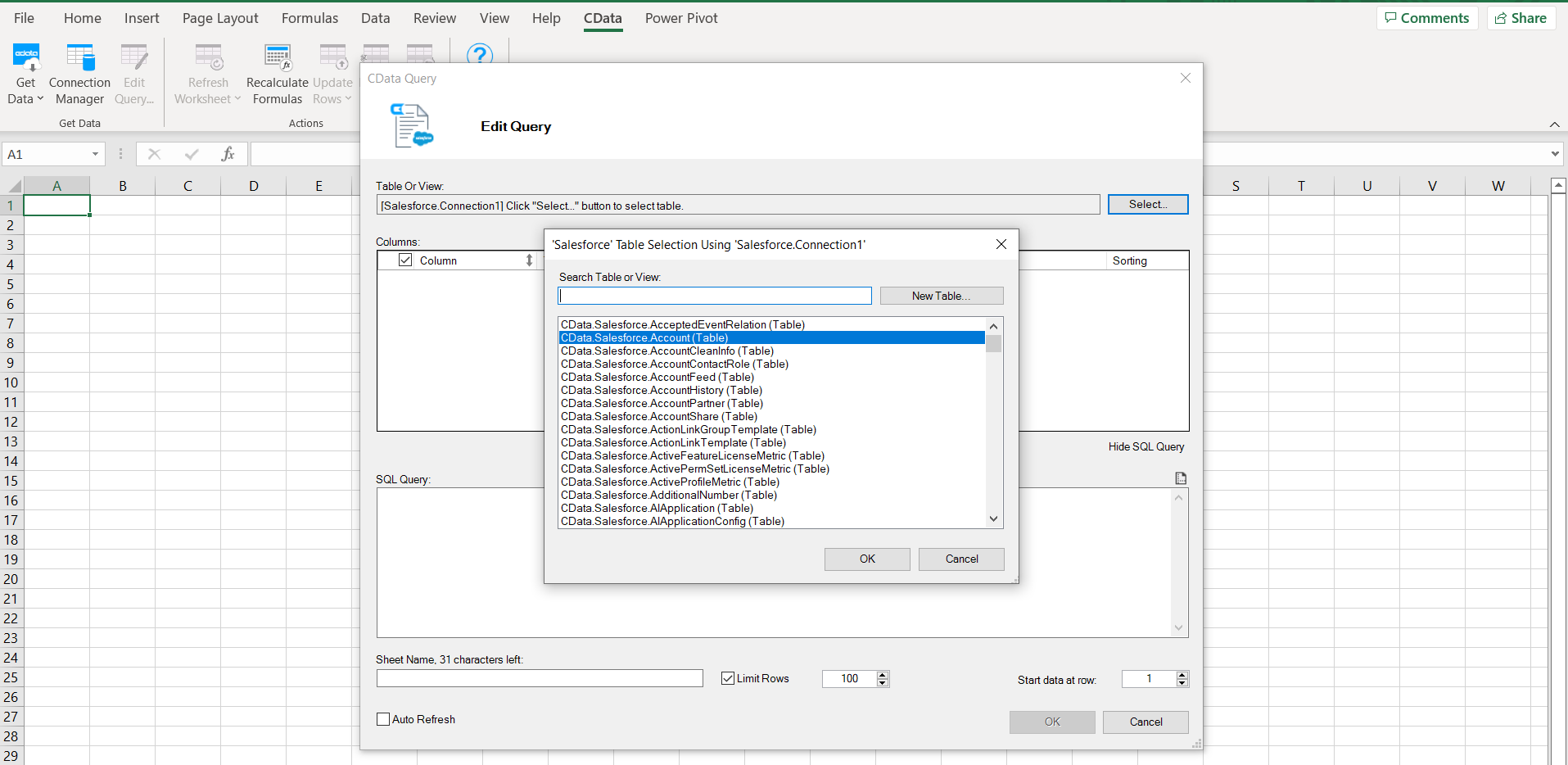
- From the CData ribbon, click Get Data > From SQL Server and choose the connection you just made
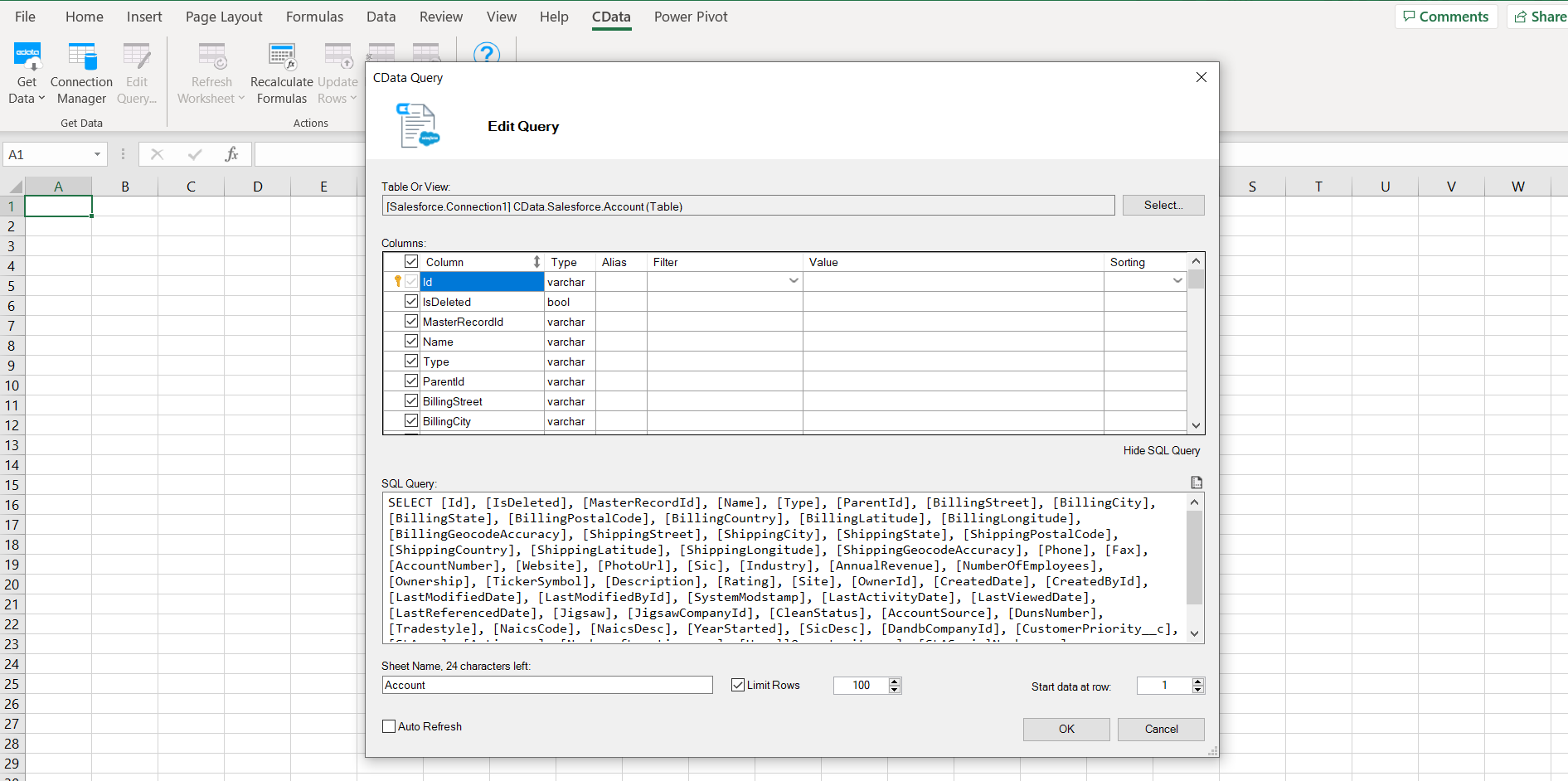
- The CData Query window opens. Click Select to choose a table or view
- Select your desired table and click OK
Running the Query
- A SQL query is automatically generated for your selected table
- Review the query (optional), then click OK to run it
- The results populate directly into your Excel worksheet
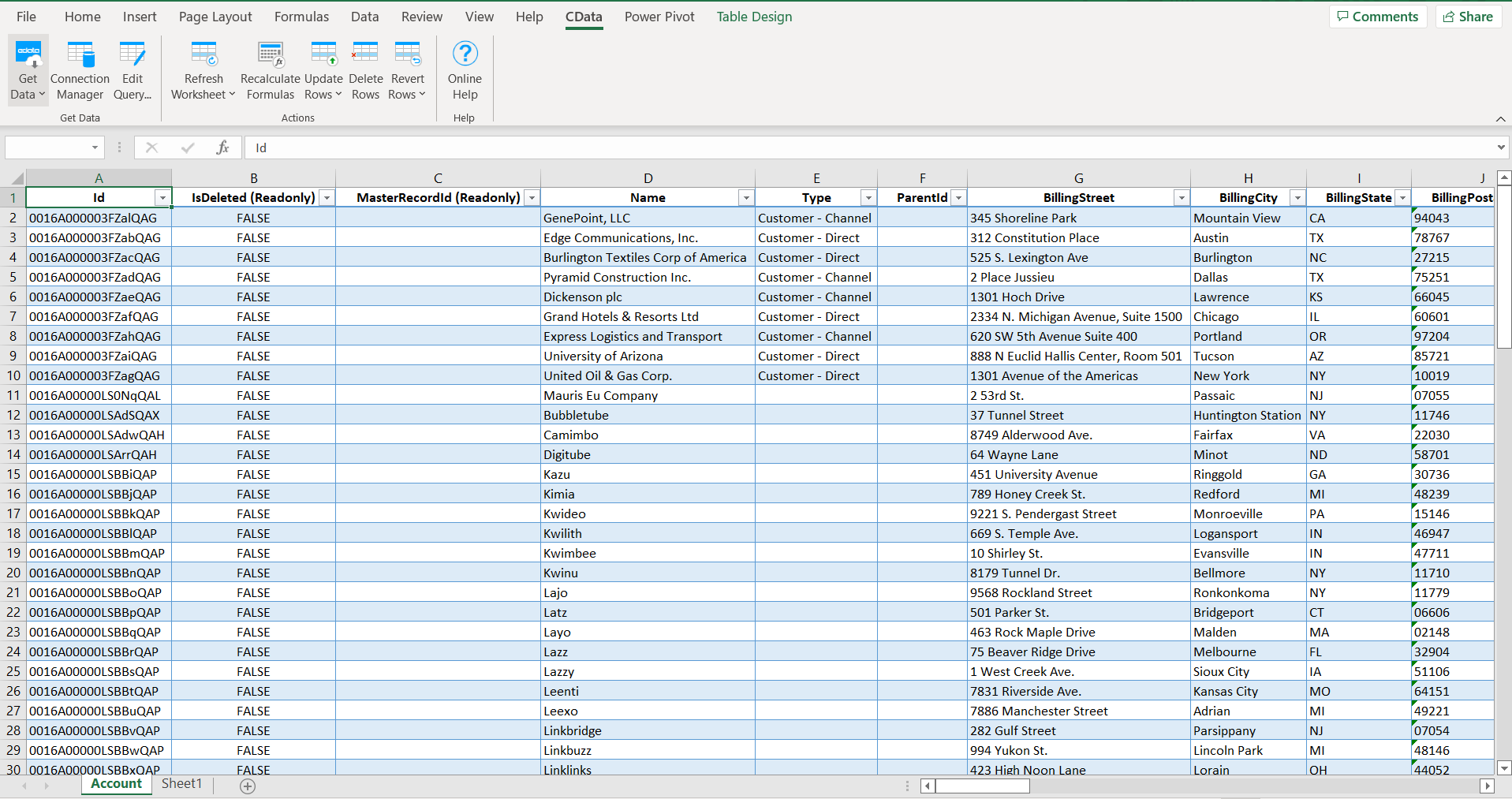
You can now build pivot tables, charts, or use Excel formulas to analyze your SQL Server data.
Common Connection Issues
Authentication Failed
Solution: Verify your credentials or OAuth configuration. Ensure that your SQL Server account has the required API permissions.
Cannot Connect to SQL Server
Solution: Check your internet connection, firewall settings, or proxy configuration. Contact [email protected] for specific port requirements.
Table Not Found
Solution: Confirm your account has access to the selected SQL Server data object. Use the table selector in the Query window to browse available resources.
Query Returned No Results
Solution: Verify any filters or WHERE clauses in the generated SQL. Remove or adjust filters to broaden your query.
What's Next
Now that you have installed, licensed, and configured the Excel Add-In, explore how to automate reporting, refresh live dashboards, and build advanced queries using SQL or Excel functions.
| Excel Add-In | Article Title |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Excel | Transfer Data from Excel to SQL Server |
Get Support
If you need assistance at any point:
- Technical Support: [email protected]
- Community Forum: CData Community Site
- Help Documentation: Installed locally and available online
FAQs
Installation & Licensing
- Does Excel require administrator rights to install the add-in?
Administrative privileges are required for installation. - How do I activate a license?
Licensing occurs during installation. Licensed installers automatically apply subscription keys.
Connecting
- Can I use multiple SQL Server accounts?
Each time you click Get Data, you can configure a new connection. - Can I connect through a proxy?
You can configure proxy settings in the Connection dialog.
Performance & Troubleshooting
- Why is my query slow?
Add filters using the query editor or narrow the selected fields. - How do I enable logging?
Add the following to your connection manager:
- Logfile: /path/to/logfile.log
- Verbosity: 3
Be prepared to securely upload the log file upon request when reaching out to [email protected] for troubleshooting analysis.
- How do I refresh data?
Select the imported table and click Refresh from the CData ribbon.
For questions not covered in this FAQ, contact [email protected].





