 Odoo has become a go-to ERP and CRM platform for growing businesses. And Power BI dominates the analytics landscape with over 30 million active users and adoption by 97% of Fortune 500 companies. As Odoo 18 introduced native Power BI capabilities, interest in connecting these systems has surged.
Odoo has become a go-to ERP and CRM platform for growing businesses. And Power BI dominates the analytics landscape with over 30 million active users and adoption by 97% of Fortune 500 companies. As Odoo 18 introduced native Power BI capabilities, interest in connecting these systems has surged.
The challenge is not building dashboards. It is getting live Odoo data into Power BI without custom API development or data replication.
A sales manager asking, "Which deals closed this quarter?" needs data from Odoo's sales orders, invoices, and CRM pipeline, all joined and visualized in seconds. Without proper connectivity, teams resort to manual exports, stale snapshots, or fragile custom scripts that break with every Odoo update.
This guide walks you through evaluating connection methods, preparing security requirements, implementing connectivity step by step, and optimizing your data model for performance.
Evaluate your connection options
Before jumping into configuration, understand what is technically possible given your Odoo deployment. The right connection method depends on where Odoo is hosted, whether you need live or scheduled data, and your governance requirements.
Choose the right method for your Odoo hosting
Each Odoo hosting option imposes different database access restrictions. Here is a quick overview of Odoo hosting types:
Hosting Type | Direct DB Access | Typical Method | Best For |
Odoo Online (SaaS) | None | API connector | Teams prioritizing simplicity |
Odoo.sh (PaaS) | Dedicated tier only | API connector or dedicated DB | Growing organizations |
Self-hosted | Full | Direct PostgreSQL or API | Enterprises with IT resources |
Self-hosted refers to an Odoo deployment you control on your own servers or cloud VMs, giving you direct PostgreSQL database access with proper security hardening.
The decision rule is straightforward. Use an API connector for Odoo Online and Odoo.sh standard tiers and consider direct database access only for self-hosted deployments.
Decide between live data and scheduled refresh
Once you know your hosting constraints, decide how fresh your data needs to be.
Live data (DirectQuery):
Always current, which means queries hit the source on every interaction
No data movement or storage costs
Best for operational dashboards and governed self-service
Scheduled refresh (Import):
Fast visuals and leverages Power BI's in-memory compression
Full DAX support for complex transformations
Best for historical analytics and complex models
Microsoft recommends Import mode by default. Move to DirectQuery when real-time accuracy or dataset size constraints make it necessary.
Prepare security and governance requirements
With your connection method selected, ensure your environment meets security standards before connecting production data.
Enforce least-privilege access (read-only credentials where possible)
Use token or SSO authentication instead of shared passwords
Configure network allowlists or IP restrictions for database access
Document data sensitivity classifications and PII fields requiring masking
Decide where to enforce Row-Level Security, whether within the connector or in Power BI
Establish audit logging for compliance requirements
Row-Level Security (RLS) is a rule-based filter that restricts each user to only the rows they are allowed to see at query time.
With prerequisites confirmed, you are ready to implement your chosen connection method.
Method 1: Connect Odoo to Power BI with CData Connect AI
CData Connect AI provides a no-code approach to connecting live Odoo data to Power BI without data movement. This method works for all Odoo hosting types because it uses Odoo's API rather than direct database access.
Key capabilities:
Live data access across Odoo objects without ETL
No install, no gateway for cloud-to-cloud scenarios
Fine-grained access controls and audit trails
350+ enterprise connectors for multi-source models
Every data copy introduces security exposure, compliance overhead, and staleness. Querying data in place eliminates these problems entirely.
Prerequisites:
Step 1: Create an Odoo connection in CData Connect AI
Sign in to CData Connect AI and select Sources, then +Add Connection
Choose Odoo from the connector library
Enter your Odoo URL, User, database name (if applicable), and credentials or token
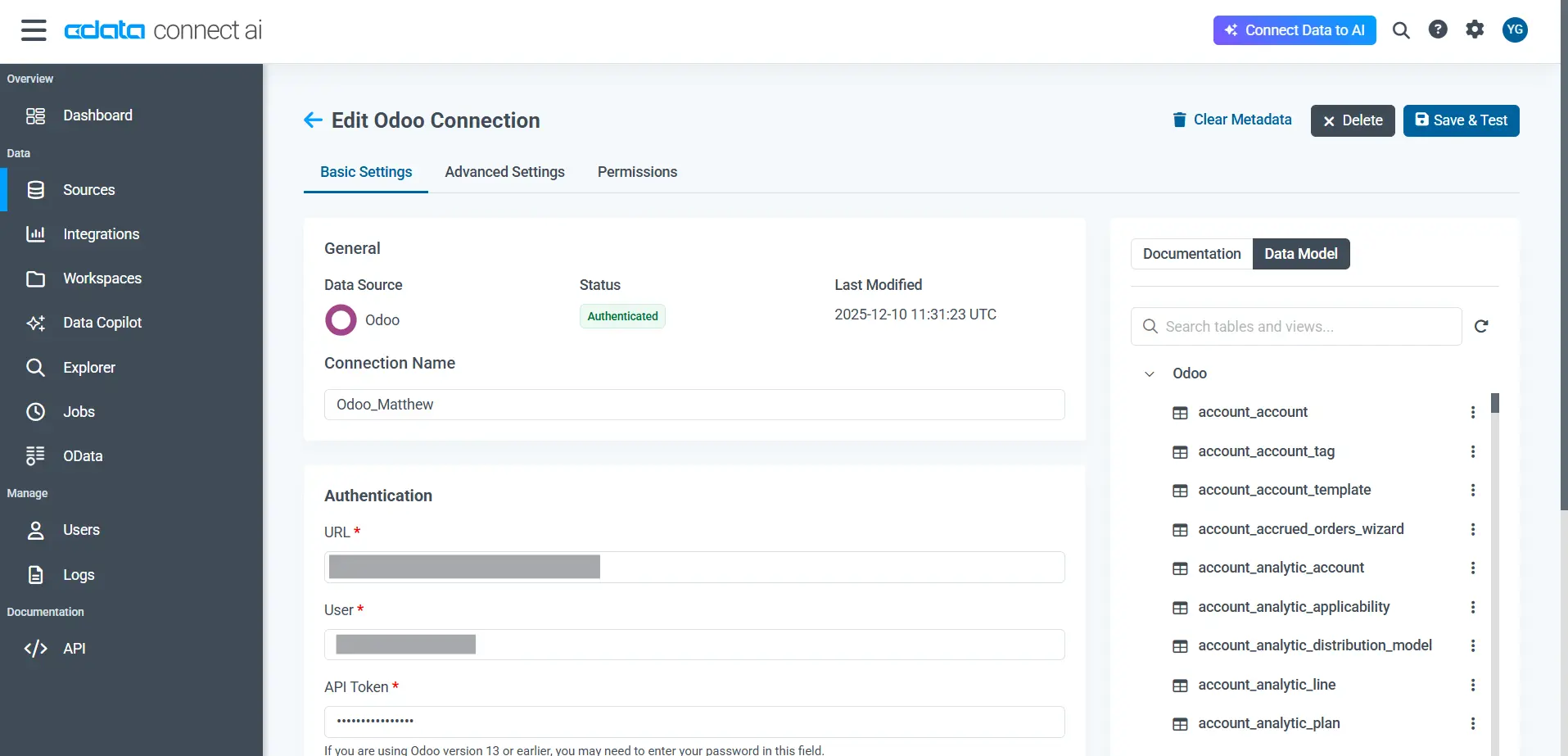
Click Save & Test to verify access to the connection
Step 2: Connect from Power BI Desktop
Open Power BI Desktop and select Get Data > Online Services > CData Connect Cloud
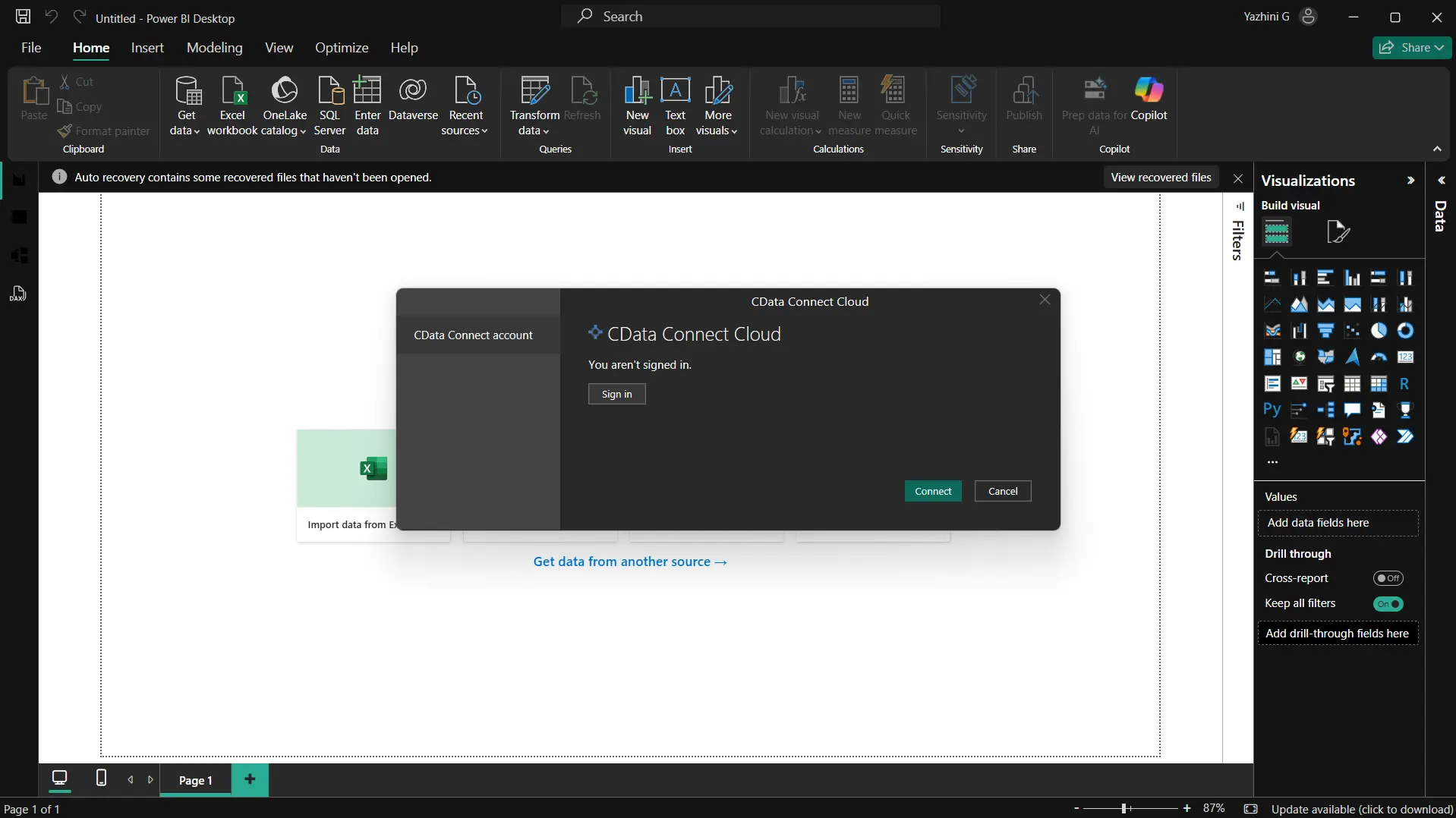
Click Connect and authenticate with your Connect AI account
Select the Odoo connection in Navigator
Choose the tables you would like to load. Here are some tables you might encounter:
sale_order: Sales order headers with dates, totals, and customer references
sale_order_line: Line-item details for each sales order
account_move: Journal entries including invoices, bills, and credit notes
crm_lead: Pipeline opportunities with expected revenue and stage
res_partner: Master table for customers, vendors, and contacts
Choose DirectQuery for live data or Import for snapshots
Click Load to bring data into Power BI
Step 3: Build visualizations and reports
In Report view, drag fields from the Fields pane onto the canvas
Select dimensions (res_partner.name, crm_lead.stage_id) and measures (sale_order.amount_total)
Choose chart types appropriate for your analysis
Apply filters and configure access policies in Connect AI as needed
Now, here is why this approach works. This method keeps data in Odoo while enforcing governance and user-level access control through Connect AI. You reduce risk by avoiding data sprawl, support self-service analytics with central oversight, and scale to additional sources without rearchitecting pipelines.
For organizations connecting AI agents alongside BI tools, CData's managed MCP platform for enterprise AI agents extends the same governed connectivity to Claude, GPT, and other AI assistants.
Method 2: Use Odoo's native Power BI integration
If your reporting needs are straightforward and you are running Odoo 18, the native integration offers a simpler alternative for baseline dashboards using prebuilt datasets.
Step 1: Enable the module and authenticate
Enable the Power BI integration module in Odoo 18 settings
Authenticate with your Microsoft account to allow publishing
Confirm required permissions in your Azure AD tenant
Validate workspace assignment and capacity requirements
Step 2: Select datasets and publish
Choose from prebuilt Odoo datasets and visuals
Publish to Power BI Service
Assign workspace permissions appropriate for your team
Configure refresh schedules and governance policies
Limitations to consider
Limited coverage of custom tables and fields
Fewer options for complex relationships and transformations
Difficult to blend with non-Odoo sources in one governed model
For governed, multi-source scenarios, Connect AI provides broader flexibility.
Model and optimize Odoo data in Power BI
Connecting to Odoo is only half the work. How you structure relationships between tables determines whether your reports load in seconds or time out.
Design a star schema
Power BI performs best with a star schema, a structure where transactional tables (facts) sit at the center and descriptive tables (dimensions) surround them.
In Odoo terms, fact tables hold the transactions you want to analyze. These are events that happen over time: sale_order captures each sale, account_move records every invoice and journal entry, and crm_lead tracks opportunities as they move through your pipeline. Facts grow continuously as your business operates.
Dimension tables provide context that makes facts meaningful. When you ask, "How much did Customer X buy last quarter?", the sale_order table has the transaction amounts, but res_partner tells you who Customer X actually is. Common Odoo dimensions include res_partner for customers and vendors, res_users for salespeople and assignees, and product_product for item details. Dimensions change infrequently compared to facts.
When building relationships between these tables, follow these principles:
Use single direction, many to one relationship. Many sales orders link to one customer, not the reverse. This keeps the model clean and queries efficient
Avoid bidirectional filtering unless necessary. It slows queries and creates ambiguity when Power BI cannot determine which path to follow between tables
Create a dedicated Date table and mark it as your date table in Power BI. This unlocks time intelligence functions like year over year comparisons and rolling averages, which would otherwise require complex DAX workarounds
Recommended tables and joins
With your star schema in place, here is how to structure joins for the most common Odoo reporting scenarios:
Sales analysis:
Invoice tracking:
The account_move table holds all journal entries, so filter by move_type = 'out_invoice' to isolate customer invoices
Join to account_move_line via move_id for line-item details
CRM pipeline:
Choose the right storage mode
Once your model is built, decide how Power BI should access the data. This choice directly impacts both performance and freshness.
DirectQuery queries Odoo on every report interaction, which means users always see current data. The tradeoff is performance. Every click, filter, and drill-down sends a query to your Odoo instance. Use this for operational dashboards where freshness matters more than speed.
Import takes the opposite approach. Power BI caches data locally using its compression engine, so reports load quickly regardless of Odoo's performance. Data only updates on your refresh schedule. Use this for historical analysis, complex DAX calculations, or when your Odoo instance cannot handle live query loads.
Composite models let you combine both. Import large historical fact tables for performance but keep dimension tables or recent transactions on DirectQuery so they stay current. This works well when you need fast aggregations over years of data but also want today's orders to appear immediately.
Incremental refresh solves a different problem. Instead of reloading entire tables on each refresh, Power BI updates only recent partitions. Configure this when full refreshes take too long or put unnecessary load on your Odoo instance.
Optimize for performance
With connectivity and modeling complete, three factors determine whether your reports feel responsive or not.
Query folding is the most impactful. When Power BI can push filters and calculations to the source, Odoo does the heavy lifting instead of Power BI processing millions of rows locally. Apply filters as early as possible in Power Query. To verify that folding is working, right-click any step in the Applied Steps pane. If "View Native Query" appears, that operation is being pushed to Odoo.
Visual density catches many report builders off guard. Each visual on a page sends its own query. A dashboard with 15 charts means 15 separate queries on every interaction. Limit visuals per page, reduce the number of distinct values in slicers, and consider aggregation tables for high volume fact data.
Time zone handling requires planning upfront. Odoo stores all datetimes in UTC. Decide early whether to convert time zones during data load in Power Query or dynamically in DAX measures based on user context.
Frequently asked questions
Does Odoo Online allow direct PostgreSQL access to Power BI?
No. Use an API connector like CData Connect AI or the native Odoo 18 integration.
Can I achieve live dashboards without a gateway?
Yes. CData Connect AI supports DirectQuery without an on-premises gateway in cloud-to-cloud scenarios.
How do I implement row-level security for Odoo data?
Define roles and DAX filters in Power BI Desktop or enforce row filters in Connect AI with user context pass-through.
What if I hit API rate limits with Odoo SaaS?
Implement pagination, schedule incremental refresh, or use a connector that optimizes queries and caching.
Can I write back from Power BI to Odoo?
Power BI is read-focused. For write-back, use Power Apps or custom applications calling Odoo APIs.
How do I handle multi-company data?
Model a Company dimension, enforce RLS by company, and publish separate workspaces if strict separation is required.
Start connecting Odoo to Power BI with CData Connect AI
CData Connect AI delivers governed, real-time access to Odoo data alongside 350+ other enterprise systems through a unified SQL interface. No custom API code, no database credential management, no ETL pipelines to maintain.
Ready to connect Odoo to Power BI in minutes? Download a free 14-day trial of CData Connect AI today! As always, our world-class Support Team is available to assist you with any questions you may have.
Explore CData Connect AI today
See how Connect AI excels at streamlining business processes for real-time insights




